Aquatic Biomes
Diunggah oleh
dacspinlac0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
2K tayangan1 halamanA summary of the interactions between abiotic and biotic components of aquatic (freshwater and marine) biomes.
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniA summary of the interactions between abiotic and biotic components of aquatic (freshwater and marine) biomes.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
2K tayangan1 halamanAquatic Biomes
Diunggah oleh
dacspinlacA summary of the interactions between abiotic and biotic components of aquatic (freshwater and marine) biomes.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 1
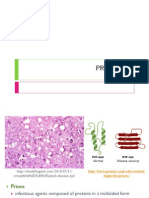
Abiotic and Biotic Factors of Aquatic Biomes
Biome
Freshwater
Abiotic Biotic Interactions
Salinity: < 1-3% Standing water: ponds, lakes isolated species diversity Distance from shoreline: depth, sunlight, temp life zones littoral zone: near shore sunlight photosynthesis species diversity limnetic zone: near-surface open water w/ plankton base of food chain profundal zone: deep water sunlight, temp no photosynthesis, no O2 (only anaerobic organisms live here), species diversity Flowing water: streams, rivers different conditions at different points different adaptations of organisms depth + width species diversity flow O2 species diversity (e.g., catfish, carp) flow sediments light photosynthesis species diversity flow animals w/ hooks, suckers, flattened bodies flow species similar to pond/lake inhabitants Salinity: >3% Distance from shoreline: depth, sunlight, temp life zones intertidal: low/high tide area constantly changing conditions constantly changing communities light + O2 + nutrients highly productive ecosystem pelagic: open ocean producers limited to photic zone remains sink to ocean floor nutrients benthic: ocean floor remains + decomposers nutrients (stuck here) abyssal: deep ocean o temp (3 C) + PH2O + no light species diversity hydrothermal vents w/ chemosynthetic bacteria (use H 2S) Salinity: freshwater < estuarine < marine organisms highly tolerant to salt Organic material deposited by river/stream; depth sunlight highly productive ecosystem spawning & nursing grounds
Marine
Estuarine
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- BIO1 - Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, AnnelidaDokumen15 halamanBIO1 - Platyhelminthes, Nematoda, AnnelidadacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - ArthropodaDokumen19 halamanBIO1 - ArthropodadacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - EchinodermataDokumen22 halamanBIO1 - EchinodermatadacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - MolluscaDokumen22 halamanBIO1 - MolluscadacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - Control of Gene ExpressionDokumen12 halamanBIO3 - Control of Gene ExpressiondacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - MutationsDokumen12 halamanBIO3 - MutationsdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - DNA TechnologyDokumen9 halamanBIO3 - DNA TechnologydacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - Ferns and Their RelativesDokumen9 halamanBIO1 - Ferns and Their Relativesdacspinlac0% (1)
- BIO1 - Plantlike ProtistsDokumen31 halamanBIO1 - Plantlike ProtistsdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - Handout On Lac OperonDokumen1 halamanBIO3 - Handout On Lac OperondacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - Transcription and TranslationDokumen6 halamanBIO3 - Transcription and TranslationdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - Fungi and Funguslike ProtistsDokumen21 halamanBIO1 - Fungi and Funguslike ProtistsdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - ProtozoaDokumen8 halamanBIO1 - ProtozoadacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - Gymno and Angio Life CyclesDokumen4 halamanBIO1 - Gymno and Angio Life CyclesdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - DNA ReplicationDokumen9 halamanBIO3 - DNA ReplicationdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - DNA, Search For Genetic MaterialDokumen12 halamanBIO3 - DNA, Search For Genetic MaterialdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - Nonvascular PlantsDokumen18 halamanBIO1 - Nonvascular PlantsdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - Multicellular Algae Part 2Dokumen13 halamanBIO1 - Multicellular Algae Part 2dacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - EnzymesDokumen11 halamanBIO3 - EnzymesdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- As Discussed in Campbell Biology, 9 Ed. and in Essentials of Genetics (Klug and Cummings), 3 EdDokumen20 halamanAs Discussed in Campbell Biology, 9 Ed. and in Essentials of Genetics (Klug and Cummings), 3 EddacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO1 - Multicellular Algae Part 1Dokumen34 halamanBIO1 - Multicellular Algae Part 1dacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- BIO3 - ProteinsDokumen17 halamanBIO3 - ProteinsdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- Genes and ChromosomesDokumen7 halamanGenes and ChromosomesdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- Omnis Cellula e CellulaDokumen9 halamanOmnis Cellula e CelluladacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- Origins of Evolutionary Thought - Miller and LevineDokumen1 halamanOrigins of Evolutionary Thought - Miller and LevinedacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- Incomplete Dominance, Codominance, Multiple Alleles, Polygenic InheritanceDokumen7 halamanIncomplete Dominance, Codominance, Multiple Alleles, Polygenic InheritancedacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- As Discussed in Campbell Biology, 9 EdDokumen5 halamanAs Discussed in Campbell Biology, 9 Eddacspinlac0% (1)
- Meiosis, Gametogenesis, & Errors in Cell DivisionDokumen17 halamanMeiosis, Gametogenesis, & Errors in Cell DivisiondacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Cycle Control and CancerDokumen13 halamanCell Cycle Control and CancerdacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- HW: Keywords For Cell ReproductionDokumen1 halamanHW: Keywords For Cell ReproductiondacspinlacBelum ada peringkat
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)