G P H S A U: Eometry Atterson IGH Chool LL Nits
Diunggah oleh
Nicholas YatesJudul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
G P H S A U: Eometry Atterson IGH Chool LL Nits
Diunggah oleh
Nicholas YatesHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
GEOMETRY PATTERSON HIGH SCHOOL ALL UNITS
COURSE OUTLINE.
Core Learning Goal 2: The student will demonstrate the ability to solve
mathematical and real-world problems using measurement and
geometric models and will justify solutions and explain processes used.
Expectation 2.1: The student will represent and analyze two- and
three-dimensional figures using tools and technology when
appropriate.
Expectation 2.2: The student will apply geometric properties and
relationships to solve problems using tools and technology when
appropriate.
Expectation 2.3: The student will apply concepts of measurement
using tools and technology when appropriate.
Unit 1: Measurement
(CLG Indicators 2.1.1: The student will analyze the properties of geometric figures.
2.1.2: The student will identify and/or verify properties of geometric figures using
the coordinate plane and concepts from algebra.
2.1.4: The student will construct and/or draw and/or validate properties of
geometric figures using appropriate tools and technology.
2.3.1: The student will use algebraic and/or geometric properties to measure
indirectly.
2.3.2: The student will use techniques of measurement and will estimate,
calculate, and/or compare perimeter, circumference, area, volume, and/or
surface area of two- and three-dimensional figures and their parts.)
I. Dimension (CLG 2.1.1)
A. =number of distinct directions something is extended in
B. 0: point
C. 1: line, ray, line segment
D. 2: plane, square, any polygon
E. 3: space, cube, any real object you see
II. Naming (CLG 2.1.1)
A. Lines
B. Line segments
C. Rays
D. Angles
E. Planes
III. Distance (CLG 2.3.2)
A. Counting line segments
B. In body-based units (span, digit, palm)
C. Appropriate units and sizes (also CLG 2.1.4)
D. Using a ruler (inches, centimeters) ___________
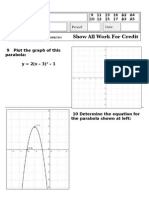
E. Using the distance formula D = √(∆x)2+(∆y)2
(also CLGs 2.1.2 & 2.3.1)
IV. Perimeter (CLG 2.3.2)
A. Distance around = add up all side lengths
B. If equilateral n-gon with congruent sides of length s, P = n*s
V. Area (CLG 2.3.2)
A. Counting squares
B. For rectangles, A = l*w
VI. Volume (CLG 2.3.2)
A. Counting cubes
B. For rectangular prisms, V = l*w*h
VII. Converting Units: Dimensional Analysis (CLG 2.3.2)
A. Informal: in to cm (2.54)
B. Formal: any units, multiplying fractional forms of 1
VIII. Angle Measure (various CLGs—see below)
A. Measuring angles (line up the vertex and one side of angle)
(CLG 2.3.2)
B. Drawing angles (CLG 2.1.4)
C. Units are degrees (convenient) (CLG 2.3.2)
D. Acute/Obtuse/Right/Straight/Reflex (CLG 2.1.1)
E. Complementary and Supplementary Angles (CLG 2.1.1)
F. Congruent Angles (CLG 2.1.1)
Unit 2: Shape Relationships
(CLG Indicators 2.1.1: The student will analyze the properties of geometric figures.
2.1.2: The student will identify and/or verify properties of geometric figures using
the coordinate plane and concepts from algebra.
2.1.3: The student will use transformations to move figures, create designs,
and/or demonstrate geometric properties.
2.2.1: The student will identify and/or verify congruent and similar figures
and/or apply equality or proportionality of their corresponding parts.
2.2.2: The student will solve problems using two-dimensional figures and/or
right-triangle trigonometry.
2.3.1: The student will use algebraic and/or geometric properties to measure
indirectly.)
