Myoma
Diunggah oleh
Eleazar Bagon0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
279 tayangan7 halamanIn order for a normal cell to transform into a cancer cell, genes which regulate cell growth and differentiation must be altered. Exposure of normal cells to some etiologic agent may transform normal cells into cancer cells. Chemical carcinogens. These chemicals cause cell mutation or alter the cell enzymes and proteins.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
myoma
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniIn order for a normal cell to transform into a cancer cell, genes which regulate cell growth and differentiation must be altered. Exposure of normal cells to some etiologic agent may transform normal cells into cancer cells. Chemical carcinogens. These chemicals cause cell mutation or alter the cell enzymes and proteins.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
279 tayangan7 halamanMyoma
Diunggah oleh
Eleazar BagonIn order for a normal cell to transform into a cancer cell, genes which regulate cell growth and differentiation must be altered. Exposure of normal cells to some etiologic agent may transform normal cells into cancer cells. Chemical carcinogens. These chemicals cause cell mutation or alter the cell enzymes and proteins.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
Definition of Cancer 2.
Women are more prone to breast, uterine and
Cancer is disease of regulation of tissue growth. In this cervical cancer
disease, the cells of the body display uncontrolled 3. Men are more prone prostate and lung cancer
growth, invasion that intrudes and destroys adjacent 4. Urban dwellers
tissues and spreads to other body locations. In order for 5. Chemical factory workers
a normal cell to transform into a cancer cell, genes 6. Farmers
which regulate cell growth and differentiation must be 7. Personnel of radiology department
altered. 8. Family history
Theories about Cancer 9. Obesity
1. Cellular transformation and Derangement 10. Stress
theory. In this theory, exposure of normal cells Pathophysiology of Cancer
to some etiologic agent may transform normal A healthy cell becomes a cancer cell by undergoing the
cells into cancer cells. following processes:
2. Failure of the Immune Response Theory. This 1. Proto-oncogenes are changed to oncogenes.
theory conceptualizes that all individuals possess Proto-oncogenes are genes that are coded to
cancer cells but these cancer cells are NOT maintain normal cell growth. In cases of a
recognized by the immune system. Thus, cancer developing cancer, oncogene takes its place.
cells undergo destruction. Failure of the immune Oncogene is a gene that makes cells grow and
response system to kill or destroy the cancer divide rapidly.
cells leads to cancer. 2. Cancer cell grows and divides rapidly.
Etiologic Factors or Carcinogens 3. Alteration of the tumor suppression genes takes
• Viruses or Oncogenic Viruses. Prolonged and place.
recurrent viral infections may lead to the 4. DNA repair genes are altered and turned off.
breakdown of the immune system. The Uterine fibroids
overwhelmed immune system may fail to Leiomyoma; Fibromyoma; Myoma; Fibroids
destroy the cancer cells present in the body. The Uterine fibroids are noncancerous (benign) tumors that
human papillomavirus (HPV) are particularly develop in the uterus (womb), a female reproductive
common cancer-causing virus which is well- organ.
known for causing genital warts and all cases of Causes, incidence, and risk factors
cervical cancer. Uterine fibroids are the most common pelvic tumor. As
• Chemical carcinogens. These chemicals cause many as 1 in 5 women may have fibroids during their
cell mutation or alter the cell enzymes and childbearing years (the time after starting menstruation
proteins. for the first time and before menopause).
Industrial Compounds Fibroids usually affect women over age 30. They are
1. Vinyl chloride – plastic manufacture, asbestos rare in women under 20, and often shrink and cause no
factories, construction works symptoms in women who have gone through
2. Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons menopause. They are more common in African
3. Fertilizers Americans than Caucasians.
4. Weed killers The cause of uterine fibroid tumors is unknown.
5. Dyes – analine dyes (most commonly found in However, fibroid growth seems to depend on the
beauty shops and used at homes), hair bleach hormone estrogen. As long as a woman with fibroids is
6. Drugs – cytotoxic drugs, tar nicotine in tobacco, menstruating, a fibroid will probably continue to grow,
alcohol usually slowly.
