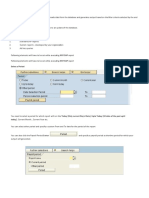
SAP and Its Concepts Overview
Diunggah oleh
puranamravinderJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SAP and Its Concepts Overview
Diunggah oleh
puranamravinderHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Ravinder Puranam
SAP:
SAP (Systems Applications and Products for data processing) is a ERP software. It was
developed by five former IBM employees in Germany by the company named SAP
SAP R/3 system is to provide a suite of tightly integrated, large scale business
applications. Following are the standard set of applications or functional module in R/3
system:
- PP (Production Planning)
- SD (Sales and Distribution)
- MM (Material Management)
- FICO (Finance and Controlling)
- AM (Fixed Asset Management)
- PS (Project System)
- WF (Work Flow)
- IS (Industry Solution)
- HR (Human Resource)
- PM (Plant Maintenance)
- QM (Quality Management)
SAP based on the architecture of R/3 on a three-tier client/server
1. Presentation Server (GUI)
2. Application Server
3. Database Server
SAP allows the IT supported processing of a multitude of tasks, accruing in a typical
company or bank. SAP ERP is differing from R/3 mainly because it is based on SAP
NetWeaver: core components can be implemented in ABAP and in Java and new functional
areas are mostly no longer created as part of the previous ERP system, with closely
interconnected constituents, but as self-contained components or even systems.
Presentation server is actually a program named sapgui.exe. It is usually installed on a
client machine. User can interact with the system with the help of this server. Application
server is a set of executables that collectively interpret the ABAP/4 programs. Database
server is a set of executables that accept database requests from the application server
In three-tier client/server architecture the presentation servers, application servers and
database servers all run on separate machines. For large systems this is the most common
configuration and is common in production.
In two-tier client/server architecture, the presentation and application servers are combined
and the database server is separate. This configuration is used in conjunction with other
application server.
Application Server
An application server is a collection of executable s that collectively interprets the ABAP/4
(Advanced Business Application Programming / 4th Generation) programs and manages the
input and output for them. When an application server is started, these executables all start
at the same time. When an application server is stopped, they all shut down together. The
Ravinder Puranam
number of processes that start up when you bring up the application server is defined in a
single configuration file called the application server profile. Each application server has a
profile that specifies its characteristics when it starts up and while it is running. For
example, an application server profile specifies:
* Number of processes and their types
* Amount of memory each process may use
* Length of time a user is inactive before being automatically logged off.
The Application layer consists of one or more application servers and a message server.
Each application server contains a set of services used to run the R/3 system. Not practical,
only one application server is needed to run an R/3 system. But in practice, the services are
distributed across more than one application server. This means that not all application
servers will provide the full range of services. The message server is responsible for
communication between the application servers. It passes requests from one application
server to another within the system. It also contains information about application server
groups and the current load balancing within them. It uses this information to choose an
appropriate server when a user logs onto the system.
The application server exists to interpret ABAP/4 programs, and they only run there-the
programs do not run on the presentation server. An ABAP/4 program can start an
executable on the presentation server, but an ABAP/4 program cannot execute there. If
your ABAP/4 program requests information from the database, the application server will
format the request and send it to the database server.cvb.
Database Server
The database server handles the user's request for addition, retrieval and modifications in
the data.
Security
Server-to-server communications can be encrypted with the SAP cryptographic library.
However, the SAP cryptographic library does not cover client-to-server encrypted
communications; an external technology covering Secure Network Communications and
Secure Socket Layer would have to be provided.
SAP Testing:
SAP Testing is same as manual testing but here the applications are SAP R/3 and Enterprise
portal. Whenever there is change in R/3 and Portal and you need to design test cases
according the change request and test the application.
If you have knowledge in the module (like HR, CRM, SD, SRM), which you are going to test
would be helpful to you.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Ganesh Pooja Book - TeluguDokumen11 halamanGanesh Pooja Book - Telugupuranamravinder94% (64)
- Bangalore HangoutsDokumen59 halamanBangalore HangoutspuranamravinderBelum ada peringkat
- Ganesh Pooja Book-EnglishDokumen10 halamanGanesh Pooja Book-EnglishHarshad Ashodiya Interior Designer50% (2)
