Computer Network Boklet
Diunggah oleh
Vinod GandhiHak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Computer Network Boklet
Diunggah oleh
Vinod GandhiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 1
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
COMPUTER NETWORKS
1. Network. A network is an interconnected collection of autonomous computers.
2. Nodes. The terminals attached to the network and share the resources of the network are called
nodes.
3. Server. The node, which provides service to the network and at a fixed address is called server.
4. LAN. A digital communication system cable of interconnecting a large number of computers,
terminals and other peripheral devices confined to relatively small areas such as a building or a
group of buildings.
5. WAN. Wide area network spans a large area-possibly several continents.
6. MAN. The scope of metropolitan area network lies between LANs and WANs, i.e., spanning a
small city or a town.
7. Communication channels. The connecting cables are the communication channels between the
different channel workstations. The three main types of cables are twisted pair cable, coaxial
cable and optical fiber cable.
8. Modem. The device that convert data from digital to analog form and vice versa.
9. Topology. The pattern of interconnection of nodes in a network is called the topology.
10. Internet. The internet is a global network of computers that are linked together by cables and
telephone lines making communication possible among them.
11. Repeater. Repeater is used to regenerate data and voice signals.
12. Bridges. A bridge is used to connect Two LANs which are physically separate but logically
same.
13. Router. Router is used to load balance various paths that exist on networks. Routers can attach
physically different networks.
14. Gateway. The special machine, which allows different electronic networks to talk to Internet that
uses TCP/IP, is called gateway.
15. E-Mail. E-mail is a popular way of communication on the Internet. By which you can send main
to any part of the world within few seconds and without spending huge amount of money.
16. Usenet. These are the special groups set up by the people who want to share common interests.
17. Gopher. Gopher present the Internet as a series of hierarchical menus containing items that point
to another menu or file of a directory within a remote host as a telnet services or the articles of a
Usenet newsgroup or to a variety of other things.
18. WWW. The World Wide Web is described as a “wide-area hypermedia information initiative
aiming to give universal access to large universe of documents”.
19. Archie. Archie tries to locate files in public ftp archives.
20. Veronica. Veronica is the one of the menu item of gopher. It is an acronym for Very Easy
Rodent Oriented Net-wide Index to Computer Archives.
21. WAIS. Wide Area Information System.
22. Protocol. There are some rules that govern to work on the network and these rule are also called
protocol.
PREVIOUS YEARS’ QUESTIONS {1 Mark}
1. What are repeaters? [Delhi1998, 99]
2. What is the difference between LAN and MAN? [Delhi 1998]
3. What do you understand by backbone network? [Delhi 1998]
4. What are Routers? [AI 1998]
5. What is the purpose of using a MODEM? [AI 1998]
6. What is the difference between LAN and Internet? [AI 1998]
7. What is the purpose of using Router? [AI 1999]
8. What is the difference between LAN and WAN? [AI 1999]
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 2
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
9. What is a bridge? [Delhi 1999]
10. What is the purpose of using FTP? [Delhi 1999]
11. What is the difference between WAN and MAN? [Delhi 1999]
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 3
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS {1 Mark}
12. What are the services provided by the internet? [CBSE Quan Book]
13. What is meant by full connectivity?
14. What is the function of the MODEM?
15. What is the Geographical scope of MAN? [CBSE Quan Book]
16. What is meant by network topology? [CBSE Quan Book]
17. What is Gateway? [CBSE Quan Book]
18. What is meant by Internet?
19. What is Archie? [CBSE Quan Book]
20. Define telnet.
21. Give the full form of FTP.
22. Draw a diagram showing five computer nodes connected to a server in ring topology.
23. Which of the following provides the maximum bandwidth:
(i) Optical fiber, (ii) Thin Ethernet, (iii) Arcnet.
24. What is Mosaic used for?
25. What is the full form of WWW?
26. A company wants to form a network on their six computers to a server within the company premises.
Represent STAR and RING topologies diagrammatically for the above network.
27. State two reasons for which you many like to have a network of computers instead of having stand
alone computers.
28. Name two browsers of the Internet.
29. Define server.
30. What is the function of TELNET?
31. A school would like to go in for network of all the computers. Which topology would you
recommend and why?
32. Name the device which performs modulation and demodulation.
33. Which of the following is not a transmission medium:
(i) Telephone lines, (ii) Coaxial cable, (iii) Modem, (iv) Microwave systems?
