Bio 5
Diunggah oleh
dnjsgudDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Bio 5
Diunggah oleh
dnjsgudHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
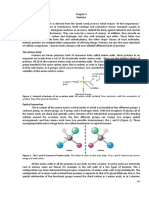
Amino Acids - are the basic units from which proteins are made.
- Plants can manufacture all the amino acids they require from simpler molecules , but animals obtain a certain number of ready-made amino acids (called essentia l amino acids) from their diet. - Amino acids can combine to form peptide chains in condensation reaction. the r everse reaction, which breaks up peptide chains uses water and is called hydroly sis. - Structure of Amino acids: there are over 150 amino acids found in cells, but o nly 20 occur commonly in proteins - the remaining, non-protein amino acids have specialized roles as intermediates in metabolic reactions, or as neurotransmitters and hormones. - the only difference between the different types lies with the "R" group in the general formula. - this group is variable, which means that it is different in each kind of amino acid. - carboxyl group makes the molecule behave like a weak acid. - in cysteine (one kind of amino acid), the "R" group can form disulfide bridges with other cysteines to create cross linkages in a polypeptide chain . - in lysine, the R group gives the amino acid an alkaline property. - in Aspartic acid, R group gives the amino acid an acidic property. - several amino acids act as neurotransmitters in the central nervous system. Gl utamic acid and GABA are the most common neurotransmitters in the brain. - amino acids tend to stabilize the PH of solutions in which they are present be cause they will remove excess H+ or OH- ions. they retain this buffer capacity e ven when incorporated into peptides and proteins. - amino acids are widely available as dietary supplements for specific purposes. lysine is sold as a relief for herpes infections and glucosamine supplements ar e used for alleviating the symptoms of arthritis and other joint disorder. questions: 1) discuss the various biological roles of amino acids: there are over 150 maim acids found in cells, but only 20 occur commonly in proteins. some proteins act as catalyst for metabolic reactions. the remaining, non-protein amino acids have specialized roles as intermediate in metabolic reactions, or as neurotransmitte rs and hormones. 2) Describe what makes each of the 20 amino acids found in proteins unique: the 20 amino acids found in protein can function as biological catalyst for meta bolic reactions. and they can form various proteins. 3) Describe the process that determines the sequence in which amino acids are li nked together to form polypeptide chains: ? 4) Explain how the chemistry of amino acids enables them to act as buffers in bi ological tissues: amino acids tend to stabilize the ph solutions in which they a re present because they will remove excess of H+ or OH- ions. 5) Giving examples, explain what is meant by an essential amino acid: plants can manufacture all their amino acids however, animal obtain a certain nu mber of amino acids from their diet. the amino acids that animal have to obtain from diet is called essential amino acid. 6) Describe the processes by which amino acids are joined together and broken do wn: amino acids are linked together by condensation reaction. during this reacti on, the water is released and form polypeptide bond. in contrast, during hydrolysis reaction, amino acids are broken down by adding w ater; the water gives hydroxyl group.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesDari EverandThe Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesBelum ada peringkat
- Proteins and Amino Acid-NoteDokumen13 halamanProteins and Amino Acid-NoteHABIBUR RAHAMANBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Biochemistry Aminoacids & Proteins-1Dokumen22 halamanUnit 1 Biochemistry Aminoacids & Proteins-1kamsjain6802Belum ada peringkat
- ProteinDokumen6 halamanProteinAbdullah Al MamunBelum ada peringkat
- Foods and Nutrition Paper OneDokumen119 halamanFoods and Nutrition Paper OneNaduku EridadiBelum ada peringkat
- Titration of Amino Acids and PeptidesDokumen2 halamanTitration of Amino Acids and PeptidesAbi Diciembre Briones100% (1)
