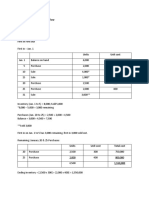
Acctg 100C 03 PDF
Diunggah oleh
Quid Damity0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
394 tayangan6 halamanThe document appears to be a review test for accounting students covering topics related to inventories. It contains 31 multiple choice questions testing concepts such as:
- Items that are and are not considered inventory under accounting standards
- Treatment of goods held on consignment, in transit, or returned by customers
- Inventory costing methods like FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average
- Calculating inventory values using methods like gross profit, retail, and estimation
- Disclosure requirements regarding pledged or destroyed inventory
The questions cover a wide range of inventory accounting concepts and indicate this is a comprehensive review of topics for students.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
ACCTG-100C-03.pdf
Hak Cipta
© © All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniThe document appears to be a review test for accounting students covering topics related to inventories. It contains 31 multiple choice questions testing concepts such as:
- Items that are and are not considered inventory under accounting standards
- Treatment of goods held on consignment, in transit, or returned by customers
- Inventory costing methods like FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average
- Calculating inventory values using methods like gross profit, retail, and estimation
- Disclosure requirements regarding pledged or destroyed inventory
The questions cover a wide range of inventory accounting concepts and indicate this is a comprehensive review of topics for students.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
394 tayangan6 halamanAcctg 100C 03 PDF
Diunggah oleh
Quid DamityThe document appears to be a review test for accounting students covering topics related to inventories. It contains 31 multiple choice questions testing concepts such as:
- Items that are and are not considered inventory under accounting standards
- Treatment of goods held on consignment, in transit, or returned by customers
- Inventory costing methods like FIFO, LIFO, and weighted average
- Calculating inventory values using methods like gross profit, retail, and estimation
- Disclosure requirements regarding pledged or destroyed inventory
The questions cover a wide range of inventory accounting concepts and indicate this is a comprehensive review of topics for students.
Hak Cipta:
© All Rights Reserved
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 6
Pamantasan ng Cabuyao
Katapatan Subd., Banay Banay, City of Cabuyao
Accounting Review III - Practical Accounting I (ACCTG100C) P1 - 03
INVENTORIES
1. Under PAS 2, which is not considered as items of inventory?
A. Supplies and materials awaiting use in the production
B. Land and other property purchased and held for resale
C. Costs of service for which a service provider has not yet recognized the related revenue
D. Abnormal amounts of wasted materials, labor and other production costs
2. The inventory of a service provider may be described as
A. Work in progress C. Progress billings
B. Service goods D. Unearned revenue
3. An entity shall include in its inventory all goods
A. Owned but not possessed by the entity at the balance sheet date
B. Owned and possessed by the entity at the balance sheet date
C. Owned by the entity at the balance sheet date, regardless of location
D. Possessed but not owned by the entity at the balance sheet date
4. Goods on consignment should be included in the inventory of
A. Consignor but not the consignee C. The consignee but not the consignor
B. Both the consignor and the consignee D. Neither the consignor nor the consignee
5. Freight and other handling charges incurred in the transfer of goods from consignor to consignee are
A. Expense on the part of the consignee C. Inventoriable by the consignee
B. Expense on the part of the consignor D. Inventoriable by the consignor
6. Which of the following items should be excluded in inventory at year-end?
A. Goods in transit to which title is held C. Goods held on consignment
B. Goods out on consignment D. Goods returned by customer
7. F.O.B. Destination shall mean that
A. The freight charge is actually to be paid by the seller
B. The freight charge is actually to be paid by the buyer
C. The ownership of the goods is transferred upon receipt of the goods by the buyer at the point of the destination and the seller
is the owner of the goods while in transit.
D. The ownership of the goods is transferred upon the shipment of the goods by the seller and the buyer is the owner of the
goods while in transit.
