Bilingual Exercises Unit 3
Diunggah oleh
Hadrián Susavila Vilas0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
78 tayangan5 halamanThe document provides an overview of the Industrial Revolution through several sections:
1. It describes the economic, political, and social conditions in Europe before the Industrial Revolution, as well as the agricultural, demographic, and technological changes that paved the way for industrialization.
2. Key innovations like the steam engine, textile machinery, and iron and steel production transformed these industries and helped launch the First Industrial Revolution in Britain. Transportation networks expanded through new forms of land and water transport.
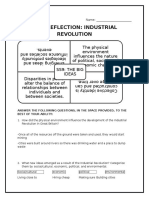
3. The emergence of industrial capitalism brought new social classes and living/working conditions for both the bourgeoisie and workers. Labor movements arose to advocate for workers' rights in response to long hours and dangerous working conditions, especially for children
Deskripsi Asli:
ZxZxX
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThe document provides an overview of the Industrial Revolution through several sections:
1. It describes the economic, political, and social conditions in Europe before the Industrial Revolution, as well as the agricultural, demographic, and technological changes that paved the way for industrialization.
2. Key innovations like the steam engine, textile machinery, and iron and steel production transformed these industries and helped launch the First Industrial Revolution in Britain. Transportation networks expanded through new forms of land and water transport.
3. The emergence of industrial capitalism brought new social classes and living/working conditions for both the bourgeoisie and workers. Labor movements arose to advocate for workers' rights in response to long hours and dangerous working conditions, especially for children
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
78 tayangan5 halamanBilingual Exercises Unit 3
Diunggah oleh
Hadrián Susavila VilasThe document provides an overview of the Industrial Revolution through several sections:
1. It describes the economic, political, and social conditions in Europe before the Industrial Revolution, as well as the agricultural, demographic, and technological changes that paved the way for industrialization.
2. Key innovations like the steam engine, textile machinery, and iron and steel production transformed these industries and helped launch the First Industrial Revolution in Britain. Transportation networks expanded through new forms of land and water transport.
3. The emergence of industrial capitalism brought new social classes and living/working conditions for both the bourgeoisie and workers. Labor movements arose to advocate for workers' rights in response to long hours and dangerous working conditions, especially for children
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 5
BILINGUAL EXERCISES UNIT 3.
- THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
1.- INTRODUCTION AND PRE-INDUSTRIAL ECONOMY
1.- Where and when did the Industrial revolution begin? Why do you think it started
there?
2.- Make a simple diagram about the political, economic and social situation before the
Industrial Revolution
2.- PRE-INDUSTRIALIZATION
3.-Explain the differences between Domestic System, Putting Out System and Factory
System completing the table.
DOMESTIC SYSTEM PUTTING OUT SYSTEM FACTORY SYSTEM
PLACE
WORKERS
SYSTEM OF
PRODUCTION
SALARY OR WAGE
3.- THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
3.1.- THE AGRICULTURAL REVOLUTION
4.- How did the enclosure acts increase productivity? Which social classes benefited
most from these acts?
5.- What was the Norfolk Crop Rotation System? What this system is better than the last?
6.- What other improvements were made in agriculture? What were the consequences of
all these improvements?
3.2.- THE DEMOGRAPHIC REVOLUTION
7- Look at the graphic of the slide 11 in the PPT, and describe the population growth in
each country for each period ( grew from____ to_____/ grew more than______/ The greatest
growth took place in_______)
8.- Explain the causes and consequences of population growth in Europe during the
eighteenth century
3.3.- TECHNOLOGICAL INNOVATIONS
9.- What energy sources were used prior to the revolution?
10.- Explain how a steam engine worked. Who invented it? When was it invented? What
energy source did it use? What fuel was used in the boiler?
11.- Why was the invention of the steam engine so important to the industrial revolution?
12.- Define working division and expertise. Why were beneficial innovations for
factories?
3.4.- PIONEER INDUSTRY: TEXTILE AND STEEL
13.- Why were the textile and steel the first to be developed and in which innovations
were introduced?
14.- What machines or technical innovations are associated with the textile industry?
And the steel industry?
3.5.- THE TRANSPORT REVOLUTION AND INCREASED TRADE
15.- What improvements took place in traditional forms of land and wáter transport? Find
out who were the inventors of each.
16.- When and what cities connecting the first passenger railway line?
17.- What advantages represented these two new means of transport? Think about all the
improvements and consequences it had for trade, industry and the general population
18.- Indicate the differences between:
-- Subsistence farming and market economy:
-- Free trade and protectionism:
4.- INDUSTRIAL CAPITALISM
19.- Who is the father of economic liberalism? What is his most important work?