34. Name one advantage of using fiber optics data transmission.
35. Most data communication involving telegraph lines are .
36. What is multiplexer?
37. Name the communication line which is most suited for interactive processing application.
38. Give one example of analog communication method.
39. When was modem invented and in which country?
40. Who invented the modem?
41. What is the name of the network topology in which there are bi-directional links between each
possible node?
42. What is the commonly used unit for measuring the speed of data transmission?
43. What are the most commonly used transmission speeds in BPS used in data communication?
44. Name the device which is responsible for the transfer of data from a CPU to peripheral device of a
computer.
45. Which transmission mode is used for data communication along telephone lines?
46. Name the basic components of data communication system.
47. Define baud.
48. Which topology use point-point subnet?
49. What is an Rs. 232 interface?
50. What is X.25 protocol?
51. What is the full form of TCP/IP?
52. Name the places which are using WAN.
53. What is home page?
54. What is HTML?
55. What is SMTP?
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 4
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
PREVIOUS YEARS QUESTION [2 MARKS]
1. Describe the following brief:
(i) MOSAIC, (ii) Usenet. [Delhi 1998]
2. Write the two advantages and two disadvantages of the following topologies in network. [AI 1998]
(i) Bus Topology, (ii) Star Topology. [AI 1998]
3. Give two advantages and two disadvantages of the following network topologies:
(i) BUS, (ii) Tree. [AI 1999]
4. Give two advantages and two disadvantages of the following network topologies:
(i) Star, (ii) Tree. [Delhi 1999]
IMPORTANT QUESTIONS [3 Marks]
5. Name two network topologies and list one merit and one demerit of each. [CBSE Quan Book]
6. Write the capabilities and services supported by LAN. [CBSE Quan Book]
7. What are the facilities provided by the SERVER in a network environment? [CBSE Quan Book]
8. Give at least two advantages of the E-Mail. [CBSE Quan Book]
9. Write the difference between LAN, MAN and WAN.
10. What is meant by Client/Server environment? [CBSE Quan Book]
11. Define nodes and dumb terminals.
12. What is the difference between e-mail and the fax?
13. Differentiate between Circuit switching and Message switching.
14. What is packet switching?
15. Differentiate between DEDICATED and NON-DEDICATED SERVERS.
16. What is client/server environment?
17. What is the difference between Bridge and Router?
18. How does communication takes place in Ring Topology?
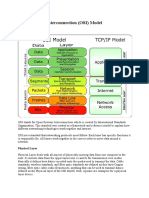
19. Name different layer of the ISO QSI layer.
20. What is the different switching techniques employed to provide communication between computers?
21. Give one advantage and one disadvantage of Ring Topology.
22. Give merit and demerit of star topology.
CBSE QUESTIONS
1. (a) What is a router?
(b) What is the use of MODEM?
(c) Give the full from of WWW.
(d) A company wants to form a network on their six computers to a server within the company
premises. Represent STAR and RING topologies diagrammatically for the above network?
2. (a) Give two reasons why you think networks are required.
(b) Give one merit and one demerit each of the following topologies:
(i) Star (ii) Ring.
(c) Why do you understand by Client Server Architecture?
(d) What is ARCHIE?
3. (a) Differentiate between Star and bus topology of network.
(b) Write names of two communication medium used to physically connected the terminals on the
network.
(c) What are ISO-OSI layers of network?
(d) What do you understand by e-mail and FTP?
4. (a) What is WAIS?
(b) Sharing resources is one of the sue of the networking comment.
(c) Differentiate between circuit switching and message switching.
(d) What is protocol?
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 5
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
5. (a) What is a bridge?
(b) What is the purpose of using FTP?
(c) Give two advantages and two disadvantages of following network topologies:
(i) Star (ii) Tree
(d) What is the difference between WAN and MAN?
SOME IMPORTANT BOARD QUESTIONS
Q1. (a) What are Routers?
(b) What is the purpose of using Modem?
(c) Write the two advantages and two disadvantages of Bus Topology in network.
(d) What is the difference between LAN and WAN?
Ans. (a) On Internet it is not necessary that all the packets will follow the same path from source to
destination. A special machine router tries to load balance between various paths that exists on
networks.
(b) MODEM is used to convert digital data into analog form and vice versa.
