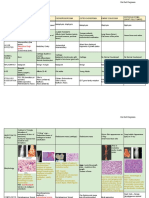
Cancer Epidemiology Pathogenesis Lab/Gross Clinical Features Prognosis/Tx
Diunggah oleh
Caryn Robertson0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
497 tayangan7 halamanUsually solitary - usually found in middle-age adults - Associated with Gardner syndrome (if multiple) Pathogenesis - Slow growing - frequently arise / found inside skull or facial bones Lab / Gross - composed of woven / lamellar bone - Bosselated, round to oval sessile tumors - Deposited in a cortical pattern w / haversian-like systems.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Bone Cancer Chart
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniUsually solitary - usually found in middle-age adults - Associated with Gardner syndrome (if multiple) Pathogenesis - Slow growing - frequently arise / found inside skull or facial bones Lab / Gross - composed of woven / lamellar bone - Bosselated, round to oval sessile tumors - Deposited in a cortical pattern w / haversian-like systems.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
497 tayangan7 halamanCancer Epidemiology Pathogenesis Lab/Gross Clinical Features Prognosis/Tx
Diunggah oleh
Caryn RobertsonUsually solitary - usually found in middle-age adults - Associated with Gardner syndrome (if multiple) Pathogenesis - Slow growing - frequently arise / found inside skull or facial bones Lab / Gross - composed of woven / lamellar bone - Bosselated, round to oval sessile tumors - Deposited in a cortical pattern w / haversian-like systems.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 7
Cancer Epidemiology Pathogenesis Lab/Gross Clinical Features Prognosis/Tx
- Usually solitary - Composed of - Of little
- Usually found - Slow growing woven/lamellar bone significance unless
Osteoma in middle-age - Frequently arise/found - Bosselated, round to they cause - Do NOT transform
adults inside skull or facial bones oval sessile tumors obstruction/imping to osteosarcoma
- Associated with - Deposited in a e on structures
Gardner cortical pattern w/ (brain/eye),
syndrome (if haversian-like interfere w/ fx of
multiple) systems oral cavity or cause
cosmetic problems
- By definition less
- Predilection for than 2 cm in greatest - Painful due to - Readily treated
Osteoid - Patients usually appendicular skeleton dimension excess PGE2 by conservative
Osteoma in teens/twenties (femur/tibia most common) - Round to oval release from surgery
- Men > women - Commonly arise in bone masses of osteoblasts - Malignant
(2:1) cortex hemorrhagic gritty (nocturnal pain) transformation is
tan tissue - Dramatically remote (except
- Well circumscribed relieved by ASA when treated with
and composed of a radiation; which
morass of randomly promotes
interconnecting malignant trans.)
trabeculae of woven
bone; rimmed by
osteoblasts
- Greater than or
equal to 2 cm in size
- Round to oval - Readily treated
- More frequently involves masses of - Dull, achy pain by conservative
Osteoblasto the spine hemorrhagic gritty - Not responsive to surgery
ma - Commonly arise in bone tan tissue salicylates - Malignant
cortex - Well circumscribed transformation is
and composed of a remote (except
morass of randomly when treated with
interconnecting radiation; which
trabeculae of woven promotes
bone; rimmed by malignant trans.)
