2010 Endocrine System Chart
Diunggah oleh
Alexander QianDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2010 Endocrine System Chart
Diunggah oleh
Alexander QianHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
2010 Health Science
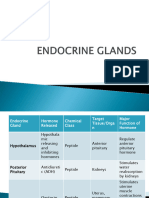
Endocrine System –Hormones
Gland/hormone Function Dysfunction/Disorders Chemical
Composition
Anterior Pituitary
Growth Hormone (GH) Stimulates the growth of all organs in the Hypersecretion results in gigantism Protein
(somatotropism) body, mobilizes food molecules increasing and acromegaly
the blood glucose concentration
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH) Stimulates synthesis and dispersion of the Hyposecretion results in the darkening Protein
pigment melanin in the skin of the skin
Adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH) Stimulates secretion of adrenal cortex Hypersecretion or hyposecretion of Polypeptide
hormones adrenal cortex
Follicle-stimulating hormone Males: Stimulates production and growth Hyposecretion inhibits sexual Glycoprotein
(FSH) of sperm in seminiferous tubules of testes development and causes sterility
Female: Stimulates development of
follicles in ovaries and secretion of
estrogen
Luteinizing hormone (LH) Males: stimulates secretion of testosterone Hyposecretion inhibits sexual Glycoprotein
by the interstitial cells of the testes development and causes sterility
Female: Stimulates the secretion of
estrogen stimulates maturation of ovarian
follicle and ovum, ,triggers ovulation, and
stimulates the development of the corpus
luteum or lutenization
Prolactin Stimulates breast development during Hypersecretion causes inappropriate Protein
pregnancy and milk development after lactation in nonnursing women and in
pregnancy men.
Hyposecretion causes insufficient
lactation in nursing women
Posterior Pituitary (synthesized in Hypothalamus but
released in posterior pituitary)
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Stimulates water retention by the kidnesy Hypersecretion results in abnormal Peptide
water retention
Hyposecretion causes diatetes
insipidus
Oxyotocin Stimulates uterine contractions at the end Hypersecretion causes inappropriate Peptide
of pregnancy and the release of milk into ejection of milk in lactating women
the ducts of the breast Hyposecretion may cause prolonged
or difficult labor and delivery
Hypothalamus Stimulates anterior pituitary to release Hypersecretion causes hypersecretion Protein
(Releasing hormones) hormones by anterior pituitary
Hyposecretion causes hyposecretion
by pituitary
Thyroid
Thyroxine (T4) and thiiodothyronine (T3) Stimulates energy metabolic activities of Hypersecretion causes Iodinated protein
cells hyperthyroidism, Graves disease
Hypersecretion causes
hypothyroidism, (pre-adult) cretinism,
(adult) myxedema, goiter
Calcitonin Inhibits breakdown of bone and causes Hypersecretion can cause Polypeptide
decreases in blood calcium concentrations hypocalcemia
Hyposecretion can cause
hypercalcemia
Parathyroid
Parathyroid hormone (PTH) Stimulates the breakdown of bone and Hypersecretion can cause Polypeptide
causes increase in blood calcium hypercalcemia
concentrations Hyposecretion can cause
hypocalcemia
Adrenal Cortex
Mineralocorticoids aldosterone Regulate electrolyte and fluid homeostasis Hypersecretion causes increased water Steroid
or balance retention
Hyposecretion causes abnormal water
loss or dehydration
Cortisol (hydrocortisone)and other glucocorticoids Stimulates gluconeogenesis, causing an Hypersecretion causes Cushing’s Steroid
increase in blood glucose concentrations Syndrome
and has anti-inflammatory, anti-immunity, Hyposecretion causes Addison’s
and anti-allergy effects disease
Sex hormones (androgens) Stimulate sexual drive in females but have Hypersecretion causes premature Steroids
little effects in males sexual development in females and
masculinization of females
Hyposecretion has no significant
effect
Adrenal Medulla
Epinephrine (adrenalin) and norepinephrine Intensifies and prolongs the sympathetic Hypersecretion causes effects of stress Catecholamines (amino
response during stress Hyposecretion has no significant acid derivatives)
effect
Pancreatic Islets
Glucagon Stimulates glycogenolysis causing an Uncertain Polypeptides
increase in blood glucose concentration
Insulin Promotes glucose entry into cells causing Hypersecretion causes severe insulin Polypeptides
