Chem102DHE3 Fall 2010 - A
Diunggah oleh
Kavita SureshJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chem102DHE3 Fall 2010 - A
Diunggah oleh
Kavita SureshHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CHEMISTRY 102 Fall 2010
Hour Exam III Page 1
1. My answers for this Chemistry 102 exam should be graded with the answer sheet associated
with:
a) Form A b) Form B c) Form C d) Form D e) Form E
Consider the titration of 30.0 mL of 0.30 M HCN by 0.10 M KOH for the next five questions.
Ka for HCN = 6.2 × 10–10.
2. Calculate the pH when 0.0 mL of KOH has been added.
a) 9.73 b) 4.27 c) 3.61 d) 4.87 e) 5.29
3. Calculate the pH after 10.0 mL of KOH has been added.
a) 8.30 b) 10.11 c) 9.09 d) 4.79 e) 9.21
4. Calculate the pH after 45.0 mL of KOH has been added.
a) 8.30 b) 10.11 c) 9.09 d) 4.79 e) 9.21
5. Calculate the pH after 120.0 mL of KOH has been added.
a) 12.00 b) 12.30 c) 12.50 d) 12.70 e) 13.00
6. Calculate the pH at the equivalence point in this titration.
a) 11.04 b) 10.33 c) 12.08 d) 8.83 e) 7.00
CHEMISTRY 102 Fall 2010
Hour Exam III Page 2
7. H2CO3 and H2SO4 are both diprotic acids. For H2CO3, K a1 = 4.3 × 10–7 and K a 2 =
5.6 × 10–11. For H2SO4, K a1 >> 1 and K a 2 = 1.2 × 10–2. Which of the following
statements concerning a 0.10 M H2CO3 solution and a 0.10 M H2SO4 solution is true?
a) The [H+] in the 0.10 M H2CO3 solution will be greater than the [H+] in the 0.10 M
H2SO4 solution.
b) The [H+] in the 0.10 M H2SO4 solution will be less than 0.10 M ([H+] < 0.10 M).
c) At equilibrium, the [SO42–] will be greater than the [CO32–] ([SO42–] > [CO32–]).
d) The pH of the 0.10 M H2CO3 solution will be less than 1.0 (pH < 1.0).
e) At equilibrium, [H2SO4] > [HSO4−] in the 0.10 M H2SO4 solution.
8 Consider a 0.10 M solution of a weak acid HA. If pH = 3.00 for this solution, determine the
equilibrium concentration of the conjugate base ([A–] = ?).
a) 1.0 × 10–4 M b) 1.0 × 10–3 M c) 1.0 × 10–2 M d) 1.0 M e) 1.0 × 10–5 M
9. Which of the following statements is false?
a) The pH of a 0.10 M solution of HClO4 solution is 1.00.
b) The pH of a 10. M solution of KOH is 15.00.
c) The pH of a 1.0 × 10−12 M solution of HCl is 7.00.
d) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of Ba(OH)2 is 13.30.
e) The pH of a 10. M solution of HCl is −1.00.
10. What is the pH of a 0.015 M solution of aniline, C6H5NH2? Kb for C6H5NH2 is
3.8 × 10−10.
a) 11.24 b) 7.00 c) 8.38 d) 2.76 e) 5.62
11. A weak acid, HA, is dissolved in water and no other substance is added. Which of these
statements (to a close approximation) is true?
a) [H3O+] = [OH−] b) [HA] = [A−] c) [A−] = [OH−]
d) [HA] = [OH−] e) [H3O+] = [A−]
CHEMISTRY 102 Fall 2010
Hour Exam III Page 3
12. A sample of S8(g) is placed in an otherwise empty rigid container at 1325 K at an initial
concentration of 1.000 M. The S8(g) decomposes to S2(g) by the reaction:
S8(g) 4 S2(g)
At equilibrium, the concentration of S8 is 0.250 M. Calculate the value of K for this
reaction at 1325 K.
a. 324 b. 12.0 c. 1.27 d. 0.750 e. 0.100
13. Four different bases all with the same initial concentration and volume are each titrated
with 0.1 M HNO3. Which base titration has the highest pH at the halfway point to
equivalence?
