Guide To Oxygen Delivery System
Diunggah oleh
Darwin VillestasDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Guide To Oxygen Delivery System
Diunggah oleh
Darwin VillestasHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Guide to Oxygen Delivery System By Brenda Swant BSN, RN Low-Flow Oxygen Systems: The FiO2 in low flow systems
(items 1-4) will vary depending on the oxygen delivery device and the patients respiratory/oxygenation needs. Important Respiratory Numbers Phone highe Adult 6-6322 Pediatric 6-6320
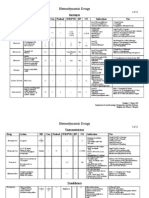
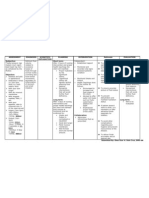
Device/Where Obtained 1. Nasal Cannula Liter Flow (LPM 1-6 1=25% 2=29% 3=33% 4=37% 5=41% 6=45% O2 Concentration (FiO2) 22-45% Advantages -effective for low oxygen concentrations.
Pager 1-7815 1-7816
Disadvantages Administration Guidelines Maximum flow is 5-6 LPM. Change to another O2 device if patient requires >5 LPM. -humidify for liter flows >4 LPM -use on patients with adequate tidal volume and normal vital signs A minimum of 6 LPM is required for all masks to flush expired carbon dioxide and prevent rebreathing of CO2. Do not use humid ifier and fit firmly. -use for severe asthma, pneumonia, trauma, or severe sepsis Reservoir bag must remain inflated at all times Do not use humidifier bottle -if bag collapses, increase flow rate until inflated -ensure free expansion, no twisting or kinks
-will not deliver oxygen concentrations higher than 40% -dry mucous membranes
2. Simple Mask
6-10
25-60%
-delivers oxygen concentrations up to 60%
-tight seal is required for higher oxygen concentrations: hot and confining impractical long-term
3. Partial non-rebreather
8-12
35-60%
-flaps stay open -valves allow expired CO2 to leave the mask
-requires a tight seal -impractical for longterm
4. Non-Rebreather
10-15
80-95%
-delivers the highest possible oxygen concentration without intubation -short-term therapy
-requires a tight seal -impractical for longterm
Reservoir bag must remain inflated at all times Do not use humidifier bottle -if bag collapses, increase flow rate until inflated -ensure free expansion, no twisting or kinks
High-Flow Oxygen Systems: These devices (items 5-6) meet or exceed the patients minute volume or inspiratory demands. They deliver fixed concentration of oxygen, regardless of the inspiratory flow or breathing pattern.
Table 1 Guide to colors of Venturi valves Venturi valve color Blue White Yellow Red Green Flow rate (l/min) 2 4 6 8 12 Oxygen delivered (%) 24 28 35 40 60
Treatment with oxygen 60% or/>101 rebreathing 90-94
Device/Where Obtained Liter Flow (LPM) Varies Mixes a specific volume of air and oxygen O2 Concentrati on (FiO2) 24-60% FiO2 is determined by the color of the venture device as stated above Advantages Disadvantages Administration Guidelines Accurate O2 concentration depends on oxygen liter flow and color of attached venture device. Always use the clear plastic collar, to guarantee the oxygen concentration delivered. Do not use a humidifier bottle 6. Aerosol/Large volume Nebulizers 10-15 28-100% -administers large volumes of mist -indicated for thick secretions -condensation may collect in the trach. Collar or tubing. Use on COPD patients -Observe for signs of overhydration, pulmonary edema, crackles. -connected to a wide corrugated tubing that receives oxygen from a jet nebulizer.
5. Venturi Mask
-delivers highly accurate oxygen concentration for the same amount of air always enters.