20.- Indicate whether the following statements about capitalism are true or false. Match
each stamen with his characteristic of liberalism. Correct false statements.
A) In Spain the salary of a cleaner tends to be higher because their job is harder.
B) People should be in solidarity with others and do not think about their own benefit, in
this way the common good would be achieved
C) The government should decide the prices of products and the quantity produced, so the
economy is under control and the crisis will not occur.
D) Gold is very expensive because there is little, if any more gold, its price would fall.
21.- Explain how the mechanism of wages works in the capitalist system.
22. What are two ways to get the banks money?
23.- Look at the slide of corporations (anonymous society) in the PPT and answer these
questions:
A) What is the value of the company?
B) How many parts the company is divided? What do you call these parts?
C) How many people own the business? What part of the company has each one in cash?
D) How are the benefits distributed?
E) What is the board of directors? Who compose it? What does each do?
5.- THE SECOND INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
24.- Complete the table comparing the first and second Industrial Revolution
FIRST INDUSTRIAL SECOND INDUSTRIAL
REVOLUTION REVOLUTION
CHRONOLOGY
COUNTRIES LEADERS
INDUSTRIAL
ORGANIZATION
ENERGY SOURCES
INDUSTRIES LEADERS
MAIN INVENTIONS
25.- Define Taylorism y Fordism
26.- Explain the main characteristics of a Cartel, a Trust and a Holding. Think or find real
life examples of a Cartel, a Trust and a Holding.
6.- THE NEW INDUSTRIAL SOCIETY
27.- What is a class society? What differences exist with the estamental society?
28.- What four classes existed in the new industrial society? Who had the political and
economic power?
29.- Which class does each profession belong to: Factory owner/ lawyer/ shopkeeper/
day labourer/ civil servant/ office worker/ banker.
30.- Think and make table to compare living and working conditions for the bourgeoisie
and the workers.
31.- Read the text and answer the questions:
“In the early days of industry, child labour was common. Children of working families didn´t go to
school or they left at a very early age (7 or 8) to work in factories for 12 or 14 hours a day.
Their meager salary was essential for working families, whose income could barely sustain
them. They performed poorly paid, very repetitive and dangerous jobs, such as pulling wagons
in the mines or knotting the threads under the looms”
Describe child labour during the industrial revolution: hours, schooling, income, type of
jobs. Why did children have to work?
7.- THE LABOR MOVEMENTS
32.- Define Luddite, Trade Unions and Friendly Societies
33.- What were the main goals of Trade Unions?
34.- Which of the following statements indicates which refer to Marxism and Anarchism
A) They oppose the workers' participation in politics and the creation of political parties
B) The workers must gain power through revolution
C) After the conquest of power must impose the dictatorship of the proletariat
D) The revolution must be spontaneously through a general strike
E) There would be no private property
35.- Who were the major Marxist and anarchist thinkers?
GLOSSARY UNIT 3
1.- SPREAD/ ENERGY SOURCE/ COAL/ STEAM/ PROLETARIAT
2.- HANDICRAFTS/ TRADER/ DEALER/ WAGE/ FACTORY
3.- BUSINESS/ PROFIT/ ENCIRCLE/ FENCE/ LIVESTOCK/ THRESER/ SEEDER/ REAPER/
SURPLUS/ FAMINE/ DISEASE/ VACCINE/ STEAM ENGINE/ BOILER/ PIONEER/ ACQUIRE/
WEAVE/ SPIN/ LOOM/ IRON/ STEEL/ RAILROAD/ RAILWAY/ SAILBOAT/ STEAMBOAT/
PURCHASE/
4.- BOOST/ WEALTH/ PURSUIT/ REFRAIN/ SUPPLY/ DROP/ RISE/ FUND/
CORNERSTONE/ ENTREPRENEURS/ LOAN/ CORPORATIONS/ INTEREST/ SHARES/
WORTH/ STOCK EXCHANGE
5.- LEADERSHIP/ OIL/ ENGINE/ BATTERY/ LIGHT BULB/ TRAM/ STAINLESS/
SKYSCRAPERS/ CAN/ AROSE/ THEREFORE/ ASSEMBLY/ MERGE/ PUMP/
6.- ENTERPREUNERSHIP/ PEERAGES/ FLAUNT/ RETIREMENT/ HEALTH INSURANCE/
LACK/ REJECT/ RELY/ LABORERS
