CS Study Material on Networking Essentials
Diunggah oleh
eee007Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CS Study Material on Networking Essentials
Diunggah oleh
eee007Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CSStudyMaterial
+ Skill LearningAcademy
CSStudyMaterial
NetworkingEssentials
Introduction
Anetworkisagroupofsystemsthatareinterconnectedtoallowsharingoffiles orsharingofresources(likeprinters)orforthepurposeofsharingserviceslikeinternet. Objective Thismodulewillfocuson Understandingcomputernetworksanditsimportance. Differentwaysofclassifyingcomputernetworks. TransmissionMedia MediaAccessMethods LANTechnologies
Classificationofcomputernetworks
Network
Basedon Geographical Distance
Basedon functional Relationship
Basedon Topology
LAN
WAN MAN
Bus Hybrid Star Ring Mesh PeertoPeer ClientServer
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
CSStudyMaterial
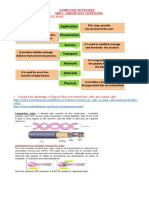
Computernetworkscan beclassifiedonvariouswaysbasedon
GeographicalDistance:Computernetworksmaybeclassifiedaccordingtothescaleor extent of reach of the network as Local Area Network (LAN), Metropolitan Area Network(MAN)andWideAreaNetwork(WAN). Local Area Network (LAN): A network that is limited to a relatively small spatialarea suchasaroom,asingle building,a ship,oranaircraft isrefferedas LAN. Theyaresometimescalled asingle location network.eg.Asmalloffice networkortwo computersisahouseconnectedusingacable. Metropolitan Area Network (MAN): A network that connects two or more Local Area Networks together but does not extend beyond the boundaries of the immediate town, city, or metropolitan area is called as MAN. eg. A branch office connectedtothemainofficeinthesamecity. WideAreaNetwork(WAN): A WAN is adatacommunications networkthat covers a relatively broad geographic area and that often uses transmission facilities providedbycommoncarriers,suchastelephonecompaniesetc.Eg.Internetorabranch officeinIndiaconnectedtoitsCorporateofficeinUnitedStates. Functional Relationship: Based on the relationship that computers share in a network theycanbeclassifedasPeerPeerandClientServerarchitechturesornetworks. PeertoPeer:Apeertopeernetwork(alsocalledasWorkgroupbyMicrosoft)is builtwithouttheuseofacentralserverandeachpeercomputercanshareitsresources withtheothercomputersonthenetworkindependently.Specialsoftwareprotocolssuch as Microsoft NetBEUI and Apples LocalTalk are used for establishing communication acrossPeertoPeernetwork.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
CSStudyMaterial
Advantages
Lowcostasexpensivesoftwareandhardwarearenotrequired. Easytoimplement. Resourcesharingcontrolledbyusers. Noneedofadedicatednetworkadministator.
Disadvantages
Lowlevelofsecurity Heavyloadoncomputersbecauseofresourcesharing. Sizeofnetworklimitedtoapproximately10computers. ClientServer: In ClientServer architechure a centralized computer is used to facilitatethesharingofdataand hardwarewithothercomputersonthe network.These centralcomputersarecalledServersandthecomputersusingtheserverarecalledclients.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
CSStudyMaterial
Advantages Strongcentralsecurity. Centralfilestorage. Resourcesharingcontrolledbyadministrators. Easymanagementoflargenumberofusers.
Disadvantages Costofserverhardwareandsoftware. Dedicated and well trained network administrator is needed to main this typeofarchitecture. Network Topology: Network Topology is defined as the way in which computers are arranged in a network. Computer networks may be classified according to the network topology upon which the network is based, such as Bus network, Star network, Ring network, Meshnetwork,Hybridnetwork,etc.