-requires a tight seal -intake ports can be blocked
Trach
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Cardiovascular & Hematologic SystemDokumen163 halamanCardiovascular & Hematologic SystemRellie CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Arterial Lines in PACU: Presented by Autum Jacobs RN, BSNDokumen34 halamanArterial Lines in PACU: Presented by Autum Jacobs RN, BSNinuko1212Belum ada peringkat
- 1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefDokumen35 halaman1538 Exam 4 Cell Reg & GriefJade EdanoBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiomyopathy Joisy AloorDokumen31 halamanCardiomyopathy Joisy AloorJoisy AloorBelum ada peringkat
- CardiopathophysiologyDokumen63 halamanCardiopathophysiologyapplesncoreBelum ada peringkat
- Diagn Approach of Abdominal PainDokumen53 halamanDiagn Approach of Abdominal PainNuriBelum ada peringkat
- ICU Cheat SheetDokumen2 halamanICU Cheat SheetPrescilla Randazzo100% (1)
- MS2 Cards Wigger DiagramDokumen1 halamanMS2 Cards Wigger DiagramCharlieBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Severe Hypertension, Hypertension in Special ConditionDokumen43 halamanManagement of Severe Hypertension, Hypertension in Special Conditionabhandlung100% (3)
- Acid-Base BalanceDokumen5 halamanAcid-Base BalanceCarl Earvin L. FavoritoBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDokumen12 halamanCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxBelum ada peringkat
- ATI Flash Cards 05, Medications Affecting The Nervous SystemDokumen110 halamanATI Flash Cards 05, Medications Affecting The Nervous SystemGiovanni MictilBelum ada peringkat
- CardioDokumen7 halamanCardioGerald AndrinBelum ada peringkat
- Electrolyte DisordersDokumen10 halamanElectrolyte DisordersSlavicaBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine System - NURSINGDokumen3 halamanEndocrine System - NURSINGFrancesca GraingerBelum ada peringkat
- Critical Care Drugs 1Dokumen21 halamanCritical Care Drugs 1Asri ErnadiBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Disorders Proper 1232011849539043 1Dokumen111 halamanCardiovascular Disorders Proper 1232011849539043 1api-19824701Belum ada peringkat
- Hepatobiliary Disorders: Katrina Saludar Jimenez, R. NDokumen42 halamanHepatobiliary Disorders: Katrina Saludar Jimenez, R. NKatrinaJimenezBelum ada peringkat
- ACLS Algorithms Adult 2010 Revised May 31 2011Dokumen12 halamanACLS Algorithms Adult 2010 Revised May 31 2011arturschander3614Belum ada peringkat
- Critical Care Drugs OverviewDokumen23 halamanCritical Care Drugs OverviewAsri Ernadi100% (1)
- EndocrineDokumen23 halamanEndocrinensvickneswaranBelum ada peringkat
- Dysrhythmia TestsDokumen3 halamanDysrhythmia TestsKimberly WhitesideBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimDokumen14 halamanPreparation Worksheets For NUR 345 Heart Failure SimclarimerBelum ada peringkat
- Inotropes and Vasopressors: Understanding Their Uses in ShockDokumen71 halamanInotropes and Vasopressors: Understanding Their Uses in Shockankur100% (1)
- Coumadin Dosing GuideDokumen3 halamanCoumadin Dosing Guidemorale28Belum ada peringkat
- BWH Hyperglycemia GuidelinesDokumen7 halamanBWH Hyperglycemia Guidelinespmahesh107100% (1)
- Anti-Arrhythmic DrugsDokumen45 halamanAnti-Arrhythmic Drugssultan khabeebBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenDokumen23 halamanELECTROCARDIOGRAM by Aldrin Jayson AlmadenItsMe AJBelum ada peringkat
- Pharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106Dokumen47 halamanPharm Fall Cardiovascular Pharmacology Study Guide-106sean liyanageBelum ada peringkat