decrease in blood glucose concentration shock or hypoglycemia
Hyposecretion causes diabetes
mellitus
Ovary
Estrogen Promotes development and maintenance of Hypersecretion causes premature Steroids
female sexual characteristics sexual development in females and
infertility
Hyposecretion causes lack of female
sexual development, infertility and
osteoporosis
Progesterone Promotes conditions needed for pregnancy Hyposecretion causes sterility Steroids
Testis
Testosterone Promotes development and maintenance of Hypersecretion causes premature male Steroids
male sexual characteristics sexual development and muscle
hypertrophy
Hyposecretion causes lack of sexual
development in males
Thymus
Thymosin Promotes development of immune system Hyposecretion depresses immune Protein
cells system
Placenta
Chorionic gonadotropin, estrogens, progesterone Promotes conditions required during early Hyposecretion causes miscarriage or Steroids
pregnancy spontaneous abortion
Pineal
Melatonin Inhibits tropic hormones which affect the Hypersecretion causes winter Catecholamine
ovaries and may involve the internal clock depression and other possible effects
of the body
Heart (atria of heart)
Atrial natriuretic Regulates fluid and electrolyte balance or (uncertain) Peptide
homeostasis
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Ayurvedic Vegan Kitchen PDFDokumen203 halamanThe Ayurvedic Vegan Kitchen PDFRuvaly MzBelum ada peringkat
- List of Hormones Hypersecretion and Hyposecretion PDFDokumen11 halamanList of Hormones Hypersecretion and Hyposecretion PDFAnil Kumar100% (1)
- Essay, How Microscopes Have Contributed To Our Understanding of Living OrganismsDokumen2 halamanEssay, How Microscopes Have Contributed To Our Understanding of Living Organismslinanqikiki82% (11)
- Dr. Mike Israetel Training Volume Landmarks Hypertrophy RoutineDokumen26 halamanDr. Mike Israetel Training Volume Landmarks Hypertrophy RoutineJose Fernando PereiraBelum ada peringkat
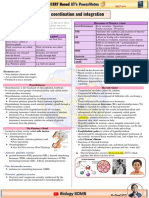
- Chapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationDokumen4 halamanChapter 22 - Chemical Coordination and IntegrationanuminiatureBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyDokumen8 halamanEndocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees Endocrinologyzonia kilashBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyDokumen8 halamanEndocrinology: Byu Pdbio 305 Dr. Rhees EndocrinologyMohammad AlHamdanyBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemDokumen41 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The Endocrine SystemJessica Glitter100% (2)
- Biology Lecture 5 Hormone ChartDokumen2 halamanBiology Lecture 5 Hormone Chartmark_pedersen_6Belum ada peringkat
- Source Hormone Major Action: Adrenal CortexDokumen3 halamanSource Hormone Major Action: Adrenal CortexReisha FungoBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen35 halamanEndocrine Systemmbok diyirBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Science - TableDokumen4 halamanActivity Science - TableMiranda MirandaBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System PresentationDokumen231 halamanEndocrine System PresentationKim GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System NoteDokumen4 halamanEndocrine System NoteFumzy AdelakunBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezDokumen144 halamanEndocrine System: By: Trixie Rose E. CortezTrixie Rose Ebona CortezBelum ada peringkat
- HORMONESDokumen2 halamanHORMONESDa HernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Pregnancy and LactationDokumen16 halamanPregnancy and LactationsukantaryBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDokumen3 halamanEndocrinology Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaBelum ada peringkat
- Sistema EndocrinoDokumen31 halamanSistema EndocrinoJhon Alexis M ArgoteBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine Physology 2023 SharedDokumen121 halamanEndocrine Physology 2023 SharedputracahyaBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System: Mahayag Abuloc Labiste Sagayno VillaruelDokumen32 halamanEndocrine System: Mahayag Abuloc Labiste Sagayno VillaruelJJ AlmagroBelum ada peringkat
- Important Interview TipsDokumen2 halamanImportant Interview TipsyasirtanoliBelum ada peringkat