(c) Advantages of BUS Topology:
(i) Short cable length – Because there is single common data path connecting all nodes.
(ii) Easy to extend – Additional nodes can be connected to an existing bus network at any
point along its length.
Disadvantages of BUS Topology:
(i) Fault diagnosis is difficult – Although the bus topology is very simple, but in this topology
fault detection is very difficult.
(ii) Nodes must be intelligent – Each node on the network is directly connected to the central
bus. This means that some way of deciding who can use the network at any given time
must be performed in each node. It tends it increase the cost of the nodes irrespective of
whether this is performed in hardware or software.
(d) (i) A LAN is confined to restricted distance up to one building or near by building. On the other
hand scope of WAN is up to one continent.
(ii) Because of the short distances involved, the error rates in LANs are much lower than WANs.
Q2. (a) What are Repeaters?
(b) Name the device used to connect a computer to an analog telephone line.
(c) Briefly mention two advantages and two disadvantages of Star topology in network.
(d) What is the difference between MAN and WAN?
Ans. (a) Sometimes the signals on the Internet are become weaker before reaching the destination node.
Repeater is used to regenerate data and voice signals. Repeater read the incoming signals and
amplified it and transmitted to another segment of the network.
(b) MODEM
(c) Advantages of Star Topology:
(i) Ease of service – The star topology has a number of concentration point i.e., at the central
node or at intermediate wiring closets. These provide easy occurs for service or re-
configuration of the network.
(ii) One device per connection: In star topology, failure of a single connection typically
involves disconnecting one node from an other.
Disadvantages of Star Topology:
(i) Long cable length : Because each node in star topology is directly connected to the center,
the star topology requires a large quantity of cable.
(ii) Central node dependency : If the central node fails the network get failed.
(d) (i) A MAN is confined to ONE CITY OR TOWN. On the other hand scope of WAN is up to one
continent.
(ii) Because of the short distances involved, the error rates in MANs are much lower than WANs.
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 6
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
Q3. (a) What are Bridges?
(b) Mention the advantages of e-mail over conventional mailing system.
(c) Briefly mention two advantages and disadvantages of Ring topology in network.
(d) What is the difference between MAN and LAN?
Ans. (a) A bridge is used to connect two LANs, which are physically separated but logically same.
(b) E-Mail is the electronic mail. Electronic mail is usually used to exchange messages and data files
than conventional mailing system. Each used is assigned an electronic mailbox. Using the
appropriate command, the used can scan a list of the messages in the mailbox, display the contents
of a particular message, send a message to another user and so forth.
(c) Advantages of Ring Topology:
(i) Short cable length. In ring topology less connections will be needed which increase
network reliability.
(ii) The amount of cable needed in this topology is comparable to bus and small relative to
star.
Disadvantages of Ring Topology:
(i) Node failure causes network failure: Since each node in this network connected to its
neighboring node and data is travel through each node. So, there is one traffic flow until
defective node is removed.
(d) (i) A MAN is confined to ONE CITY OR TOWN. On the other hand scope of WAN is up to one
continent.
(ii) A LAN is confined to restricted distance up to one building or near by building or near by
building. On the other hand scope of WAN is up to one continent.
Q4. (a) What are backbone networks?
(b) Name two switching circuits and explain any one.
(c) Mention one difference between Circular and Star topologies in networking.
Ans. (a) When we connect number of LANs to form one WAN the network, which is used as a backbone
to connect the LANs is called backbone network.
(b) The two switching circuits are : Circuit switching and Message switching.
Circuit Switching: In this technique, first the complete physical connection between two
computers is established and then data is transmitted from the source computer to the destination
computer.
(c) the circular topology has:
Short cable length. In circular topology less connections will be needed which increase network
reliability. The amount of cable needed in this topology is comparable to bus and small relative to
star topologies.
The star topology has: One Device per connection and Long cable length.
Q5. (a) What is NFS?
(b) Mention one advantage of networking.
(c) Name two communication channels used in networking and explain any one.
(d) Mention one difference between Linear and Star topologies in networking.
Ans. (a) NFS (Network File System) allow computers to share files across a network or networks. NFS is
computer – independent and is also independent of lower layers, such as the transport layer,
because it rests above the RPC (Remote Procedure Calls).
(b) The advantage of networking is to share computer equipment and programs, messages and the
information available at one site.
