Energy Systems (5 6 78)
Diunggah oleh
amyhowarth0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
81 tayangan4 halamanEnergy is required for all kinds of bodily processes including growth, development, repair, the transport of various substances between cells and of course muscle contraction. The body extracts energy from food and transfers it to the protein in the muscle. The release of the phosphate molecule through hydrolysis liberates approximately 12,000 calories of energy.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Energy Systems (5 6 78 )
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
ODT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniEnergy is required for all kinds of bodily processes including growth, development, repair, the transport of various substances between cells and of course muscle contraction. The body extracts energy from food and transfers it to the protein in the muscle. The release of the phosphate molecule through hydrolysis liberates approximately 12,000 calories of energy.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai ODT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
81 tayangan4 halamanEnergy Systems (5 6 78)
Diunggah oleh
amyhowarthEnergy is required for all kinds of bodily processes including growth, development, repair, the transport of various substances between cells and of course muscle contraction. The body extracts energy from food and transfers it to the protein in the muscle. The release of the phosphate molecule through hydrolysis liberates approximately 12,000 calories of energy.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai ODT, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 4
Energy Systems
The body is able to maintain a continuous supply of energy through the
use of ATP, which is known as adenosine triphosphate.
Energy is required for all kinds of bodily processes including growth,
development, repair, the transport of various substances between cells
and of course muscle contraction. (www.sport-fitness-advisor.com)
The body extracts energy from food and transfers it to the protein in the
muscle. This then determines your capacity to exercise for different
durations at different intensities.
ATP releases energy by bonding with water, a process called hydrolysis.
This causes one of the phosphate molecules to be released, resulting in
the formation of a new compound called adenosine diphosphate (ADP).
The release of the phosphate molecule through hydrolysis liberates
approximately 12,000 calories of energy. This energy is used in a number
of different ways.
ATP , is used in cell life forms. The more work that needs to be done the
more ATP that must be used.
Energy can be stored as
carbohydrates or lipids but
the energy in the chemical
bonds must be transferred to
ATP before it can be used in
the cell.(kentsimmons.com)
ATP can lose its terminal
phosphate and in the process,
release the energy stored in
it. This energy is then used to
work in the cells. It will in
turn produces ADP and the
phosphate which itself may
become part of the chemical
reaction.
(kentsimmons.com)
To generate ATP again from ADP free phosphate you have to add energy
back in order to create the terminal energy bond. The new energy, ATP
can then be reused again. The energy to create ATP from ADP mainly
comes from the sun via photosynthesis, where the extra energy is stored
as glucose. Glucose itself can be used as a "fuel" to create more ATP.
(kentsimmons.com)
The ATP bond will break through a cycle called hydrolysis, whereby
ATP looses a phosphate group where the energy is stored and becomes
adensosine diphosphate (ADP). So when the bond is broken, energy is
subsequently released. The ATP bond is broken because the nucleotide is
no longer APT, it is a different molecule.
This means the human body has developed three distinct mechanisms for
the transfer of food to energy within muscle. These mechanisms are
commonly knows as energy systems. (www.sport-fitness-advisor.com)
All three energy systems - anaerobic, lactic acid and aerobic , contribute
at the start of exercise but the contribution depends upon the individual
and the effort applied or the rate at which energy is used.
(www.sagewoodwellness.com)
The Anaerobic (ATP-CP) Energy System
The anaerobic energy system is where there is a lot of high intensity
activity. This happens because the creatine phosphate molecule is broken
down quickly and is used to turn ADP into ATP. The phosphate system is
suitable for single or continuous short bursts of energy of around 10
seconds. This happens as soon as the ATP is broken down to ADP, which
can then be restored to ATP. This system would be used for events such
as the long jump and 100 metres sprint. The amount of creatine phosphate
in muscles is limited, which is why athletes often use creatine phosphate
supplements. This system is also called the ATP/PC system.
(www.shoppingtrolley.net/)
To develop this energy system, sessions of 4 to 8 seconds of high
intensity work at near peak velocity are required:
• 3 × 10 × 30 metres with recovery of 30 seconds/repetition and 3
minutes/set.
• 15 × 60 metres with 60 seconds recovery
• 20 × 20 metres shuttle runs with 45 seconds recovery
The length of recovery between repetitions is important in the recovery of
power output through the resynthesis of CP. (sport-fitness-
advisor.com/energysystems)
The Lactic Acid System
The lactic acid system depends on a chemical process known as
Glycolysis. Carbohydrates are stored in the muscles as glycogen, these
are high in power but low in capacity as there is not much glycogen.