BusTopology:Abusnetworktopologyisanetworkarchitectureinwhichaset ofclientsareconnectedinalinearfashionviaasharedcommunicationsline(backbone), calledabus.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
CSStudyMaterial
BusTopology
With a bustopology,whenacomputersendsouta signal,the signaltravelsthe cable length in bothdirections fromthesending computer.Whenthe signalreachesthe endofthecablelength,itbouncesbackandreturnsinthedirectionitcamefrom(signal bounce).Signalbounceisaproblem,becauseifanothersignalissentonthecablelength as the same time, the two signals will collide and be destroyed and then must be retransmitted. For this reason, at each end of the cable there is a terminator. The terminator is designed to absorb the signal when the signal reaches the end, preventing signalbounce. Advantages Easytoimplementandextend. Requireslesscablelengthwhencomparedtostartopology. Well suited for temporary or small networks not requiring high speeds (quicksetup). Costeffectivethatothertopologies. Disadvantages Difficulttoadminister/troubleshoot. Scalabilityisverylow. Problemwiththebackbonecableleadstoentirenetworkfailure. Performancedegradesasadditionalcomputersareaddedoronheavy traffic.(Ifmanycomputersareattached,theamountofdataflowing causesthenetworktoslowdown.)
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
CSStudyMaterial StarTopology:Instartopology,allcomputersareconnectedthroughonecentraldevice knownasahuboraswitch.Allthepheripheralnodes(computers)canthuscommunicate with allothersbytransmittingtoandreceivingfrom,thecentralnode(hub/switch)only.
StarTopology
Advantages Scalable,easytosetupandtoexpand. Failureofasinglecableorasinglecomputerdoesnotaffecttheentire network. Easytoaadminister/troubleshoot. Datapacketsaresentquicklyastheydonothavetotravelthroughany unnecessarynodes. Disadvantages Extrahardware(Hub/Switch)required. FailureofHub/Switchleadstoentirenetworkfailure.
Ring Topology: A ring network is a network topology in which each node connectstoexactlytwoothernodes,formingacircularpathwayforsignals:aring.Data travelsinonedirectionfromnodetonode,witheachnodehandlingeverymessage.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
CSStudyMaterial
RingTopology
D
Advantages Signal degeration is low because each workstation is responsible for regeneratingorboostingthesignal. Disadvantages Thebiggestproblemwithringtopologyisthatif onecomputerfailsorthe cablelinkisbrokentheentirenetworkcouldgodown. When there is a cable change or when a workstation is moved in the network, brief disconnection can interrupt or bring down the entire network.
MeshTopology: Ameshtopologyconsistsofanetworkwhereeverydeviceon thenetworkisphysicallyconnectedtoeveryotherdeviceonthenetwork.
MeshTopology
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
CSStudyMaterial
Advantages
FaultTolerance Providesgreatdealofperformanceandreliability. Disadvantages Veryhardtoadministerandmanagebecauseofnumerousconnections. Costlybecauseoftheadditionalcablingandnetworkinterfacestocreate multiplepathwaysbetweeneachsystem.
HybridTopology:Ahybridtopologyisacombinationofanytwoormore networktopologies.ForExample,apopularhybridtopologyisthestarbustopology,in whichanumberofstartopologiesareconnectedbyacentralbustopology. TransmissionMedia
Thefoundationofanynetworkisthetransmissionmediaorthecircuitry usedto interconnectandcarrynetworksignalsbetweensystems.Transmissionmediaprovidethe pathforonecomputertotransferinformationtoanother.Thepurposeoftransmission mediaistotransportarawbitstreamfromonemachinetoanother.
TransmissionMedia
Wired
Wireless
CopperCable
Fibre OpticCable
RadioWaves Infrared
Microwave
Coaxial
TwistedPair
Thicknet
Thinnet STP UTP
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
CSStudyMaterial Wecanclassifytransmissionmediaintotwobroadcategories, WiredMedia. WirelessMedia.
WiredMedia
Themostcommolyusedwiredmediaare Coppercable,whichcarrieselectricalsignals. Fibreopticcable,whichcarriesopticsignals.
Copper Cable: Copper cables uses differences in voltage inorder to transmitt and
receivedata.Thedifferenttypesofcoppercablesusedinnetworkingare Coaxialcables Twistedpaircables.
Coaxialcable:Acoaxialcableconsistsofastiffcopperwireasthecore,surrounded
by an insulating material. The insulator is encased by a mesh of conducting material, wovenasabraidedmesh.Theouterconductoriscoveredinaprotectiveplasticsheath.