8. The buyer actually paid the freight charges but is not legally responsible for the same.
A. FOB destination, freight prepaid C. FOB shipping point, freight prepaid
B. FOB destination, freight collect D. FOB shipping point, freight collect
9. An entity should include one of the following items in its merchandise inventory
A. Goods purchased FOB destination still en route
B. Goods held for pick-up by the buyer
C. Goods sold FOB shipping point still en route
D. Goods purchased FOB shipping point still en route
10. Inventories should be measured at
A. Cost or net realizable value, whichever is higher
B. Cost or fair value less cost to sell, whichever is lower
C. Lower of cost or net realizable value, item by item
D. Lower of cost or net realizable value, by total
11. For a merchandising concern, inventory cost shall exclude
A. Purchase price C. Trade discounts and rebates
B. Transportation and handling costs D. Import duties and other taxes
12. For a manufacturing concern, inventory cost shall include
A. Abnormal waste C. Variable administrative expenses
B. Storage and selling costs D. Fixed manufacturing overhead
13. Net realizable value (NRV) is computed as
A. Estimated selling price less estimated cost to sell
B. Estimated selling price less estimated cost to complete
C. Estimated selling price less estimated cost to complete and estimated cost to sell
D. Estimated selling price less estimated cost to complete, estimated cost to sell and normal profit margin
14. Under PAS 2, they are “individuals who buy and sell commodities for others or on their own account”.
A. Commission brokers C. Finders
B. Broker-traders D. Seekers
15. Under PAS 2, commodities of broker-traders are measured at
A. Cost C. Fair value
B. Net realizable value D. Fair value less cost to sell
16. The proper cost method for inventories that are not ordinarily interchangeable and goods or services produced and segregated for
specific projects is the
A. Specific identification C. Last-In, First-Out
B. First-In, First-Out D. Weighted average
17. If the specific identification of costing inventory is impractible under the circumstances, the cost of the inventories is assigned by
using which set of cost flow assumptions?
A. First-In, First-Out (FIFO) or Weighted average
B. Last-In, First-Out, (LIFO) or Weighted average
C. First-In, First-Out (FIFO) or Last-In, First-Out, (LIFO)
D. Last-In, Last-Out, (LILO) or Last-In, First-Out, (LIFO)
18. Which inventory costing method is most conservative in periods of declining inventory costs?
A. First-In, First-Out (FIFO)
B. Last-In, First-Out, (LIFO)
C. Weighted average
D. Cannot be determined without more information
19. Which costing method results in inventory being stated at the most recent acquisition costs?
A. Specific identification C. Last-In, First-Out
B. First-In, First-Out D. Weighted average
20. Under the periodic inventory system, the opening stock is the
A. Net purchases minus the total goods sold
B. Net purchases minus the closing stock
C. Total goods available for sale minus the net purchases
D. Total goods available for sale minus the total goods sold
21. Which of the following pairs of inventory terms would NOT usually go together?
A. Periodic inventory system <> Freight-In account
B. Perpetual inventory system <> Cost of goods sold account
C. Gross price method <> Purchase discount taken account
D. Net price method <> Purchase discount loss account
22. Determine the true statement regarding discounts on the price of inventory
A. Trade discount and cash discount are one and the same
B. Both trade discount and cash discount are recorded on the accounting records
C. Cash discount is recorded in the accounting records while trade discount is not
D. Trade discount is given as incentive to customers for early payments of amount due
23. Theoretically, cash discounts permitted on purchased of raw materials should be
A. Added to other income, whether taken or not
B. Added to other income, only if taken
C. Deducted from inventory, whether taken or not
D. Deducted from inventory, only if taken
24. Which will not require inventory estimation?
A. Inventory destroyed by a major fire incident in the production facility
B. Proof of the reasonable accuracy of the physical inventory count
C. External and internal interim financial statements are prepared
D. Year-end reporting for the inventory shown on the face of the balance sheet
25. Under the gross profit method, if the gross profit rate is based on sales, the cost of sales is computed as
A. Gross sales divided by sales ratio C. Net Sales divide by cost ratio
B. Gross sales times cost ratio D. Net sales times cost ratio
26. Under the gross profit method, if the gross profit rate is based on cost, the cost of sales is computed as
A. Gross sales divided by sales ratio C. Net sales divide by sales ratio
B. Gross sales times cost ratio D. Net sales times cost ratio
27. The gross margin method of estimating ending inventory may be used for all of the following except
A. Internal as well as external interim reports
B. Internal as well as external year-end reports
C. Estimate of inventory destroyed by fire or other casualty
D. Rough test of the validity of an inventory cost determined under either periodic or perpetual system
28. The retail inventory method would include which of the following in the calculation of the goods available for sale at both cost and
retail?