a) CH3NH2 (Kb = 4.4 × 10–4) b) NH3 (Kb = 1.8 × 10–5)
c) C5H5N (Kb = 1.7 × 10–9) d) C6H5NH2 (Kb = 3.8 × 10–10)
14. The Ka value for acetic acid (HC2H3O2) is 1.8 × 10–5 and the Kb value for ammonia
(NH3) is 1.8 × 10–5. Which of the following statements is true?
a) A 1.0 M solution of NaC2H3O2 would have a lower pH than a 1.0 M solution of
NH4Cl.
b) C2H3O2– is a stronger base than NH3.
c) A 1.0 M solution of HC2H3O2 would have a higher pH than a 1.0 M solution of
NH4Cl.
d) NH4+ is a stronger acid than HC2H3O2.
e) A 1.0 M solution of NH3 would have a higher pH than a 1.0 M solution of NaC2H3O2.
15. Phosphate buffers are important in regulating the pH of intracellular fluids at pH = 7.10.
The equilibrium reaction utilized in this buffer system is:
H2PO4–(aq) + H2O ⇌ HPO42–(aq) + H3O+ (aq) Ka = 6.2 × 10–8
At pH = 7.10, calculate the concentration ratio of HPO42– to H2PO4– in intracellular fluids
⎛ [HPO 4 2− ] ⎞
⎜ = ? ⎟.
⎜ [H PO − ] ⎟
⎝ 2 4 ⎠
a) 0.78 b) 0.11 c) 1.0 d) 9.1 e) 1.3
CHEMISTRY 102 Fall 2010
Hour Exam III Page 4
16. Calculate the [H3O+] in a solution containing 0.50 M HNO2 and 0.10 M NaNO2.
Ka for HNO2 = 4.0 × 10–4
a) 2.0 × 10–3 M b) 8.0 × 10–4 M c) 4.0 × 10–4 M
d) 8.0 × 10–5 M e) 1.0 × 10–5 M
17. Consider 1.0 L of a solution containing 0.50 M HNO2 and 0.10 M NaNO2. How many
moles of KOH must be added so that the resulting solution has pH = pKa for HNO2?
Ka for HNO2 = 4.0 × 10–4.
a) 0.50 mol b) 0.40 mol c) 0.25 mol d) 0.20 mol e) 0.10 mol
18. Consider the following reaction at 250°C:
N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 2 NH3(g) K = 0.278
Initially 1.00 mol of N2, 1.00 mol of H2, and 1.00 mol of NH3 are placed in a 2.00 L
container. Which way will the reaction shift to reach equilibrium and which reagent will
have the smallest concentration at equilibrium?
a. Reaction will shift right; [NH3] will be smallest.
b. Reaction will shift left; [H2] will be smallest.
c. Reaction will shift left; [NH3] will be smallest.
d. Reaction will shift right; [N2] will be smallest.
e. Reaction will shift right; [H2] will be smallest.
19. How many of the following statements (I-IV) about a 1.0 M solution of weak acid is/are
true?
I. As the Ka value increases, the pH of the solution decreases.
II. As the Ka value increases, the percent dissociation of the acid increases.
III. As the Ka value increases, the Kb value of the conjugate base decreases.
IV. As the Ka value increases, the [H3O+] in solution increases.
a) 0 (none; all are false) b) 1 c) 2 d) 3 e) 4 (All are true)
CHEMISTRY 102 Fall 2010
Hour Exam III Page 5
20. Arrange 0.10 M solutions of the following compounds by increasing pH:
HC2H3O2 HF NH3 C5H5N
(Ka = 1.8x10-5) (Ka = 7.2x10-4) (Kb = 1.8x10-5) (Kb = 1.7x10-9)
a) HF < HC2H3O2 < NH3 < C5H5N
b) HF < HC2H3O2 < C5H5N < NH3
c) HC2H3O2 < HF < NH3 < C5H5N
d) HC2H3O2 < HF < C5H5N < NH3
e) NH3 < C5H5N < HF < HC2H3O2
21. Which of the following reactions is correctly identified with the appropriate equilibrium
constant?
a) C5H5N(aq) + H2O(l) C5H5NH+(aq) + OH−(aq)
Ka reaction for C5H5N
b) NH3(aq) + H3O+(aq) NH4+(aq) + H2O(l)
Kb reaction for NH3
c) H3O+(aq) + OH−(aq) H2O(l) + H2O(l)
Kb reaction for H3O+
d) HC3H5O2(aq) + H2O(l) C3H5O2−(aq) + H3O+(aq)
Ka reaction for HC3H5O2
22. How many of the following 0.25 M solutions are acidic?
NaCN KI NH4Cl Ca(NO3)2 Na2O
a. 0 (none of these solutions are acidic) b. 1 c. 3
d. 4 e. 5 (all of these solutions are acidic)
CHEMISTRY 102 Fall 2010
Hour Exam III Page 6
Consider the titration of 50.0 mL of 0.20 M ascorbic acid (H2C6H6O6) by 0.20 M NaOH for the
next two questions. For H2C6H6O6, K a1 = 7.9 × 10−5 and K a 2 = 1.6 × 10−12.