- BCH 201 DR Saliu Lecture NotesDokumen19 halamanBCH 201 DR Saliu Lecture NotesAdekunle FestusBelum ada peringkat
- Protein Intake PTC8 PDFDokumen110 halamanProtein Intake PTC8 PDFvBelum ada peringkat
- BCH206 NURSING, Ana & PhysiologyDokumen199 halamanBCH206 NURSING, Ana & PhysiologyjunaidukabirnabadeBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids and PeptideDokumen7 halamanAmino Acids and PeptideHƯNG LIÊU MẠNHBelum ada peringkat
- Proteins Unit STUDENTS For IBDokumen12 halamanProteins Unit STUDENTS For IBhjhjhBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 6.1. Protein Structure and FunctionDokumen18 halamanLesson 6.1. Protein Structure and FunctionCreeper RulezBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 14:-Biomoulecules: ProjectDokumen4 halamanUnit 14:-Biomoulecules: ProjectAnkit KumarBelum ada peringkat
- C4 ProteinsDokumen34 halamanC4 ProteinsSoraya Al-obinayBelum ada peringkat
- BiomoleculesDokumen4 halamanBiomoleculesiyahh5.comBelum ada peringkat
- Amino AcidsDokumen16 halamanAmino AcidsMIAN NASIRBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids - Properties, Structure, Classification, FunctionsDokumen6 halamanAmino Acids - Properties, Structure, Classification, Functionssattyadev95Belum ada peringkat
- 6-7 ProteinDokumen17 halaman6-7 Proteinyr44grf94kBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Amino AcidsDokumen45 halaman3 Amino AcidsBereket Agumas KegneBelum ada peringkat
- 03aamo LicyayoDokumen6 halaman03aamo LicyayoMohamidin MamalapatBelum ada peringkat
- ProteinDokumen31 halamanProteinShiela Marie BanggotBelum ada peringkat
- Biochemistery:: Asparagine Is The 1Dokumen12 halamanBiochemistery:: Asparagine Is The 1Naima AmjadBelum ada peringkat
- Notes in BiochemistryDokumen13 halamanNotes in Biochemistrylian jaeBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids, Essential Amino Acids, Isoelectric Point, ZwitterionsDokumen10 halamanAmino Acids, Essential Amino Acids, Isoelectric Point, ZwitterionsZafar IqbalBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry of Amino AcidsDokumen48 halamanChemistry of Amino Acidsshadrack mungutiBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDokumen23 halamanAmino Acids and ProteinsShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniBelum ada peringkat
- Proteins: Submitted To: Mam Saima Khubaib Submitted By: Muhammad HannanDokumen13 halamanProteins: Submitted To: Mam Saima Khubaib Submitted By: Muhammad HannanMuhammad HannanBelum ada peringkat
- Amino AcidsDokumen24 halamanAmino AcidsAdam GawracdidBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids and Proteins: Larry Scheffler Lincoln High School Portland ORDokumen35 halamanAmino Acids and Proteins: Larry Scheffler Lincoln High School Portland ORchuck55Belum ada peringkat
- Amino AcidDokumen53 halamanAmino AcidRAJA AYYABelum ada peringkat
- CHY 47 Topic 4 2nd Sem 2018-2019 Protein Amino Acid PDFDokumen129 halamanCHY 47 Topic 4 2nd Sem 2018-2019 Protein Amino Acid PDFHA REBelum ada peringkat
- Amino AcidsDokumen7 halamanAmino Acidsrida khanBelum ada peringkat
- Proteins: Amino AcidsDokumen14 halamanProteins: Amino AcidsShivam KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Amino AcidsDokumen32 halamanAmino AcidsWakjira GemedaBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDokumen48 halamanAmino Acids and ProteinsSteph VeeBelum ada peringkat
- Chem ProjectDokumen9 halamanChem Projectguptaom9839Belum ada peringkat
- ProteinsDokumen3 halamanProteinsJun Hong TeeBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids Lippincott Chapter 1: Nanuka Tsiklauri, MDDokumen19 halamanAmino Acids Lippincott Chapter 1: Nanuka Tsiklauri, MDMiri Hahiashvilli100% (1)
- Protein Notes (Dipesh Routh)Dokumen7 halamanProtein Notes (Dipesh Routh)Dipesh RouthBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids Ms. Sarah ShakeelDokumen35 halamanAmino Acids Ms. Sarah ShakeelRachna KhatriBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acid: Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine HistidineDokumen16 halamanAmino Acid: Isoleucine Leucine Lysine Methionine Phenylalanine Threonine Tryptophan Valine HistidineCrystal GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- All About ProteinsDokumen16 halamanAll About ProteinsLenore ClyneBelum ada peringkat