Therearetwotypesofcoaxialcablesthicknetandthinnetcoaxialcables. ThinnetCoaxialCables(10Base2):Thinnetreferstocoaxialcablesthat arelesserindiameterandinwhichthethebraidedmeshislooselyoven.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
10
CSStudyMaterial
Thicknet Coaxial Cables (10 Base 5): Thickent refers to cables that are thickerandinwhichthebraidedmeshistightlywoven.
ThicknetversusThinnet
CoaxType Cable Grade Thickness Maximum Distance Transfer Rate Connector
Thinknet
RG58
.25inch
185m
10Mbps
BNC
Thicknet
RG8
.5inch
500m
10Mbps
AUI
Twisted Pair Cables (10 Base T): A twisted pair cable consists of four pairs (eight individual wires), which are twisted one on the top of the other. Each wire is coveredbyauniquecolourcodedplasticsheath,whichallowswirestobedistinguished fromoneanother.Allofthewiresarethenencapsulatedinaplasticsheath.Themaximum distancethattwistedpaircablescancarrysignaleffectivelyisupto100meters.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
11
CSStudyMaterial
Therearetwotypesoftwistedpaircables Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) Cable: STP cabling includes metal shieldingovereachindividualpairofcopperwires.Thistypeofshielding protects cable from external EMI (electromagnetic interference). These cablesareoften usedforTokenringnetworks.
Unsheilded Twisted Pair (UTP) Cable: UTP cables as the name indicatesareunshieldedandlackanadditionalmetalshielding.Basedon thenumberoftwistsperinchUTPcablesarecatetogorisedintodifferent categories. CategoriesofUnshieldedTwistedPair
Type
TransferRate
Use
Category1
1Mbps(Voice)
TelephoneWire
Category2
4Mbps(Data)
LocalTalk
Category3
10Mbps(Data)
Ethernet
Category4
16Mbps(Data)
TokenRing
Category5
100Mbps(Data)
FastEthernet
Category5e
1000Mbps(Data)
GigabitEthernet
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
12
CSStudyMaterial
Connectors used for Twisted pair cables: RJ 11 and RJ 45 are the
connectors used for twisted pair cables.RJ, stands for Registerd Jack implying that the connectorfollowsastandardborrowedfromthetelephoneindustry.RJ11forfourwire telephonecableandRJ45foreightwirenetworkcables.
RJ11andRJ45 WiringScheme CAT 5 UTP cabling usually uses only four wires when sending and receivinginformationonthenetwork.Thefourwiresoftheeigththatareusedarewires 1,2,3and6. When you configurethewire forthesamepinateitherendofthecable,this is knownasastraightthroughcable.Thistypeofcableisusedforconnectingdissimilar devices.Forexample,computerandastandardportinaswitch. Whenyou switchwires1and2withwires3 and6atoneendthenthattypeof cable is called as crossover cable. This type of cable is used for connecting similar devices.Forexample,connectingtwocomputersdirectly.
FibreOpticCables:FibreOpticcablesuseoptical fibresthatcarrydigitaldata signalsintheformofmodulatedpulsesoflight.Anopticalfibreconsistsofanextremely thincylinderofglass,calledthecore,surroundedbyaconcentriclayerofglassknownas thecladding.Therearetwofibrespercableonetotransmitandonetoreceive.Thecore alsocan beanopticalqualityclearplastic,andthecladdingcanbemadeupofagelthat
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
13
CSStudyMaterial
StraightThrough&CrossOverCablePinouts
reflects signals back into the fibre to reduce signal loss. This type of cable can carrysignaluptoandbeyond2Kilometersatahighspeedof1+Gbps.
