Anatomy and Physiology
Diunggah oleh
Clint-Marie LaxaHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Anatomy and Physiology
Diunggah oleh
Clint-Marie LaxaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
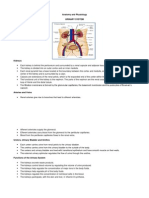
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
The Cardiovascular System
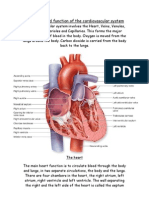
The cardiovascular system refers to the heart, blood vessels and the blood. Blood contains oxygen
and other nutrients which your body needs to survive. The body takes these essential nutrients
from the blood. At the same time, the body dumps waste products like carbon dioxide, back into
the blood, so they can be removed. The main function of the cardiovascular system is therefore to
maintain blood flow to all parts of the body, to allow it to survive. Veins deliver used blood from
the body back to the heart. Blood in the veins is low in oxygen (as it has been taken out by the
body) and high in carbon dioxide (as the body has unloaded it back into the blood). All the veins
drain into the superior and inferior vena cava which then drain into the right atrium. The right
atrium pumps blood into the right ventricle. Then the right ventricle pumps blood to the
pulmonary trunk, through the pulmonary arteries and into the lungs. In the lungs the blood picks
up oxygen that we breathe in and gets rid of carbon dioxide, which we breathe out. The blood is
becomes rich in oxygen which the body can use. From the lungs, blood drains into the left atrium
and is then pumped into the left ventricle. The left ventricle then pumps this oxygen-rich blood
out into the aorta which then distributes it to the rest of the body through other arteries. The main
arteries which branch off the aorta and take blood to specific parts of the body are:
Carotid arteries, which take blood to the neck and head
Coronary arteries, which provide blood supply to the heart itself
Hepatic artery, which takes blood to the liver with branches going to the stomach
Mesenteric artery, which takes blood to the intestines
Renal arteries, which takes blood to the kidneys
Femoral arteries, which take blood to the legs
The body is then able to use the oxygen in the blood to carry out its normal functions. This blood
will again return back to the heart through the veins and the cycle continues.
Function and Location of the Heart
The heart's job is to pump blood around the body. The heart is located in between the two
lungs. It lies left of the middle of the chest.
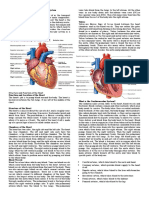
Structure of the Heart
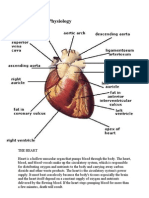
The heart is a muscle about the size of a fist, and is roughly cone-shaped. It is about 12cm
long, 9cm across the broadest point and about 6cm thick. The pericardium is a fibrous
covering which wraps around the whole heart. It holds the heart in place but allows it to
move as it beats. The wall of the heart itself is made up of a special type of muscle
called cardiac muscle.
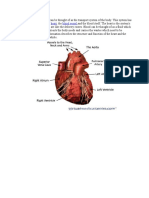
Chambers of the Heart
The heart has two sides, the right side and the left side. The heart has four chambers. The
left and right side each have two chambers, a top chamber and a bottom chamber. The
two top chambers are known as the left and right atria (singular: atrium). The atria
receive blood from different sources. The left atrium receives blood from the lungs and
the right atrium receives blood from the rest of the body. The bottom two chambers are
known as the left and right ventricles. The ventricles pump blood out to different parts of
the body. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs while the left ventricle pumps out
blood to the rest of the body. The ventricles have much thicker walls than the atria which
allows them to perform more work by pumping out blood to the whole body.
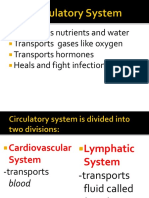
Blood Vessels
Blood Vessel are tubes which carry blood. Veins are blood vessels which carry blood
from the body back to the heart.Arteries are blood vessels which carry blood from the
heart to the body. There are also microscopic blood vessels which connect arteries and
veins together called capillaries. There are a few main blood vessels which connect to
different chambers of the heart. The aorta is the largest artery in our body. The left
ventricle pumps blood into the aorta which then carries it to the rest of the body through
smaller arteries. The pulmonary trunk is the large artery which the right ventricle pumps
into. It splits into pulmonary arteries which take the blood to the lungs. The pulmonary
veins take blood from the lungs to the left atrium. All the other veins in our body drain
into the inferior vena cava (IVC) or thesuperior vena cava (SVC). These two large veins
then take the blood from the rest of the body into the right atrium.
