Micro Fridge Case Study Marketing Strategy
Diunggah oleh
Vaibhav MaheshwariDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Micro Fridge Case Study Marketing Strategy
Diunggah oleh
Vaibhav MaheshwariHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SIBM- 2009-11 (EMBA) Vaibhav Maheshwari
12/7/2010
Micro Fridge: Case Study:-
1. Central Issue:
(a) How to produce?
(b) For whom to produce?
(c) If he should go with the Sanyo offer?
(d) If he should only use distributors to supply his product to the market or go
with house accounts?
(e) How much should be the cost of the micro fridge that could fetch him
decent % of profit.
2. Objectives to be achieved:
(a) To be able to introduce the micro fridge the market with $50000 capital.
(b) To convince the dormitories and other targeted customers.
(c) To set up a price that earns him return of minimum 15% initially on the
selling price.
(d) To find a manufacturer that fits his budget.
3. Situation analysis & alternatives available:
Situation analysis:
(a) Low capital: Robert Bennett has $50,000 in hand to start up his new
business which is not enough.
(b) Manufacturing problem: After speaking with few home appliances
manufacturers out of which only SANYO and Samsung agreed to
manufacture his product provided Bennett pays all the upfront cost of
$170,000. Being low on budget Bennett has to think over the offer.
(c) Administration, Legal, Patent & other miscellaneous expenses: Besides
upfront and basic product cost Bennett has to pay for these expenses as
well.
(d) Potential buyers: The potential buyers he was targeting were not very
sure if they would like to buy the product from an unknown brand like his.
Alternatives available:
(a) The electronic circuitry should be patented and later find the buyer of the
concept and keep getting a permanent royalty or a flexible royalty on the
Case Study-1 Prof Banarbanas Marketing Management
1
SIBM- 2009-11 (EMBA) Vaibhav Maheshwari
12/7/2010
basis of increase in sales. This way Bennett can retain his job as well as
introduce his concept in the market.
(b) As Sanyo and Samsung are ready to manufacture the product. Bennett
should negotiate with them, if he can pay the upfront cost of $170,000
once the sales start to pick up and pay the per unit cost with a credit
period of 45-60 days after the delivery from the manufacturer. That ways
he would have enough time in hand to arrange the money from the sales
of the units.
(c) Taking loans from the financial institutions for the upfront &
administration cost.
(d) If he decides to go for the direct sales the price could be quoted as $350
to $375/unit initially which fetches him a profit of 30% to 40%, after
paying $263/unit to the manufacturer but because of direct sales volume
would be less and more manpower would be required. Delivery of product
in perfect condition in another hassle.
(e) If he decided to go to the end user via distributor’s channel, he can share
his profit of 30% to 40% with the distributors. In this case he should quote
them a price of $309 to $ 315(depending on the volume) & the
distributors further sell it for $350 to $375/unit. In this case both the will
get a profit of 14% to 20% but in return Bennett can ensure to supply in
bulk at a time creating high revenue in the long run. Distributors on the
other hand will be happy too to save that extra few % of profit by selling
the product directly to the end user than through the vendors.
4. Suggested Alternative & why?
The positives of this products: - patentable product, less space consuming,
less power consuming, tie up with SANYO or Samsung will ensure good
quality product and a large potential market like:- college housing, hotels,
motels, military quarters, service apartments, old age homes, Small offices
might attract some investor to invest in this idea.
Step 1: Having a capital of $50,000 look for a partner or a financial
institution who could invest equal or more money in this business.
Step 2: create awareness about the product. Set up a marketing team to do
detailed market survey. The marketing people could be Bennett and his
partners and besides that he can hire few marketing researchers with his
little capital for the process.
Case Study-1 Prof Banarbanas Marketing Management
2
SIBM- 2009-11 (EMBA) Vaibhav Maheshwari
12/7/2010
Step 3: Subcontract the manufacturing part to Sanyo or Samsung who will
ensure that the labor cost is low due to the offshore manufacturing. And as
this product is patentable, manufacturer according to the contract should not
be selling the product to anyone or leaking the concept to any competitor.
