WO9010337 Magnetic Motor
Diunggah oleh
Andras Kondrat0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
694 tayangan23 halamanThis document summarizes a patent application for a magnetic motor. The motor uses repelling forces between fixed and rotating magnets to drive a rotating disk flywheel. Stationary magnets are placed adjacent to equally spaced rotating magnets around the disk perimeter. Injector pins are used to kick a crankshaft and flywheel over center as driven by the rotating magnets, continuing the motor's rotation. The motor has potential applications as an alternative to traditional combustion engines.
Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThis document summarizes a patent application for a magnetic motor. The motor uses repelling forces between fixed and rotating magnets to drive a rotating disk flywheel. Stationary magnets are placed adjacent to equally spaced rotating magnets around the disk perimeter. Injector pins are used to kick a crankshaft and flywheel over center as driven by the rotating magnets, continuing the motor's rotation. The motor has potential applications as an alternative to traditional combustion engines.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
694 tayangan23 halamanWO9010337 Magnetic Motor
Diunggah oleh
Andras KondratThis document summarizes a patent application for a magnetic motor. The motor uses repelling forces between fixed and rotating magnets to drive a rotating disk flywheel. Stationary magnets are placed adjacent to equally spaced rotating magnets around the disk perimeter. Injector pins are used to kick a crankshaft and flywheel over center as driven by the rotating magnets, continuing the motor's rotation. The motor has potential applications as an alternative to traditional combustion engines.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 23
Takes the place of EP0461179 (art.158 of the EPC)
PCT [WORLD INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY ORGANIZATION @
INTERNATIONAL APPLICATION PUBLISHED UNDER THE PATENT COOPERATION TREATY (PCT)
(61) International Patent Classification 5 ; (11) International Publication Number: WO 90/10337
HO2K 7/02, 21/22, 1/00 AL | (4 tatrnatonl Publication Date: 7 September 1990 (07.0990)
(21) Inerstionl Applicaton Number: PCT/US90/01100| Published
Wh international search report
(22) International Filing Date: 27 February 1990 (27.02.90) Before the expiration of the time limit for amending the
edison eben eee of be ec of
mentions
(20 Port data:
317838 1 March 1989(01.0389) US
(7172) Applicant and Inventor: REED, Troy, G. [US/US]; 7724
East 104th Street, Tulse, OK 74133 (US).
(74) Agent: HEAD, James, R.; Head & Johnson, 228 West 17th
‘Place, Tulsa, OK 74119 (US).
(G1) Designated States: AT (European patent), BE (European
patent), CH (European patent), DE (European patent),
DK (European patent), ES (Europeen patent, FR (Euro:
pean patent), GB (European patent), IT (European pa
teat), 3, LU (European patel), NL (European patent), |
SE (European pate)
(§#)Tille: MAGNETIC MOTOR
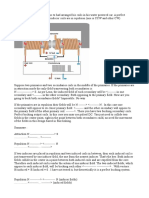
| G7) Abstract
‘A magnetic motor is driven by the repelling forces of fixed
and rotating magnets. The rotating magnets (22, 32) are mounted
equally spaced about the perimeter ofa disk (20) which rotates as
the flywheel of the motor. Stationary magnets (18, 28) are sup-
ported adjacent the rotating magnets (22,32). There are four in-
Jector pins (76A, 76B, 76C, 76D), much like the common injector
pins on ball point pens, which are set and released by an injector
pad (48A, 48B, 48C, 489) driven by the crankshaft (14) ofthe en-
sine. The crankshaft (14) and flywheel are driven by the repulsive
forces created by the fixed and rotary magnets (22, 32) with the in-
Jector pin system (34, 36, 38, 40) operating to kick the crankshaft
(14) and the flywheel over center.