IX. Shape classification (CLG 2.1.1)
A. Triangles, by angle types
B. Triangles, by side lengths
C. Quadrilaterals
D. Regular vs. Irregular shapes
X. Transformations (CLG 2.1.3)
A. Classify as an isometry or not
B. Classify by type (Rotation, Reflection, Translation, Glide Reflection)
C. Draw the result of a transformation
D. Find lines of symmetry in figures
E. Classify shapes and patterns by type of symmetries
XI. Similar Triangles (CLG 2.2.1)
A. Congruent angles, Proportional sides
B. Find the scale factor and apply it
C. Decide whether pair of triangles is similar, using scale factor or
proportions
D. Use scale factor or proportions to find missing side lengths
(also CLGs 2.1.2 & 2.2.2)
E. Apply to real-world situations (also CLGs 2.1.2, 2.2.2, & 2.3.1)
Shadows
Mirrors
Triangulation at sea
XII. Angle Relationships (CLGs 2.1.1 & 2.2.1)
A. Complementary/Supplementary/Vertical/Corresponding/Triang
ular
B. Use relationships to find missing angles in a figure
C. Apply these relationships to help prove triangles congruent (like by
SAS or ASA or AAS – see Unit 3)
Unit 3: Triangles and Proof
(CLG Indicators 2.1.2: The student will identify and/or verify properties of geometric figures using
the coordinate plane and concepts from algebra.
2.1.4: The student will construct and/or draw and/or validate properties of
geometric figures using appropriate tools and technology.
2.2.1: The student will identify and/or verify congruent and similar figures
and/or apply equality or proportionality of their corresponding parts.
2.2.2: The student will solve problems using two-dimensional figures and/or
right-triangle trigonometry.
2.2.3: The student will use inductive or deductive reasoning.
2.3.1: The student will use algebraic and/or geometric properties to measure
indirectly.)
XIII. Triangle Construction (CLG 2.1.4)
A. Tell if a triangle can be constructed
• Angles must add to 180°
• Triangle Inequality: sides a + b > c
B. Tell how many can be constructed (1, 2, or infinity)
C. Construct triangles from given information
XIV. Congruent Triangles (CLGs 2.2.1 & 2.2.3)
A. Prove triangles congruent using congruence postulates (SSS, ASA,
SAS, AAS)
B. Explain why AAA is not enough to prove congruence
C. Determine if enough information is available to prove congruence
D. Use congruence to find missing sides and angle measurements
(also CLG 2.2.2)
XV. Proofs (CLG 2.2.3)
A. Read and understand a paragraph proof
B. Read and understand a two-column (statements and reasons) proof
C. Supply missing reasons for statements in a two-column proof
XVI. Pythagorean Theorem (CLGs 2.1.2 & 2.2.2)
A. For right triangles only!
B. a2 + b2 = c2
C. Solve for missing hypotenuse
D. Solve for missing leg
E. Apply converse of the PT to determine if a triangle is right, acute,
or obtuse
F. In a 45-45-90 triangle, solve for two sides given one side length
G. In a 30-60-90 triangle, solve for two sides given one side length
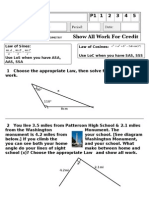
XVII. Trigonometry (CLGs 2.1.2 & 2.2.2)
A. For right triangles
B. Use a trig table to find values of sine, cosine, tangent for an angle
C. Use a trig table to find angle given a sine, cosine, or tangent value
D. Apply the definition of sine, cosine, and tangent to find values
based on a given triangle—SOHCAHTOA
E. Solve for any side of a right triangle given one other side and an
angle
F. Solve for any angle in a right triangle with given sides
G. Draw diagrams of real-life situations (also CLG 2.1.4)
H. Find right triangles in diagrams of real-life situations, and
determine unknown distances and angles using trigonometry
(parts E and F) (also CLG 2.3.1)
Unit 4: Circles
(CLG Indicators 2.1.1: The student will analyze the properties of geometric figures.
2.1.2: The student will identify and/or verify properties of geometric figures using
the coordinate plane and concepts from algebra.