FiberOptic
Therearetwotypesoffibreopticcables:singlemodefibreandmultimodefibre. Singlemodefibreusesasinglerayoflighttocarrythetransmissionoverlongdistances. Multimodefibreusesmultipleraysoflightsimultaneouslywitheachrayoflightrunning atadifferentreflectionangletocarrythetransmissionovershortdistances. Connectors used for fibreoptic cables are Straight Tip (ST) and Subscriber Connector (SC). Fibreoptic cables are by far the expensive of these cabling methods, and are not desirableforsmallnetworks.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
14
CSStudyMaterial
WirelessMedia
Wirless media makes use of the atmosphere, hence referred to as unbound medium a circuit with no formal boundaries. This types of medium doesnot use any physical connectors between the two devices that are communicating. Transmissions of waves take place in the electromagnetic (EM) spectrum. The carrier frequency of the data is expressedincyclespersecondcalledhertz(Hz).Thethreebroadcategoriesofwireless mediaare: Radio Waves 10 KHz to 1 GHz. The Federal communications Commission (FCC) regulates the assignment of these frequencies. Frequenciesforunregulateduseare: 902928MHz 2.4GHz 5.725.85GHz
Microwave Used to link networks over long distances but the two microwavetowersmusthavealineofsightbetweenthem.Thefrequency isusually46GHzor2123GHz.Speedisoften110Mbps.Thesignal isnormallyencryptedforprivacy.
Infrared Infrared is just below the visible range of light between 100 GHz and 1000 THz. A light emitting diode (LED) or laser is used to transmit the signal. The signal cannot travel through objects and line of sightisamust.
MediaAccessMethods
An access method determines how nodes on a network, place the data/packet on the media. There are three different types of LAN access methodsCSMA/CD, CSMA/CA, TokenPassing.
CarrierSenseMultipleAccessCollisionDetection(CSMA/CD)istheprotocolusedin Ethernetnetworks(IEEE802.3)toensurethatonlyonenetworknodeistransmittingon thenetwork mediaata time.WithCSMA/CD,everyhosthasequalaccesstothemediaif ahostwishestotransmitthedata,itwillsensethemedia(CarrierSense)anddetermine
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
15
CSStudyMaterial
whetherthereisasignalalreadyonthewireifthereis,thehostwillwaittotransmitthe dataif not it transmits the data immediately. The problem with this process is that, if there are two systems on the media that sense the media at the same time to see if the mediaisfree,theywillbothsendthedataoutatthesametime(MultipleAccess)leading tocollisionwhichgeneratesahighvoltagejamsignalmakingallthehostsinthemedia stopsendingthedataforarandomtimeintervalbeforeresendingthedataframethereby preventingacollisionthesecondtime(CollisionDetection).
Collision
Carrier Sense Multiple Access Collision Avoidance (CSMA/CA) is a network contentionprotocolusedpopularly in Wireless networks(IEEE802.11)whichattempts to prevent collisions before they happen. With CSMA/CA, before a host sends data on themediaitwillsensethemediatoseeifthewireisfreeofsignalsoncethechannelis clear,astationsendsasignaltellingallotherstationsnottotransmit,andthensendsthe packet.
TokenPassingisaLANaccessmethodwherea"token"ispassedaroundthenodesina roundrobin fashion that authorizes the node to communicate. Here only the system whichhasthe"token"cancommunicate.Thetokenisacontrolmechanismwhichgives authority tothe system to communicate or use the resources of that network. Once the communicationisover,thetokenispassedtothenextcandidateinasequentialmanner. Forexample,ifWorkstation1wantstosenddataonthewire,itwouldwaitforthetoken, whichiscirclinginthenetworkmillionsoftimespersecond.Oncethetokenhasreached theWorkstation1,itwouldtakethetokenoffthenetwork,pakageitwithdataandlabel itwiththesourceaddressanddestinationaddressandpassessitontothenext
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
16
CSStudyMaterial
CSMA/CA
workstation in the network. All systems will look atthe token, but will not process it sinceitisnotdestinedforthem.However,thesystemthatistheintendeddestinationwill takethedataandpasstheemptytokentothenextcomputerinthesequence.Thisaccess methodisdeployedinTokenringnetworks(IEEE802.5).
LANTechnologies
Each computer in a LAN can effectively send and receive any information addressedtoit.Thisinformationisintheformofdata'packets'.Thestandardsfollowed
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
17
CSStudyMaterial
toregularizethetransmissionofpackets,arecalledLANstandards.TherearemanyLAN standardssuchasEthernet,TokenRingandFDDI.UsuallyLANstandardsdifferdueto theirmediaaccesstechnologyandthephysical transmissionmedium.