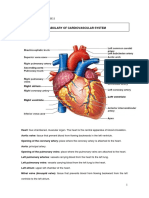
Valves
Valves are fibrous flaps of tissue found between the heart chambers and in the blood
vessels. They are rather like gates which prevent blood from flowing in the wrong
direction. They are found in a number of places. Valves between the atria and ventricles
are known as the right and left atrioventricular valves, otherwise known as the tricuspid
and mitral valves respectively. Valves between the ventricles and the great arteries are
known as the semilunar valves. Theaortic valve is found at the base of the aorta, while
the pulmonary valve is found the base of the pulmonary trunk. There are also many
valves found in veins throughout the body. However, there are no valves found in any of
the other arteries besides the aorta and pulmonary trunk.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cardiovascular AnatomyDokumen5 halamanCardiovascular AnatomyDibb Fabiania Delos ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular SystemDokumen9 halamanCardiovascular SystemWild RiftBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen4 halamanAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLuis WashingtonBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular SystemDokumen7 halamanCardiovascular SystemAbdallah AlasalBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory_System_in_Humans_Dokumen4 halamanCirculatory_System_in_Humans_petra.t.ayalBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and PhysiologyCherry Oña AntoninoBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Structure, Function & Location in 40 CharactersDokumen4 halamanHeart Structure, Function & Location in 40 CharactershahahahaaaaaaaBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen4 halamanAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.Belum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen4 halamanAn Introduction To The Cardiovascular SystemLili M.Belum ada peringkat
- Structure and Function of the HeartDokumen5 halamanStructure and Function of the Heartdrowned_clarkeBelum ada peringkat
- Structure and Function of the HeartDokumen5 halamanStructure and Function of the Heartdrowned_clarkeBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Heart - RyanDokumen5 halamanAnatomy of Heart - Ryandrowned_clarkeBelum ada peringkat
- CirculatoryDokumen8 halamanCirculatoryKristel Faye DioBelum ada peringkat
- Blood CirculationDokumen8 halamanBlood CirculationnorafidaishakBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesDokumen6 halamanCardiovascular System: Halabja Technical College of Applied SciencesELYANBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o oDokumen5 halamanCardiovascular System (Heart) : o o o o okayaldrBelum ada peringkat
- CVS IDokumen7 halamanCVS Itemple samBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory SystemDokumen1 halamanCirculatory Systemandrzej36Belum ada peringkat
- Vocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Dokumen7 halamanVocabulary of Cardiovascular System: Ingles Medico Ii - Clase 2Agustín Bravo Arreyes100% (2)
- Minggu 13 Peredaran DarahDokumen11 halamanMinggu 13 Peredaran Darahcuksam27Belum ada peringkat
- Circulatory SystemDokumen111 halamanCirculatory SystemYounas Bhatti100% (1)
- Circulatory System Sci 6Dokumen26 halamanCirculatory System Sci 6Regin BaguioBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory SystemDokumen2 halamanCirculatory SystemGO BIGBelum ada peringkat
- Handouts Science and Health VI The HeartDokumen3 halamanHandouts Science and Health VI The HeartjairaestrellaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular System OverviewDokumen5 halamanCardiovascular System OverviewJohnferson S. BornalesBelum ada peringkat
- The Circulatory System: How Blood Flows Through the Heart & BodyDokumen3 halamanThe Circulatory System: How Blood Flows Through the Heart & BodyNinaBelum ada peringkat
- The Circulatory SystemDokumen5 halamanThe Circulatory SystemJ Byrone B NatividadBelum ada peringkat