A. Freight in C. Markups
B. Purchase returns D. Markdowns
29. In computing the cost ratio, the conservative/conventional retail method should
A. Include markup and markdown C. Include markup but not markdown
B. Exclude markup and markdown D. Exclude markup but not markdown
30. When a portion of an inventories had been pledged as a security on a loan
A. An equal amount of retained earnings should be appropriated
B. The fact should be disclosed but the amount of the current assets should not be affected
C. The value of the inventory pledged should be subtracted from the loan balance
D. The cost of the pledged inventories should be transferred from current assets to noncurrent assets
31. Assume that a company records purchases net of discount. If the company bought merchandise valued at P10,000 on credit terms
3/15, n/30, the entry to record the payment for half of the purchase within the discount period would include a debit to
A. Accounts Payable for P4,850 and a credit to Cash for P4,850.
B. Accounts Payable for P5,000 and credit to Cash for P5,000.
C. Accounts Payable for P4,850 and to Interest Expense for P150 and a credit to Cash for P5,000.
D. Accounts Payable for P5,000 and credit to Interest Revenue for P150 and to Cash for P4,850.
32. Amoy Retailers purchased merchandise with a list price of P100,000, subject to trade discount of 20% and credit terms of 2/10,
n/30. At what amount should Amoy record the cost of this merchandise if the gross method is used?
A. P100,000 C. P98,000
B. 80,000 D. 78,000
33. On August 1, ST Company recorded purchases of inventory of P80,000 and P100,000 under credit terms of 2/15, n/30. The
payment due on the P80,000 purchases was remitted on August 14. The payment due on the P100,000 purchased was remitted on
August 29. Under the net method and the gross method, these purchases should be included at what respective net amounts in the
determination of cost of goods available for sale?
Net Method Gross Method
A. P178,400 P176,400
B. 176,400 176,400
C. 176,400 178,400
D. 180,000 176,400
34. Hold Co., a manufacturer had inventories at the beginning and end of its current year as follows:
Beginning End
Raw Materials P11,000 P15,000
Work in Process 20,000 24,000
Finished Goods 12,500 9,000
During the year, the following cost and expenses were incurred:
Raw materials purchased P150,000
Direct labor cost 60,000
Indirect factory labor 30,000
Taxes and depreciation on factory building 10,000
Taxes and depreciation on sales room and office 7,500
Sales salaries 20,000
Office salaries 12,000
Utilities (60% applicable to factory, 20% to sales room,
and 20% to office) 25,000
Hold’s cost of good sold for the year is
A. P257,000 C. P 261,000
B. 260,500 D. 269,500
35. Gomez Company’s inventory at June 30, 2017, was P750,000 based on the physical count of goods priced at cost, and before any
necessary year-end adjustment relating to the following:
• Included on the physical count were goods billed to a customer FOB shipping point on June 30. These goods had a cost
of P15, 000 and were picked up by the carrier on July 10, 2017.
• Goods shipped FOB destination on June 28, 2013 from a vendor to Gomez was received on
July 3, 2017. The invoice cost was P25, 000.
What amount should Gomez report as inventory on its June 30, 2017 balance sheet?
A. P735,000 C. P750,000
B. 740,000 D. 765,000
36. The balance sheet of MB Company’s accounts payable account on December 31, 2017, was P1,100,000 before considering the
following information:
• Goods shipped FOB shipping point on December 31, 2017, from a vendor to MB were lost in transit. The invoice
cost of P20,000 was not recorded by MB. On January 6, 2018, MB filed at P20,000 claims against the common
carrier.
• Goods shipped FOB destination on December 21, 2017, from a vendor to MB were lost in transit. The invoice cost of
P45,000 was not recorded by MB. On December 28, 2017, MB notified the vendor of the lost shipment.
• On December 27, 2017, a vendor authorized MB to return, for full credit, goods shipped and billed a P35,000 on
December 2, 2017. The returned goods were shipped by MB on December 27, 2017. A P35,000 credit memo was
received and recorded by MB on January 6, 2018.