osteoblasts
- Does not induce a
marked bony reaction
- Distal femur, proximal - Standard:
tibia; metaphysic plates - Hemorrhagic & - Painful, chemotherapy and
- Most common in head, cystic progressively limb salvage
- 75% in ages < shoulder, hip and knee* - Infiltrate marrow enlarging masses - @ time of dx: 10-
Osteosarcom 20 - Genetic mutations are - Bulky tumors; gritty, - Sudden fractures 20% have
a - More common fundamental gray-white - Codman’s pulmonary mets
in men than - RB, p53, INK4A, CDK4, p16, - Formation of bone is triangle: triangular - 90% who die
women CYCLIN D1, MDM2 characteristic; shadow between have metastases to
- Cell cycle regulator genes cartilage/fibrous the cortex & raised the lung, bone,
- Subtypes grouped tissue may be present ends of periosteum brain and
according to anatomic - Pleomorphic cells w/ elsewhere
portion, degree of diff, large hyperchromatic - Long term
multicentricity, nuclei; bizarre giant survival 60-70%
primary/secondary cells
- Cartilage capped - Slow growing
- Aka: exostosis - Develops in bones of outgrowth attached - Can be painful if
- Multiple: endochondral origin; arise to underlying impinge on nerve - Rarely give rise to
Multiple Heredity from metaphysic near the skeleton by bony - Frequently chondrosarcoma or
Osteochondr Exostosis (AD; growth plate of long tubular stalk (protruding detected other sarcoma
oma inactivation of bones (especially knee) mushroom) incidentally - Risk of malignant
both EXT genes); - Occasionally found in - Range from 1-20 cm - In hereditary transformation is
childhood pelvis, scapula and ribs - Composed of form: underlying higher in
- Solitary: late - Rarely involve short tubular hyaline cartilage bones may be hereditary
adolescence, bones of hands/feet covered peripherally bowed or syndrome
early adulthood by perichondrium shortened
- Men>women - Appearance of - Usually stop
(3:1) disorganized growth growing @ time of
plate growth plate
closure
- Benign tumor of hyaline
cartilage - Usually < 3cm
- Enchondroma (in medullary - Blue, gray-blue - Solitary
cavity) – most common - or translucent color with chondromas rarely
subperiosteal/juxtacortical a nodular - Most are undergo malignant
- (on bone surface) configuration asymptomatic transformation
Chondroma Endochondroma - Endochondromas are - Nodules of cartilage - Detected -
are usually found primarily found in short and are well- incidentally Enchondromatoses
in pts age 20-50 tubular bones (hand/feet) circumscribed w/ - Occasionally are are more
& are solitary - Ollier disease = multiple hyaline matrix painful & cause associated with
enchondromas - The cartilage @ the pathologic malignant
Maffucci syndrome = periphery undergoes fractures transformation
enchondromatosis + soft enchondral - Maffucci
tissue hemangiomas ossification and the syndrome patients
- Develop from the remains center frequently are at risk for other
of growth plate cartilage in calcifies & dies malignancies
bones that undergo - On x-ray: O ring sign (ovarian CA, brain
enchondral ossification is present glioma)
- Highly cellular,
hyperlobulated nuclei
w/ longitudinal
- Benign tumor grooves
- Rare - Most commonly found in - Sheets of compact - Usually painful - Distant
Chondroblas - Young patients knee – less commonly found polyhedral (due to location metastases to the
toma in teens in the pelvis/ribs and in older chondroblasts w/ well- near joint) lung are rare
- Male: female = pts defined borders - Recurrences not (usually after
2:1 - Predilection for epiphyses - Mitotic activity & uncommon fracture/curettage)
and apophyses necrosis frequently
found
- Chicken-wire pattern
- Non-neoplastic
osteoclast giant cells
are scattered
throughout
- X-ray: well-defined
lucency w/ spotty
calc.
- Well-circumscribed,
solid, glistening tan-
gray tumor
- Nodules of hyaline
cartilage and myxoid
- Teens and tissue w/ fibrous - Simple curettage
Chondromyx twenties - Most frequently in septae - Localized, dull - Do not pose a
oid - Male metaphysic of long tubular - Greatest cellularity achy pain threat for
Fibroma predominance bones @ periphery malignant
- Rarest cartilage - In cartilaginous transformation
tumor regions: tumor cells
are in lacunae; in
myxoid areas: cells
are stellate
- Varying degrees of
cytologic atypia w/
hyperchromatic
nuclei
- X-ray: eccentric
geographic lucency
that is well delineated
from bone by rim of
sclerosis
- Composed of - Low grade:
malignant hyaline & causes reactive
myxoid cartilage thickening of the
- Myxoid: viscous, cortex
- Patients are - Broad spectrum of findings ooze when cut; spotty - High grade:
usually 40+ - Subclassifications: calcifications & destroys the cortex
- Men are 2x Site: intramedullary or central necrosis; and forms soft
more likely to be juxtacortical adjacent cortex is tissue mass
affected than Histo: conventional, clear thickened/eroded - Painful, - Correlation
Chondrosarc women cell, dedifferentiated or - Dediff: Low-grade progressively between grade &
oma - No race mesenchymal w/ second high-grade enlarging masses biological behavior
predilection - Significant number arise in component - None of grade 1
- Clear cell & association w/ pre-existing - Clear cell: sheets of metastasized
mesenchymal enchondroma large, malignant cells - Size is another
varients in - Arise in central portions of w/ abundant clear prognostic feature
younger patients skeleton (pelvis, shoulder, cytoplasm, (> 10 cm behave
(teens/twenties) ribs) osteoclast-type GC more aggressively)
- Clear cell variant originates and intralesional - Metastasize
in epiphyses of long tubular reaction bone preferentially to
bones formation the lungs/skeleton
- Rarely involves distal - Mesenchymal: - Tx = wide
extremities Islands of well-diff surgical excision
hyaline cartilage - Mesenchymal &
surrounded by small dediff additionally
round cells treated w/ chemo
- X-ray: Prominent
endosteal scalloping;
more radiolucent =
high grade
- FCD:
- FCD: Developmental asymptomatic; - FCD: for those
Fibrous - FCD: Found in defect; found in distal incidentally found; that enlarge;
Cortical 30%-50% of femur/prox tibia limited growth require biopsy to
Defects & children >2 - Those that grow frequently potential and most r/o other type of
Nonossifying develop into NF; one half are undergo tumor
Fibroma bilateral/multiple spontaneous
resolution; few
progressively
enlarge & can
cause path.