pees)
oR
nth
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Dony WatssDokumen49 halamanDony WatssvbugaianBelum ada peringkat
- Chas Campbell's Large GeneratorDokumen8 halamanChas Campbell's Large GeneratorkwagBelum ada peringkat
- Motor de Energia Livre - Muammer YildizDokumen11 halamanMotor de Energia Livre - Muammer YildizAsh TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Manual Book HHO GENERATOR Fuel EfficientDokumen56 halamanManual Book HHO GENERATOR Fuel EfficientLuis Enrique Jarquin AramburoBelum ada peringkat
- Power Generation by Foot Step Method - Rack and PinionDokumen13 halamanPower Generation by Foot Step Method - Rack and Pinionprem53100% (2)
- Hojo MotorDokumen206 halamanHojo MotorLaterBelum ada peringkat
- !!!! Technisch Sehr Gute Bucking Coil BeschreibungDokumen2 halaman!!!! Technisch Sehr Gute Bucking Coil BeschreibungIchbins100% (1)
- Hojo Motor ManuelDokumen51 halamanHojo Motor ManuelMick Duval0% (1)
- Hybrid Tech Eat On Fuel CellDokumen13 halamanHybrid Tech Eat On Fuel CellhhojonBelum ada peringkat
- Ijiset V6 I8 18Dokumen5 halamanIjiset V6 I8 18TeotiaBelum ada peringkat
- MAGLEV Wind Mill Power GenerationDokumen16 halamanMAGLEV Wind Mill Power GenerationNagabhushanaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Best Cell Plate ConfigurationDokumen19 halamanWhat Is The Best Cell Plate Configurationjctorres100% (1)
- Charcoal by Gary GilmoreDokumen10 halamanCharcoal by Gary GilmoreMarky MaypoBelum ada peringkat
- Geet Fuel Processor PlansDokumen11 halamanGeet Fuel Processor Plansdag57Belum ada peringkat
- Ukraine Ethernal Lantern Perpetum MobileDokumen9 halamanUkraine Ethernal Lantern Perpetum MobileMihai Daniel100% (1)
- No. 390,721, Patented 00 T. 9, 1888.: Best Avalable Cop N, TeslaDokumen4 halamanNo. 390,721, Patented 00 T. 9, 1888.: Best Avalable Cop N, TeslaAtharva Deshpande100% (1)
- The TransformerDokumen21 halamanThe TransformerAshok KumarBelum ada peringkat
- SSG STARTERS GUIDE-One PDFDokumen18 halamanSSG STARTERS GUIDE-One PDFMihai Iulian CristeaBelum ada peringkat
- HV GeneratorDokumen6 halamanHV GeneratorNatasaBugaianBelum ada peringkat
- Build A 3-Band Shortwave Converter For Your CarDokumen2 halamanBuild A 3-Band Shortwave Converter For Your CarbobbyunlockBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic AmplifierDokumen4 halamanMagnetic AmplifierShobha SainiBelum ada peringkat
- Top TenDokumen12 halamanTop TentelkonBelum ada peringkat
- Rotary Valve Steam EngineDokumen13 halamanRotary Valve Steam EnginedeckyBelum ada peringkat
- Bedini Replica - PART3 - Coil Preparation, First Testrun Ronny GeyDokumen8 halamanBedini Replica - PART3 - Coil Preparation, First Testrun Ronny GeyBastien Gall de Sillé0% (1)
- Home Built Hydraulic Ram PumpsDokumen84 halamanHome Built Hydraulic Ram PumpsZwq92yBelum ada peringkat
- Geet Reactor RodDokumen11 halamanGeet Reactor RodthenjhomebuyerBelum ada peringkat
- (Free Energy) Kunel PatentDokumen9 halaman(Free Energy) Kunel PatentIra Weinstein100% (1)
- Patent eDokumen5 halamanPatent eDaniel OliveiraBelum ada peringkat
- Vortex Tube ManufacturingDokumen3 halamanVortex Tube ManufacturingSameer JainBelum ada peringkat
- Moving Pulse GeneratorDokumen99 halamanMoving Pulse Generatorabc1000100% (1)
- GOAL of Creating This Document Is To Add The Latest July 2018 Supporting Knowledge To Maxes Work From RWG ForumDokumen102 halamanGOAL of Creating This Document Is To Add The Latest July 2018 Supporting Knowledge To Maxes Work From RWG ForumcesamavBelum ada peringkat
- BedinisgDokumen8 halamanBedinisgfinebdBelum ada peringkat
- Motionless Free Energy: Because It Opposes Itself, It Can Never Be More Than 100% Efficient. We AreDokumen6 halamanMotionless Free Energy: Because It Opposes Itself, It Can Never Be More Than 100% Efficient. We AreRolling76Belum ada peringkat