• Goods were in transit from a vendor to MB on December 31, 2017. The invoice cost was P60,000 and the goods
were shipped FOB shipping point on December 28, 2017. MB received the good on January 6, 2018.
What amount should MB report as account payable in its December 31, 2017 balance sheet?
A. P1,145,000 C. P1,125,000
B. !,190,000 D. !,180,000
Questions 37 and 38 are based on the following information.
Miss U Co. is a wholesaler of office supplies. The activity for Model AA calculators during August is shown below:
Date Balance/Transaction Units Cost
August 1 Inventory 2,000 P36.00
7 Purchase 3,000 37.20
12 Sales 3,600
21 Purchase 4,800 38.00
22 Sales 3,800
29 Purchase 1,600 38.60
37. If Miss U uses a FIFO periodic inventory system, the ending inventory of Model AA calculators at August 31 is reported as
A. P150,080 C. P152,288
B. 150,160 D. 152,960
38. If Miss U uses FIFO perpetual inventory, the ending inventory of Model AA calculators at August 31 is reported as
A. P146,400 C. P150,160
B. 150,080 D. 152,960
Questions 39 and 40 are based on the following information.
Iluvit Co. is a wholesaler of condoms. The activity for the Ultra Thin With Wings Condom during July is shown below:
Date Balance/Transaction Units Cost
July 1 Inventory 2,000 P36.00
7 Purchase 3,000 37.00
12 Sales 3,600
21 Purchase 5,000 37.88
22 Sales 3,800
29 Purchase 1,600 38.11
39. If Iluvit Co. uses the average cost method to account for inventory, the ending inventory of Ultra Thin With Wings Condom at July
31 is reported as
A. P153,400 C. P158,736
B. 156,912 D. 159,464
40. If Iluvit Co. uses moving average perpetual inventory system, the ending inventory of Ultra Thin With Wings Condom at July 31 is
reported as
A. P153,400 C. P158,736
B. 156,912 D. 159,464
41. The following information was taken from FF Company’s accounting records:
Increase in raw materials inventory P 7,500
Decrease in finished goods inventory 17,500
Raw materials purchases 215,000
Direct labor payroll 100,000
Factory overhead 150,000
Freight-out 22,500
There was no work-in process inventory at the beginning or at the end of the year. FF’s cost of goods sold is
A. P497,500 C. P482,500
B. 487,500 D. 475,000
42. On January 1, 2017, La Union Corporation signed a three-year, noncancellable purchase contract, which allows La Union to
purchase up to 5,000 units of computer part annually from Abacus Supply Company at P50 per unit and guarantees a minimum
annual purchase of 1,000 units. During 2017, the part unexpectedly became obsolete. La Union had 2,500 units of this inventory at
December 31, 2017, and believe these parts can be sold as a scrap for P10 per unit.
What amount of probable loss from the purchase commitment should La Union report in its 2017 income statement?
A. P120,000 C. P80,000
B. 100,000 D. 40,000
43. Pampanga Company has determined its December 31, 2017 inventory on a FIFO basis to be P2,000,000. Information relating to
that inventory is as follows:
Estimated selling price P 2,040,000
Estimated cost of disposal 100,000
Normal profit margin 300,000
Current replacement cost 1,800,000
Pampanga records losses that results from applying the lower of cost or market rule. At December 31, 2017, what should be the
net carrying value of Pampanga’s inventory?
A. P2,000,000 C. P1,800,000
B. 1,940,000 D. 1,640,000
44. On November 30, 2017, Noon Company cosigned 30 freezers to Wong Company for sale at P32,000 each and paid P24,000 in
transportation costs. An account sales was received on December 30, 2017 from Wong reporting the sales of 10 freezers, together
with a remittance of P272,000 balance due. The remittance was net of the agreed 15% commission.
How much, and in what month, should Noon recognized as consignment sales revenue?
November 2017 December 2017
A. P 0 P320,000
B. 0 272,000
C. 816,000 0
D. 960,000 0
45. A major portion of Volvo Company’s inventory was stolen on the night of February 14, 2018. A physical count the next day revealed
that the goods costing P1,200,000 were still on hand. Your examination of the company’s accounting records reveals the following.