Ethernet
Thisisthemostpopularnetworkarchitectureforlocalarenetworks(LAN).Ethernetuses CarrierSenseMultipleAccesswithCollisionDetection(CSMA/CD)protocoltocontrol access to network.Ethernet specifications define the function thatoccur atthe physical and datalink layer of the OSI reference model and package data into frames for transmissiononthewire.Itisavailableinthreespeeds: 10MbpswhichiscalledEthernet IEEE802.3 100MbpswhichisFastEthernet IEEE802.3u 1000Mbpsor1GbpswhichiscalledGigabitEthernet IEEE802.3ab
TokenRing(IEEE802.5)
Token ring is a LAN technology that was developed by IBM. This is a 4Mbps or 16 Mbps tokenpassing method, operating in a ring topology. Devices on a Token Ring networkgetaccesstothemediathroughtokenpassing.
FDDI(FiberDistributedDataInterface)
Its a highspeed networking technology used mainly for campus backbones. FDDI provides data speed at 100Mbps which is faster than Token Ring and Ethernet LANs. FDDIcomprisetwoindependent,counterrotatingrings:aprimaryringandasecondary ring.Dataflowsinoppositedirectionsontherings.Thecounterrotatingringarchitecture preventsdatalossintheeventofalinkfailure,anodefailure,orthefailureofboththe primary and secondary links between any two nodes. This technology is usually implementedforabackbonenetwork.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
18
CSStudyMaterial
References
Network+ GeneE.Clarke NetworkingEssentialsJohnNash EncyclopediaofNetworkingMitchTullochandIngridTulloch CCNAStudyGuideToddLammle www.microsoft.com/technet www.firewall.cx
Review
Networkreferstotheinterconnectionofcomputersornetworkingdevicesforthe purposeoffilesharingandresourcesharing. Networks can be classified based on geographical distance as LAN, MAN and WANbasedonfunctionalrelationshipaspeerpeerandclientserverbasedon topologyasbus,star, ring,meshandhybridnetworks. Transmissionmediaprovidesthepathforonecomputertotransferinformationto another. This can either be a wired or a wireless medium. Wired mdium uses cables copper cables or fibre optic, whereas the wireless uses Radio waves or infraredormicrowaveradiationinordertosendandreceivedata. Mediaaccessmethods:CSMA/CD(IEEE802.3),CSMA/CA(IEEE802.11)and TokenPassing(IEEE802.5). LANaccessmethods: Ethernet,TokenRingandFDDI.
ReviewQuestions
1. Acompanyhasoffices in Chennaiand Bangalore.Bothnetworksareconnected to allow the two locations to communicate. This is considered as what type of network? a. LAN b. CAN c. MAN d. WAN
2.Whichnetworktopologyrequirestheuseofterminators?
3.Thedistancelimitationof10Base2is_________meters.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
19
CSStudyMaterial
4. ____________cablesendsthesignalaspulsesoflightthroughaglasscore?
5. WhichnetworkarchitectureisdefinedastheIEEE802.3standard?
6. Nametheconnectorsusedforconnectingtwistedpaircables?
7. Whattypeofcableisusedforconnectingacomputerwithanothercomputer?
8. ExplainhownodesinanEthernetnetworkdetectcollision?
9. Whataretheradiofrequenciesthatarepreferredforwirelesstransmission?
10. HubandSwitcharedevicesthatworkin__________topology.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
20
CSStudyMaterial
LAB
1. Fromthegivencablesidentifythefollowingandalsonotedownyourobservation intheformofadiagram.
a. StraightThroughCable
b. CrossOverCable
c. Telephonecable
d. CoaxialCable
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
21
CSStudyMaterial
2. Fromthegivenconnectorsidentifythefollowingandnotedownyourobservation informofadiagram.Alsomentionthetypeofcableforwhichitcabeused.
a. RJ11
b. RJ45
c. BNC
d. AUI
ELO(ExpectedLearningOutcome)
Networkanditsimportance. Differentwaysofclassifyingnetworks. Basicunderstandingofthedifferentnetworktopologies. Know and appreciate the different types of media, along with their advantages,disadvantagesandtheirconnectors. In depth understanding of the different media access methods, like, CSMA/CD,CSMA/CAandTokenPassing. AwarenessaboutthedifferentLANtechnologies.