Negotiate with manufacturer about the credit payment period of 6 months-1
year for upfront cost of $170,000 and 45 days- 60 days for the product per
unit cost of $263.
Step4: He and his marketing team create a market for the product in the
initial stage by doing direct marketing with the cost of $350 to $375/unit to
the end user.
Step 5: Once the awareness is created supply the product to the
interested distributors at
$309 to $ 315. Though going via distributors will result into low margin of
profits but will ensure
a large volume once the market is created. Distributors on the other side
will be happy too to
save some % of profit for not going through the dealers and supplying the
product directly. Per
unit payment from the distributors is the rapid cash flow that should be
recovered within the
credit payment of 30 days.
Step6: The minimum margin of 17.4% that he gets every month from the
difference of
$309-$263/unit should be further used to get the product patented within 6
months so that the
electric circuitry and the concept is not copied. By the time a big
manufacturer comes up with its
own electric circuitry and concept Micro fridge will have enough goodwill to
sustain in the market.
Case Study-1 Prof Banarbanas Marketing Management
3
SIBM- 2009-11 (EMBA) Vaibhav Maheshwari
12/7/2010
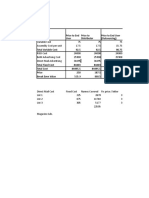
COST MANAGEMENT:
Cash in hand: $50,000
Upfront cost: $170,000
Admin&sales cost: $300,000/12=$25,000
Patent cost: $60,000
Price/unit: $263
Selling price: $309
Initial 1 year we cannot expect much of sales as Bennett would be busy marketing
his product and as not many people know about it, there will be less buyers. He
should target for a breakeven point in initial year, i.e. selling at least 13,000 units.
13,000*$315 = $4,095,000
13,000*$263 = $3,419,000 (manufacturer payment)
Balance = 676000
This amount could be used for paying the upfront cost, admin cost, advertising,
patent, rent for office & misc expenses.
Once the market is made he should target for minimum 30,000units/year he gets:
Dealer payment : 30,000*$309=$9,270,000
Sanyo payment : 30,000*$263=$7,890,000
Balance : $1,380,000/12= $115,000/month
Case Study-1 Prof Banarbanas Marketing Management
4
SIBM- 2009-11 (EMBA) Vaibhav Maheshwari
12/7/2010
And every semester the sales should improve at least by 10%
If x is no. of units:
309x= 263x+476000
263x-309x=476000
46x=476000
X=47600/46=10348pcs
10348*309(selling price) =3.2 million
If 3.2 million of revenue is reached the recurring cost & cost price for SANYO will be
taken care of.
Case Study-1 Prof Banarbanas Marketing Management
5
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Group 7B - MicroFridgeDokumen3 halamanGroup 7B - MicroFridgeVinay Tejasvi YallapragadaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Write Up - MM (Microfridge)Dokumen2 halamanCase Write Up - MM (Microfridge)Anshuk PolasBelum ada peringkat
- Microfridge Marketing CaseDokumen5 halamanMicrofridge Marketing CaseSALONI CHOUDHARYBelum ada peringkat
- Microfridge: The ConceptDokumen4 halamanMicrofridge: The ConceptManu GaurangBelum ada peringkat
- MicroFridge Case Study: Developing an Innovative Product and Expanding into New MarketsDokumen18 halamanMicroFridge Case Study: Developing an Innovative Product and Expanding into New Marketsagarhemant100% (1)
- MicroFridge Product Description & Marketing PlanDokumen7 halamanMicroFridge Product Description & Marketing PlanSATYANSH BHATNAGARBelum ada peringkat