Inventory, January 1 P2,500,000
Transactions, January 1 through February 14, 2018
Purchases 9,700,000
Purchase returns 200,000
Freight in 600,000
Sales 14,500,000
Sales returns 500,000
The company began operations early in 2017, and its income statement for the year is presented below:
Net sales P19,500,000
Cost of goods sold (11,700,000)
Gross margin on sales P 7,800,000
Operating expenses (2,800,000)
Income before income tax P 5,000,000
Income tax 1,600,000
Net income P 3,400,000
The estimated cost of inventory that was stolen should be reported at
A. P5,800,000 C. P4,200,000
B. 2,700,000 D. 3,000,000
46. On the night of September 30, 2017, a fire destroyed most of the merchandise inventory of Bulacan Company. All goods were
completely destroyed except for partially damaged goods that normally sells for P50,000 and that had an estimated realizable value
of P12,500 and undamaged goods that normally sells for P30,000. The following data are available:
Inventory, January 1, 2017 P 330,000
Net purchases, January through September 30 2,120,000
Net Sales, January 1 through September 30 2,800,000
Total 2016 2015 2004
Net Sales P4,500,000 P2,500,000 P1,500,000 P500,000
Cost of sales 3,375,000 1,920,000 1,100,000 355,000
Gross income P1,125,000 P 580,000 P 400,000 P145,000
What is the estimated amount of fire loss on September 30, 2017?
A. P290,000 C. P350,000
B. 315,000 D. 307,000
Questions 47 through 48 are based on the following information:
At December 31, 2017, the following information was available from Olongapo Company’s accounting records:
Cost Retail
Inventory, January 1, 2017 P100,000 P200,000
Net Purchases 500,000 800,000
Net markups 250,000
Net markdowns 50,000
Sales 800,000
47. What is the inventory at FIFO cost?
A. P200,000 C. P192,000
B. 190,480 D. 400,000
48. What is the ending inventory at average cost?
A. P200,000 C. P192,000
B. 190,480 D. 400,000
49. Batangas’ Superstore’s inventory records show the following information at December 31, 2017:
Cost Retail
Inventory, January 1, 2017 P 280,000 P 700,000
Sales 4,700,000
Purchases 2,500,000 5,190,000
Departmental transfer – credit 20,000 30,000
Freight in 75,000
Mark up cancellation 500,000
Markdown 60,000
Markdown cancellation 250,000
Employee discounts 50,000
Estimated normal shrinkage is 2.5% of sales 300,000
Batangas uses the conventional retail inventory method in estimating the value of its inventory. The estimated cost of inventory at
December 31, 2017 is
A. P230,000 C. P495,000
B. 438,000 D. 536,250
50. On January 1, 2017, the stock inventory of Manila Store was P500,000 at retail and P280,000 at cost. During the year, the store
registered the following purchases:
Cost P2,000,000
Retail price 3,100,000
Original price 1,100,000
The net sales were P2,700,000. The following reductions were made in the retail price:
To meet price competition P25,000
To dispose of overstock 15,000
Miscellaneous reductions 60,000
During the year, the selling price of a certain inventory increased from P100 to P150. This additional markup applied to 5,000 items
but was later cancelled on the remaining 1,000 items. What is the estimated cost of the inventory on December 31, 2017 using the
retail method?