Hormones Fibroids can be so tiny that you need a microscope to
1. Estrogen see them. However, they can grow very large. They may
2. Diethystilbesterol (DES) fill the entire uterus, and may weigh several pounds.
Foods, preservatives Although it is possible for just one fibroid to develop,
1. Nitrites in bacon or smoked meat usually there are more than one.
2. Talc (polished rice, salami and chewing gum) Fibroids are often described by their location in the
3. Food sweeteners uterus:
4. Nitrosomines (rubber baby nipples) • Myometrial -- in the muscle wall of the uterus
5. Aflatoxins (mold in nuts, grains, milk, cheese • Submucosal -- just under the surface of the
and peanut butter) uterine lining
6. Polycyclic hydrocarbons • Subserosal -- just under the outside covering of
• Physical agents the uterus
Radiation • Pendunculated -- occurring on a long stalk on
1. From x-rays or radioactive isotopes the outside of the uterus or inside the cavity of
2. From sunlight or UV rays the uterus
Physical irritation or trauma Symptoms
1. Pipe smoking More common symptoms of uterine fibroids are:
2. Multiple deliveries • Abdominal fullness, gas, or constipation
• Genetics • Bleeding between periods
Risk Factors • Increase in urinary frequency
1. Older individuals
• Heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia), • Uterine artery embolization: This procedure
sometimes with the passage of blood clots stops the blood supply to the fibroid, causing it
• Menstrual periods that may last longer than to die and shrink. Women who may want to
normal become pregnant in the future should discuss
• Pelvic cramping or pain with periods this procedure with their health care provider.
• Sensation of fullness or pressure in lower • Myomectomy: This surgery removes the fibroids.
abdomen It is often the chosen treatment for women who
• Pain during intercourse want to have children, because it usually can
Note: There are often no symptoms. preserve fertility. More fibroids can develop after
Signs and tests a myomectomy.
A pelvic examination may show an irregularly shaped, • Hysterectomy: This invasive surgery may be an
lumpy, or enlarged uterus. Frequently, this diagnosis is option if medicines do not work and other
reliable. In some cases, it is difficult to diagnose fibroids, surgeries and procedures are not an option.
especially in obese women. Fibroid tumors have been Support Groups
mistaken for: National Uterine Fibroid Foundation - www.nuff.org
• Pregnancy Expectations (prognosis)
Some women with fibroids have no symptoms and may
• Ovarian tumors
not need treatment.
• Inflammation of the fallopian tubes During a pregnancy, existing fibroids may grow due to
• Uterine adenomyosis (a condition in which the the increased blood flow and estrogen levels. The
uterine lining grows into the muscle wall of the fibroids usually return to their original size after the
uterus) baby is delivered.
A transvaginal ultrasound or pelvic ultrasound may be Complications
done to confirm the diagnosis of fibroids. Sometimes, a Fibroids may cause pregnancy complications, although
pelvic MRI is used to confirm the diagnosis. the risk is thought to be small:
An endometrial biopsy (biopsy of the uterine lining) or • Most women are able to carry their babies to
laparoscopy may be needed to rule out cancer. term, but some end up delivering prematurely
Treatment because there is not enough room in the uterus.
Treatment depends on various factors, including:
• Some pregnant women with fibroids may need a
• Age cesarean section because fibroids can
• General health occasionally block the birth canal or cause the
• Severity of symptoms baby to be positioned wrong.
• Type of fibroids • Some pregnant women with fibroids have heavy
• Whether you are pregnant bleeding immediately after giving birth.
• If you want children in the future Other complications of fibroids include:
Some women may just need pelvic exams or • Severe pain or excessively heavy bleeding that
ultrasounds every once in a while to monitor the fibroid's may require emergency surgery
growth. • A pedunculated fibroid can become twisted and
Treatment for the symptoms of fibroids may include: cause a kink in the blood vessels feeding the
• Birth control pills (oral contraceptives) to help tumor (this type of fibroid may need surgery)
control heavy periods • Anemia (which may be severe if the bleeding is
• Intrauterine devices (IUDs) that release the very heavy)
hormone progestin to help reduce heavy • Urinary tract infections, if pressure from the
bleeding and pain fibroid prevents the bladder from fully emptying
• Iron supplements to prevent or treat anemia due • Cancerous changes called leiomyosarcoma (in
to heavy periods rare cases)
• Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) • Infertility (rarely)
such as ibuprofen or naprosyn for cramps or Calling your health care provider
pain Call your health care provider if:
Hormonal therapy (gonadotropin releasing hormone • You have gradual changes in your menstrual
(GnRH) agonists or Depo Leuprolide injections) may be pattern, including a heavier flow, increased
used to help shrink the fibroids. This therapy is used cramping, or bleeding between periods
only for a short period of time, either before surgery to • Fullness or heaviness develops in your lower
remove a fibroid or when a woman is expected to reach abdomen
menopause soon. Side effects include hot flashes and A uterine fibroid (also uterine leiomyoma,[1]
vaginal dryness. myoma, fibromyoma, leiofibromyoma,
Surgery and procedures used to treat fibroids include: fibroleiomyoma, and fibroma) (the plural of myoma is
• Hysteroscopic resection of fibroids: Women who myomas or myomata) is a benign (non-cancerous)
have fibroids growing inside the uterine cavity tumor that originates from the smooth muscle layer
may need this outpatient procedure. In this (myometrium) and the accompanying connective tissue
procedure, a small camera and instruments are of the uterus.