+ Skill LearningAcademy
Notes
22
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- PC Hardware and NetworkingDokumen93 halamanPC Hardware and NetworkingPrince DeuelBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3Dokumen15 halamanLesson 3Kean Rafael MarianoBelum ada peringkat
- A Computer NetworkDokumen11 halamanA Computer NetworkBridget DindiBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 Networking Fundamentals RevisedDokumen34 halamanLecture 1 Networking Fundamentals RevisedLouis RuhashaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Networks 1Dokumen18 halamanComputer Networks 1Edwin NfehBelum ada peringkat
- DCN NOTES For COURSE FILEDokumen13 halamanDCN NOTES For COURSE FILEÃmît TíwârìBelum ada peringkat
- Computer NetworkingDokumen26 halamanComputer Networkingprashanth100% (2)
- Lecture 2Dokumen27 halamanLecture 2Mstafa MhamadBelum ada peringkat
- 12 IpDokumen9 halaman12 IpGoogle DoodleBelum ada peringkat
- Ch1 - Introduction To Data CommunicationDokumen60 halamanCh1 - Introduction To Data Communicationit89Belum ada peringkat
- CN Unit 1Dokumen26 halamanCN Unit 1vijayBelum ada peringkat
- NC Sem 4Dokumen8 halamanNC Sem 4divyasharmade98Belum ada peringkat
- Administer Network HardwareDokumen62 halamanAdminister Network HardwareMintesnot AdeBelum ada peringkat
- CDCDokumen9 halamanCDCMelvin P. FiguraBelum ada peringkat
- INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeDokumen6 halamanINTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER NETWORK Cyber CrimeAkriti SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1-1Dokumen43 halamanLecture 1-1joeh angeloBelum ada peringkat
- Set-Up Computer Networks Install Network Cables Learning Outcome 01: Installing Network Cables Assessment CriteriaDokumen12 halamanSet-Up Computer Networks Install Network Cables Learning Outcome 01: Installing Network Cables Assessment CriteriaSheena FondavillaBelum ada peringkat
- Practice WordDokumen25 halamanPractice WordDasale DaposBelum ada peringkat
- COMPUTER NETWORK Basic ConceptsDokumen16 halamanCOMPUTER NETWORK Basic ConceptsaarshcomputerBelum ada peringkat
- Basic NetworksDokumen14 halamanBasic NetworksGilgamesh berserkerBelum ada peringkat
- Question Bank - CN SolvedDokumen27 halamanQuestion Bank - CN SolvedThe CreatorsBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Network LAN MAN WANDokumen52 halamanComputer Network LAN MAN WANmushikhan2024Belum ada peringkat
- Networking Basics GuideDokumen59 halamanNetworking Basics GuideS M Shamim শামীমBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Networking Class XII Introduction/TITLEDokumen47 halamanComputer Networking Class XII Introduction/TITLESanjyoti SinghBelum ada peringkat
- A Computer Network Is A Collection of Interconnected Computers and Other Devices Which Are Able To Communicate With Each OtherDokumen3 halamanA Computer Network Is A Collection of Interconnected Computers and Other Devices Which Are Able To Communicate With Each OtherGagan Deep SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Computer NetworkDokumen58 halamanComputer Networkshivang.goyal02Belum ada peringkat
- Oho MajeDokumen36 halamanOho MajeyjadarahaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Network and TopologyDokumen23 halamanComputer Network and TopologySarthak MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 8 second term noteDokumen21 halamanGrade 8 second term noteThiseni De SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Administrating Network and Hardware Peripherals LO 3Dokumen26 halamanAdministrating Network and Hardware Peripherals LO 3abebawBelum ada peringkat
- Nguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 1 NetworkingDokumen13 halamanNguyễn Quốc An (BKC18348) - Assignment 1 NetworkingKatonguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Computer NetworkDokumen351 halamanComputer NetworkRanjan Saini100% (1)