- ProteinsDokumen8 halamanProteins10m29satyamsinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Protein BiochemistryDokumen50 halamanProtein BiochemistrySudipta MandolBelum ada peringkat
- Amino AcidsDokumen33 halamanAmino AcidsANAND sBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids: ChemistryDokumen6 halamanAmino Acids: ChemistryCarlosSchlozJuniorBelum ada peringkat
- Nitrogen Containing Compounds: Amino AcidsDokumen10 halamanNitrogen Containing Compounds: Amino AcidsakshodhiniBelum ada peringkat
- PROTEINS p1Dokumen5 halamanPROTEINS p1Biang AbdullahBelum ada peringkat
- LU2 Proteins - Part 1 UpdateDokumen29 halamanLU2 Proteins - Part 1 UpdateLouis ThianBelum ada peringkat
- Protein FinalDokumen60 halamanProtein FinalKim John BolardeBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids and ProteinDokumen44 halamanAmino Acids and ProteinAliyu MohammedBelum ada peringkat
- PROTEIN (Biology Report) .PPTX FinalDokumen20 halamanPROTEIN (Biology Report) .PPTX FinalHanz NazarenoBelum ada peringkat
- Proteinsoct 2016Dokumen28 halamanProteinsoct 2016Abhimanyu BalyanBelum ada peringkat
- Protein 2021Dokumen29 halamanProtein 2021Dr. Mohamed ShamsBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids and Protein 88Dokumen32 halamanAmino Acids and Protein 88Omega ZuluBelum ada peringkat
- Protiens, Amino Acid, AminesDokumen5 halamanProtiens, Amino Acid, AminesAnshika BhartiBelum ada peringkat
- 3 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Protein Structure and Function - Chapter-3Dokumen21 halaman3 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Protein Structure and Function - Chapter-3MD. SAJID GHUFRANBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Amino AcidsDokumen47 halaman3 Amino AcidsBereket Agumas KegneBelum ada peringkat
- Amino Acids and PeptidesDokumen35 halamanAmino Acids and PeptidesNur Raineer laden GuialalBelum ada peringkat
- Proteins and Amino AcidsDokumen50 halamanProteins and Amino Acidsraddag100% (2)
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General CertificateDokumen20 halamanUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General CertificateHubbak KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Learning AvogadroDokumen192 halamanLearning AvogadroJose Rene Gomez PerezBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 Biochemistry 2023-2024Dokumen26 halamanLecture 1 Biochemistry 2023-2024fatimakareem0623Belum ada peringkat
- Biological Molecules - ProteinsDokumen1 halamanBiological Molecules - Proteinsrobgardner1Belum ada peringkat
- Biol 1700 Lab 4 Procedure Report FinalDokumen14 halamanBiol 1700 Lab 4 Procedure Report Finalapi-535286920Belum ada peringkat
- Lecture 2: Enzymes: Computational Systems BiologyDokumen19 halamanLecture 2: Enzymes: Computational Systems Biologyahmad aliBelum ada peringkat
- Ocular Drug Delivery SystemDokumen67 halamanOcular Drug Delivery Systemmskhatri3Belum ada peringkat
- CBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesDokumen8 halamanCBSE Quick Revision Notes CBSE Class-11 Biology Chapter-09 BiomoleculesabhiBelum ada peringkat
- Ucl Chem 114aDokumen3 halamanUcl Chem 114aKelLYSBelum ada peringkat
- Amino AcidsDokumen16 halamanAmino AcidsMIAN NASIRBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotics For Research Applications - BioFiles Issue 4.3Dokumen24 halamanAntibiotics For Research Applications - BioFiles Issue 4.3Sigma-AldrichBelum ada peringkat
- Determination of Protein Content SpectrophotometricallyDokumen10 halamanDetermination of Protein Content SpectrophotometricallyTsabit AlbananiBelum ada peringkat
- AQA BIOL2 W QP Jan11Dokumen28 halamanAQA BIOL2 W QP Jan11Arize Kilik OkaforBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis of A D - Enzyme 1992Dokumen5 halamanSynthesis of A D - Enzyme 1992Brenda ContrerasBelum ada peringkat
- BIOL1514 Lecture Slides Chapter 1 and 2 - 2023Dokumen50 halamanBIOL1514 Lecture Slides Chapter 1 and 2 - 2023Phang MakhandaBelum ada peringkat
- Biochem - Lec 05Dokumen3 halamanBiochem - Lec 05Louis FortunatoBelum ada peringkat
- Act. 5 Lab Biochem Pre FinalDokumen14 halamanAct. 5 Lab Biochem Pre FinalBillie May Albin0% (1)
- SAQ - OxytocinDokumen3 halamanSAQ - Oxytocinanaeshkl100% (1)