inserted through the cervix into the uterus to Fibroids are the most common benign tumors in females
remove the fibroid tumors. and typically found during the middle and later
reproductive years. While most fibroids are
asymptomatic, they can grow and cause heavy and this location may lead to bleeding and infertility.
painful menstruation, painful sexual intercourse, and A pedunculated lesion within the cavity is
urinary frequency and urgency. Some fibroids may termed an intracavitary fibroid and can be
interfere with pregnancy although this appears to be passed through the cervix.
very rare.[2] • Cervical fibroids are located in the wall of the
In the US, symptoms caused by uterine fibroids are a cervix (neck of the uterus). Rarely fibroids are
very frequent indication for hysterectomy.[3] Fibroids are found in the supporting structures (round
often multiple and if the uterus contains too many ligament, broad ligament, or uterosacral
leiomyomatas to count, it is referred to as diffuse ligament) of the uterus that also contain smooth
uterine leiomyomatosis. The malignant version of a muscle tissue.
fibroid is extremely uncommon and termed a Fibroids may be single or multiple. Most fibroids start in
leiomyosarcoma. an intramural location, that is the layer of the muscle of
• the uterus. With further growth, some lesions may
Prevalence develop towards the outside of the uterus or towards the
A relatively large submucosal leiomyoma; it fills out the internal cavity. Secondary changes that may develop
major part of the endometrial cavity within fibroids are hemorrhage, necrosis, calcification,
About 20–40% of women will be diagnosed with and cystic changes.
leiomyoma but only a fraction of those will cause Aetiology and pathogenesis
problems or require treatment.[3] Fibroids are monoclonal tumors, approximately 40 to
The condition is about twice as common in black women 50% show karyotypically detectable chromosomal
as white women.[4][5] abnormalities. When multiple fibroids are present they
Leiomyoma are more common in overweight women will usually have mostly unrelated genetic defects. Exact
(perhaps because of increased estrogen from adipose aetiology is not nearly understood, current working
aromatase activity).[6] Fibroids are dependent on hypothesis is that genetic predispositions, prenatal
estrogen and progesterone to grow and therefore hormone exposure and the effects of hormones, growth
relevant only during the reproductive years, they are factors and xenoestrogens cause fibroid growth. Known
expected to shrink after menopause. risk factors are African-American descent, nulliparity,
Pathology and histology obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, diabetes and
Leiomyomas grossly appear as round, well circumscribed hypertension.[7]
(but not encapsulated), solid nodules that are white or Fibroid growth is strongly dependent on estrogen and
tan, and show whorled appearance on histological progesterone. Although both estrogen and progesterone
section. The size varies, from microscopic to lesions of are usually regarded as growth promoting they will also
considerable size. Typically lesions the size of a cause growth restriction in some circumstances.
grapefruit or bigger are felt by the patient herself Paradoxically fibroids will rarely grow during pregnancy
through the abdominal wall. despite very high steroid hormone levels and pregnancy
Microscopically, tumor cells resemble normal cells appears to exert a certain protective effect.[2] This
(elongated, spindle-shaped, with a cigar-shaped protective effect might be partially mediated by an
nucleus) and form bundles with different directions interaction estrogen and the oxytocin receptor.[8]
(whorled). These cells are uniform in size and shape, It is believed that estrogen and progesterone have both
with scarce mitoses. There are three benign variants: mitogenic effect on leiomyoma cells and also act by
bizarre (atypical); cellular; and mitotically active. influencing (directly and indirectly) a large number of
Location growth factors, cytokines and apoptotic factors as well
Growth and location are the main factors that determine as other hormones. Furthermore the actions of estrogen
if a fibroid leads to symptoms and problems.[3] A and progesterone are modulated by the cross-talk
small lesion can be symptomatic if located within between estrogen, progesterone and prolactin signalling
the uterine cavity while a large lesion on the which controls the expression of the respective nuclear
outside of the uterus may go unnoticed. receptors. It is believed that estrogen is growth
Different locations are classified as follows: promoting by up-regulating IGF-1, EGFR, TGF-beta1,
• Intramural Fibroids are located within the wall TGF-beta3 and PDGF, promotes aberrant survival of
of the uterus and are the most common type; leiomyoma cells by down-regulating p53, increasing
unless large, they may be asymptomatic. expression of the anti-apoptotic factor PCP4 and
Intramural fibroids begin as small nodules in the antagonizing PPAR-gamma signalling. Progesterone is
muscular wall of the uterus. With time, thought to promote the growth of leiomyoma through
intramural fibroids may expand inwards, causing up-regulating EGF, TGF-beta1 and TGF-beta3, and the
distortion and elongation of the uterine cavity. survival through up-regulating Bcl-2 expression and
• Subserosal fibroids are located underneath down-regulating TNF-alpha. Progesterone is believed to
the mucosal (peritoneal) surface of the uterus counteract growth by downregulating IGF-1.[9][10][11]
and can become very large. They can also grow Expression of transforming growth interacting factor
out in a papillary manner to become (TGIF) is increased in leiomyoma compared with
pedunculated fibroids. These pedunculated myometrium.[12] TGIF is a potential repressor of TGF-β
growths can actually detach from the uterus to pathways in myometrial cells.[12]
become a parasitic leiomyoma. Whereas in premenopausal fibroids the ER-beta, ER-
alpha and progesterone receptors are found
• Submucosal fibroids are located in the muscle
overexpressed, in the rare postmenopausal fibroids only
beneath the endometrium of the uterus and
ER-beta was found significantly overexpressed.[13] Most
distort the uterine cavity; even small lesion in
studies found that polymorphisms in ER and PR gene fibroid. During pregnancy they may be the cause of
encodings are not correlated with incidence of fibroids in miscarriage, bleeding, premature labor, or interference
Caucasian populations [14][15] however a special ER-alpha with the position of the fetus.