- Systemic Circulatory SystemDokumen4 halamanSystemic Circulatory SystemTinaRahmawatiKadabraBelum ada peringkat
- CNCQ Basic Reading Chapter 7Dokumen10 halamanCNCQ Basic Reading Chapter 7Thiện NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- P.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2ADokumen29 halamanP.E. 3 First AID: Submitted By: Jolifa Kairan Gary Section: Bachelor of Science and Criminology 2AAlea Jane AranjuezBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory System of HumanDokumen4 halamanCirculatory System of HumanLaraibBelum ada peringkat
- The Circulatory System: Agriscience 332 Animal Science #8646-A TEKS: (C) (2) (A) and (C) (2) (B)Dokumen111 halamanThe Circulatory System: Agriscience 332 Animal Science #8646-A TEKS: (C) (2) (A) and (C) (2) (B)brdaisyBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 1 The Organs of The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen37 halamanLesson 1 The Organs of The Cardiovascular SystemCarla BuzetaBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 3 GcsDokumen14 halamanCHAPTER 3 GcsNurse NotesBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory Long ActivityDokumen5 halamanCirculatory Long Activity26jmuzychenkoBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio Vascular SystemDokumen8 halamanCardio Vascular SystemguptaasitBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of Cardiovascular SystemDokumen23 halamanAnatomy of Cardiovascular SystemElvira Wisakhadewi100% (1)
- The MyocardiumDokumen8 halamanThe MyocardiumKyrene San Pedro RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Dokumen9 halamanBIO 302L Laboratory Report - Circulatory System - Group 5Jv Dela CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory System SystemDokumen4 halamanCirculatory System Systemleah rualesBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseDokumen10 halamanA Case Study About Cardiovascular DiseaseBarben Balaquit100% (1)
- Structure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemDokumen5 halamanStructure and Function of The Cardiovascular SystemRachelHatcher123Belum ada peringkat
- Branching Blood VesselsDokumen2 halamanBranching Blood VesselsMarjia TulyBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Circulation of BloodDokumen5 halamanTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Circulation of BloodDokumen4 halamanTypes of Circulation of BloodZerria Ashley PatocBelum ada peringkat
- Parts of the Heart ExplainedDokumen2 halamanParts of the Heart ExplainedKc MolinaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartjeffcaselBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovasuclar SystemDokumen13 halamanCardiovasuclar SystemGreatle Mae D. BasbañoBelum ada peringkat
- The Circulatory System IsDokumen4 halamanThe Circulatory System IsKieth ObaobBelum ada peringkat
- Heart and Circulatory SystemDokumen5 halamanHeart and Circulatory SystemBryent GawBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of A Human HeartDokumen3 halamanAnatomy of A Human HeartKina KinaBelum ada peringkat
- Transports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsDokumen46 halamanTransports Nutrients and Water Transports Gases Like Oxygen Transports Hormones Heals and Fight InfectionsElla LlamasBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HeartDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The HeartMuri CajucomBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy Physiology HeartDokumen9 halamanAnatomy Physiology HeartAlvheen JoaquinBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 5 (Heart)Dokumen10 halamanLecture 5 (Heart)Άγγελος ΧαβέλαςBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular SystemDokumen6 halamanCardiovascular Systemtasneem8Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksDari EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideDari EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuidePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Human Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionDari EverandHuman Body Book | Introduction to the Circulatory System | Children's Anatomy & Physiology EditionBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Training Bodyweight Routine for RunnersDokumen9 halamanCircuit Training Bodyweight Routine for RunnersMonopoly46Belum ada peringkat