- GeneratorDokumen43 halamanGeneratorNeeraja ManemBelum ada peringkat
- BEMF-Recoil Recovery Battery Charger - by KoneheadXDokumen19 halamanBEMF-Recoil Recovery Battery Charger - by KoneheadXlittledigger100% (1)
- Barbosa 150426021227 Conversion Gate01Dokumen6 halamanBarbosa 150426021227 Conversion Gate01zac2351Belum ada peringkat
- GEET Fuel Processor Plans: WARNING: This Information Is Clasified As EXPERIMENTAL!Dokumen10 halamanGEET Fuel Processor Plans: WARNING: This Information Is Clasified As EXPERIMENTAL!John BlackBelum ada peringkat
- Simple Free-Energy Devices: Chapter 23: Power From InertiaDokumen3 halamanSimple Free-Energy Devices: Chapter 23: Power From InertiaLuc BerBelum ada peringkat
- A Self-Powered GeneratorDokumen16 halamanA Self-Powered Generatorkwag100% (1)
- Bedini SG Intermediate HandbookDokumen8 halamanBedini SG Intermediate HandbookVlad Adrian0% (1)
- Technical Description Steam EnginesDokumen6 halamanTechnical Description Steam Enginescarzante100% (1)
- Daniel McFarland Cook's Electro-Magnetic BatteryDokumen5 halamanDaniel McFarland Cook's Electro-Magnetic Batterychaiyoon100% (2)
- Kapanadze Patent WO 2008 103129 A1Dokumen11 halamanKapanadze Patent WO 2008 103129 A1armandoaltomare100% (1)
- The Making of The Källe-GasifierDokumen15 halamanThe Making of The Källe-GasifierMarky Maypo100% (1)
- PPMT Technology White PaperDokumen5 halamanPPMT Technology White Papermjstrand1Belum ada peringkat
- TEPZZ - 98 - Z9B - T: European Patent SpecificationDokumen30 halamanTEPZZ - 98 - Z9B - T: European Patent SpecificationMrSebolliniBelum ada peringkat
- European Patent Specification: ElementsDokumen12 halamanEuropean Patent Specification: ElementstonyBelum ada peringkat
- Lift RailDokumen15 halamanLift RailNguyen Cong MinhBelum ada peringkat
- Official Journal 01052009 Part II PDFDokumen255 halamanOfficial Journal 01052009 Part II PDFSam JacobBelum ada peringkat
- United States Patent: Fiigel US 6,840,540 B2Dokumen12 halamanUnited States Patent: Fiigel US 6,840,540 B2jemanuelvBelum ada peringkat
- TEPZZ 4979Z B - T: European Patent SpecificationDokumen12 halamanTEPZZ 4979Z B - T: European Patent SpecificationAna LisaBelum ada peringkat
- EP07752630NWB1Dokumen21 halamanEP07752630NWB1Sy Nguyen VietBelum ada peringkat
- Cryogenic Centrifugal Pump.Dokumen28 halamanCryogenic Centrifugal Pump.SIDDARAJU NBelum ada peringkat
- WO2018201118A1, SLB, IPEU For Drilling MachineDokumen44 halamanWO2018201118A1, SLB, IPEU For Drilling MachineDhrubajyoti BoraBelum ada peringkat
- EP1539573B1Dokumen21 halamanEP1539573B1雷黎明Belum ada peringkat
- US7915777 RingCoilDokumen7 halamanUS7915777 RingCoilscainiBelum ada peringkat
- Multitubular Reactor DesignDokumen26 halamanMultitubular Reactor DesignManoj BBelum ada peringkat
- EP0725696B1Dokumen19 halamanEP0725696B1Ashkan AsefiBelum ada peringkat
- TEPZZ 89 8 - B - T: European Patent SpecificationDokumen31 halamanTEPZZ 89 8 - B - T: European Patent SpecificationAna LisaBelum ada peringkat
- How to Find Out About Patents: The Commonwealth and International Library: Libraries and Technical Information DivisionDari EverandHow to Find Out About Patents: The Commonwealth and International Library: Libraries and Technical Information DivisionBelum ada peringkat
- Welcome in The Game - PagesDokumen11 halamanWelcome in The Game - PagesAndras KondratBelum ada peringkat
- KatowiceDokumen43 halamanKatowiceAndras KondratBelum ada peringkat
- KrakowDokumen75 halamanKrakowAndras KondratBelum ada peringkat
- Wang Shen He Magnetic - Motor1Dokumen48 halamanWang Shen He Magnetic - Motor1Bastien Gall de SilléBelum ada peringkat
- Polish Words Minimum To Learn DictionaryDokumen69 halamanPolish Words Minimum To Learn DictionaryAndras KondratBelum ada peringkat