(c) Two communication channels are: Twisted pair cable and Coaxial cable.
Twisted pair cable. The most common form of wiring in data communication applications is the
wiring. It consists of two identical wires in the pair have the same impedance to ground, making
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 7
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
it a balanced medium. This characteristic helps to lower the cable’susceptibility to noise from
neighboring cables or external sources.
(d) The linear topology has short Cable length and easy to extend.
The star topology has one Device per connection and easy to access.
Q6. (a) Compare coaxial and optical fiber cable.
(b) Write the following abbreviations in their full form:
LAN, OSI
(c) What is the purpose of Telnet?
(d) Write two advantages and disadvantages of the following topologies in network:
(i) Star
(ii) Tree
Ans. (a) Coaxial cable. It consists of a solid wire core surrounded by one or more foil or braided wire
shields, each separated from the other by some kind of plastic insulator. It is mostly used in the
cables wires.
Optical fibre cable. It consists of thin strands of glass or glass-line material which are so
connected that they carry light from source at one end to destination at the other end. The main
advantage of this cable is their complete immunity to noise. But this cable is very expensive as
compared to the coaxial cable.
(b) LAN – Local area Network
OSI – Open Systems Interconnection.
(c) Telnet is an Internet facility that facilitates remote login.
(d) (i) Advantages of STAR topology
1. One Device per connection
2. Easy to access
Disadvantages of STAR topology
1. Long cable length
2. Central node dependency
(ii) Advantages of TREE topology
1. Easy to extend
2. Fault isolation is easy
Disadvantages of TREE topology
1. Dependent on the root computer
2. Complex access protocols
Q7. (a) What is MODEM?
(b) Write the following abbreviations in their full form:
FTP, WAN, WWW
(c) Mention one difference between circuit switching and packet switching.
(d) Write two advantages and disadvantages of the following topologies in network:
(i) Bus
(ii) Ring
Ans. (a) A modem is a device which is used to convert digital data into analog form and vice versa.
(b) FTP. File Transfer Protocol
WAN. Wide Area Network
WWW. World Wide Web.
(c) Circuit Switching. In this technique firstly the complete physical connection between two
computers is established and then data is transmitted from the source computer to the destination
computer.
A Packet Switching network divides the data traffic into blocks called packets that have a
maximum length. Each packet of user data travels in a data envelope, which gives the destination
address of the packet and a variety of control information.
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 8
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
(d) Advantages of BUS topology:
(i) Short cable length – Because there is single common data path connecting all nodes.
(ii) Easy to extend – Additional nodes can be connected to an existing bus network at any
point along its length.
Disadvantages of BUS topology:
(i) Fault diagnosis is difficult – Although the bus topology is very simple, but in this topology
fault detection is very difficult.
(ii) Nodes must be intelligent – Each node on the network is directly connected to the central
bus. This means that some way of deciding who can use the network at any given time
must be performed in each node. It tends to increase the cost of the nodes irrespective of
whether this is performed in hardware or software.
Advantages of Ring topology:
(i) Short cable length – In ring topology less connections will be needed which increases
network reliability.
(ii) The amount of cable needed in this topology is comparable to bus and relatively small to
star.
Disadvantages of Ring topology:
(i) Node failure causes network failure – Since each node in this network is connected to its
neighbouring node and data travels through each node, there is one traffic flow until
defective node is removed.
(ii) Each node must handle the data being transferred on the ring.
