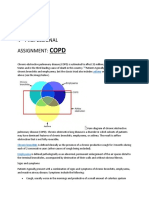
Why We Investigate Asthma Patients
Diunggah oleh
ustaztDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Why We Investigate Asthma Patients
Diunggah oleh
ustaztHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Why we investigate asthma patients?
Ads For classification and assessment of severity For diagnosis of concomitant illness For exclusion of other causes of cough, wheeze dyspnoea or chest tightness
What are the investigations for asthma?
We should do four basic investigations of all patients.
1. Blood for TC, DC, ESR, Hb% and : Total circulating Eosinophil (TCE) (where eosinophil count > 20%).
To exclude Tropical pulmonary eosinophilia
2. Sputum for AFB and Eosinophil :
To exclude Pulmonary tuberculosis & for the diagnostic evidence of Pulmonary eosinophilia/Asthma.
3. Chest X-ray P/A view :
To exclude Pulmonary tuberculosis, Consolidation, Pneumothorax, Pulmonary oe FB in airway etc.
4. Pulmonary Function Tests (P.F.T) :
Spirometric analysis to differentiate obstructive from restrictive disorders and asth COPD.
After 40 years of age or in suspected cases we should also advise: 5. Blood glucose to exclude Diabetes mellitus. 6. ECG/Echocardiography to exclude cardiac diseases. CFT/IFAT for filaria is suggestive but not confirmatory for the diagnosis of tropical pulmonary eosinophilia. What other concomitant illnesses of an asthma patient should be investigated? The following problems, which may be present in association with asthma, should be investigated properly.
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7.
Atopic dermatitis (Eczema) Allergic rhinoconjunctivitis Chronic bronchitis or COPD Cor-pulmonale Diabetes mellitus Hypertension Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)
Spirometry Spirometry is a method of assessing lung function by measuring the volume of air that the patient is able to expel from the lungs after a maximal inspiration. It is a reliable method of differentiating between obstructive airway disorders (e.g. COPD, Asthma) and restrictive diseases (e.g. ILD). Spirometry can also be used to determine the severity of COPD. This is important because the severity of COPD can not be predicted simply from the clinical signs and symptoms. Spirometry gives 3 important measures: FEV1: The volume of air that the patient is able to exhale in the first-second of forced expiration. FVC: The total volume of air that the patient can forcibly exhale in one breath. FEV1/FVC: The ratio of FEV1 to FVC expressed as a percentage. Values of FEV1 and FVC are expressed as a percentage of predicted normal for a person of the same sex, age and height. Slowly progressive respiratory symptoms in a middle aged and elderly smoker are likely to indicate COPD. However, such patients may also have asthma. Patients whose symptoms started before the age of 40 years are more likely to be asthmatic, particularly if they are non-smokers with symptoms that vary in severity. Serial peak flow monitoring, looking for diurnal variation of greater than 20%, may help to differentiate these conditions. Alternatively bronchodilator reversibility tests can be used. A change in FEV1, that is, both a >12% increase and >200 ml over pre-bronchodilator levels indicates positive reversibility test. COPD patients with smaller changes are likely to benefit from bronchodilator therapy symptomatically. Spirometry indicates the presence of an abnormality if any of the following are recorded: - FEV1Obstructive disorder shows : - FEV1 reduced (Restrictive disorder shows: - FEV1 reduced (<80% of predicted value) - FVC reduced (<80% of predicted value) - FEV1/FVC ratio normal (>70%) Broncho- Provocation test:
Fall of FEV1 >20% after inhalation of methacholine or hypertonic saline is used for diagnosis of hyper-responsiveness of airways in susceptible patients with normal spirometry. Susceptible patients are: (i) Patient with cough variant asthma, (ii) Mild intermittent asthma, (iii) Chronic Bronchitis. Exercise Challenge test: Fall of FEV1 or PEFR >15% after vigorous exercise indicates Exercise Induced Asthma. The fall starts at 5 to 10 minutes after exercise and peaks at 20 to 30 minutes and then resolves. See Also: Definition of Asthma Etiology of Asthma Classification of Asthma Diagnosis of Asthma Medicines of Asthma Further Reading:
Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America: http://www.aafa.org/ American Asthma Foundation: http://www.americanasthmafoundation.org/ Asthma, UK: http://www.asthma.org.uk/all_about_asthma/index.html
Topics: Kids and Teenage Health Aging and Seniors Disease and Treatment
Comments Post new comment
Top of Form
Subject:
Type the two words:
Save
Preview
Bottom of Form
Similar Topics
Definition of Asthma
Why do we define asthma? We define asthma to identify the disease correctly and to differentiate it from other diseases. To fulfill this
Etiology of Asthma
What Causes Asthma Episodes? The exact etiology or causes of asthma is still unknown. The airways of the asthmatics are found to be
Classification of Asthma
Why do we classify asthma? We classify asthma for the purpose of precise and efficient management. Aim of our management is not merely
Diagnosis of Asthma
What are the Diagnostic Criteria of Asthma? There are four diagnostic criteria of asthma: 1. Cardinal features of asthma Paroxysmal
Medicines for Asthma
What are the medicines used to treat asthma? There are basically three kinds of medicines: Relievers (Bronchodilators) are medicines
Chicken Pox can be Prevented
Doctors in a seminar opined in favour of getting jab of Chicken Pox vaccine to avoid this infectious disease for those who are not yet
Drug Addiction and Its Remedies
In recent years Drug Addiction has significantly increased in Bangladesh. This agent of human devastation has spread its tentacles
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Spirometry InterpretationDokumen4 halamanSpirometry InterpretationSSBelum ada peringkat
- Spirometry (PPT & Words) 1Dokumen5 halamanSpirometry (PPT & Words) 1Fluffyyy BabyyyBelum ada peringkat
- The PFT LexiconDokumen3 halamanThe PFT Lexiconjmel67Belum ada peringkat
- PBL 1 RSDokumen7 halamanPBL 1 RSmarams8bBelum ada peringkat
- History and Physical Exam For COPDDokumen10 halamanHistory and Physical Exam For COPDCathy GuerreroBelum ada peringkat
- lr5 - ILHAASHINI (012021090323) - Lab 5 DoneDokumen7 halamanlr5 - ILHAASHINI (012021090323) - Lab 5 DoneIlhaashini krishnanBelum ada peringkat
- Key Points on Diagnosing and Assessing Severity of COPDDokumen12 halamanKey Points on Diagnosing and Assessing Severity of COPDfallenczarBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function TestsDokumen16 halamanPulmonary Function TestsRashed ShatnawiBelum ada peringkat
- Peak Flow MeterDokumen3 halamanPeak Flow MeterNicole PramonoBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Rowshne Jahan Spirometry Presentation-1Dokumen40 halamanDr. Rowshne Jahan Spirometry Presentation-1Shahadat Hossain BabuBelum ada peringkat
- Spiro Me Try Cheat Sheet 09Dokumen2 halamanSpiro Me Try Cheat Sheet 09Yudha Perwira PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma Copd OverlapDokumen16 halamanAsthma Copd OverlapMaryam BurhanuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma, COPD and Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome (GINA 2014)Dokumen16 halamanAsthma, COPD and Asthma-COPD Overlap Syndrome (GINA 2014)dinh son myBelum ada peringkat
- Chronic Illness Module OutcomesDokumen12 halamanChronic Illness Module OutcomesOmar IzzoBelum ada peringkat
- Copd by Musa Afridi 17-029Dokumen6 halamanCopd by Musa Afridi 17-029Essa AfridiBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of Respiratory FunctionDokumen1 halamanAssessment of Respiratory FunctionRoderick AgbuyaBelum ada peringkat
- Merged 37Dokumen21 halamanMerged 37abdulkreemsalem4Belum ada peringkat
- COPD - Salmorin & SatairapanDokumen13 halamanCOPD - Salmorin & SatairapanMichelle SatairapanBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function Testing1Dokumen51 halamanPulmonary Function Testing1kusaarBelum ada peringkat
- ER Treatment for Asthmatic PatientDokumen4 halamanER Treatment for Asthmatic PatientEver Green100% (2)
- Copd Case StudyDokumen6 halamanCopd Case StudyChrischia Yvonne GualbertoBelum ada peringkat
- Bed Side Assessment of Adult Patient GuideDokumen60 halamanBed Side Assessment of Adult Patient GuideDheeraj RaiBelum ada peringkat
- COPD Guide: Diagnosis, Assessment, TreatmentDokumen34 halamanCOPD Guide: Diagnosis, Assessment, TreatmentFa9v 1Belum ada peringkat