fracture
- Benign tumor; likened to - Well-circumscribed,
- Monoostotic: localized developmental intramedullary
boys=girls, most arrest lesions; vary greatly
common in early - Components of normal in size - Rare to have
adolescence bone are present, but do not - Moderately cellular sarcomatous
Fibrous - Polyostotic: differentiate - Trabeculae mimic transformation
Dysplasia manifests - Monoostotic: most Chinese characters (polyostotic
slightly earlier common; ribs, femur, tibia, - Nodules of hyaline involvement
than jawbones, calvaria and cartilage w/ required)
monoostotic humerus; don’t evolve disorganized growth - Use of radiation
- Polyostotic - Polyostotic: femur, skull, plate appearance increases risk of
disease: somatic tibia; craniofacial - Cystic degeneration, malignant
mutations in G- involvement present in half; hemorrhage and transformation
protein leads to all forms have propensity to foamy macs are
excess cAMP; involve shoulder/pelvic common findings
girls more girdle - Xray: ground glass
frequently - Polyostotic Disease: appearance w/ well-
affected than multiple bones + defined margins
boys endocrinopathies; McCune-
Albright syndrome; sexual
precocity, hyperthyroidism,
adrenal hyperplasia; bone &
café-au-lait spots frequently
unilateral
- Large, hemorrhagic,
tan-white masses
- Destroy underlying
- Middle aged & - Fibroblastic collagen- bone - Enlarging painful
Fibrosarcom elderly producing sarcomas of bone - Frequently extend masses - Prognosis
a& - Fibrosarcoma: - Usually arise de novo; into soft tissue - Pathologic depends on grade;
Malignant male=female some secondary tumors - Fibrosarcoma: fracture is a high-grade have
Fibrous - MFH: men more - Usually in metaphyses of malignant fibroblasts frequent poor prognosis
Histiocytoma frequently long bones & pelvic flat arranged in a complication
affected bones herringbone pattern;
most low-
intermediate grade
- MFH: Background of
spindle fibroblasts
arranged in storiform
pattern; large, ovoid,
bizarre multinuc
tumor GC intermixed;
generally high-grade
- Xray:
permeative/lytic
- Average= 10- - Arise in medullary
15 years old cavity
- Boys more freq. - Usually invade
than girls cortex & periosteum - Present as
- More common producing soft tissue painful, enlarging - Treatment
in whites - Primary malignant small mass masses includes
Ewing - t(11;22) most round cell tumors - Composed of sheets - Affected site is chemotherapy and
Sarcoma common; also - Usually arises in diaphyses of uniform, small tender, warm and surgical excision w/
& t(21;21) or of long tubular bones round cells that are swollen or w/o radiation
PNET t(7;22) (femur, flat bones of pelvis) slightly larger than - Some patients - At least 50% of
- Fusion of EWS lymphocytes have systemic cases are long
gene to a - Tan-white tumor findings: fever, term cures; 75% 5
member of ETS that contains areas of elevated SED rate, year survival
family hemorrhage & anemia,
transcription necrosis leukocytoses
factor (mainly - Scant cytoplasm,
FLT1) rich in glycogen
- EWS-FLI1 forms - Homer-Wright
dominant rosettes is indicative
oncogene; of neural diff
constitutively - Contains fibrous
active septae but generally
transcription little stroma
factor - Xray: destructive
stimulating cell lytic tumor w/
proliferation permeative margins
and extension into
soft tissue
- Large and red-brown
- Believed to have monocyte - Uniform oval
macrophage lineage mononuclear cells - Conservative
- Uncommon benign tumor; that have indistinct - Location leads to surgery (40-60%
Giant Cell - Patients but locally aggressive cell membrane and complaints of recurrence rate)