- Potassium and Sodium Level Imbalances: Hyperkalemia, Hypokalemia, Hypernatremia, HyponatremiaDokumen5 halamanPotassium and Sodium Level Imbalances: Hyperkalemia, Hypokalemia, Hypernatremia, HyponatremiaChariza Trompeta100% (1)
- Tara's Anatomy and Physiology - Aehlert ECGs Made EasyDokumen16 halamanTara's Anatomy and Physiology - Aehlert ECGs Made EasyTara McNeillBelum ada peringkat
- Emergency Drug (Finale)Dokumen49 halamanEmergency Drug (Finale)SN. CaR67% (3)
- New in ICUDokumen30 halamanNew in ICUJoseAlonzoBelum ada peringkat
- ABG InterpretationDokumen10 halamanABG InterpretationNisha MathewBelum ada peringkat
- Condition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsDokumen5 halamanCondition Drug Class: Cardiovascular MedicationsCasey Fioravante100% (1)
- Alkalosis Acidosis ChartDokumen1 halamanAlkalosis Acidosis ChartrobingailBelum ada peringkat
- HW InotropesDokumen3 halamanHW InotropesNatalie YeohBelum ada peringkat
- ACLS Drug TherapyDokumen8 halamanACLS Drug TherapySahrensBelum ada peringkat
- Chad Pressors HandoutDokumen12 halamanChad Pressors HandoutquelspectacleBelum ada peringkat
- Hematology summary guideDokumen91 halamanHematology summary guidePeter Shirima100% (1)
- 2 Cardiovascular System: Describe The Systemic Circulation in The Body and Give Its ImportanceDokumen28 halaman2 Cardiovascular System: Describe The Systemic Circulation in The Body and Give Its ImportanceBhavin ChangelaBelum ada peringkat
- Understand Acid-Base DisordersDokumen89 halamanUnderstand Acid-Base DisordersEdouinaBelum ada peringkat
- Normal Laboratory Values - Patient Test Reference RangesDokumen10 halamanNormal Laboratory Values - Patient Test Reference RangesGita Elisa Berlina GintingBelum ada peringkat
- ACLS Algorithms (2011)Dokumen6 halamanACLS Algorithms (2011)senbonsakuraBelum ada peringkat
- Disorders of The Circulatory System Table-AnswersDokumen2 halamanDisorders of The Circulatory System Table-Answersapi-281108263Belum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology RevisedDokumen59 halamanPharmacology Revisedjohnstockton12100% (1)
- Pre-op Evaluation SummaryDokumen1 halamanPre-op Evaluation Summarysabbo morsBelum ada peringkat
- EVD PosterDokumen1 halamanEVD PosterDwie 'keonk' UnisaspalaBelum ada peringkat
- vSim CLINICAL REPLACEMENT PACKETDokumen14 halamanvSim CLINICAL REPLACEMENT PACKETBhargav DaveBelum ada peringkat
- Body CavitiesDokumen22 halamanBody Cavitiesapi-421876553Belum ada peringkat
- Cardiac CatheterizationDokumen3 halamanCardiac CatheterizationAmir ZiadBelum ada peringkat
- Operating Room Preparation: Philipp Acaso Ralph ArcoDokumen158 halamanOperating Room Preparation: Philipp Acaso Ralph ArcoTiffany Luv Adrias100% (1)
- EKG Rhythms: SVT, Atrial Fibrillation, AV Blocks (39Dokumen10 halamanEKG Rhythms: SVT, Atrial Fibrillation, AV Blocks (39Saidel ElizondoBelum ada peringkat
- Vasopressors and InotropesDokumen31 halamanVasopressors and InotropesReza Prakosa SedyatamaBelum ada peringkat
- NURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideDari EverandNURSING CARE OF ADULTS II: Passbooks Study GuideBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDari EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Memo RespondentDokumen27 halamanMemo RespondentNiteshMaheshwari100% (2)
- E.N.T-Otorhinolaryngology Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Then Select The Single Best Answer Part I: Otology/EarDokumen3 halamanE.N.T-Otorhinolaryngology Instructions: Read Each Question Carefully and Then Select The Single Best Answer Part I: Otology/EarJohn M. Hemsworth100% (1)