23. At what volume of NaOH added does the resulting solution have [HC6H6O6−] =
[C6H6O62−]?
a) 0.0 mL NaOH added b) 25.0 mL NaOH added
c) 50.0 mL NaOH added d) 75.0 mL NaOH added
e) 100.0 mL NaOH added
24. Calculate the pH after 50.0 mL of NaOH has been added.
a) 4.10 b) 6.71 c) 7.95 d) 9.23 e) 11.80
______________________________________________________________________________
25. The pOH of a sample of baking soda dissolved in water is 5.74 at 25oC. Calculate the
[H3O+] in this baking soda solution.
a) 1.0 × 10–7 M b) 5.5 × 10–9 M c) 1.8 × 10–6 M
d) 1.9 × 10–9 M e) 6.2 × 10–6 M
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Consider the titration of 200.0 mL of 0.10 M HNO3 titrated by 0.10 M Ca(OH)2 for the next two
questions.
26. Determine the [H+] of the resulting solution after 50.0 mL of 0.10 M Ca(OH)2 has been
added.
a) 0.10 M b) 0.050 M c) 0.040 M d) 0.020 M e) 0.010 M
27. At what volume of Ca(OH)2 added does the resulting solution have [H+] = 1.0 × 10–7 M?
a) 100.0 mL b) 125.0 mL c) 150.0 mL d) 175.0 mL e) 200.0 mL
CHEMISTRY 102 Fall 2010
Hour Exam III Page 7
28. A 0.10 M solution of the salt NaX has a pH of 11.50. Calculate the pH of a 1.0 M
solution of HX.
a) 3.00 b) 4.00 c) 5.00 d) 6.00 e) 11.00
29. A chemist wishes to prepare a buffer at pH = 3.5 and has the following acids available,
along with the potassium salts of their conjugate bases. Which acid/salt combination is
the best choice for preparing the buffer?
a) HC2H3O2 (Ka = 1.8 × 10−5)/KC2H3O2 b) HOCl (Ka = 3.5 × 10−8)/KOCl
c) HNO2 (Ka = 4.0 × 10−4)/KNO2 d) HCN (Ka = 6.2 × 10−10)/KCN
e) HClO2 (Ka = 1.2 × 10−2)/KClO2
30. Consider a buffer solution containing NaF and HF. Which of the following statements is
false?
a) If [F−] = [HF], then the pH of the solution equals the pKa value for HF.
b) If [F−] > [HF], then the pH of the solution is greater than the pKa value for HF.
c) If [HF] > [F−], then the [H3O+] of the solution is greater than the Ka value for HF.
d) If HCl is added to the buffer, then the [F−] of the resulting solution should increase.
e) If NaOH is added to the buffer, then the pH of the resulting solution should increase.
31. Consider the following endothermic reaction at equilibrium:
SiHCl3(g) + 3 H2O(l) SiH(OH)3(s) + 3 HCl(g) ΔH = +450 kJ
How many of the following changes will cause the amount of SiH(OH)3(s) to increase?