- Microfridge and Rin CaseDokumen5 halamanMicrofridge and Rin CaseGopichand AthukuriBelum ada peringkat
- Microfridge: A 3-in-1 device for hostel rooms, military bases, and motelsDokumen10 halamanMicrofridge: A 3-in-1 device for hostel rooms, military bases, and motelsagarhemant50% (2)
- Barco Case AnalysisDokumen2 halamanBarco Case Analysisaparna jethaniBelum ada peringkat
- Capgemini - The Execution: D. AdditionallyDokumen2 halamanCapgemini - The Execution: D. AdditionallyAnanyaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Analysis of Micro FridgeDokumen8 halamanCase Analysis of Micro Fridgeamitmahar100% (1)
- Bennett'S Microfridge: Needs Met by Microfridge and Value CreatedDokumen5 halamanBennett'S Microfridge: Needs Met by Microfridge and Value CreatedgauravpalgarimapalBelum ada peringkat
- MICROFRIDGEDokumen3 halamanMICROFRIDGEAchal GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Micro FridgeDokumen20 halamanMicro FridgeSachin Gupta100% (1)
- Designing Unique Boutique Hotel ExperiencesDokumen9 halamanDesigning Unique Boutique Hotel ExperiencesTejashwi KumarBelum ada peringkat
- MedisysDokumen5 halamanMedisysMayank_Gupta_1995100% (1)
- MM GROUP 1 (MicroFridge)Dokumen11 halamanMM GROUP 1 (MicroFridge)AKASH SOIEBelum ada peringkat
- ITC E-ChoupalDokumen23 halamanITC E-ChoupalRick GangulyBelum ada peringkat
- Montreaux AnalysisDokumen16 halamanMontreaux Analysisanil14bits87100% (2)
- IDEO Case Study Summary by Harshit JindalDokumen2 halamanIDEO Case Study Summary by Harshit JindalharshitBelum ada peringkat
- Group Process in Challenger Launch Decision: Lack of Coordination Led to TragedyDokumen2 halamanGroup Process in Challenger Launch Decision: Lack of Coordination Led to TragedyEric Justice100% (1)
- MGMT CaseDokumen5 halamanMGMT CaseAnonymous a2SDmQl30Belum ada peringkat
- MICROFRIDGE SWOT ANALYSISDokumen2 halamanMICROFRIDGE SWOT ANALYSISMeme MBA100% (1)
- The Essence of EntrepreneurshipDokumen14 halamanThe Essence of EntrepreneurshipParin ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Optical Distortion Case StudyDokumen6 halamanOptical Distortion Case Studygenesisolivero100% (1)
- Case Analysis Topic - Working Capital Management & ROI Case - An Irate Distributor Submitted by - Srishti Joshi (PGFC1934)Dokumen5 halamanCase Analysis Topic - Working Capital Management & ROI Case - An Irate Distributor Submitted by - Srishti Joshi (PGFC1934)Surbhi SabharwalBelum ada peringkat
- Emirates Airline Success Behind Solid GrowthDokumen1 halamanEmirates Airline Success Behind Solid GrowthChRehanAliBelum ada peringkat
- TBS 908 Assessment 1 - CoatsDokumen4 halamanTBS 908 Assessment 1 - CoatsdoctorfayBelum ada peringkat
- Product Innovation Charter MicrofridgeDokumen1 halamanProduct Innovation Charter MicrofridgeTatsat PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Rupesh Kumar Gupta-1421229 (Conglomerate Inc Case Study)Dokumen8 halamanRupesh Kumar Gupta-1421229 (Conglomerate Inc Case Study)RupeshGupta50% (2)
- MBA 644 2019 Individual Assignment 1 - Gautam SaseedharanDokumen6 halamanMBA 644 2019 Individual Assignment 1 - Gautam SaseedharanGautamBelum ada peringkat
- Microfridge 1for DTNDokumen2 halamanMicrofridge 1for DTNNimmi PandeyBelum ada peringkat
- Stepsmart Fitness Case Study: Group-2, Sec-ADokumen10 halamanStepsmart Fitness Case Study: Group-2, Sec-ASHIVAM DUBEYBelum ada peringkat
- Loctite Case StatsDokumen8 halamanLoctite Case StatsBharat SinghBelum ada peringkat