genotype was found correlated with incidence and size Fibroids, particularly when small, may be entirely
of fibroids. The higher prevalence of this genotype in asymptomatic. The U.S. Department of Health & Human
black women may also explain the high incidence of Services states that "Fibroids are almost always benign
fibroids in this group.[16] (not cancerous). Rarely (less than one in 1,000) a
Uterine leiomyoma was more sensitive than normal cancerous fibroid will occur. This is called
myometrium to PPAR-gamma receptor activation leiomyosarcoma. Doctors think that these cancers do
resulting in reduced survival and apoptosis of leiomyoma not arise from an already-existing fibroid. Having
cells. The mechanism is thought to involve negative fibroids does not increase the risk of developing a
cross-talk between ER and PPAR signaling pathways. cancerous fibroid. Having fibroids also does not increase
Several PPAR-gamma ligands were considered as a woman's chances of getting other forms of cancer in
potential treatment.[17] PPAR-gamma agonists may also the uterus."[29]
counteract leiomyoma growth by several other While fibroids are common, they are not a typical cause
mechanisms of action such as TGF-beta3 expression for infertility accounting for about 3% of reasons why a
inhibition.[18] woman may not have a child.[30] Typically in such cases
Hypertension is significantly correlated with fibroids. a fibroid is located in a submucosal position and it is
Although a causal relationships is not at all clear the thought that this location may interfere with the function
hypothesis has been formulated that atherosclerotic of the lining and the ability of the embryo to implant.[30]
injury to uterine blood vessels and the resulting Also larger fibroids may distort or block the fallopian
inflammatory state may play a role. Furthermore tubes.
endocrine factors related to blood pressure such as Diagnosis
angiotensin II are suspected to cause fibroid While a bimanual examination typically can identify the
proliferation via angiotensin II type 1 receptor.[19][20] presence of larger fibroids, gynecologic ultrasonography
Aromatase and 17beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (ultrasound) has evolved as the standard tool to
are aberrantly expressed in fibroids, indicating that evaluate the uterus for fibroids. Sonography will depict
fibroids can convert circulating androstenedione into the fibroids as focal masses with a heterogeneous
estradiol.[21] Similar mechanism of action has been texture, which usually cause shadowing of the
elucidated in endometriosis and other endometrial ultrasound beam. The location can be determined and
diseases.[22] Aromatase inhibotors are currently dimensions of the lesion measured. Also magnetic
considered for treatment, at certain doses they would resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to define the
completely inhibit estrogen production in the fibroid depiction of the size and location of the fibroids within
while not largely affecting ovarian production of the uterus.
estrogen (and thus systemic levels of it). Aromatase Imaging modalities cannot clearly distinguish between
overexpression is particularly pronounced in Afro- the benign uterine leiomyoma and the malignant uterine
American women [23] leiomyosarcoma, however, the latter is quite rare.
Genetic and hereditary causes are being considered and However fast growth or unexpected growth such as
several epidemiologic findings indicate considerable enlargement of a lesion after the menopause raise the
genetic influence especially for early onset cases. First level of suspicion that the lesion might be a sarcoma.
degree relatives have a 2.5-fold risk, and nearly 6-fold Also, with advanced malignant lesions there may be
risk when considering early onset cases. Monozygotic evidence of local invasion. A more recent study has
twins have double concordance rate for hysterectomy suggested that diagnostic capabilities using MRI have
compared to dizygotic twins.[24] improved the ability to detect sarcomatous lesions.[31]
Like keloids, fibroids have disregulated production of Biopsy is rarely performed and if performed, is rarely
extracellular matrix. Recent studies suggest that this diagnostic. Should there be an uncertain diagnosis after
production may represent an abnormal response to ultrasounds and MRI imaging, surgery is generally
ischemic and mechanical tissue stress.[25] Several factors indicated.