A. P1,000,000 C. P270,000
B. 1,200,000 D. 600,000
--END--
wep/ACCTG100C/inventories
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- PAS 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodDokumen2 halamanPAS 10 Events After The Reporting PeriodJennicaBailonBelum ada peringkat
- Government Grants: Use The Following Information For The Next Three QuestionsDokumen2 halamanGovernment Grants: Use The Following Information For The Next Three QuestionsJEFFERSON CUTEBelum ada peringkat
- 2 To 20 Years - Girls Stature-For-Age and Weight-For-Age PercentilesDokumen1 halaman2 To 20 Years - Girls Stature-For-Age and Weight-For-Age PercentilesRajalakshmi Vengadasamy0% (1)
- Organic Chemistry 1Dokumen265 halamanOrganic Chemistry 1Israk Mustakim IslamBelum ada peringkat
- CH 04Dokumen19 halamanCH 04Charmaine Bernados BrucalBelum ada peringkat
- (Chp10-12) Pas 2 - Inventory, Inventory Valuation and Inventory EstimationDokumen10 halaman(Chp10-12) Pas 2 - Inventory, Inventory Valuation and Inventory Estimationbigbaek0% (3)
- A17NB - InventoryDokumen4 halamanA17NB - Inventoryhellohello100% (1)
- Quiz 3 PDFDokumen20 halamanQuiz 3 PDFGirly CrisostomoBelum ada peringkat
- INTACC1 Inventory ProblemsDokumen3 halamanINTACC1 Inventory ProblemsButterfly 0719Belum ada peringkat
- 1-1-2017 Petty Cash FundDokumen4 halaman1-1-2017 Petty Cash FundMr. CopernicusBelum ada peringkat
- Notes Rec. Valix Intermediate AccountDokumen9 halamanNotes Rec. Valix Intermediate AccountJi BaltazarBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture Notes On Inventory Estimation - 000Dokumen4 halamanLecture Notes On Inventory Estimation - 000judel ArielBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz VIII - ARDokumen3 halamanQuiz VIII - ARBLACKPINKLisaRoseJisooJennieBelum ada peringkat
- 2.1 Assessment Test 2.2: Receivables Prelim Exam Intermediate AccountingDokumen9 halaman2.1 Assessment Test 2.2: Receivables Prelim Exam Intermediate AccountingWinoah HubaldeBelum ada peringkat
- 7 Cost Formulas and LCNRVDokumen6 halaman7 Cost Formulas and LCNRVJorufel PapasinBelum ada peringkat
- MidtermsDokumen8 halamanMidtermsRhea BadanaBelum ada peringkat
- Notes On Partnership FormationDokumen11 halamanNotes On Partnership FormationSarah Mae EscutonBelum ada peringkat
- Partnership Dissolution ProblemsDokumen9 halamanPartnership Dissolution ProblemsKristel DayritBelum ada peringkat
- Answer To Problems On Cash & Cash Equivalents - Reinforcement DiscussionDokumen8 halamanAnswer To Problems On Cash & Cash Equivalents - Reinforcement DiscussionAnnie RapanutBelum ada peringkat
- This Study Resource Was: Problem 1Dokumen2 halamanThis Study Resource Was: Problem 1Michelle J UrbodaBelum ada peringkat
- CASH QuestionsDokumen9 halamanCASH QuestionsKenncyBelum ada peringkat
- AC 3 - Intermediate Acctg' 1 (Ate Jan Ver)Dokumen119 halamanAC 3 - Intermediate Acctg' 1 (Ate Jan Ver)John Renier Bernardo100% (1)
- Cash and Cash EquivalentsDokumen5 halamanCash and Cash EquivalentsFelsie Jane PenasoBelum ada peringkat
- Property, Plant and EquipmentDokumen40 halamanProperty, Plant and EquipmentNatalie SerranoBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 1 P2 FinmanDokumen3 halamanQuiz 1 P2 FinmanRochelle Joyce CosmeBelum ada peringkat
- Midterm Examination AnswersDokumen3 halamanMidterm Examination AnswersMilani Joy LazoBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set 2Dokumen4 halamanProblem Set 2Michael Jay LingerasBelum ada peringkat
- Pas 37 38 40 41 PFRS 1Dokumen5 halamanPas 37 38 40 41 PFRS 1LALALA LULULUBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz 4 - Unit 4 - Investment in Equity Securities Quiz InstructionsDokumen22 halamanQuiz 4 - Unit 4 - Investment in Equity Securities Quiz InstructionsCharmaine Mari OlmosBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz No. 2 - ReceivablesDokumen1 halamanQuiz No. 2 - ReceivablesJi BaltazarBelum ada peringkat