2.1.4: The student will construct and/or draw and/or validate properties of
geometric figures using appropriate tools and technology.
2.2.2: The student will solve problems using two-dimensional figures and/or
right-triangle trigonometry.
2.3.2: The student will use techniques of measurement and will estimate,
calculate, and/or compare perimeter, circumference, area, volume, and/or
surface area of two- and three-dimensional figures and their parts.)
XVIII. Circle Construction (CLG 2.1.4)
A. General use of a compass
B. Construction of parts of a circle/disk (i.e. vocab words)
C. How to make circles passing through one point
D. How to make circles passing through two points
E. How to make circle passing through three non-collinear points
XIX. Circle Measurement (CLG 2.3.2)
A. Measure the radius and/or diameter
B. Use of pi (π)
C. Calculate circle’s circumference
D. Calculate length of an arc
E. Calculate circle’s area
F. Calculate area of a sector
G. Calculate area of a segment
H. Comparison of circle’s circumference to polygon’s perimeter
XX. Circles, Arcs, and Angles (various CLGs—see below)
A. Identify central angles and inscribed angles (CLG 2.1.1)
B. Categorize angles based on vertex (at center, on circle, inside circle,
outside of circle) (CLG 2.1.1)
C. Arc sum of a circle is 360° (CLG 2.1.1)
D. Find missing arcs (CLGs 2.1.2 & 2.2.2)
E. Determine the measure of angles based on intercepted arcs
(CLGs 2.1.2 & 2.2.2)
F. Determine the measure of intercepted arcs based on angles
(CLGs 2.1.2 & 2.2.2)
Unit 5: Three Dimensions
(CLG Indicators 2.1.1: The student will analyze the properties of geometric figures.
2.1.2: The student will identify and/or verify properties of geometric figures using
the coordinate plane and concepts from algebra.
2.1.4: The student will construct and/or draw and/or validate properties of
geometric figures using appropriate tools and technology.
2.2.3: The student will use inductive or deductive reasoning.
2.3.2: The student will use techniques of measurement and will estimate,
calculate, and/or compare perimeter, circumference, area, volume, and/or
surface area of two- and three-dimensional figures and their parts.)
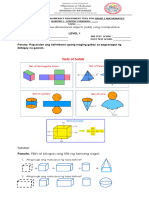
XXI. Nets and Polyhedra (various CLGs—see below)
A. Cut, fold, and tape a net to form a polyhedron (CLG 2.1.4)
B. Match a net to the polyhedron it forms (CLG 2.1.4)
C. Identify and count faces, edges, and vertices on polyhedra
(CLG 2.1.1)
D. Verify Euler’s Formula V – E + F = 2 (CLGs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, & 2.2.3)
E. Identify regular polyhedra (all faces are the same regular polygon)
(CLG 2.1.1)