Tumor twenties to - Involve both epiphyses and appear to grow in a arthritis-type - Up to 4%
forties metaphyses in adults; syncytium symptoms metastasize to the
confined to growth plate in - Mitoses are frequent - Occasionally lung
adolescents - Necrosis, present as - Sarcomatous
- Most commonly arise in hemorrhage, pathologic fracture transformation is
knee hemosideran rare
- Most are solitary deposition and
reactive bone
formation are
common secondary
features
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryDokumen1 halamanPa Tho Physiology of Spinal Cord InjuryGenel Joseph Jacildo Peñaflor100% (2)
- Taro 2016 ComentadoDokumen42 halamanTaro 2016 ComentadoneossmedBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Cancer Chart 2012Dokumen8 halamanBone Cancer Chart 2012BigBoostingBelum ada peringkat
- Orthopedic Surgery NotesDokumen3 halamanOrthopedic Surgery NotesJoel Salu100% (1)
- The A To Z of Bones, Joints and LigamentsDokumen267 halamanThe A To Z of Bones, Joints and LigamentsPSDM100% (1)
- 2.bones of The Lower Limbs PDFDokumen14 halaman2.bones of The Lower Limbs PDFYahya Alkamali100% (1)
- Diseases of The Bone and Soft TissuesDokumen8 halamanDiseases of The Bone and Soft TissuesMarieCrisBelum ada peringkat
- Bone TumorDokumen36 halamanBone TumorMoch NizamBelum ada peringkat
- Tumor Flash Cards - Osteochondroma and Multiple Hereditary ExostosisDokumen23 halamanTumor Flash Cards - Osteochondroma and Multiple Hereditary Exostosislaxge54Belum ada peringkat
- INBDEBooster Bone Lesions Cheat SheetDokumen4 halamanINBDEBooster Bone Lesions Cheat SheetHelena KalmatBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Tumors2Dokumen18 halamanBone Tumors2Evelin Isa Kristin100% (1)
- Bone TumorsDokumen10 halamanBone Tumorscyrus kirwaBelum ada peringkat
- Bone and Soft Tissue TumoursDokumen9 halamanBone and Soft Tissue TumoursSurgicalgownBelum ada peringkat
- Bone TumorsDokumen2 halamanBone TumorsDrashty DesaiBelum ada peringkat
- Bones JointsDokumen11 halamanBones JointszeeathrBelum ada peringkat
- Benign Bone TumorsDokumen20 halamanBenign Bone TumorsNazir KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar W4 - Bone & Soft Tissue TumoursDokumen123 halamanSeminar W4 - Bone & Soft Tissue TumoursUN EPBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Aspects of Anatomy - 1Dokumen4 halamanClinical Aspects of Anatomy - 1AakashBelum ada peringkat
- Benign Bone Tumors - AMBOSSDokumen1 halamanBenign Bone Tumors - AMBOSSMohammedBelum ada peringkat
- MR OsteosarcomaDokumen41 halamanMR OsteosarcomaAdi Wasis PrakosaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Bone TumorsDokumen8 halaman5 Bone TumorsKatBelum ada peringkat
- Injury SX Generator MOI Primary Complaint Clinical Presentation Dermatomes/ Myotomes/ DTR's Special Tests/ Examination InterventionsDokumen6 halamanInjury SX Generator MOI Primary Complaint Clinical Presentation Dermatomes/ Myotomes/ DTR's Special Tests/ Examination InterventionsMegan RalstinBelum ada peringkat
- Bone TumorsDokumen1 halamanBone Tumorsbfk777Belum ada peringkat
- jnu bone tumors - 複本Dokumen130 halamanjnu bone tumors - 複本Wai Kwong ChiuBelum ada peringkat
- BenignOsseousTumorsofBoneOsteoblastomaandOsteoid OsteDokumen203 halamanBenignOsseousTumorsofBoneOsteoblastomaandOsteoid OstechikkisaurusBelum ada peringkat
- PathologyDokumen12 halamanPathologyKetmia ZamoraBelum ada peringkat
- Sarcomas: Chondro Ewing's Sarcoma Fibro SarcomaDokumen23 halamanSarcomas: Chondro Ewing's Sarcoma Fibro SarcomaRawda NajjarBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Diseases Lec 1Dokumen7 halamanBone Diseases Lec 1s748jBelum ada peringkat