- Vallix QuestionnairesDokumen14 halamanVallix QuestionnairesKathleen LucasBelum ada peringkat
- Included Investment Related Problems/questionsDokumen22 halamanIncluded Investment Related Problems/questionsJanine LerumBelum ada peringkat
- Intermediate Accounting 1 Departmental Exam MidtermsDokumen6 halamanIntermediate Accounting 1 Departmental Exam MidtermsCharles AtimBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Concepts Revenue Cycle: List Price, Trade Discount, Prepaid Freight, Cash DiscountDokumen50 halamanBasic Concepts Revenue Cycle: List Price, Trade Discount, Prepaid Freight, Cash DiscountJean MaeBelum ada peringkat
- Answer:: TotalDokumen2 halamanAnswer:: TotalCarla Jane ApolinarioBelum ada peringkat
- ReceivablesDokumen31 halamanReceivablesKate MercadoBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Assets at Fair Value (Investments) Basic ConceptsDokumen2 halamanFinancial Assets at Fair Value (Investments) Basic ConceptsMonica Monica0% (1)
- Problems 3 PRELIM TASK FINALDokumen4 halamanProblems 3 PRELIM TASK FINALJohn Francis RosasBelum ada peringkat
- Merchadising MOCK QUIZDokumen5 halamanMerchadising MOCK QUIZCarl Dhaniel Garcia SalenBelum ada peringkat
- CAE 10 CG Strategic Cost ManagementDokumen23 halamanCAE 10 CG Strategic Cost ManagementAmie Jane MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 4Dokumen65 halamanChapter 4NCTBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 11 - Inventory Cost FlowDokumen6 halamanChapter 11 - Inventory Cost FlowLorence IbañezBelum ada peringkat
- Quizzes PremidDokumen80 halamanQuizzes PremidJosh Sean Kervin SevillaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen8 halamanChapter 2cindyBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsDokumen3 halaman1 Cash and Cash EquivalentsJohn Aries Reyes100% (1)
- Quiz 1 Finals BSA2102 With SolutionDokumen6 halamanQuiz 1 Finals BSA2102 With SolutionJohn ryan Del RosarioBelum ada peringkat
- C8 Statement of Financial PositionDokumen14 halamanC8 Statement of Financial PositionAllaine ElfaBelum ada peringkat
- FAR 02 23 Leases PDFDokumen13 halamanFAR 02 23 Leases PDFSherri BonquinBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Accounting and Reporting IDokumen5 halamanFinancial Accounting and Reporting IKim Cristian Maaño50% (2)
- Chapter 13 - Gross Profit MethodDokumen7 halamanChapter 13 - Gross Profit MethodLorence IbañezBelum ada peringkat
- Correct Amount of Inventory 677,500Dokumen8 halamanCorrect Amount of Inventory 677,500Maria Kathreena Andrea AdevaBelum ada peringkat
- Pre FinactDokumen6 halamanPre FinactMenardBelum ada peringkat
- Financial Accounting and Reporting Test Bank 8152017 - 1: Problem 1 - Statement of Financial PositionDokumen29 halamanFinancial Accounting and Reporting Test Bank 8152017 - 1: Problem 1 - Statement of Financial PositionBernadette PalermoBelum ada peringkat
- Peer Quiz No.1: Partnership Formation: TotalDokumen13 halamanPeer Quiz No.1: Partnership Formation: Totaldianel villaricoBelum ada peringkat
- Prob 3Dokumen3 halamanProb 3jikee11Belum ada peringkat
- Article 1475Dokumen2 halamanArticle 1475Sintas Ng SapatosBelum ada peringkat
- (Intermediate Accounting 1A) : Lecture AidDokumen25 halaman(Intermediate Accounting 1A) : Lecture AidShe RC100% (2)
- Chapter 1-Basic-Concepts-and-Job-Order-Cost-CycleDokumen21 halamanChapter 1-Basic-Concepts-and-Job-Order-Cost-CycleRhodoraBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Wasting Assets PDFDokumen2 halaman8 Wasting Assets PDFGayle LalloBelum ada peringkat
- C14 - PAS 2 InventoriesDokumen20 halamanC14 - PAS 2 InventoriesAllaine ElfaBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Task 1-1Dokumen10 halamanAssessment Task 1-1hahahahaBelum ada peringkat