I. Increase the volume of the reaction container.
II. Increase the temperature.
III. Add H2O(l).
IV. Remove HCl(g).
a. 0 (none) b. 1 c. 2 d. 3 e. 4 (all)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Heat Transfer IES GATE IAS 20 Years Question and Answers PDFDokumen97 halamanHeat Transfer IES GATE IAS 20 Years Question and Answers PDFKumar GauravBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Report Final 5206Dokumen12 halamanLab Report Final 5206Tanvir AhamedBelum ada peringkat
- Atmosphere DEMODokumen24 halamanAtmosphere DEMOJasmine DanaBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry of Living Organisms Measuring PH Lab Activity PDFDokumen6 halamanChemistry of Living Organisms Measuring PH Lab Activity PDFHaris KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Temperature Conversions: Temperature and Thermometric ScaleDokumen75 halamanTemperature Conversions: Temperature and Thermometric ScaleMedz MelegritoBelum ada peringkat
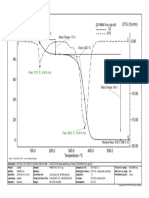
- TG /% DTG / (%/min) : Onset: 130.3 °C Mass Change: - 15 %Dokumen1 halamanTG /% DTG / (%/min) : Onset: 130.3 °C Mass Change: - 15 %Danay ManzoBelum ada peringkat
- Cooling With Thermally-Active Mass in Extreme Climatic ConditionsDokumen7 halamanCooling With Thermally-Active Mass in Extreme Climatic Conditionsalpha607Belum ada peringkat
- 2nd Lawof Thermodynamics Part1Dokumen55 halaman2nd Lawof Thermodynamics Part1ShreyashBelum ada peringkat
- PDFDokumen13 halamanPDFpsychic_jason0071319Belum ada peringkat
- PH Lab - Student VersionDokumen6 halamanPH Lab - Student VersionTeachLABScIBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of Heated Seat and Foot Heater On ThermalDokumen11 halamanEffects of Heated Seat and Foot Heater On ThermalDendra FebriawanBelum ada peringkat
- Using Peltier Devices For Temperature Control: MSL Technical Guide 41Dokumen5 halamanUsing Peltier Devices For Temperature Control: MSL Technical Guide 41Aldrin HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Book-3 - Psychrometrics - 2013 Code Update - Atlanta Mar 2015 - FinalDokumen77 halamanBook-3 - Psychrometrics - 2013 Code Update - Atlanta Mar 2015 - FinalMilton RemacheBelum ada peringkat
- Relaxation Method PDFDokumen3 halamanRelaxation Method PDFRonit MohapatraBelum ada peringkat
- Of Water 4.187 KJ/KG K)Dokumen2 halamanOf Water 4.187 KJ/KG K)Ramoji Aditya CharyBelum ada peringkat
- ME8693 Heat and Mass Transfer L T P C 3 2 0 4 ObjectivesDokumen2 halamanME8693 Heat and Mass Transfer L T P C 3 2 0 4 ObjectivesGEJENDHIRAN SBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter02 PDFDokumen74 halamanChapter02 PDFedis666100% (3)
- Batang GuroDokumen2 halamanBatang GuroMerida BravoBelum ada peringkat
- Non Aqueous TitrationDokumen26 halamanNon Aqueous TitrationRahul Malik83% (6)
- Heat and TemperatureDokumen125 halamanHeat and TemperatureNovelynLozano-EdrosoBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2 Theoretical Parametric Study of Wrap-Around Heat Pipe (WAHP) in Air PDFDokumen19 halamanPaper 2 Theoretical Parametric Study of Wrap-Around Heat Pipe (WAHP) in Air PDFAnonymous 7pJU2NFhABelum ada peringkat
- HMT CO, CO-PO and CO-PSO MappingDokumen2 halamanHMT CO, CO-PO and CO-PSO Mappingpradeep.kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Part-2Dokumen14 halamanPhysics Part-2Thor hmBelum ada peringkat
- Project: Techcalc-Projekt: Boundary ConditionsDokumen5 halamanProject: Techcalc-Projekt: Boundary ConditionsBogdan LucianBelum ada peringkat
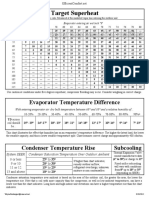
- Charging and TD Chart PlusDokumen1 halamanCharging and TD Chart PlusFaquruddin AliBelum ada peringkat
- Psychrometry PDFDokumen10 halamanPsychrometry PDFmukund holkarBelum ada peringkat
- Thermische Behaglichkeit Folder eDokumen16 halamanThermische Behaglichkeit Folder efernandoguedes_1953Belum ada peringkat
- 11 Chemistry Notes Ch07 EquilibriumDokumen8 halaman11 Chemistry Notes Ch07 EquilibriumShishirRanjanBelum ada peringkat
- HMT Question BankDokumen10 halamanHMT Question Banksanthanam102Belum ada peringkat
- Esd - Psychrometric ChartDokumen2 halamanEsd - Psychrometric ChartDedi KartiwaBelum ada peringkat