indicate significant involvement of extracellular signaling Other imaging techniques that may be helpful
pathways such as ERK1 and ERK2, which in fibroids are specifically in the evaluation of lesions that affect the
prominently influenced by hormones.[26] Paradoxically uterine cavity are hysterosalpingography or
and unlike most other conditions involving significant sonohysterography.
fibrosis the Cyr61 gene has been found downregulated Coexisting disorders
in fibroids.[27] Fibroids that lead to heavy vaginal bleeding lead to
Cyr61 is also known for its role as tumor suppressing anemia and iron deficiency. Due to pressure effects
factor and in angiogenesis. Hence fibroids are one of the gastrointestinal problems are possible such as
very few tumors with reduced vascular density.[27] constipation and bloatedness. Compression of the ureter
Symptoms may lead to hydronephrosis. Fibroids may also present
Generally, symptoms relate to the location of the lesion alongside endometriosis, which itself may cause
and its size (mass effect). Important symptoms include infertility. Adenomyosis may be mistaken for or coexist
abnormal gynecologic hemorrhage, heavy or painful with fibroids.
periods, abdominal discomfort or bloating, painful In very rare cases, malignant (cancerous) growths,
defecation, back ache, urinary frequency or retention, leiomyosarcoma, of the myometrium can develop.[32]
and in some cases, infertility.[28] There may also be pain Treatment
during intercourse, depending on the location of the
Most fibroids do not require treatment unless they are Aromatase inhibitors have been used experimentally to
causing symptoms. After menopause fibroids shrink and reduce fibroids. The effect is believed to be due partially
it is unusual for fibroids to cause problems. by lowering systemic estrogen levels and partially by
Symptomatic uterine fibroids can be treated by: inhibiting locally overexpressed aromatase in fibroids.[35]
• medication to control symptoms Experience from experimental aromatase inhibitor
• medication aimed at shrinking tumours treatment of endometriosis indicates that aromatase
• ultrasound fibroid destruction inhibitors might be particularly useful in combination
with a progestogenic ovulation inhibitor.
• various surgically aided methods to reduce blood
Progesterone antagonists have been shown in small
supply of fibroids
studies to decrease the size of uterine fibroids.
• myomectomy or radio frequency ablation Mifepristone was effective in a placebo-controlled pilot
• hysterectomy study.[38][39]Selective progesterone receptor modulators,
Herbal treatment such as Progenta, have been under investigation.
Most frequently used herbal treatments are Vitex agnus- The selective progesterone receptor modulator Asoprisnil
castus, Yarrow and Capsella bursa-pastoris. There is no is currently tested with very promising results as a
clinical evidence supporting their use in the treatment of possible use as a treatment for fibroids - the hope is
fibroids, however for Vitex[33] and Yarrow[citation needed]there that it will provide the advantages of progesterone
is evidence that they can reduce menstrual bleeding and antangonitst without their adverse effects.[35]
PMS symptoms. The long term safety of progesterone antagonists as well
Medication as selective progesterone receptor modulators has yet to
A number of medications are in use to control symptoms be established.[40][41]
caused by fibroids. NSAIDs can be used to reduce Magnetic Resonance-Guided Focused Ultrasound
painful menses. Oral contraceptive pills are prescribed to Magnetic Resonance guided Focused Ultrasound
reduce uterine bleeding and cramps.[30] Anemia may (MRgFUS), is a non-invasive intervention (requiring no
have to be treated with iron supplementation. incision) that uses high intensity focused ultrasound
Levonorgestrel intrauterine devices are highly effective (HIFU) waves to ablate (destroy) tissue in combination
in limiting menstrual blood flow. Side effects are with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), which guides
typically very moderate because the levonorgestrel (a and monitors the treatment. This technique was
progestin) is released in low concentration locally. While approved by the FDA in 2004. Ultrasound is a form of
most Levongestrel-IUD studies concentrated on energy that passes through skin, muscle, fat and other
treatment of women without fibroids a few reported very soft tissue. High intensity focused ultrasound energy,
good results specifically for women with fibroids focused on a small target volume (tumor), provides a
including a substantial regression of fibroids.[34] One therapeutic effect by raising the tissue temperature of
reported problem is that women with large fibroids had the target (tumor) high enough to destroy it. This is
more frequently spontaneous expulsion of the IUD, similar to the manner in which sunlight focused by a
however many of those asked for reinsertion of the magnifying glass can create sufficient heat to start a
device indicating a high rate of satisfaction despite the fire. The use of heat to destroy tissue is called thermal
expulsion.[35][36] ablation. Treatments consist of multiple exoposures of
Danazol is an effective treatment to shrink fibroids and focused energy or sonications. MRgFUS uses a Magnetic
control symptoms. Its use is limited by unpleasant side Resonance Imaging (MRI) scanner to identify tissues in
effects. Mechanism of action is thought to be the body and plan the treatment. During the procedure,
antiestrogenic effects. Recent experience indicates that delivery of focused ultrasound energy is guided and
safety and side effect profile can be improved by more controlled using MR thermal imaging. • MR imaging