- 5 GTU Computer Network Mid Sem Exam PaperDokumen14 halaman5 GTU Computer Network Mid Sem Exam PaperNickHenryBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of NetworksDokumen66 halamanBasics of NetworksBibin Jose100% (1)
- Data Communication and Computer Networking: ContentDokumen42 halamanData Communication and Computer Networking: ContentMubaarak NuurBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Networks: A Guide to LAN, MAN, WAN Topologies & ComponentsDokumen18 halamanComputer Networks: A Guide to LAN, MAN, WAN Topologies & ComponentsTuhina MistryBelum ada peringkat
- Important Questions For MID I CNDokumen14 halamanImportant Questions For MID I CN20H51A0540-NAKKA SREEKAR B.Tech CSE (2020-24)Belum ada peringkat
- Notes On Computer Networks Unit1Dokumen14 halamanNotes On Computer Networks Unit1Rohit Chaudhary100% (4)
- ESSENTIAL NETWORK COMPONENTSDokumen41 halamanESSENTIAL NETWORK COMPONENTSPrashanth KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Network Topologies, Protocols and StandardsDokumen37 halamanNetwork Topologies, Protocols and Standardsnarasimharao P.V.Belum ada peringkat
- Review of Network Concepts: Packets, Frames and Error DetectionDokumen15 halamanReview of Network Concepts: Packets, Frames and Error Detectiontuniya4Belum ada peringkat
- Discuss The Benefits and Constraints of Different Network Types and StandardsDokumen31 halamanDiscuss The Benefits and Constraints of Different Network Types and StandardsNguyen Manh TaiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1: Introduction To NetworkingDokumen12 halamanModule 1: Introduction To NetworkingKihxan Poi Alonzo PaduaBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Network SeminarDokumen32 halamanComputer Network SeminarRaveena GunreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Networking: Two Types of Networking ConfigurationDokumen8 halamanNetworking: Two Types of Networking ConfigurationEdajBass AmadeoBelum ada peringkat
- Comminication 2Dokumen54 halamanComminication 2Abinet AlemuBelum ada peringkat
- Computer NetworksDokumen21 halamanComputer NetworksJOYS NANCTBelum ada peringkat
- NetworkDokumen57 halamanNetwork.BrWa.Belum ada peringkat
- BASIC IT SKILLS FOR NETWORKING FUNDAMENTALSDokumen38 halamanBASIC IT SKILLS FOR NETWORKING FUNDAMENTALSZudjian WarriorBelum ada peringkat
- NetworkingDokumen7 halamanNetworkingVikash JhunjhunwallaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 13Dokumen11 halamanUnit 13Luis Norbert SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Computer TopologyDokumen14 halamanComputer TopologytamnumakamseuBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Networks and Data Communication: Definition of Terms I) NetworkDokumen9 halamanComputer Networks and Data Communication: Definition of Terms I) NetworkJamesBelum ada peringkat
- Intro to Computer Networking ConceptsDokumen10 halamanIntro to Computer Networking ConceptsMehari KirosBelum ada peringkat
- Data Communication & NetworksDokumen35 halamanData Communication & NetworksAnonymous oP2FCuffBelum ada peringkat
- Administrate Net Work and Hard WarwDokumen19 halamanAdministrate Net Work and Hard WarwAbdissaTadeseBelum ada peringkat
- COMPUTER NETWORKING INTRODUCTIONDokumen33 halamanCOMPUTER NETWORKING INTRODUCTIONApeh Usman IsahBelum ada peringkat
- Networking ConceptDokumen81 halamanNetworking ConceptMaghairBelum ada peringkat
- Course Contents: Data Communications Grade Prof. Dr. Hassan H. Soliman Dr. Mostafa ElgayarDokumen11 halamanCourse Contents: Data Communications Grade Prof. Dr. Hassan H. Soliman Dr. Mostafa Elgayarsaher waleedBelum ada peringkat