- InventoriesDokumen6 halamanInventoriesheythereitsclaireBelum ada peringkat
- Inventories - Theories - Please AnswerDokumen7 halamanInventories - Theories - Please AnswerAbbygailBelum ada peringkat
- Acctg 100C 25 PDFDokumen2 halamanAcctg 100C 25 PDFQuid DamityBelum ada peringkat
- Acctg 100C 16 PDFDokumen4 halamanAcctg 100C 16 PDFQuid DamityBelum ada peringkat
- Acctg 100C 04 PDFDokumen2 halamanAcctg 100C 04 PDFQuid DamityBelum ada peringkat
- Acctg 100C 06 PDFDokumen2 halamanAcctg 100C 06 PDFQuid DamityBelum ada peringkat
- Brigade Product Catalogue Edition 20 EnglishDokumen88 halamanBrigade Product Catalogue Edition 20 EnglishPelotudoPeloteroBelum ada peringkat
- Civ Beyond Earth HotkeysDokumen1 halamanCiv Beyond Earth HotkeysExirtisBelum ada peringkat
- PE MELCs Grade 3Dokumen4 halamanPE MELCs Grade 3MARISSA BERNALDOBelum ada peringkat
- HFE0106 TraskPart2Dokumen5 halamanHFE0106 TraskPart2arunkr1Belum ada peringkat
- Module 1 Lesson 2Dokumen31 halamanModule 1 Lesson 2Angela Rose BanastasBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To DifferentiationDokumen10 halamanIntroduction To DifferentiationaurennosBelum ada peringkat
- Grid Pattern PortraitDokumen8 halamanGrid Pattern PortraitEmma FravigarBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2Dokumen8 halamanChapter 2Fahmia MidtimbangBelum ada peringkat
- Hydro Electric Fire HistoryDokumen3 halamanHydro Electric Fire HistorygdmurfBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding PTS Security PDFDokumen37 halamanUnderstanding PTS Security PDFNeon LogicBelum ada peringkat
- Low Budget Music Promotion and PublicityDokumen41 halamanLow Budget Music Promotion and PublicityFola Folayan100% (3)
- Santu BabaDokumen2 halamanSantu Babaamveryhot0950% (2)
- TraceDokumen5 halamanTraceNorma TellezBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Bacterial DeseaseDokumen108 halaman1 Bacterial DeseasechachaBelum ada peringkat
- 19c Upgrade Oracle Database Manually From 12C To 19CDokumen26 halaman19c Upgrade Oracle Database Manually From 12C To 19Cjanmarkowski23Belum ada peringkat
- When A Snobbish Gangster Meets A Pervert CassanovaDokumen62 halamanWhen A Snobbish Gangster Meets A Pervert CassanovaMaria Shiela Mae Baratas100% (1)
- Guidelines For Prescription Drug Marketing in India-OPPIDokumen23 halamanGuidelines For Prescription Drug Marketing in India-OPPINeelesh Bhandari100% (2)
- Expression of Interest (Consultancy) (BDC)Dokumen4 halamanExpression of Interest (Consultancy) (BDC)Brave zizBelum ada peringkat
- Hazardous Locations: C.E.C. ClassificationsDokumen4 halamanHazardous Locations: C.E.C. ClassificationsThananuwat SuksaroBelum ada peringkat
- Recruitment SelectionDokumen11 halamanRecruitment SelectionMOHAMMED KHAYYUMBelum ada peringkat
- ThorpeDokumen267 halamanThorpezaeem73Belum ada peringkat
- CAA Safety Plan 2011 To 2013Dokumen46 halamanCAA Safety Plan 2011 To 2013cookie01543Belum ada peringkat
- 1.SDH Basics PDFDokumen37 halaman1.SDH Basics PDFsafder wahabBelum ada peringkat
- Design and Analysis of Modified Front Double Wishbone Suspension For A Three Wheel Hybrid VehicleDokumen4 halamanDesign and Analysis of Modified Front Double Wishbone Suspension For A Three Wheel Hybrid VehicleRima AroraBelum ada peringkat
- Bajaj Vs Hero HondaDokumen63 halamanBajaj Vs Hero HondaHansini Premi100% (1)
- Power Curbers, Inc. v. E. D. Etnyre & Co. and A. E. Finley & Associates, Inc., 298 F.2d 484, 4th Cir. (1962)Dokumen18 halamanPower Curbers, Inc. v. E. D. Etnyre & Co. and A. E. Finley & Associates, Inc., 298 F.2d 484, 4th Cir. (1962)Scribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Ci Thai RiceDokumen4 halamanCi Thai RiceMakkah Madina riceBelum ada peringkat