- Radio Lec 04 MusculoskeletalDokumen4 halamanRadio Lec 04 Musculoskeletalapi-3704562Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 3 MuskDokumen8 halamanLecture 3 MuskElgilani zaherBelum ada peringkat
- Pagets Disease: Osteoporosis Decrease in The Density of Bone, Decreasing ItsDokumen4 halamanPagets Disease: Osteoporosis Decrease in The Density of Bone, Decreasing ItsRanee Diane AnanayoBelum ada peringkat
- Tumor Frequency Age (Median) at Diagnosis Typical Location Radiologic Features CommentsDokumen12 halamanTumor Frequency Age (Median) at Diagnosis Typical Location Radiologic Features CommentskoxBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Radiology - DENT 445 - Benign Tumors of The Jaws - Reading MaterialDokumen39 halamanOral Radiology - DENT 445 - Benign Tumors of The Jaws - Reading MaterialiWellyFoxBelum ada peringkat
- Safe homeopathic treatment for painful spinal stenosisDokumen7 halamanSafe homeopathic treatment for painful spinal stenosisSangram007Belum ada peringkat
- Disease and Characteristics Age Common Locations How To Diagnose and TreatmentDokumen2 halamanDisease and Characteristics Age Common Locations How To Diagnose and TreatmentShiroBelum ada peringkat
- Cartilage TumorsDokumen4 halamanCartilage TumorsHalla BennaaBelum ada peringkat
- Medsurg 1.0 - GeneralitiesDokumen5 halamanMedsurg 1.0 - GeneralitiesDK'S PATATABelum ada peringkat
- 2.1.3. MSK Radiology For CONTRAST 2021Dokumen64 halaman2.1.3. MSK Radiology For CONTRAST 2021Noura AdzmiaBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Tumor Osteochondroma GuideDokumen16 halamanBone Tumor Osteochondroma GuideJohn KingoriBelum ada peringkat
- Bedah 2 Batch 3 2018Dokumen87 halamanBedah 2 Batch 3 2018Meiza Ihsan FakhriBelum ada peringkat
- Diaphyseal AclasisDokumen1 halamanDiaphyseal AclasisABCBelum ada peringkat
- BoneDokumen35 halamanBoneSumanth KaiwarBelum ada peringkat
- Mnemonic: Erotica: MGT For FractureDokumen6 halamanMnemonic: Erotica: MGT For FractureBianx Flores DosdosBelum ada peringkat
- Paget Disease, Fibrous Dysplasia, Osteosarcoma DiffrentiationDokumen3 halamanPaget Disease, Fibrous Dysplasia, Osteosarcoma Diffrentiationreason131Belum ada peringkat
- MSK Week 2 Catatan Ci JDASDokumen7 halamanMSK Week 2 Catatan Ci JDASFirmanHidayatBelum ada peringkat
- Bone TumorsDokumen15 halamanBone Tumorssarguss1450% (2)
- Important Tables of Oral PathologyDokumen17 halamanImportant Tables of Oral PathologyEasy Med LecturesBelum ada peringkat
- Radiological characteristics of periosteal reactionsDokumen9 halamanRadiological characteristics of periosteal reactionsVesna PavlovicBelum ada peringkat
- DifferentialsDokumen4 halamanDifferentialsRizzalyn Abduraup-YusopBelum ada peringkat
- Osteochondroma: Common Bone Tumor That Usually Stops GrowingDokumen12 halamanOsteochondroma: Common Bone Tumor That Usually Stops Growingpresentator dadakanBelum ada peringkat
- fINAL of Octeochondroma in C - SpineDokumen1 halamanfINAL of Octeochondroma in C - SpineadilBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology: Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorscadayBelum ada peringkat
- Benign Non Odontogenic Tumors: Ossifying FibromaDokumen10 halamanBenign Non Odontogenic Tumors: Ossifying FibromaIsabelle TanBelum ada peringkat
- Ortho. CompDokumen51 halamanOrtho. CompSakshi ChoudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Cysts and TumoursDokumen15 halamanCysts and TumourssmurplerBelum ada peringkat
- Classification Assessment Signs and Symptoms Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen1 halamanClassification Assessment Signs and Symptoms Anatomy and PhysiologykyawBelum ada peringkat