(physical education and the study of sport – RJ Davis ect)
Energy is derived from the fast break down of glucose from glycogen and
blood sugar. Glycogen is stored in the liver and the muscles. When
glycogen is broken down, it produces ATP and pyruvic acid. This process
is called Anaerobic Glycolysis, because the glycogen is not fully broken
down but leaves a by product called Lactic Acid. When lactic acid
accumulates in the muscles it results in muscle fatigue and weakness.
(www.shoppingtrolley.net/)
The lactic acid system provides energy for a longer duration than the
anaerobic system. This is between 10 - 90 seconds, which would be
required for a 100m swim, or a 400-800m run.
Sessions to develop this energy system:
• 5 to 8 × 300 metres fast - 45 seconds recovery - until pace
significantly slows
• 150 metre intervals at 400 metre pace - 20 seconds recovery - until
pace significantly slows
• 8 × 300 metres - 3 minutes recovery (lactate recovery training)
(sport-fitness-advisor.com/energysystems)
The Aerobic Energy System
The aerobic system, releases energy slowly by using oxygen to breaking
down glucose. It provides lots of long term energy suitable for every day
activities and endurance events. It can also break down fats to make ATP.
As we get fitter, the amount of oxygen used by muscles increases. Energy
is produced by the mitochondria by products of water, which we sweat or
wee. It is also the CO2 which we exhale. (www.shoppingtrolley.net)
This energy system can be developed with various intensity (Tempo)
runs. The types of Tempo runs are:
• Continuous Tempo - long slow runs at 50 to 70% of maximum
heart rate. This places demands on muscle and liver glycogen. The
normal response by the system is to enhance muscle and liver
glycogen storage capacities and glycolytic activity associated with
these processes
• Extensive Tempo - continuous runs at 60 to 80% of maximum heart
rate. This places demands on the system to cope with lactate
production. Running at this level assists the removal and turnover
of lactate and the body's ability to tolerate greater levels of lactate
• Intensive Tempo - continuous runs at 80 to 90% of maximum heart
rate. Lactate levels become high as these runs boarder on speed
endurance and special endurance. Intensive tempo training
provides the base for the development of anaerobic energy systems
(sport-fitness-advisor.com/energysystems)
All three energy systems are active at any given time, but this will depend
on the intensity an duration of the activity which is undertaken.
Bibliography
• Physical Education and the study of sport – RJ Davis, CR
Bull, JV Roscoe and DA Roscoe
• www.shoppingtrolley.net
• www.sport-fitness-advisor.com/energysystems
• www.sagewoodwellness.com
• Kentsimmons.uwinnipeg.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Understanding How Quality Is Measured in Sports DevelopmentDokumen12 halamanUnderstanding How Quality Is Measured in Sports DevelopmentamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- Providers of Sports DevelopmentDokumen5 halamanProviders of Sports DevelopmentamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- Evens RespiortyDokumen4 halamanEvens RespiortyamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- Providers of Sports DevelopmentDokumen5 halamanProviders of Sports DevelopmentamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- Know The Effect of Personality and Motivation On Sports PerformanceDokumen5 halamanKnow The Effect of Personality and Motivation On Sports PerformanceamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- MOTIVATIONDokumen10 halamanMOTIVATIONamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- Barriers To ParticipationDokumen5 halamanBarriers To ParticipationamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
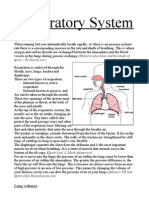