cautious dosing.[35] provides a three-dimensional view of the target tissue,
Dostinex in a moderate and well tolerated dosis has allowing for precise focusing of ultrasound energy within
been shown in 2 studies to shrink fibroids effectively. a desired volume. • Additionally, the MR imaging
Mechanism of action is completely unclear.[35][37] provides quantitative, real-time, thermal images of the
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogs cause treated area. This allows the physician to ensure that
temporary regression of fibroids by decreasing estrogen the temperature generated during each cycle of
levels. Because of the limitations and side effects of this ultrasound energy is sufficient to cause thermal ablation
medication it is rarely recommended other than for within the desired tissue and if not, to adapt the
preoperative use to shrink the size of the fibroids and parameters. The advantage and value of MR guidance
uterus before surgery. Its is typically used for a ensures safe and accurate treatment. [42] • Patients who
maximum of 6 months or shorter because after longer have symptomatic fibroids, who desire a non-invasive
use they could cause osteoporosis and other typically treatment option and who do not have contraindictions
postmenopausal complications. The main side effects are for MRI are candidates for MRgFUS. About 60% of
transient postmenopausal symptoms. In many cases the patients qualify. It is an outpatient procedure and takes
fibroids will regrow after cessation of treatment, one to three hours depending on the size of the fibroids.
however significant benefits may persists for much It is safe and effective.[43] For patients who have a total
longer time in some cases. Several variations are fibroid volume of more than 500cc, they may be
possible, such as GnRH agonists with add-back regimens pretreated for 3 months with a gonadotropin-releasing
intended to decrease the adverse effects of estrogen hormone (GnRH) analogue (e.g. leuprorelin) to reduce
deficiency. Several add-back regimes are possible, leiomyoma size and subsequently, improve thermal
tibolone, raloxifene, progestogens alone, estrogen alone, ablation efficacy.[44] Fibroid characteristics (T2
and combined estrogens and progestogens.[35] hypointensity, smaller size, intramural location, fewer
number) are important predictor of treatment success. the recurrence of fibroids at a later date, such surgery is
[45][46][47][48]
Symptomatic improvement is sustained for increasingly recommended, especially in the case of
two plus years.[49] Need for additional treatment varies women who have not completed bearing children or who
from 16-20% and is largely dependent on the amount of express an explicit desire to retain the uterus. There are
fibroid that can be safely ablated; the higher the ablated three different types of myomectomy:
volume, the lower the re-treatment rate.[50] • In • In a hysteroscopic myomectomy, the fibroid is
comparison to available treatment options, the cost removed by the use of a resectoscope, an
effectiveness of MRgFUS in the U.S. and U.K. has been endoscopic instrument that can use high-
found to be reasonable and comparable to alternative frequency electrical energy to cut tissue.
treatments (hysterectomy, pharmacotherapy, uterine Hysteroscopic myomectomies can be done as an
artery embolization).[51][52] • The largest hurdle for outpatient procedure, with either local or general
patients who desire MRgFUS is insurance coverage. Most anesthesia used. Hysteroscopic myomectomy is
insurers will not cover MRgFUS even though there is a most often recommended for submucosal
large body of evidence to support its efficacy and safety. fibroids. A French study collected results from
The most likely reason is because there are no 235 patients suffering from submucous myomas
randomized trial between MRgFUS and UAE. A multi- who were treated with hysteroscopic
center trial is underway to investigate the efficacy of myomectomies; in none of these cases was the
MRgFUS vs. UAE. fibroid greater than 5 cm.[59]
Uterine artery embolization • A laparoscopic myomectomy requires a small
Uterine artery embolization (UAE): Using incision near the navel. The physician then
interventional radiology techniques, the interventional inserts a laparoscope into the uterus and uses
radiologist occludes both uterine arteries, thus reducing surgical instruments to remove the fibroids.
blood supply to the fibroid.[53] A small catheter (1 mm in Studies have suggested that laparoscopic
diameter) is inserted into the femoral artery at the level myomectomy leads to lower morbidity rates and
of the groin under local anesthesia. Under imaging faster recovery than does laparotomic
guidance, the interventional radiologist will enter myomectomy.[60] As with hysteroscopic
selectively into both uterine arteries and inject small myomectomy, laparoscopic myomectomy is not
(500 µm) particles that will block the blood supply to the generally used on very large fibroids. A study of
fibroids. A patient will usually recover from the laparoscopic myomectomies conducted between
procedure within a few days. The UAE procedure should January 1990 and October 1998 examined 106
result in limited blood supply to the fibroids which cases of laparoscopic myomectomy, in which the
should prevent them from further growth, heavy fibroids were intramural or subserous and
bleeding and possibly shrink them. ranged in size from 3 to 10 cm.[61]
A retrospective cohort study showed that UAE has much • A laparotomic myomectomy (also known as an
fewer serious adverse effects than hysterectomy (odds open or abdominal myomectomy) is the most
ratio 0.25) and similar rates of satisfaction. In this invasive surgical procedure to remove fibroids.