- Pulmonology LastDokumen82 halamanPulmonology LastAbdallah K. Ramadan100% (1)
- Lesson 3 Responses To Altered Ventilatory FunctionDokumen136 halamanLesson 3 Responses To Altered Ventilatory FunctionMonasque PamelaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Presentation On Copd - Shaik NazmaDokumen29 halamanCase Presentation On Copd - Shaik NazmaDeepikaBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Presentation On Chronic Obstructive Disease (COPD)Dokumen18 halamanA Case Presentation On Chronic Obstructive Disease (COPD)Harvey T. Dato-onBelum ada peringkat
- COPD Student Lec DR Atef Alkarn 6-2022Dokumen42 halamanCOPD Student Lec DR Atef Alkarn 6-2022mohamed albnaBelum ada peringkat
- Respiratory Function TestDokumen7 halamanRespiratory Function TestMarivic DianoBelum ada peringkat
- ARDSDokumen57 halamanARDSnesjohnvBelum ada peringkat
- Dyspnea and Cough DiagnosisDokumen5 halamanDyspnea and Cough DiagnosisJayson Joseph AngloBelum ada peringkat
- 01 05 05 Occs10080)Dokumen7 halaman01 05 05 Occs10080)IJIRAE- International Journal of Innovative Research in Advanced EngineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function Testing: Camilla Hollen, MMS, PA-C PA 530Dokumen49 halamanPulmonary Function Testing: Camilla Hollen, MMS, PA-C PA 530KatherynSotoBelum ada peringkat
- PFT Tests Measure Lung FunctionDokumen19 halamanPFT Tests Measure Lung FunctionAshenafi BerhanuBelum ada peringkat
- Zhunussova DDokumen18 halamanZhunussova DAnanth Sai BadetiBelum ada peringkat
- Evaluation Checklist Case 7 Bronchial AsthmaDokumen7 halamanEvaluation Checklist Case 7 Bronchial AsthmaChristian MendiolaBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function TestsDokumen29 halamanPulmonary Function TestsOrion JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma: Chronic Inflammation of The Airways. The Hyper-Responsive Airways Typical of AsthmaDokumen7 halamanAsthma: Chronic Inflammation of The Airways. The Hyper-Responsive Airways Typical of AsthmaRaj PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function TestDokumen7 halamanPulmonary Function TestGhada HusseinBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma-COPD Overlap SyndromeDokumen38 halamanAsthma-COPD Overlap SyndromeSanjay NavaleBelum ada peringkat
- Annals AsthmaDokumen16 halamanAnnals AsthmaewbBelum ada peringkat
- Status Asthmaticus: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokumen4 halamanStatus Asthmaticus: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentJez Dominic LlenesBelum ada peringkat
- Best Practice in The Use of SpirometryDokumen6 halamanBest Practice in The Use of SpirometryDennis CobbBelum ada peringkat
- Bronchial Asthma: Suryadi Susanto FK Ukrida Department of PediatricsDokumen84 halamanBronchial Asthma: Suryadi Susanto FK Ukrida Department of PediatricsfaerellaBelum ada peringkat
- COPD Dr. Omnia SaeedDokumen23 halamanCOPD Dr. Omnia SaeedOmnia SaeedBelum ada peringkat
- Description: Back To TopDokumen21 halamanDescription: Back To Toprovergzz88Belum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function Tests-Nursing MasenoDokumen43 halamanPulmonary Function Tests-Nursing Masenoakoeljames8543Belum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Hypertension GuideDokumen9 halamanPulmonary Hypertension GuideChryst Louise SaavedraBelum ada peringkat
- Week 4 - Ms1 Course Task - Cu 4 - RoveroDokumen2 halamanWeek 4 - Ms1 Course Task - Cu 4 - RoveroJohnmarkLorenzanaRoveroBelum ada peringkat
- Measurements.: Spirometry Is The Name of The Test, Whilst A Spirometer Is The Device That Is Used To Make TheDokumen7 halamanMeasurements.: Spirometry Is The Name of The Test, Whilst A Spirometer Is The Device That Is Used To Make TheDebasis SahooBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function TestsDokumen24 halamanPulmonary Function TestsSachin KonkaniBelum ada peringkat
- BBB 1 - Pulmonary Function Tests InterpretationDokumen14 halamanBBB 1 - Pulmonary Function Tests InterpretationArhanBelum ada peringkat
- AfsDokumen4 halamanAfsRafli AfriansyahBelum ada peringkat
- COPD Risk Factors & Spirometry StagingDokumen38 halamanCOPD Risk Factors & Spirometry StagingKudingLimMingYaoBelum ada peringkat
- CopdDokumen47 halamanCopdNingshesil Ny HermantBelum ada peringkat