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 9
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
COMPUTERS NETWORK
TERMINOLOGIES USED IN NETWORKING
1. N.I.U : NETWORK INTERFACE UNIT
2. TAP : TERMINAL ACCESS POINT
3. ARPANET : ADVANCED RESEARCH PROJECT NETWORK
4. NSF NET : NATIONAL SCIENCE FOUNDATION NETWORK
5. INTERNET : INTER CONNECTION OF NETWORKS (INTERNETWORKING)
6. TCP/IP : TRANSMISSION CONTROL PROTOCOL / INTERNET
PROTOCOL
7. VGM : VOICE GRADE MEDIUM
8. DGM : DATA GRADE MEDIUM
9. bPS : BITS PER SECOND
10. BPS : BYTES PER SECOND (1 BYTE = 8 BITS)
11. KbPS : KILO BITS PER SECOND
12. KBPS : KILO BYTES PER SECOND
13. mbps : MEGA BITS PER SECOND
14. Mbps : MEGA BYTES PER SECOND (106)
15. TBPS : TERA BYTES PER SECOND (1012)
16. LAN : LOCAL AREA NETWORK
17. WAN : WIDE AREA NETWORK
18. MAN : METROPOLITAN AREA NETWORK
19. P2P : POINT-TO-POINT
20. W.S. : WORK STATION
21. FTP : FILE TRANSFER PROTOCOL
22. SLIP : SERIAL LINE INTERNET PROTOCOL
23. PPP : POINT TO POINT PROTOCOL
24. IPCP : INTERNET PROTOCOL CONTROL PROTOCOL
25. NCPS ; NETWORK CONTROL PROTOCOL
26. LCP : LINK CONTROL PROTOCOL
27. GSM : GLOBAL SYSTEM FOR MOBILE COMMUNICATION
28. SIM : SUBSCRIBER IDENTIFICATION MODULE
29. TDMA : TIME DIVISION MULTIPLE ACCESS
30. IDEN : INTEGRATED DIGITAL ENHANCED NETWORK
31. CDMA : CODE-DIVISION MULTIPLE ACCESS
32. WLL : WIRELESS IN LOCAL LOOP OR WILL
33. PSTN : PUBLIC SWITCHED TELEPHONE NETWORK
34. 3G : THIRD GENERATION
35. EDGE : ENHANCED DATA RATES FOR GLOBAL EVOLUTION
36. SMS : SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE
37. SMSC : SHORT MESSAGE SERVICE CENTRE
38. E MAIL : ELECTRONIC MAIL
39. WWW : WORLD WIDE WEB
40. HTTP : HYPER TEXT TRANSFER PROTOCOL
41. URL : UNIFORM RESOURCE LOCATOR
42. HTML : HYPER TEXT MARKUP LANGUAGE
43. DNS : DOMAIN-NAME SYSTEM
44. POP : POST OFFICE PROTOCOL
45. SMTP : SIMPLE MAIL TRANSFER PROTOCOL
46. XML : EXTENSIBLE MARK-UP LANGUAGE
47. DHTML : DYNAMIC HTML
SPECTRUM STUDY CIRCLE (The Acme of Excellence) 10
15/22 IInd Floor Ashok Nagar, New Delhi-110018. Ph.: 25499279, 55711031(O), 9810865706(M)