- HP CaseDokumen3 halamanHP Casepoly_wizkidBelum ada peringkat
- CiscoDokumen6 halamanCiscoNatalia Kogan0% (2)
- Case Analysis On Merloni Elettrodomestici SpaDokumen6 halamanCase Analysis On Merloni Elettrodomestici SpaKrishna Raj ShailBelum ada peringkat
- Tupelo Medical: Managing Price ErosionDokumen3 halamanTupelo Medical: Managing Price Erosionshyam kumarBelum ada peringkat
- B2B - Group 3 - Jackson Case StudyDokumen5 halamanB2B - Group 3 - Jackson Case Studyriya agrawallaBelum ada peringkat
- New Year Eve CrisisDokumen6 halamanNew Year Eve CrisisManoj Kumar MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Best Buy's History, Industry, and Future ChallengesDokumen16 halamanBest Buy's History, Industry, and Future ChallengesPurna WayanBelum ada peringkat
- Base CampDokumen1 halamanBase CampPranav TyagiBelum ada peringkat
- Creativity at GunDokumen4 halamanCreativity at GunGuntashsingh AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Clinique Pens: The Writing Implements Division of U.S. HomeDokumen3 halamanClinique Pens: The Writing Implements Division of U.S. HomeSakshi Shah100% (1)
- The Failure of Amazon in Chinese Market and Prediction For Emerging MarketDokumen11 halamanThe Failure of Amazon in Chinese Market and Prediction For Emerging MarketDo Thu Huong50% (2)
- Necanko, Inc.Dokumen9 halamanNecanko, Inc.Rizki Setyo Pratomo0% (1)
- Coca Cola On FacebookDokumen5 halamanCoca Cola On FacebookNaseeba MubeenBelum ada peringkat
- Bergerac Systems Group 10Dokumen7 halamanBergerac Systems Group 10Aman Anshu0% (1)
- Computron IncDokumen7 halamanComputron IncJD_04100% (1)
- Northern Chemical Company Business Marketing Plan Targets Architects, ContractorsDokumen9 halamanNorthern Chemical Company Business Marketing Plan Targets Architects, ContractorsEshan GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Micro FridgeDokumen20 halamanMicro FridgeDivya Yadav100% (2)
- CFL FinalDokumen3 halamanCFL FinalAnonymous nfLFi1q1Belum ada peringkat
- Aqualisa Case QuestionsDokumen3 halamanAqualisa Case Questionspunksta18250% (2)
- Peak Sealing TechnologiesDokumen11 halamanPeak Sealing TechnologiesNishan ShettyBelum ada peringkat
- Cottle-Taylor: Expanding The Oral Care Group in India: Submitted By: Group B32Dokumen7 halamanCottle-Taylor: Expanding The Oral Care Group in India: Submitted By: Group B32Janani Ramanathan0% (1)
- Design by Kate: The Power of Direct Sales: Group: 6, Section BDokumen6 halamanDesign by Kate: The Power of Direct Sales: Group: 6, Section BSumit DasBelum ada peringkat
- Micro Fridge 1 Analysis PartDokumen2 halamanMicro Fridge 1 Analysis PartVikash MaskaraBelum ada peringkat
- Darden Casebook 2009 For Case Interview Practice - MasterTheCaseDokumen82 halamanDarden Casebook 2009 For Case Interview Practice - MasterTheCaseMasterTheCase.comBelum ada peringkat
- DardenDokumen81 halamanDardenPeter YXBelum ada peringkat
- b5 Life Cycle (Q&A 2018Dokumen11 halamanb5 Life Cycle (Q&A 2018Issa Adiema100% (1)
- Probe Filter 5.1 SNMP Support Reference GuideDokumen8 halamanProbe Filter 5.1 SNMP Support Reference GuideOrlando MondlaneBelum ada peringkat
- Tucker Northlake SLUPsDokumen182 halamanTucker Northlake SLUPsZachary HansenBelum ada peringkat
- Frias Lindsay Iste Stds Self AssessmentDokumen4 halamanFrias Lindsay Iste Stds Self Assessmentapi-572977540Belum ada peringkat