study, 86% of women treated with UAE would The physician makes an incision in the
recommend the treatment to a friend compared to 70% abdominal wall and removes the fibroid from the
of those treated by hysterectomy.[54] uterus. A particularly extensive laparotomic
Uterine artery ligation procedure may necessitate that any future births
Uterine artery ligation, sometimes also laparoscopic be conducted by Caesarean section.[30] Recovery
occlusion of uterine arteries are minimaly invasive time from a laparatomic procedure is generally
methods to limit blood supply of the uterus by a small expected to be four to six weeks.
surgery that can be performed transvaginally or Hysterectomy is the classical method of treating fibroids.
laparoscopically. The principal mechanism of action may Although it is now recommended only as last option it is
be similar like in UAE. This is a relatively new method still the leading cause of hysterectomies in the US.
which demonstrated similar efficacy similar like UAE but Endometrial ablation
is easier to perform and for this reason fewer side Endometrial ablation can be used if the fibroids are
effects are expected.[55][56][57] UAE currently appears only within the uterus and not intramural and relatively
much more effective than this method in direct small. High failure and recurrence rates are expected in
comparison.Cite error: Invalid <ref> tag; invalid the presence of larger or intramural fibroids.
names, e.g. too many; see the help page Other
Radio frequency ablation The use of vitex herbal medicine lacks supporting
Radiofrequency ablation: One of the newest evidence.
minimally invasive treatments for fibroids is Malignancy
radiofrequency ablation.[58] In this technique the fibroid About 1 out of 1000 lesions[30] are or become malignant,
is shrunk by inserting a needle-like device into the typically as a leiomyosarcoma on histology. A sign that a
fibroid through the abdomen and heating it with radio- lesion may be malignant is growth after menopause.[30]
frequency (RF) electrical energy to cause necrosis of There is no consensus among pathologists regarding the
cells. The treatment is a potential option for women who transformation of Leiomyoma into a sarcoma. Most
have fibroids, have completed child-bearing and want to pathologists believe that a Leiomyosarcoma is a de novo
avoid a hysterectomy. disease[citation needed].
Surgery Metastasis
It is possible to remove multiple fibroids during a
myomectomy. Although a myomectomy cannot prevent
There are a number of rare conditions in which fibroids
metastasize. They still grow in a benign fashion, but can
be dangerous depending on their location.[62]
• In leiomyoma with vascular invasion, an
ordinary-appearing fibroid invades into a vessel
but there is no risk of recurrence.
• In Intravenous leiomyomatosis, leiomyomata
grow in veins with uterine fibroids as their
source. Cardiac involvement can be fatal.
• In benign metastasizing leiomyoma,
leiomyomata grow in more distant sites such as
the lungs and lymph nodes. The source is not
entirely clear. Pulmonary involvement can be
fatal.
• In disseminated intraperitoneal
leiomyomatosis, leiomyomata grow diffusely
on the peritoneal and omental surfaces, with
uterine fibroids as their source. This can
simulate a malignant tumor but behaves
benignly.
What are Common symptoms of uterine myoma (fibroids)?