Class: XII C++
48. MODEM : MODULATOR – DEMODULATOR
49. AM : AMPLITUDE MODULATION
50. FM : FREQUENCY MODULATION
51. PM : PHASE MODULATION
52. RJ-45 : REGISTER JACK – 45
53. DCE : DATA COMMUNICATION EQUIPMENT
54. BNC : BAYONE NEILL CONCETMAN
55. WAIS : WIDE AREA INFORMATION SYSTEM
56. RPC : REMOTE PROCEDURE CALLS
57. OSI : OPEN SYSTEMS INTERCONNECTION
58. ISP : INTERNET SERVICE PROVIDER
59. NIC : NETWORK INTERFACE CARD
60. NFS : NETWORK FILE SYSTEM
61. UTP : UNSHIELDED TWISTED PAIR CABLE.
62. STP : SHIELDED TWISTED PAIR CABLE
63. DTE : DATA TERMINAL EQUIPMENT
64. VFIR : VERY FAST INFRARED
65. PDA : PERSONAL DATA ASSISTANT
66. WCDMA : WIDE BAND CDMA
67. HLR : HOME LOCATION REGISTER
68. IE : INTERNET EXPLORER
69. NTP : NETWORK TIME PROTOCOL
70. IMAP : INTERNET MAIL ACCESS PROTOCOL
71. LEDS : LIGHT EMITTING PAIR
72. LDS : LASER DIODES
73. KHZ : KILOHERTZ
74. MHZ : MEGAHERTZ
75. GHZ : GIGAHERTZ
76. THZ : TERAHERTZ
77. A/F : AUDIO FREQUENCY
78. DTR : DATA TERMINAL READY
79. DSR : DATA SET READY
80. RTS : REQUEST TO SEND
81. CD : CARRIER DETECT
82. CTS : CLEAR TO SEND
83. SNA : SYSTEMS NETWORK ARCHITECTURE
84. URI : UNIFORM RESOURCE IDENTIFIER
85. URN : UNIFORM RESOURCE NAME
86. LCP : LINK CONTROL PROTOCOL
87. USC : UNIQUE SPREADING CODE.
88. WLL/WILL : WIRELESS IS LOCAL LOOP
89. UMTS : UNIVERSAL MOBILE TELECOMMUNICATION SYSTEMS
90. WCDMA : WIDE BAND CDMA.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Black & Decker International Case Study Vinod Gandhi PGDMHR IMIDokumen20 halamanBlack & Decker International Case Study Vinod Gandhi PGDMHR IMIVinod Gandhi100% (3)
- SentiencSentience, Systematics Club Magazinee, Systematics Club MagazineDokumen18 halamanSentiencSentience, Systematics Club Magazinee, Systematics Club MagazineVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- CrossRoads Feb2013Dokumen11 halamanCrossRoads Feb2013Vinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Talent Management Trends For 2017Dokumen5 halaman5 Talent Management Trends For 2017Vinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- NOVA Methodology - BY VINOD GANDHIDokumen5 halamanNOVA Methodology - BY VINOD GANDHIVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- NIKE Book Review by Vinod Gandhi International Management Institute, IMI DelhiDokumen13 halamanNIKE Book Review by Vinod Gandhi International Management Institute, IMI DelhiVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- MarkUp Markazine Nov SoftCopyLVersion3Dokumen20 halamanMarkUp Markazine Nov SoftCopyLVersion3Vinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Aristos 2012Dokumen3 halamanAristos 2012Vinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- SOS: Sense OF Session 5&6: Group "Spartan"Dokumen3 halamanSOS: Sense OF Session 5&6: Group "Spartan"Vinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Cash Flow Statement PracticeDokumen6 halamanCash Flow Statement PracticeVinod Gandhi100% (3)
- W.L. GORE Associates Case StudyDokumen8 halamanW.L. GORE Associates Case StudyVinod Gandhi88% (16)
- New Holland India Team Case Study - Vinod Gandhi - International Management InstituteDokumen11 halamanNew Holland India Team Case Study - Vinod Gandhi - International Management InstituteVinod Gandhi89% (9)
- Ratio AnalysisDokumen10 halamanRatio AnalysisVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- HR AccountingDokumen5 halamanHR AccountingVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Calculating Gross Domestic Product, Gross National Product, Net National Product, National Income EtcDokumen5 halamanCalculating Gross Domestic Product, Gross National Product, Net National Product, National Income EtcVinod Gandhi100% (1)
- FA (RBI and Its Monetary Policy)Dokumen9 halamanFA (RBI and Its Monetary Policy)Vinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- HRM Web SitesDokumen2 halamanHRM Web SitesVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Meaning & Objectives of Accounting 1Dokumen3 halamanMeaning & Objectives of Accounting 1Vinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Govt Lokpal Bill Vs Jan Lokpal BillDokumen6 halamanGovt Lokpal Bill Vs Jan Lokpal BillOutlookMagazine100% (1)
- Operating SystemsDokumen76 halamanOperating SystemsVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Prof. B. I. Khodanpur HOD - Dept. of CSE R. V. College of EngineeringDokumen23 halamanProf. B. I. Khodanpur HOD - Dept. of CSE R. V. College of EngineeringKavin ArsenalonaBelum ada peringkat