- Bone Tumor & Tumor-Like Lesions: By: Dr. Manal NageebDokumen56 halamanBone Tumor & Tumor-Like Lesions: By: Dr. Manal NageebSonny WijanarkoBelum ada peringkat
- (Mantap) Slide Materi Bedah-2 Batch 3 2018 SalinanDokumen200 halaman(Mantap) Slide Materi Bedah-2 Batch 3 2018 SalinantikaBelum ada peringkat
- Radiology NotesDokumen24 halamanRadiology NotesAaron Raestas0% (1)
- Bones, Joints, Soft Tissues and CnsDokumen5 halamanBones, Joints, Soft Tissues and CnsPreeti Joan BuxaniBelum ada peringkat
- Percutaneous Vertebroplasty and KyphoplastyDokumen316 halamanPercutaneous Vertebroplasty and KyphoplastyRamy ElmasryBelum ada peringkat
- Wrist WikiRadDokumen34 halamanWrist WikiRadGriggrogGingerBelum ada peringkat
- Learningtarget:: Activity 1 ADokumen4 halamanLearningtarget:: Activity 1 ApoonamBelum ada peringkat
- Internal Fixation ToolsDokumen22 halamanInternal Fixation ToolsChandan Kumar ChoubeyBelum ada peringkat
- Thoracic Bones FrameworkDokumen1 halamanThoracic Bones FrameworkKun HanifahBelum ada peringkat
- Radiological Signs in Orthopaedic Part 1-1Dokumen167 halamanRadiological Signs in Orthopaedic Part 1-1andrehrBelum ada peringkat
- Musculoskeletal Trauma Fracture HealingDokumen2 halamanMusculoskeletal Trauma Fracture HealingAhmed SalmanBelum ada peringkat
- Cast and TractionsDokumen3 halamanCast and TractionsMacaRonie PepeRownie del RioBelum ada peringkat
- The Skyline Patella ProjectionDokumen17 halamanThe Skyline Patella ProjectiondeepakBelum ada peringkat
- Surgery (Ortho) NotesDokumen155 halamanSurgery (Ortho) NotesprestigeuniversaltradingBelum ada peringkat
- Sameh Doss Lower Limb Computer Version 9bs DR NotesDokumen139 halamanSameh Doss Lower Limb Computer Version 9bs DR Noteslama.lamis.kharbechBelum ada peringkat
- Prevalence of Agenesis of Frontal Sinus in Human Skulls With MetopismDokumen8 halamanPrevalence of Agenesis of Frontal Sinus in Human Skulls With MetopismLorena SandreBelum ada peringkat
- CXCCDokumen24 halamanCXCCBDMBelum ada peringkat
- Chondromalacia Patellae. A Prospective Study: J Bone Joint Surg AmDokumen9 halamanChondromalacia Patellae. A Prospective Study: J Bone Joint Surg AmMladen DabićBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7 - CartilageDokumen17 halamanChapter 7 - CartilageREMAN ALINGASABelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 19: PediatricsDokumen37 halamanChapter 19: PediatricspoddataBelum ada peringkat
- Nomina AnatomicaDokumen4 halamanNomina AnatomicaIoana Purice100% (1)
- Histo Trans 1.4 - Cartilage and BoneDokumen6 halamanHisto Trans 1.4 - Cartilage and BonePim AramBelum ada peringkat
- Kütük Cubuk Uyum StandartlariDokumen2 halamanKütük Cubuk Uyum StandartlariÖZGÜRBelum ada peringkat
- Thoracic (Dorsal) SpineDokumen77 halamanThoracic (Dorsal) Spineeashoor100% (2)
- Basic Orthopedic Hardware TypesDokumen17 halamanBasic Orthopedic Hardware TypesDanica SayasBelum ada peringkat
- TMJ Anatomy and Function GuideDokumen100 halamanTMJ Anatomy and Function GuideMithileshwari Patil100% (1)
- Seitai Module 6-2007 Arm and ShoulderDokumen67 halamanSeitai Module 6-2007 Arm and ShoulderCemec Cursos100% (2)
- Khoury 2002Dokumen5 halamanKhoury 2002shu DuBelum ada peringkat
- Tracing Technique and Landmark IdentificationDokumen11 halamanTracing Technique and Landmark IdentificationnadaBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Pato II N - 1inglesDokumen7 halamanExam Pato II N - 1inglesSergio GarridoBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The Female Pelvis and Vaginal BirthDokumen104 halamanAnatomy of The Female Pelvis and Vaginal Birthsiti firdausiaBelum ada peringkat