- Configure D-Link DRO-250i RouterDokumen8 halamanConfigure D-Link DRO-250i RouterbgrdscmmcmBelum ada peringkat
- 14 Performance Analysis of Wired and Wireless LANDokumen5 halaman14 Performance Analysis of Wired and Wireless LANSigula Galuh0% (1)
- 01 - Quick Installation Guide (Windows)Dokumen32 halaman01 - Quick Installation Guide (Windows)Sri Atman jiBelum ada peringkat
- Anton Paar Manual PDFDokumen34 halamanAnton Paar Manual PDFSadegh SoltaniBelum ada peringkat
- Ajayi, Tunde Oluwagbemisola: Professional SummaryDokumen3 halamanAjayi, Tunde Oluwagbemisola: Professional SummaryAjayi oluwagbemisolaBelum ada peringkat
- Ethernet: © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Public ITE I Chapter 6Dokumen43 halamanEthernet: © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Public ITE I Chapter 6Mohamed Taher MarnaouiBelum ada peringkat
- 7.VA1-YEA-00100-I-I1-DCD-0110 - Rev DDokumen10 halaman7.VA1-YEA-00100-I-I1-DCD-0110 - Rev DKevin NgoBelum ada peringkat
- Internetworking Technology HandbookDokumen8 halamanInternetworking Technology HandbookL3nt0Belum ada peringkat
- Autometric Manual x5 PDFDokumen97 halamanAutometric Manual x5 PDFandrea772Belum ada peringkat
- Computer Networks: ReferencesDokumen169 halamanComputer Networks: ReferencesbalsamBelum ada peringkat
- Network Basics: Protocols, Topologies, and ConceptsDokumen76 halamanNetwork Basics: Protocols, Topologies, and ConceptsAbdulrahman AltrifiyBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Fundamentals NotesDokumen17 halamanComputer Fundamentals Notesjineshsurya75% (4)
- Networkingsem 32 This Assignment Talks About Networking and Equipment Used When Designing A NetworkDokumen86 halamanNetworkingsem 32 This Assignment Talks About Networking and Equipment Used When Designing A NetworkNgo Hoang Luyen (FGW HCM)Belum ada peringkat
- Network Operating System Lecture NotesDokumen21 halamanNetwork Operating System Lecture NotesPradeep BediBelum ada peringkat
- Huawei B260aDokumen36 halamanHuawei B260aeugen_2409100% (1)
- 7.3.7 Lab - View The Switch Mac Address TableDokumen4 halaman7.3.7 Lab - View The Switch Mac Address TableJad Abou ZeidBelum ada peringkat
- CN Lab Experiment1Dokumen5 halamanCN Lab Experiment1Srinivasulu ThiruveedulaBelum ada peringkat
- Growth of Lan TechnologyDokumen5 halamanGrowth of Lan TechnologyMuhammad hamzaBelum ada peringkat
- Net 101 Study Guide Module 1 1Dokumen5 halamanNet 101 Study Guide Module 1 1Cjay AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Aug 037 0 en Remote Access For Siemens s7 300400 PlcsDokumen57 halamanAug 037 0 en Remote Access For Siemens s7 300400 PlcsWil VargasBelum ada peringkat
- NetwerkDokumen2 halamanNetwerkIvan John SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Network AVADokumen20 halamanNetwork AVAyusairriBelum ada peringkat
- 787 Oral NotesDokumen55 halaman787 Oral Notesprasadktnn80% (5)
- 25 KV Traction SCADA - SPECIFICATION PDFDokumen48 halaman25 KV Traction SCADA - SPECIFICATION PDFJv RaoBelum ada peringkat
- BN68-09300D-01 Qrq900a XH L16 181008.0Dokumen356 halamanBN68-09300D-01 Qrq900a XH L16 181008.0Tsamis IoannisBelum ada peringkat
- AC-ASP 8000 Access Control System Setup GuideDokumen63 halamanAC-ASP 8000 Access Control System Setup GuideBryan BayacaBelum ada peringkat
- HG 1500 Gateway Card Data SheetDokumen6 halamanHG 1500 Gateway Card Data SheetRicardo MantoanBelum ada peringkat
- Network Assignment 2Dokumen15 halamanNetwork Assignment 2Philip BlegeBelum ada peringkat
- Pepwave Max Surf v6.3.1 User ManualDokumen218 halamanPepwave Max Surf v6.3.1 User ManualloneislandBelum ada peringkat
- How to use your WiFi ADSL Modem as a Wireless Access PointDokumen6 halamanHow to use your WiFi ADSL Modem as a Wireless Access PointKrishnamoorthy VijayalakshmiBelum ada peringkat