- Jan Lokpal Vs Govt. LokpalDokumen28 halamanJan Lokpal Vs Govt. LokpalVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Partnership FundamentalsDokumen3 halamanPartnership FundamentalsVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Step-By-Step Example: Bubble Sort Is A Simple Sorting Algorithm. It Works by Repeatedly Stepping Through TheDokumen40 halamanStep-By-Step Example: Bubble Sort Is A Simple Sorting Algorithm. It Works by Repeatedly Stepping Through Theparul91887866Belum ada peringkat
- Meaning of AccountingDokumen1 halamanMeaning of AccountingVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Principles AccountsDokumen2 halamanBasic Principles AccountsVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Strategic Human Resource Management & TCSDokumen11 halamanStrategic Human Resource Management & TCSVinod Gandhi100% (3)
- Accounting Theory3Dokumen49 halamanAccounting Theory3Vinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Indian AwakeningDokumen12 halamanIndian AwakeningVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- Accounting TheoryDokumen4 halamanAccounting TheoryVinod GandhiBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- B.Tech. ECE-IE Syllabus SRM IST - 2018 Reg.Dokumen124 halamanB.Tech. ECE-IE Syllabus SRM IST - 2018 Reg.Ss StBelum ada peringkat
- ElectronicsDokumen3 halamanElectronicsashishkumar218Belum ada peringkat
- APX MPX GeneratorDokumen2 halamanAPX MPX Generatorjohnny chanBelum ada peringkat
- Savk 61 DgsDokumen156 halamanSavk 61 Dgsall schematicBelum ada peringkat
- Manual - Sapphire Touch ScreenDokumen2 halamanManual - Sapphire Touch ScreenSamuel Castro SedanoBelum ada peringkat
- Realization of a Planar Low-Profile Broadband Phased Array AntennaDokumen120 halamanRealization of a Planar Low-Profile Broadband Phased Array AntennaCarriceiros TourBelum ada peringkat
- A Q-Band Miniature Monolithic Sub Harmonically Pumped Resistive MixerDokumen4 halamanA Q-Band Miniature Monolithic Sub Harmonically Pumped Resistive MixerLouis ChangBelum ada peringkat
- LICDokumen5 halamanLICSandesh RSBelum ada peringkat
- Router BoardDokumen6 halamanRouter BoardISLAMIC LIBRARYBelum ada peringkat
- Powertron ManualDokumen24 halamanPowertron ManualJarek KlamannBelum ada peringkat
- Car Park SolutionDokumen10 halamanCar Park SolutionKhay SaadBelum ada peringkat
- GMDSSDokumen31 halamanGMDSSJohn Gerald Lipata Reyno100% (2)
- 03 - Hit 7300 GMPLS - ASON Components and LayersDokumen46 halaman03 - Hit 7300 GMPLS - ASON Components and LayerskupeoBelum ada peringkat
- Mortek - EKKXO Cabinet - Installation Manual v1.1Dokumen4 halamanMortek - EKKXO Cabinet - Installation Manual v1.1Vasilis TserosBelum ada peringkat
- Repeater Installation and CommissioningDokumen34 halamanRepeater Installation and CommissioningTuan TocdaiBelum ada peringkat
- Lab MicroDokumen5 halamanLab MicroNashitah AlwazBelum ada peringkat
- GXT745Dokumen24 halamanGXT745Ramy Abd RabouBelum ada peringkat
- Passive Tuned Harmonic FiltersDokumen4 halamanPassive Tuned Harmonic FiltersRajendra Prasad Shukla100% (1)
- PIR Sensor Based Security System PDFDokumen42 halamanPIR Sensor Based Security System PDFzeeshan sikandarBelum ada peringkat
- DATASHEET User Info 250W Power Puck 0 - 95Dokumen4 halamanDATASHEET User Info 250W Power Puck 0 - 95bilgesu7kediBelum ada peringkat
- City". We Implemented Using PIC Microcontroller and RF ModuleDokumen56 halamanCity". We Implemented Using PIC Microcontroller and RF ModuleSai RakeshBelum ada peringkat
- ALFARABI UNIV COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE I CHAPTERDokumen13 halamanALFARABI UNIV COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE I CHAPTERMohammed Al-RahmaweeBelum ada peringkat
- MOdel OSI NoteDokumen7 halamanMOdel OSI NoteZulfadli HanaffiBelum ada peringkat
- Hcia 5G PDFDokumen6 halamanHcia 5G PDFKuda BetinaBelum ada peringkat
- Elnet LT ManualDokumen77 halamanElnet LT ManualSebastian TorresBelum ada peringkat
- Luminarios Lista09052011Dokumen116 halamanLuminarios Lista09052011NelvaBelum ada peringkat
- MD 01 Introduction PDFDokumen26 halamanMD 01 Introduction PDFJirah GicangaoBelum ada peringkat
- G2YM400VL20Dokumen4 halamanG2YM400VL20luis gonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- PS01509 LoRaWAN AT Command SpecificationDokumen46 halamanPS01509 LoRaWAN AT Command SpecificationleonardoBelum ada peringkat
- Manual de Snap Circuits Light en Español Del 82 Al 177 ProyectoDokumen39 halamanManual de Snap Circuits Light en Español Del 82 Al 177 Proyectosamuel.guardado.rodriguezBelum ada peringkat