- ISTQB Ravinder DocumentDokumen27 halamanISTQB Ravinder DocumentpuranamravinderBelum ada peringkat
- Performance Testing of Java Engines Using IBM - Rational Performance TesterDokumen39 halamanPerformance Testing of Java Engines Using IBM - Rational Performance TesterpuranamravinderBelum ada peringkat
- Istqb Foundation Level Syllabus - 2014Dokumen78 halamanIstqb Foundation Level Syllabus - 2014Joshua HolderBelum ada peringkat
- Database Management System by IDM Computer Studies (PVT) Ltd.Dokumen142 halamanDatabase Management System by IDM Computer Studies (PVT) Ltd.puranamravinder100% (1)
- Important C Questions For Written Test & Interview by Crack The InterviewDokumen236 halamanImportant C Questions For Written Test & Interview by Crack The Interviewpuranamravinder100% (8)
- Testing Related Document by RavinderDokumen7 halamanTesting Related Document by RavinderpuranamravinderBelum ada peringkat
- Top 5 Temples of IndiaDokumen10 halamanTop 5 Temples of IndiapuranamravinderBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Mobile Telephone Systems-1G, 2G, 2 5G, and 3G Wireless Technologies and ServicesDokumen20 halamanIntroduction To Mobile Telephone Systems-1G, 2G, 2 5G, and 3G Wireless Technologies and Servicespuranamravinder100% (7)
- Light Emitting Diode - by Ravinder PuranamDokumen16 halamanLight Emitting Diode - by Ravinder PuranampuranamravinderBelum ada peringkat
- Types of PCB and Wave SolderingDokumen4 halamanTypes of PCB and Wave Solderingpuranamravinder100% (2)
- SDLC and STLC by Ravinder in 2009Dokumen38 halamanSDLC and STLC by Ravinder in 2009puranamravinder100% (18)
- Mobile Testing Theory-RavinderDokumen57 halamanMobile Testing Theory-Ravinderpuranamravinder100% (2)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- TSCM60Dokumen2 halamanTSCM60Kannan Konar0% (3)
- IDP - Employee Central Core Hybrid - Employee Identifiers V1.4 PDFDokumen20 halamanIDP - Employee Central Core Hybrid - Employee Identifiers V1.4 PDFGunjan Shah100% (1)
- Sap Ehp 7 For Sap Erp 6Dokumen9 halamanSap Ehp 7 For Sap Erp 6fiestamixBelum ada peringkat
- SAP ReportsDokumen15 halamanSAP ReportsAyushman Sap100% (1)
- Sap Modules PDFDokumen5 halamanSap Modules PDFAkshay Mathur0% (1)
- How To Install Sap Ides Erp 6Dokumen10 halamanHow To Install Sap Ides Erp 6Amit RajputBelum ada peringkat
- SAP User Manual PDFDokumen55 halamanSAP User Manual PDFmadesuendaBelum ada peringkat
- Customizing and Process Flow of SD SchedulingDokumen5 halamanCustomizing and Process Flow of SD Schedulingpandu MBelum ada peringkat
- License Administration WorkbenchDokumen15 halamanLicense Administration WorkbenchVishlashak KapoorBelum ada peringkat
- Fico Sap PDF FilesDokumen2 halamanFico Sap PDF FilesAlishaBelum ada peringkat
- SAP Coupa IntegrationDokumen10 halamanSAP Coupa IntegrationHari NalluriBelum ada peringkat
- 2FM S4CLD2302 BPD en inDokumen10 halaman2FM S4CLD2302 BPD en inJayabharath SBelum ada peringkat
- Sap SRM TutorialDokumen16 halamanSap SRM TutorialAnusha Reddy50% (2)
- SAP Certification: Click HereDokumen12 halamanSAP Certification: Click HereAbhishek MishraBelum ada peringkat
- QM NotificationDokumen18 halamanQM NotificationMarco100% (1)
- WP - Sap Gts 11.0 Vs Sap Gts Edition For Sap S4hanaDokumen9 halamanWP - Sap Gts 11.0 Vs Sap Gts Edition For Sap S4hana6018.naveenBelum ada peringkat
- Sap SRM InsDokumen19 halamanSap SRM InsNaga RajBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting Information System 20192020Dokumen6 halamanAccounting Information System 20192020Acong WongBelum ada peringkat
- QMDokumen69 halamanQMKristine Jhoy Nolasco Secopito100% (1)
- Milestone Confirmation of The Process Order With Multiple Operations & With Multiple Phases Involved - SAP BlogsDokumen18 halamanMilestone Confirmation of The Process Order With Multiple Operations & With Multiple Phases Involved - SAP BlogsRaghBelum ada peringkat
- Hris Project On Erp Softwares: Submitted To: By: Ms Teena Bagga Taru Taneja Shalini BahadurDokumen23 halamanHris Project On Erp Softwares: Submitted To: By: Ms Teena Bagga Taru Taneja Shalini BahadurtarutanejaBelum ada peringkat
- Enabling A Smooth Company Code Merge With SAP® Landscape Transformation SoftwareDokumen12 halamanEnabling A Smooth Company Code Merge With SAP® Landscape Transformation SoftwareSaswat MohantyBelum ada peringkat
- Hindustan Unilever Limited (Hul) : Leading Consumer Goods Company Fulfils Business Optimisation Goals With SapDokumen4 halamanHindustan Unilever Limited (Hul) : Leading Consumer Goods Company Fulfils Business Optimisation Goals With SapNeelav RatnamBelum ada peringkat
- SB IA Incentives Administration (Sales)Dokumen4 halamanSB IA Incentives Administration (Sales)lakshmi025Belum ada peringkat
- Supply Network Planning APO SNPDokumen2 halamanSupply Network Planning APO SNPAlper SarıcıoğluBelum ada peringkat
- MTS & MTO SenariousDokumen4 halamanMTS & MTO SenariousKoustubha Khare0% (1)
- Sap Ecc and Sap S4hanaDokumen9 halamanSap Ecc and Sap S4hanaRaju BothraBelum ada peringkat
- 01-Sap HCM Paper1 (Q&A)Dokumen16 halaman01-Sap HCM Paper1 (Q&A)Anonymous Y1csGYBelum ada peringkat
- Track Intercompany Loans Using SAP's Transaction Manager Module: Part IDokumen74 halamanTrack Intercompany Loans Using SAP's Transaction Manager Module: Part IAmit Kumar100% (3)
- Procurement Transformation How To Make The Right Choice For Your JourneyDokumen19 halamanProcurement Transformation How To Make The Right Choice For Your JourneyYash VasudevaBelum ada peringkat