- Valuing Common and Preferred SharesDokumen31 halamanValuing Common and Preferred SharesAdam Mo AliBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Approach To Practice 5SDokumen4 halamanPractical Approach To Practice 5SNikola DjorovicBelum ada peringkat
- Kribhco Summer Trainning ReportDokumen106 halamanKribhco Summer Trainning ReportMihir Patel0% (1)
- (IJCST-V4I2P61) :akshika Aneja, Garima SodhiDokumen4 halaman(IJCST-V4I2P61) :akshika Aneja, Garima SodhiEighthSenseGroupBelum ada peringkat
- 8 - Vibration - F22-Vibration Isolation and AbsorptionDokumen26 halaman8 - Vibration - F22-Vibration Isolation and Absorptionالأردني JordanianBelum ada peringkat
- Spjc/Lim Lima-Callao, Peru: .Radar - Minimum.AltitudesDokumen41 halamanSpjc/Lim Lima-Callao, Peru: .Radar - Minimum.AltitudesVicente PortocarreroBelum ada peringkat
- Machine Dynamics and Vibration-Forced Vibration AssignmentDokumen4 halamanMachine Dynamics and Vibration-Forced Vibration AssignmentVijay ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 5Dokumen30 halamanChapter 5فاطمه حسينBelum ada peringkat
- Real Estate Merger Motives PDFDokumen13 halamanReal Estate Merger Motives PDFadonisghlBelum ada peringkat
- Defining Yourself As A LeaderDokumen1 halamanDefining Yourself As A Leaderrosli2503Belum ada peringkat
- CV Program Coordinator NigeriaDokumen8 halamanCV Program Coordinator NigeriaCV Program CoordinatorBelum ada peringkat
- Brushed Axial Fans: VA85-A101-96A Performance DiagramDokumen3 halamanBrushed Axial Fans: VA85-A101-96A Performance DiagramJaskaran SinghBelum ada peringkat
- InkscapePDFLaTeX PDFDokumen3 halamanInkscapePDFLaTeX PDFFrancesco ReaBelum ada peringkat
- Ascon PhivDokumen48 halamanAscon PhivSDK341431100% (1)
- Student Name Student Number Assessment Title Module Title Module Code Module Coordinator Tutor (If Applicable)Dokumen32 halamanStudent Name Student Number Assessment Title Module Title Module Code Module Coordinator Tutor (If Applicable)Exelligent Academic SolutionsBelum ada peringkat
- Central Bank Digital Currencies For Beginners A Quick Guide Into CbdcsDokumen33 halamanCentral Bank Digital Currencies For Beginners A Quick Guide Into CbdcsCarlos Bueno HorcajoBelum ada peringkat
- The Power Elite and The Secret Nazi PlanDokumen80 halamanThe Power Elite and The Secret Nazi Planpfoxworth67% (3)
- Converting WSFU To GPMDokumen6 halamanConverting WSFU To GPMDjoko SuprabowoBelum ada peringkat
- 0 Proposal Form Top Up SUBMITTED BY Markandeya Raju PDFDokumen3 halaman0 Proposal Form Top Up SUBMITTED BY Markandeya Raju PDFHOD (MVGR Civil)Belum ada peringkat
- Strict Liability - ProjectDokumen7 halamanStrict Liability - ProjectRushabh Lalan100% (1)
- Bosley Declaration - FTC VemmaDokumen69 halamanBosley Declaration - FTC VemmaThompson BurtonBelum ada peringkat
- Car NB Documents (YOPH02PC02)Dokumen21 halamanCar NB Documents (YOPH02PC02)PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Pakistan Relations With EnglandDokumen4 halamanPakistan Relations With Englandpoma7218Belum ada peringkat
- Spouses Aggabao v. Parulan, Jr. and ParulanDokumen5 halamanSpouses Aggabao v. Parulan, Jr. and ParulanGeenea VidalBelum ada peringkat
- Theory of Elinor OstromDokumen5 halamanTheory of Elinor OstromSanjana KrishnakumarBelum ada peringkat
- BS Iec 61643-32-2017 - (2020-05-04 - 04-32-37 Am)Dokumen46 halamanBS Iec 61643-32-2017 - (2020-05-04 - 04-32-37 Am)Shaiful ShazwanBelum ada peringkat
- Ceramic Disc Brakes: Haneesh James S ME8 Roll No: 20Dokumen23 halamanCeramic Disc Brakes: Haneesh James S ME8 Roll No: 20Anil GöwđaBelum ada peringkat