- Emervel Portfolio BookletDokumen8 halamanEmervel Portfolio Bookletvini_tbBelum ada peringkat
- J2011.Decompressive Craniectomy Technical NoteDokumen6 halamanJ2011.Decompressive Craniectomy Technical NoteKysy CodonBelum ada peringkat
- Orthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic CenterDokumen7 halamanOrthopedic Nursing. Lecture Notes at Philipine Orthopedic Centerhannjazz100% (5)
- Forma Larga de Taichi YangDokumen12 halamanForma Larga de Taichi YangProfe PacoBelum ada peringkat
- Foam Roller HandoutDokumen2 halamanFoam Roller Handoutsebafigueroa94Belum ada peringkat
- Multiple-Choice QuizDokumen6 halamanMultiple-Choice QuizHUAWEI HUAWEI100% (1)
- University of Minnesota Throwers Summer Program Month 1 PDFDokumen2 halamanUniversity of Minnesota Throwers Summer Program Month 1 PDFTj Newsom100% (1)
- Basic Fracture Treatment (ADULTS) Quick ReferenceDokumen1 halamanBasic Fracture Treatment (ADULTS) Quick ReferenceMuhammed ElgasimBelum ada peringkat
- BBB Month 18 Workout Log PDFDokumen8 halamanBBB Month 18 Workout Log PDFGeraldyneBelum ada peringkat
- Notes of CH 7 Control and Coordination - Class 10th Science Study RankersDokumen9 halamanNotes of CH 7 Control and Coordination - Class 10th Science Study Rankerssamy0% (1)
- Imaging of Nasopharyngeal CarcinomaDokumen9 halamanImaging of Nasopharyngeal CarcinomayohanasmjtBelum ada peringkat
- NSAA Only ManualVersion-2.0 May-2017Dokumen19 halamanNSAA Only ManualVersion-2.0 May-2017Raghu NadhBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Hpe Axis Sum21 StudentDokumen7 halaman5 Hpe Axis Sum21 StudentRAQUEL WINECKBelum ada peringkat
- DD Lumbalgia PDFDokumen22 halamanDD Lumbalgia PDFJose Antonio Giron MombielaBelum ada peringkat
- 2003 OITE AnswersDokumen278 halaman2003 OITE Answersdoos1Belum ada peringkat
- The Body Atlas - A Pictorial Guide To The Human Body by DK PDFDokumen66 halamanThe Body Atlas - A Pictorial Guide To The Human Body by DK PDFranjanjhallb100% (1)
- MYOLOGYDokumen20 halamanMYOLOGYNatty ChikumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit-II Skin Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen9 halamanUnit-II Skin Anatomy and Physiologykamal devdaBelum ada peringkat
- Henry Vernon Crock M.D., M.S., F.R.C.S., F.R.A.C.S. (Auth.) - Practice of Spinal Surgery-Springer Vienna (1983) PDFDokumen334 halamanHenry Vernon Crock M.D., M.S., F.R.C.S., F.R.A.C.S. (Auth.) - Practice of Spinal Surgery-Springer Vienna (1983) PDFIonut VladBelum ada peringkat
- Balancing The Books On Orthodontic Treatment: An Integrated Analysis of ChangeDokumen10 halamanBalancing The Books On Orthodontic Treatment: An Integrated Analysis of ChangeLikhitaBelum ada peringkat
- Mens Health Multi Gym InstructionsDokumen37 halamanMens Health Multi Gym Instructionsdaryn100% (1)
- Speech MechanismDokumen18 halamanSpeech MechanismChiara Olivo100% (1)
- Roger W. Sperry: Split-Brain PreparationDokumen18 halamanRoger W. Sperry: Split-Brain PreparationElonic AirosBelum ada peringkat
- Plant Nosodes - According To DR John Henry ClarkeDokumen29 halamanPlant Nosodes - According To DR John Henry Clarkemelos24Belum ada peringkat
- Stroke School Brockville Part 3Dokumen39 halamanStroke School Brockville Part 3Gautam KhannaBelum ada peringkat
- Structures of The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems WorksheetDokumen3 halamanStructures of The Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems Worksheetapi-508202933Belum ada peringkat
- ch116 Part2Dokumen102 halamanch116 Part2p'eng matchima h.Belum ada peringkat
- Chicken Wing DissectionDokumen4 halamanChicken Wing DissectionclaireBelum ada peringkat
- Pig Heart Dissection Lab 2012-2013finaldraftpdfDokumen21 halamanPig Heart Dissection Lab 2012-2013finaldraftpdfapi-169518406Belum ada peringkat