7.- POLITICAL PARTIES/ BLAME/ TRADE UNIONS/ ANARCHY/ STRIKE.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Unit 2 Review Sheet and Practice TestDokumen10 halamanUnit 2 Review Sheet and Practice TestjessicaraealtBelum ada peringkat
- Benjamin Coriat: Selected Summaries: SELECTED SUMMARIESDari EverandBenjamin Coriat: Selected Summaries: SELECTED SUMMARIESBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Of "Second Industrial Revolution (1850-1914)" By María Inés Barbero: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESDari EverandSummary Of "Second Industrial Revolution (1850-1914)" By María Inés Barbero: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESBelum ada peringkat
- SOL History (Old)Dokumen71 halamanSOL History (Old)Valorant SmurfBelum ada peringkat
- Greiner Ch. 10 Study Guide 1Dokumen8 halamanGreiner Ch. 10 Study Guide 1Blake SettleBelum ada peringkat
- Summary Of "The Industry We Were Able To Achieve" By Jorge Schvarzer: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESDari EverandSummary Of "The Industry We Were Able To Achieve" By Jorge Schvarzer: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESBelum ada peringkat
- The Emergence of an Industrial Labor Force in India: A Study of the Bombay Cotton Mills, 1854-1947Dari EverandThe Emergence of an Industrial Labor Force in India: A Study of the Bombay Cotton Mills, 1854-1947Belum ada peringkat
- PHAO 1000 ĐIỂM KTCT - BY S A N GDokumen32 halamanPHAO 1000 ĐIỂM KTCT - BY S A N GViên VõBelum ada peringkat
- Pre Testpost TestDokumen4 halamanPre Testpost Testhercheys aberteBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Revolution Review SheetDokumen2 halamanIndustrial Revolution Review SheetmperazzelliBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Revolution StudyDokumen2 halamanIndustrial Revolution Studyapi-263728635Belum ada peringkat
- TCW Week13 Historyofglobalmarketintergration (Siojo, Danao)Dokumen13 halamanTCW Week13 Historyofglobalmarketintergration (Siojo, Danao)ANDREA KAYE SIOJOBelum ada peringkat
- SOL His (Old)Dokumen147 halamanSOL His (Old)Valorant SmurfBelum ada peringkat
- Innovation Systems in Emerging Economies: MINT (Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey)Dari EverandInnovation Systems in Emerging Economies: MINT (Mexico, Indonesia, Nigeria, Turkey)Belum ada peringkat
- Jeremy Rifkin: Selected Summaries: SELECTED SUMMARIESDari EverandJeremy Rifkin: Selected Summaries: SELECTED SUMMARIESBelum ada peringkat
- Making Mondragón: The Growth and Dynamics of the Worker Cooperative ComplexDari EverandMaking Mondragón: The Growth and Dynamics of the Worker Cooperative ComplexBelum ada peringkat
- The Industrial Revolution and The French RevolutionDokumen3 halamanThe Industrial Revolution and The French Revolutionisaure raffinBelum ada peringkat
- The Communist Manifesto & The Capital: Including Two Important Precursors to Capital (Wage-Labour and Capital & Wages, Price and Profit)Dari EverandThe Communist Manifesto & The Capital: Including Two Important Precursors to Capital (Wage-Labour and Capital & Wages, Price and Profit)Belum ada peringkat
- Summary Of "Economy Between Two Centuries" By Jorge Saborido: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESDari EverandSummary Of "Economy Between Two Centuries" By Jorge Saborido: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESBelum ada peringkat
- What Should I Know For Module 6?: 6.00: 19th Century Changes-IntroductionDokumen7 halamanWhat Should I Know For Module 6?: 6.00: 19th Century Changes-IntroductionbekBelum ada peringkat
- Study Material-The Industrial RevolutionDokumen9 halamanStudy Material-The Industrial RevolutionTech GyanBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Social Science Sa2 Solved 05Dokumen4 halaman10 Social Science Sa2 Solved 05Anonymous 1Zepq14UarBelum ada peringkat
- Pol Science AssingementDokumen15 halamanPol Science AssingementAadhitya NarayananBelum ada peringkat
- SST Question Paper Class XDokumen3 halamanSST Question Paper Class Xmayankgoyal01Belum ada peringkat