- Respiratory System: The Lungs (WWW - Google.co - Uk)Dokumen5 halamanRespiratory System: The Lungs (WWW - Google.co - Uk)amyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- Cardio Vascular SystemDokumen4 halamanCardio Vascular SystemamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular System Part 2Dokumen3 halamanCardiovascular System Part 2amyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- Sports DevelopmentDokumen9 halamanSports DevelopmentamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- BTEC Sport: Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen15 halamanBTEC Sport: Anatomy and PhysiologyamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- BTEC Sport: Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen15 halamanBTEC Sport: Anatomy and PhysiologyamyhowarthBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Hematopoietic Stem CellDokumen8 halamanHematopoietic Stem CellMaryam ShahrasbiBelum ada peringkat
- TCA Cycle MCQDokumen2 halamanTCA Cycle MCQTinsae WorkuBelum ada peringkat
- Composition of Blood and Cellular Elements: Learning ObjectivesDokumen11 halamanComposition of Blood and Cellular Elements: Learning Objectivesmarinak_6Belum ada peringkat
- ENDO) Pancreas. For The ClassDokumen58 halamanENDO) Pancreas. For The ClassromaloiBelum ada peringkat
- Reactions of Plant Glycolysis and FermentationDokumen8 halamanReactions of Plant Glycolysis and FermentationxbBelum ada peringkat
- Degradation of TG: 1 - Fat catabolism (lipolysis) 2.β-Oxidation of Fatty acids (fatty acid oxidation)Dokumen26 halamanDegradation of TG: 1 - Fat catabolism (lipolysis) 2.β-Oxidation of Fatty acids (fatty acid oxidation)Aboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dBelum ada peringkat
- Biokimia 2 GLIKOLISISDokumen18 halamanBiokimia 2 GLIKOLISISnamharBelum ada peringkat
- Nervous Tissue-LabDokumen32 halamanNervous Tissue-LabAlexis PriceBelum ada peringkat
- Blood PropertiesDokumen38 halamanBlood PropertiesShubham BhandareBelum ada peringkat
- Lumphatic System Tortora DR - Compatibility ModeDokumen22 halamanLumphatic System Tortora DR - Compatibility Modekamalab04Belum ada peringkat
- Module 2: Hematopoiesis I. General Principles of HematopoiesisDokumen13 halamanModule 2: Hematopoiesis I. General Principles of HematopoiesisJane JapoleBelum ada peringkat
- White Blood Cells MaturationDokumen28 halamanWhite Blood Cells MaturationShalom Apura100% (1)
- BIO 202 Blood Lab 22S PDFDokumen2 halamanBIO 202 Blood Lab 22S PDFTraci GardnerBelum ada peringkat
- The Three Stages of Catabolism. A General Diagram of Aerobic Catabolism in ADokumen8 halamanThe Three Stages of Catabolism. A General Diagram of Aerobic Catabolism in Aadarling4evrBelum ada peringkat
- Module 13Dokumen26 halamanModule 13Faye Aquino100% (1)
- Coulter DXH Diluent: © 2018 Beckman Coulter, Inc. All Rights ReservedDokumen52 halamanCoulter DXH Diluent: © 2018 Beckman Coulter, Inc. All Rights ReservedGregorio De Las CasasBelum ada peringkat
- Glycolysis and TCA Cycle - ShuttlesDokumen1 halamanGlycolysis and TCA Cycle - ShuttlesDr. SHIVA AITHALBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Glikogenolisis PDFDokumen5 halaman5 Glikogenolisis PDFAri CahyaniBelum ada peringkat
- ALcohol MetabolismDokumen17 halamanALcohol MetabolismMaharij NoorBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemical Changes of Diabetes MellitusDokumen4 halamanBiochemical Changes of Diabetes MellitusGerardLum100% (3)
- 9 Glycolysis and The Krebs Cycle-S PDFDokumen8 halaman9 Glycolysis and The Krebs Cycle-S PDFmadhavi goswamiBelum ada peringkat
- Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein MetabolismDokumen3 halamanCarbohydrate, Lipid, Protein Metabolismtritone.paradoxBelum ada peringkat
- Concept of Endurance TrainingDokumen28 halamanConcept of Endurance Trainingpaulo tsuneta100% (1)
- POGIL Ox Phos S PDFDokumen5 halamanPOGIL Ox Phos S PDFDoug GilmourBelum ada peringkat
- STUDY GUIDE - Lipid and Carbohydrate CombinedDokumen5 halamanSTUDY GUIDE - Lipid and Carbohydrate CombinedMaya Abou MradBelum ada peringkat
- Эссе Кайратткызы Сабина Жм22-016Dokumen4 halamanЭссе Кайратткызы Сабина Жм22-016Sabina KoshaBelum ada peringkat
- 1.4 The Lymphatic System: Prepared By: Ling Mei TengDokumen15 halaman1.4 The Lymphatic System: Prepared By: Ling Mei TengJuliet LingBelum ada peringkat
- 364 506 3 262961301 210421160335 CBCDokumen1 halaman364 506 3 262961301 210421160335 CBCMenna EmaryBelum ada peringkat
- CAPE Biology 2013 U2 P2 MS PDFDokumen13 halamanCAPE Biology 2013 U2 P2 MS PDFYagna LallBelum ada peringkat
- Childrens FBC Reference Ranges PDFDokumen1 halamanChildrens FBC Reference Ranges PDFfabian sutrisnoBelum ada peringkat