- S9 Q4 M2 Body Regulators and Reproduction and Development LectureDokumen21 halamanS9 Q4 M2 Body Regulators and Reproduction and Development LectureJermae DizonBelum ada peringkat
- Big Picture F: MetalanguageDokumen13 halamanBig Picture F: Metalanguagejohanna deguzmanBelum ada peringkat
- Hormones Secreted by Anterior and Posterior PituitaryDokumen12 halamanHormones Secreted by Anterior and Posterior Pituitaryfarwafurqan1Belum ada peringkat
- Week 1 - Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Dokumen12 halamanWeek 1 - Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Jeremy EvansBelum ada peringkat
- Physiology Handouts Topics (42-64)Dokumen67 halamanPhysiology Handouts Topics (42-64)bc200411046Belum ada peringkat
- Estrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesDokumen57 halamanEstrogen, Progesterone, Testesterone, and Placental HormonesBramwell K. MiteiBelum ada peringkat
- TABLE 19.1 Major Reproductive Hormones in MalesDokumen4 halamanTABLE 19.1 Major Reproductive Hormones in MalesLisavil BilBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen19 halamanEndocrine System Anatomy and PhysiologyJoanna EdenBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine GlandsDokumen23 halamanEndocrine Glandsumairabbasumar786Belum ada peringkat
- X ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFDokumen9 halamanX ICSE Endocrine System-1 PDFthe lillyBelum ada peringkat
- ENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHDokumen3 halamanENDOCRINOLOGY Prepared By: Carl Leoneill Baroma, RMT, MPHCarl BaromaBelum ada peringkat
- Week 16 Endocrine SystemDokumen16 halamanWeek 16 Endocrine Systemrichard respetoBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine SystemDokumen5 halamanEndocrine SystemCHIQUI JIMENEZBelum ada peringkat
- Pituitary Gland PDFDokumen5 halamanPituitary Gland PDFLiv LeysonBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. SevillenoDokumen55 halamanAnatomy, Physiology of The Endocrine System: Geofrey S. Sevillenocoral jade cuaBelum ada peringkat
- Pituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseDokumen2 halamanPituitary Gland: Anterior: Gland Hormone Target Tissues ResponseHiraya ManawariBelum ada peringkat
- 11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)Dokumen3 halaman11 Chemical Co-Ordination N Integration-Notes Blog (Full Permission)fariha khanBelum ada peringkat
- Chart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12Dokumen2 halamanChart of The Endocrine Glands and Their Secretions Bio12andrewy888Belum ada peringkat
- Pitu TaryDokumen18 halamanPitu TaryVarsha RaniBelum ada peringkat
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3Dokumen4 halamanDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3AlbertBelum ada peringkat
- Draw and Label The Organs of Endocrine SystemDokumen6 halamanDraw and Label The Organs of Endocrine SystemShainaChescaEvansBelum ada peringkat
- Ana EndoDokumen2 halamanAna EndoFIONA DANE MAURERABelum ada peringkat
- Endocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesDokumen10 halamanEndocrinology: There Are Three Basic Types of HormonesHabi JabiBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of The Endocrine System. Violation of Hypophysis, Thyroid and Adrenal Glands. General Adaptation SyndromeDokumen123 halamanPathophysiology of The Endocrine System. Violation of Hypophysis, Thyroid and Adrenal Glands. General Adaptation SyndromeAyman RehmanBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine Hormones and Their FunctionDokumen1 halamanEndocrine Hormones and Their FunctionDee RavalBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine PDFDokumen5 halamanEndocrine PDFRegina SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Animal Endocrine SystemDokumen9 halamanAnimal Endocrine SystemAaron ZBelum ada peringkat
- Tissue/Gland Hormone Produced Target Major Action: HypothalmusDokumen3 halamanTissue/Gland Hormone Produced Target Major Action: HypothalmusSol CarnaciteBelum ada peringkat
- Anterior Pituitary GlandDokumen33 halamanAnterior Pituitary Glandmarianne.erdooBelum ada peringkat
- BSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemDokumen38 halamanBSA 1C 10-26-2021 Endocrine SystemAngelika ButaslacBelum ada peringkat
- Primary Hormones of ReproductionDokumen3 halamanPrimary Hormones of ReproductionMohd AriffBelum ada peringkat