- Public Private HEM Status AsOn2May2019 4 09pmDokumen24 halamanPublic Private HEM Status AsOn2May2019 4 09pmVaibhav MahobiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Graphic Design at Colin BuchananDokumen12 halamanGraphic Design at Colin BuchananSKM Colin Buchanan80% (5)
- K44 - Nutrition During LactationDokumen26 halamanK44 - Nutrition During Lactationbilli lisanuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Class 2Dokumen10 halamanClass 2rona putriBelum ada peringkat
- Group 1 Guide QDokumen5 halamanGroup 1 Guide QLjae NatinoBelum ada peringkat
- Philosophy - Assignment 4 2Dokumen2 halamanPhilosophy - Assignment 4 2api-489860857Belum ada peringkat
- Complete Skin Examination Is Essential in The Assessment Dermatology PatientsDokumen3 halamanComplete Skin Examination Is Essential in The Assessment Dermatology Patientsseptian88_cahyoBelum ada peringkat
- LaborDokumen8 halamanLaborPrince Calimbo VillaBelum ada peringkat
- Ramilo-Act 123Dokumen4 halamanRamilo-Act 123Jayselle ArvieBelum ada peringkat
- BMC-Pharmacist-22-10-2023-D ANSWERDokumen4 halamanBMC-Pharmacist-22-10-2023-D ANSWERPratyush swarnkarBelum ada peringkat
- NCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.Dokumen1 halamanNCP. Deficient Fluid Volume by Eben D.C.dominoredwing2024100% (1)
- 1.1 Hospital Management - Non-Clinical Support and FacilitiesDokumen6 halaman1.1 Hospital Management - Non-Clinical Support and Facilitiescb_cristianBelum ada peringkat
- Operating Room ManagementDokumen4 halamanOperating Room ManagementJeremy Lyle JabonilloBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review GRADEDDokumen7 halamanLiterature Review GRADEDkeybateBelum ada peringkat
- Iv AnsapDokumen7 halamanIv AnsapromeojrBelum ada peringkat
- Star Health Chennai HospitalDokumen1 halamanStar Health Chennai Hospitalvinodh kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Applying for a doctor position at RSUD Kramat Jati HospitalDokumen7 halamanApplying for a doctor position at RSUD Kramat Jati HospitalRuni ArumndariBelum ada peringkat
- New York State Department of Health: Medicaid Overpayments For Hospital ReadmissionsDokumen19 halamanNew York State Department of Health: Medicaid Overpayments For Hospital ReadmissionsPatricia DillonBelum ada peringkat
- Ida Jean Orlando'S Nursing Process Theory Prepared By:1. Tigist G/Maryam (BSCN) 2. Tiruye Menshaw (BSCN) Adviser: Gebre YitayihDokumen70 halamanIda Jean Orlando'S Nursing Process Theory Prepared By:1. Tigist G/Maryam (BSCN) 2. Tiruye Menshaw (BSCN) Adviser: Gebre YitayihHamza IshtiaqBelum ada peringkat
- 2014 Burn Patient Management - Clinical Practice GuidelinesDokumen70 halaman2014 Burn Patient Management - Clinical Practice Guidelinesd dBelum ada peringkat
- No.5 - Methods-Of-Patient-AssignmentDokumen7 halamanNo.5 - Methods-Of-Patient-AssignmentPawan BatthBelum ada peringkat
- Roleplay FractureDokumen5 halamanRoleplay FractureGanji GakkenBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital Disaster Management: Triage, Response and PreparednessDokumen44 halamanHospital Disaster Management: Triage, Response and PreparednessrizqiBelum ada peringkat
- UNIT 9 (Speak & Listen)Dokumen3 halamanUNIT 9 (Speak & Listen)lephammydungBelum ada peringkat
- Nurs402 Teachingprojectsummary NeuburgDokumen20 halamanNurs402 Teachingprojectsummary Neuburgapi-452041818Belum ada peringkat
- 09.Project-Hospital Management SystemDokumen37 halaman09.Project-Hospital Management Systemzahidrafique0% (1)
- Protocols EMERGENCY MEDICAL 2015 FULL MARYLAND PDFDokumen502 halamanProtocols EMERGENCY MEDICAL 2015 FULL MARYLAND PDFivancamilomariajoseBelum ada peringkat
- Maintenance of Supplies and EquipmentsDokumen11 halamanMaintenance of Supplies and EquipmentsCheranmadevi Padavettan100% (1)