• Pain in the back of the legs
• Pelvic pain or pressure
• Very heavy and prolonged menstrual periods
• Pressure on the bowel which may lead to
constipation and/or bloating
• An enlarged abdomen (this may be mistaken
for weight gain or pregnancy)
• Pain during sexual intercourse
• Pressure on the bladder which results in: a
perpetual need to urinate, incontinence, or the
inability to empty the bladder
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- GEA 1000 Tutorial 1 SolutionDokumen12 halamanGEA 1000 Tutorial 1 SolutionAudryn LeeBelum ada peringkat
- National Train Enquiry System: 12612 Nzm-Mas Garib Rath Exp Garib Rath 12434 Nzm-Mas Rajdhani Exp RajdhaniDokumen1 halamanNational Train Enquiry System: 12612 Nzm-Mas Garib Rath Exp Garib Rath 12434 Nzm-Mas Rajdhani Exp RajdhanishubhamformeBelum ada peringkat
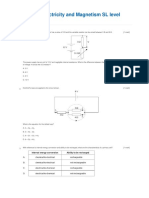
- MCQ CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (30 Marks)Dokumen11 halamanMCQ CH 5-Electricity and Magnetism SL Level: (30 Marks)Hiya ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Questionnaire For New Omani QAQC Staff - DLQ DeptDokumen7 halamanPractice Questionnaire For New Omani QAQC Staff - DLQ DeptSuliman Al RuheiliBelum ada peringkat
- APFC Accountancy Basic Study Material For APFCEPFO ExamDokumen3 halamanAPFC Accountancy Basic Study Material For APFCEPFO ExamIliasBelum ada peringkat
- Susan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Dokumen297 halamanSusan Oyama The Ontogeny of Information Developmental Systems and Evolution Science and Cultural Theory 2000Marelin Hernández SaBelum ada peringkat
- ISO 9001 internal audit criteria and examples guideDokumen22 halamanISO 9001 internal audit criteria and examples guideMukesh Yadav100% (2)
- CRUSADE of PRAYERS 1-170 Litany 1-6 For The Key To Paradise For DistributionDokumen264 halamanCRUSADE of PRAYERS 1-170 Litany 1-6 For The Key To Paradise For DistributionJESUS IS RETURNING DURING OUR GENERATION100% (10)
- Condicional Perfecto Continuo interrogativo guíaDokumen2 halamanCondicional Perfecto Continuo interrogativo guíaMaxi RamirezBelum ada peringkat
- The Basic Philosophical and Theological Notions of Saint Augustine - John C. Cooper PDFDokumen21 halamanThe Basic Philosophical and Theological Notions of Saint Augustine - John C. Cooper PDFjusrmyrBelum ada peringkat
- Mixed-Use Proposal Dormitory and Hotel High-RiseDokumen14 halamanMixed-Use Proposal Dormitory and Hotel High-RiseShanaia BualBelum ada peringkat
- Grammar Level 1 2013-2014 Part 2Dokumen54 halamanGrammar Level 1 2013-2014 Part 2Temur SaidkhodjaevBelum ada peringkat
- Magnetic Suspension System With Electricity Generation Ijariie5381Dokumen11 halamanMagnetic Suspension System With Electricity Generation Ijariie5381Jahnavi ChinnuBelum ada peringkat
- Xtreme 5 (Answer-Key)Dokumen120 halamanXtreme 5 (Answer-Key)arielsergio403Belum ada peringkat
- Real Vs Nominal Values (Blank)Dokumen4 halamanReal Vs Nominal Values (Blank)Prineet AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Sikkim Public Works Liability of Government and Contractor Act 1983Dokumen11 halamanSikkim Public Works Liability of Government and Contractor Act 1983Latest Laws TeamBelum ada peringkat
- Postmodern Dystopian Fiction: An Analysis of Bradbury's Fahrenheit 451' Maria AnwarDokumen4 halamanPostmodern Dystopian Fiction: An Analysis of Bradbury's Fahrenheit 451' Maria AnwarAbdennour MaafaBelum ada peringkat
- Hays Grading System: Group Activity 3 Groups KH PS Acct TS JG PGDokumen1 halamanHays Grading System: Group Activity 3 Groups KH PS Acct TS JG PGkuku129Belum ada peringkat
- Guest Speaker SpeechDokumen12 halamanGuest Speaker SpeechNorhana Manas83% (82)
- Compiled May 5, 2017 Case DigestDokumen16 halamanCompiled May 5, 2017 Case DigestGrace CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Fright ForwordersDokumen6 halamanFright ForworderskrishnadaskotaBelum ada peringkat
- Evirtualguru Computerscience 43 PDFDokumen8 halamanEvirtualguru Computerscience 43 PDFJAGANNATH THAWAITBelum ada peringkat
- Expectations for Students and ParentsDokumen15 halamanExpectations for Students and ParentsJasmine TaourtiBelum ada peringkat
- Quatuor Pour SaxophonesDokumen16 halamanQuatuor Pour Saxophoneslaura lopezBelum ada peringkat
- English Literature RevisionDokumen61 halamanEnglish Literature RevisionAlex Cobain Glinwood100% (1)
- A StarDokumen59 halamanA Starshahjaydip19912103Belum ada peringkat
- NAS Drive User ManualDokumen59 halamanNAS Drive User ManualCristian ScarlatBelum ada peringkat
- 3 CRIM LAW 2 CASES TO BE DIGESTED Gambling Malfeasance Misfeasance Bribery Graft Corruption and MalversationDokumen130 halaman3 CRIM LAW 2 CASES TO BE DIGESTED Gambling Malfeasance Misfeasance Bribery Graft Corruption and MalversationElma MalagionaBelum ada peringkat
- Tele Phone Directory 2023-24Dokumen10 halamanTele Phone Directory 2023-24vinoth5028Belum ada peringkat
- RITL 2007 (Full Text)Dokumen366 halamanRITL 2007 (Full Text)Institutul de Istorie și Teorie LiterarăBelum ada peringkat