- Bio 5Dokumen1 halamanBio 5dnjsgudBelum ada peringkat
- 2014 12 Lyp Chemistry 04 Outside Delhi Sol 9neDokumen8 halaman2014 12 Lyp Chemistry 04 Outside Delhi Sol 9neDivyansh WaghmareBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2: Molecular Biology: Synthesis of UreaDokumen23 halamanChapter 2: Molecular Biology: Synthesis of UreaHiya GoyalBelum ada peringkat
- Fixxxxx Kimia Asam AminoDokumen19 halamanFixxxxx Kimia Asam AminomuthiasaritilawahBelum ada peringkat
- Protein ExperimentDokumen25 halamanProtein ExperimentYulinar Fawanys100% (1)
- CH 04Dokumen29 halamanCH 04filippoBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. FarrellDokumen29 halamanChapter Three Amino Acids and Peptides: Mary K. Campbell Shawn O. Farrellnora buanBelum ada peringkat
- CaseinDokumen2 halamanCaseinjohnnyasswipeBelum ada peringkat
- BIO 361 - SBU Fall 2013 - Exam 1, Lectures 1 - 13Dokumen40 halamanBIO 361 - SBU Fall 2013 - Exam 1, Lectures 1 - 13Nerdy Notes Inc.100% (1)
- Cblechpu 19Dokumen8 halamanCblechpu 19JASU GAMINGBelum ada peringkat
- Protein SurfatanDokumen19 halamanProtein Surfatanmeilana23Belum ada peringkat
- The Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactDari EverandThe Nature of Drugs Vol. 1: History, Pharmacology, and Social ImpactPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Periodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincDari EverandPeriodic Tales: A Cultural History of the Elements, from Arsenic to ZincPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDari EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)
- AP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimeDari EverandAP® Chemistry Crash Course, For the 2020 Exam, Book + Online: Get a Higher Score in Less TimePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Sodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyDari EverandSodium Bicarbonate: Nature's Unique First Aid RemedyPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (21)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDari EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Taste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodDari EverandTaste: Surprising Stories and Science About Why Food Tastes GoodPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (20)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (90)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (14)
- Guidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsDari EverandGuidelines for Defining Process Safety Competency RequirementsPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Guidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisDari EverandGuidelines for Chemical Process Quantitative Risk AnalysisPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Oxygen: The molecule that made the worldDari EverandOxygen: The molecule that made the worldPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (108)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDari EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- AP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeDari EverandAP Chemistry Flashcards, Fourth Edition: Up-to-Date Review and PracticeBelum ada peringkat
- An Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignDari EverandAn Applied Guide to Water and Effluent Treatment Plant DesignPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Fundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionDari EverandFundamentals of Chemistry: A Modern IntroductionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideDari EverandHandbook of Formulating Dermal Applications: A Definitive Practical GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Formulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsDari EverandFormulating, Packaging, and Marketing of Natural Cosmetic ProductsBelum ada peringkat
- Tribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsDari EverandTribology: Friction and Wear of Engineering MaterialsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDari EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Well Control for Completions and InterventionsDari EverandWell Control for Completions and InterventionsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (10)