- How Growth Really Happens: The Making of Economic Miracles through Production, Governance, and SkillsDari EverandHow Growth Really Happens: The Making of Economic Miracles through Production, Governance, and SkillsBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Reflection Industrial Revolution 2017Dokumen3 halamanUnit Reflection Industrial Revolution 2017api-356226631Belum ada peringkat
- Macro HandoutsDokumen5 halamanMacro HandoutsPomsie Castillo AdamosBelum ada peringkat
- The Socialist Calculation Debate: In Search of a Planned SocietyDari EverandThe Socialist Calculation Debate: In Search of a Planned SocietyBelum ada peringkat
- David M. Kotz What Economic Structure For SocialismDokumen13 halamanDavid M. Kotz What Economic Structure For Socialismpret2046Belum ada peringkat
- Grade VIII History Ch. 2Dokumen4 halamanGrade VIII History Ch. 2avyukth.akBelum ada peringkat
- Anthony Giddens: Selected Summaries: SELECTED SUMMARIESDari EverandAnthony Giddens: Selected Summaries: SELECTED SUMMARIESBelum ada peringkat
- Study of Reasons For The Adoption of Lean Production in The Automobile Industry: Questions For The Aec IndustriesDokumen11 halamanStudy of Reasons For The Adoption of Lean Production in The Automobile Industry: Questions For The Aec IndustriesvoharakasunBelum ada peringkat
- The Capital (Vol. 1-3): Including The Communist Manifesto, Wage-Labour and Capital, & Wages, Price and ProfitDari EverandThe Capital (Vol. 1-3): Including The Communist Manifesto, Wage-Labour and Capital, & Wages, Price and ProfitBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 2 Week of 10-24-28Dokumen6 halamanUnit 2 Week of 10-24-28kristopher augustin NMSHTVBelum ada peringkat
- For Oral RecitationDokumen5 halamanFor Oral RecitationmjuhngtegBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Social Science 2018 Sample Paper 3 NEWDokumen3 halaman10 Social Science 2018 Sample Paper 3 NEWJayaprakash PrakashBelum ada peringkat
- 625 Ubd 1-3 Morgan BraunDokumen7 halaman625 Ubd 1-3 Morgan Braunapi-253749086Belum ada peringkat
- Economics Semester Exam ReviewDokumen4 halamanEconomics Semester Exam Reviewluissy78Belum ada peringkat
- Kokoi GR 9 ManualDokumen69 halamanKokoi GR 9 ManualMmakgabo MmolaBelum ada peringkat
- BBA-508 - Economic Planning and PoliciesDokumen11 halamanBBA-508 - Economic Planning and PoliciesSimanta KalitaBelum ada peringkat
- Final ProjectDokumen131 halamanFinal Projectkritesh kherBelum ada peringkat
- Planned Economy and Economic Planning What The People S Republic of Walmart Got Wrong About The Nature of Economic PlanningDokumen17 halamanPlanned Economy and Economic Planning What The People S Republic of Walmart Got Wrong About The Nature of Economic PlanningSecond DragonBelum ada peringkat
- Essay - IH - 15 - 01 - 2024Dokumen5 halamanEssay - IH - 15 - 01 - 2024Thanusri Vasanth kumar IBBelum ada peringkat
- Revolución IndustrialDokumen2 halamanRevolución IndustrialVictor CarvajalBelum ada peringkat
- Industrial Revolution-English 1-Group #4Dokumen13 halamanIndustrial Revolution-English 1-Group #4Carlos MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Reflection Industrial Revolution 2017Dokumen3 halamanUnit Reflection Industrial Revolution 2017api-348560060Belum ada peringkat
- Managerial EconomicsDokumen320 halamanManagerial EconomicsAbhishekBelum ada peringkat
- Unit Reflection Industrial RevolutionDokumen2 halamanUnit Reflection Industrial Revolutionapi-334744306Belum ada peringkat
- In the Cause of Labour: A History of British Trade UnionismDari EverandIn the Cause of Labour: A History of British Trade UnionismPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- O o o O: How Was Industrial Revolution in Countries Such As France and Prussia?Dokumen5 halamanO o o O: How Was Industrial Revolution in Countries Such As France and Prussia?nimolesaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 19 1 1yokokawaDokumen31 halaman2 19 1 1yokokawaJoao V. M. RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Subject: Class: Semester:: Economics M.A. IDokumen7 halamanSubject: Class: Semester:: Economics M.A. INAMITA BARVEBelum ada peringkat