- 1 M PhysiologyDokumen10 halaman1 M PhysiologyLorenz L. Llamas IIIBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System: Organ Hormone EffectDokumen6 halamanEndocrine System: Organ Hormone EffectEmma KowalBelum ada peringkat
- PNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNDokumen4 halamanPNKND Les 0 V 9 VWR60 B RCNaadeshthite476Belum ada peringkat
- Full Human Physiology Short NotesDokumen11 halamanFull Human Physiology Short Notesseetharaman8341Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan On Pituitary Gland (Endocrine SystemDokumen37 halamanLesson Plan On Pituitary Gland (Endocrine SystemRosalyn Angcay Quintinita100% (1)
- Chemical Control and Coordination FinalDokumen5 halamanChemical Control and Coordination Finalakhil01ajBelum ada peringkat
- Coordination and Control Ch#17Dokumen4 halamanCoordination and Control Ch#17Usman GhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Hormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelDokumen38 halamanHormo Nes: Juliet I. VillaruelJuliet Ileto Villaruel - AlmonacidBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesDokumen3 halamanChemical Coordination & Integration PowernotesSushmit SrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- As You Face Life: Pray To God and Ask His GuidanceDokumen11 halamanAs You Face Life: Pray To God and Ask His GuidancesophiegarciaBelum ada peringkat
- GNM SyllabusDokumen4 halamanGNM SyllabusVinay SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Defeat Cancer NaturallyDokumen94 halamanDefeat Cancer NaturallyRknuviprasys Low100% (3)
- Sea Shanty PrintDokumen3 halamanSea Shanty PrintDiego DracvsBelum ada peringkat
- MariaDB Onboarding Databases To Sonar Reference Guide 11-8-2023Dokumen12 halamanMariaDB Onboarding Databases To Sonar Reference Guide 11-8-2023Jateen SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Workbook No. 2 by Jimena SosaDokumen125 halamanWorkbook No. 2 by Jimena SosaLourdes de Fatima Pacheco VasquezBelum ada peringkat
- Q4 Lesson 3 Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseDokumen36 halamanQ4 Lesson 3 Hinge Theorem and Its ConverseZenn Tee100% (1)
- Catalogue Pièces Moteur R984Dokumen150 halamanCatalogue Pièces Moteur R984Eza IR100% (1)
- PPG 2020Dokumen131 halamanPPG 2020Syed Rohail AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Single Nozzle Air-Jet LoomDokumen7 halamanSingle Nozzle Air-Jet LoomRakeahkumarDabkeyaBelum ada peringkat
- G30 Developer MSDS ABDokumen6 halamanG30 Developer MSDS ABramadhanBelum ada peringkat
- 1 An Introduction Basin AnalysisDokumen29 halaman1 An Introduction Basin AnalysisMuhamadKamilAzharBelum ada peringkat
- HP Compaq 6531s Inventec Zzi MV Rev A03 (6820s)Dokumen54 halamanHP Compaq 6531s Inventec Zzi MV Rev A03 (6820s)y2k_yah7758Belum ada peringkat
- Ray OpticsDokumen10 halamanRay OpticsKesav PillaiBelum ada peringkat
- LEC - 19 - Task of Bitcoin MinersDokumen36 halamanLEC - 19 - Task of Bitcoin MinersKarunesh AnandBelum ada peringkat
- THESISDokumen44 halamanTHESISRowena Shaira AbellarBelum ada peringkat
- Teff Type-I Sourdough To ProduDokumen21 halamanTeff Type-I Sourdough To ProdudanaBelum ada peringkat
- FF - Fire Extinguisher LayoutDokumen1 halamanFF - Fire Extinguisher LayoutRanielBelum ada peringkat
- Dmbi Assignment 2: Q.1. Explain STAR Schema. Ans-1Dokumen6 halamanDmbi Assignment 2: Q.1. Explain STAR Schema. Ans-1Kanishk TestBelum ada peringkat
- Naskah Drama Beauty and The BeastDokumen39 halamanNaskah Drama Beauty and The BeastAyu Rose75% (4)
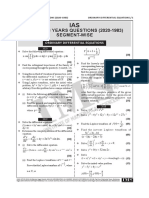
- Previous Years Questions (2020-1983) Segment-Wise: Ordinary Differential EquationsDokumen16 halamanPrevious Years Questions (2020-1983) Segment-Wise: Ordinary Differential EquationsAniket bhaiBelum ada peringkat
- List BRG TGL 12Dokumen49 halamanList BRG TGL 12Rizal MuhammarBelum ada peringkat
- AGPT04I-09 Guide To Pavement Technology Part 4I Earthworks MaterialsDokumen47 halamanAGPT04I-09 Guide To Pavement Technology Part 4I Earthworks MaterialsLeandroBelum ada peringkat
- Crane Inspection ChecklistDokumen1 halamanCrane Inspection ChecklistsudhakarBelum ada peringkat
- Warm and Humid GREEN BUILDING CASE STUDYDokumen8 halamanWarm and Humid GREEN BUILDING CASE STUDYPooja PrakashBelum ada peringkat
- 00capítulo - The Routledge Handbook of Henri Lefebvre, The City and Urban SocietyDokumen12 halaman00capítulo - The Routledge Handbook of Henri Lefebvre, The City and Urban SocietyJeronimoBelum ada peringkat