- 5-Pulmonary Function TestsDokumen35 halaman5-Pulmonary Function TestsDoha JKBelum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary Function Testing in Asthma - UpToDateDokumen17 halamanPulmonary Function Testing in Asthma - UpToDateJuan ArangurenBelum ada peringkat
- Onbrez June 2014Dokumen32 halamanOnbrez June 2014NateStephBarnardBelum ada peringkat
- Ahmed Bahri Omar 1Dokumen7 halamanAhmed Bahri Omar 1l3gsdBelum ada peringkat
- Planning Values of Housing Projects in Gaza StripDokumen38 halamanPlanning Values of Housing Projects in Gaza Stripali alnufirBelum ada peringkat
- Specific Gravity by Pycnometer MethodDokumen4 halamanSpecific Gravity by Pycnometer Methodأحمد جاسم محمدBelum ada peringkat
- Preparation Total Consecration PDFDokumen872 halamanPreparation Total Consecration PDFgbarcelonBelum ada peringkat
- Jurisidiction of MeTC, MTC, MCTC, MuTCDokumen3 halamanJurisidiction of MeTC, MTC, MCTC, MuTCKENEDY FLORESBelum ada peringkat
- 00 HR Analytics 2018Dokumen40 halaman00 HR Analytics 2018Aalya ModiBelum ada peringkat
- Reduction in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Hypertensive Patients Treated With Enalapril, Losartan or The Combination of Enalapril and LosartanDokumen7 halamanReduction in Left Ventricular Hypertrophy in Hypertensive Patients Treated With Enalapril, Losartan or The Combination of Enalapril and LosartanDiana De La CruzBelum ada peringkat
- Sheikh Yusuf Al-Qaradawi A Moderate Voice From TheDokumen14 halamanSheikh Yusuf Al-Qaradawi A Moderate Voice From ThedmpmppBelum ada peringkat
- Quieting of TitleDokumen11 halamanQuieting of TitleJONA PHOEBE MANGALINDANBelum ada peringkat
- Determinants of Cash HoldingsDokumen26 halamanDeterminants of Cash Holdingspoushal100% (1)
- Vida 7Dokumen32 halamanVida 7Silvia Rodriguez100% (1)
- Wonderland Staking and Minting Calculator (4,4)Dokumen8 halamanWonderland Staking and Minting Calculator (4,4)Dina Maya0% (4)
- (SAC, BIC, XOR, LAT, AWD) On Some Cryptographic Properties of Rijndael (Yucel)Dokumen12 halaman(SAC, BIC, XOR, LAT, AWD) On Some Cryptographic Properties of Rijndael (Yucel)Alsita Putri IrianaBelum ada peringkat
- Go Int 6 Unit 2 Extension TestDokumen4 halamanGo Int 6 Unit 2 Extension TestMiguel Anabalón TorresBelum ada peringkat
- ALL INDIA NURSING TEST REVIEWDokumen102 halamanALL INDIA NURSING TEST REVIEWDr-Sanjay SinghaniaBelum ada peringkat
- The Philosophy of EmoDokumen2 halamanThe Philosophy of EmoTed RichardsBelum ada peringkat
- Animal BitesDokumen48 halamanAnimal BitesJalouis GabalfinBelum ada peringkat
- Flow Velocities: Line Printed Heading CommentsDokumen4 halamanFlow Velocities: Line Printed Heading Commentssj_scribdBelum ada peringkat
- IvanhoeDokumen17 halamanIvanhoeRob Collins100% (4)
- WFISD Agenda Special SessionDokumen1 halamanWFISD Agenda Special SessionDenise NelsonBelum ada peringkat
- ESL S9 W3 P14-15 Project Challenge Part 2Dokumen27 halamanESL S9 W3 P14-15 Project Challenge Part 2Emma Catherine BurkeBelum ada peringkat
- The Fundamentals of Lighting PDFDokumen20 halamanThe Fundamentals of Lighting PDFVasilis Karageorgiou100% (1)
- Preventive MaintenanceDokumen19 halamanPreventive Maintenancefaizan9970% (1)
- List of TNA MaterialsDokumen166 halamanList of TNA MaterialsRamesh NayakBelum ada peringkat
- DeVry ACCT 505 Final Exam 2Dokumen12 halamanDeVry ACCT 505 Final Exam 2devryfinalexamscomBelum ada peringkat
- 5.5 Inch 24.70 VX54 6625 4000 2 (Landing String)Dokumen2 halaman5.5 Inch 24.70 VX54 6625 4000 2 (Landing String)humberto Nascimento100% (1)
- 2004 Swamee, Prabhata K. Rathie, Pushpa N. - Exact Solutions For Normal Depth ProblemDokumen9 halaman2004 Swamee, Prabhata K. Rathie, Pushpa N. - Exact Solutions For Normal Depth Problemjosue.angelo9459Belum ada peringkat
- Watch Blow Fly Arrang e Sleep Go Cook Clean Hear Cut Give Fall Open See Listen Carry Visit Buy Bring Write Bake Make Sit Play DrawDokumen3 halamanWatch Blow Fly Arrang e Sleep Go Cook Clean Hear Cut Give Fall Open See Listen Carry Visit Buy Bring Write Bake Make Sit Play DrawEmily NytBelum ada peringkat
- Empt Forming Welding Crimping and CuttingDokumen13 halamanEmpt Forming Welding Crimping and CuttingEmil MariusBelum ada peringkat
- Qualys WAS and OWASP Top 10 2017 CoverageDokumen5 halamanQualys WAS and OWASP Top 10 2017 CoverageoobyddBelum ada peringkat