- Specialization and Trade: A Re-introduction to EconomicsDari EverandSpecialization and Trade: A Re-introduction to EconomicsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- The Industrial Revolution: Starts in Great Britain ReformersDokumen39 halamanThe Industrial Revolution: Starts in Great Britain ReformersMaruf SharearBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE1 Soc Sci. 15Dokumen11 halamanMODULE1 Soc Sci. 15Johanah TenorioBelum ada peringkat
- Living in The IT Era Module 1Dokumen17 halamanLiving in The IT Era Module 1Jubylyn AficialBelum ada peringkat
- 1491816804house Property, Othersources, Salary, Clubbing, Setoff, Tax Planning PDFDokumen168 halaman1491816804house Property, Othersources, Salary, Clubbing, Setoff, Tax Planning PDFPranav PuriBelum ada peringkat
- Ftna History 5Dokumen9 halamanFtna History 5Macame Junior100% (1)
- Weber - S Least Cost TheoryDokumen12 halamanWeber - S Least Cost TheoryadityaBelum ada peringkat
- ITC ProjectDokumen54 halamanITC ProjectRahulRaushanBelum ada peringkat
- Economics Crisis of PakistanDokumen6 halamanEconomics Crisis of PakistanHassam MalhiBelum ada peringkat
- AhlanDokumen10 halamanAhlanNur FayzaBelum ada peringkat
- Final OutputDokumen44 halamanFinal OutputJopie ArandaBelum ada peringkat
- Essay On PostmanDokumen5 halamanEssay On Postmanxlfbsuwhd100% (2)
- Farewell Address WorksheetDokumen3 halamanFarewell Address Worksheetapi-261464658Belum ada peringkat
- Sony India Post GST Price SheetDokumen4 halamanSony India Post GST Price Sheetgans OliveBelum ada peringkat
- Bing SummaryDokumen3 halamanBing SummarySanta PermatasariBelum ada peringkat
- 1817 RulesDokumen24 halaman1817 RulesLuis Evangelista100% (2)
- ACSI Travel Report 2018-2019: American Customer Satisfaction IndexDokumen14 halamanACSI Travel Report 2018-2019: American Customer Satisfaction IndexJeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Operation ManagementDokumen15 halamanOperation ManagementRabia RasheedBelum ada peringkat
- Sthira Solns PVT LTD, BangaloreDokumen25 halamanSthira Solns PVT LTD, Bangaloreshanmathieswaran07Belum ada peringkat
- The Lawton Instrumental Activities of Daily Living ScaleDokumen2 halamanThe Lawton Instrumental Activities of Daily Living ScaleGEN ERIGBUAGASBelum ada peringkat
- التحفيزات الجبائيةDokumen18 halamanالتحفيزات الجبائيةbouamama bBelum ada peringkat
- Alternative Centres of PowerDokumen40 halamanAlternative Centres of PowerJigyasa Atreya0% (2)
- Balance Sheet of Tech MahindraDokumen3 halamanBalance Sheet of Tech MahindraPRAVEEN KUMAR M 18MBR070Belum ada peringkat
- chính trị học so sánhDokumen18 halamanchính trị học so sánhTrần Bích Ngọc 5Q-20ACNBelum ada peringkat
- Office Memorandum No - DGW/MAN/171 Issued by Authority of Director General of WorksDokumen2 halamanOffice Memorandum No - DGW/MAN/171 Issued by Authority of Director General of WorksDeep Prakash YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Private Credit Bureaus Around The World J13Dokumen2 halamanPrivate Credit Bureaus Around The World J13JerryBelum ada peringkat
- ITC Balance Sheet PDFDokumen1 halamanITC Balance Sheet PDFAINDRILA BERA100% (1)
- 26A Via 44 17A 72 46: Mumbai CST Bandra (T) Lokmanya Tilak (T)Dokumen1 halaman26A Via 44 17A 72 46: Mumbai CST Bandra (T) Lokmanya Tilak (T)sharmarakBelum ada peringkat
- MP Ekramul Karim ChowdhuryDokumen5 halamanMP Ekramul Karim ChowdhurySaifSaemIslamBelum ada peringkat
- 17 CIR v. Tours SpecialistsDokumen3 halaman17 CIR v. Tours SpecialistsChedeng KumaBelum ada peringkat
- LPP Excel SolverDokumen2 halamanLPP Excel SolverJayant JainBelum ada peringkat
- Nirma University Revise.Dokumen2 halamanNirma University Revise.mahayogiconsultancyBelum ada peringkat
- Banco Central de Chile - Indicadores Diarios - Euro (Pesos Por Euro) - Año 2017Dokumen9 halamanBanco Central de Chile - Indicadores Diarios - Euro (Pesos Por Euro) - Año 2017Lorena MutizábalBelum ada peringkat
- GS - Outlook For 2023Dokumen56 halamanGS - Outlook For 2023Aaron WangBelum ada peringkat