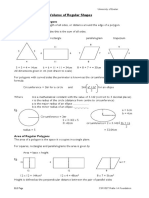
XXII. Prisms (and Cylinders) (CLGs 2.1.1 & 2.3.2)
A. Identify prisms (two parallel, congruent bases)
B. Find volume V = B * h
C. Find surface area by adding up face areas
D. Cylinder surface area is S.A. = 2B + C*h where C is circumference
XXIII. Pyramids (and Cones) (CLGs 2.1.1 & 2.3.2)
A. Identify pyramids (one base; other faces meet at a point)
B. Find volume V = 1/3 * B * h
C. Find surface area by adding up face areas
XXIV. Spheres (CLGs 2.1.1 & 2.3.2)
A. Identify spheres (vs. cylinders, cones, etc.)
B. Find volume V = 4/3πr3
C. Find surface area S.A. = 4πr2
XXV. Other Shapes (CLG 2.3.2)
A. Find volume by counting cubes
B. Find surface area by counting squares
C. Find volume by splitting into pieces
Vocabulary
Unit 1: Measurement
Dimension Parallel Ruler
Point Intersecting Protractor
Line Perpendicular Acute Angle
Plane Skew Obtuse Angle
Space Collinear Right Angle
Line Segment Coplanar Straight Angle
Ray Perimeter Reflex Angle
Angle Polygon Complementary
Vertex Area Supplementary
Congruent Volume Congruent
Units (spans, palms, digits, inches, centimeters, feet, miles, yards, millimeters,
meters, kilometers, nanometers, light years, degrees)
Unit 2: Shape Relationships
Acute Triangle Pentagon Proportion
Obtuse Triangle Equilateral Parallel Lines
Right Triangle Equiangular Corresponding
Scalene Regular Angles
Triangle Transformation Vertical Angles
Isosceles Reflection Complementary
Triangle Rotation Angles
Equilateral Translation Supplementary
Triangle Glide Reflection Angles
Quadrilateral Symmetry Congruent
Trapezoid Isometry Angles
Kite Tiling Acute Angle
Parallelogram Tessellation Obtuse Angle
Rhombus Congruent Right Angle
Rectangle Triangles Straight Angle
Square Similar Reflex Angle
Vertex
Unit 3: Triangles and Proof
Theorem 45-45-90 Sine Inverse
Proof triangle Cosine Inverse
Isosceles 30-60-90 Tangent Inverse
Triangle triangle Angle of Elevation
Base Angles Pythagorean Angle of
Vertex Angle Theorem Depression
Perpendicular Hypotenuse Stellar Parallax
Bisect Legs Corresponding
Perpendicular Opposite Angles
Bisector Adjacent Vertical Angles
Congruent Sine Complementary
Triangles Cosine Supplementary
Right Triangle Tangent
Unit 4: Circles
Circle Chord Semicircular
Center Arc segment
Disk Sector Circumference
Diameter Segment Central Angle
Radius Semicircle Inscribed Angle
Tangent Line Semicircular Intercepted Arc
Secant Line sector
Unit 5: Three Dimensions
Net Pyramid
Polyhedron Cylinder
Face Cone
Edge Sphere
Vertex Volume
Prism Surface Area
Base(s) Euler’s Formula
Lateral Faces Regular Polyhedron
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Interactions on Digital Tablets in the Context of 3D Geometry LearningDari EverandInteractions on Digital Tablets in the Context of 3D Geometry LearningBelum ada peringkat
- Mip2601assignment 2, 3 and 4 Memo 2021Dokumen25 halamanMip2601assignment 2, 3 and 4 Memo 2021Ntlotliseng MokoenaBelum ada peringkat
- Cccau 6 Parentletter 1Dokumen3 halamanCccau 6 Parentletter 1api-208514376Belum ada peringkat
- Hmd-Geometry Project 4Dokumen2 halamanHmd-Geometry Project 4api-288278295Belum ada peringkat
- Geom 1 ADokumen24 halamanGeom 1 AMuraliBelum ada peringkat
- Distance Formula WorksheetDokumen7 halamanDistance Formula Worksheetapi-735539036Belum ada peringkat
- Guided Noteboo Kin GED10 2 (Mathe Matics in The Modern World)Dokumen5 halamanGuided Noteboo Kin GED10 2 (Mathe Matics in The Modern World)Michaella Custodio LaborBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry BookDokumen249 halamanGeometry BookMarizza Bailey100% (1)
- Geometry and Trigonometry Lessons ExplainedDokumen8 halamanGeometry and Trigonometry Lessons ExplainedWhinona FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Trigonometry Notes CLO5Dokumen42 halamanTrigonometry Notes CLO5Ezy WaqaBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of a Parallelogram LessonDokumen5 halamanProperties of a Parallelogram LessonIldabay75% (4)
- High School MathDokumen8 halamanHigh School MathRochelle GabanitBelum ada peringkat
- GR 10 Euclidean Geometry Booklet SUE 2019Dokumen18 halamanGR 10 Euclidean Geometry Booklet SUE 2019Desmond SmithBelum ada peringkat
- GeometryDokumen49 halamanGeometryJennylyn MaraceBelum ada peringkat
- Explain The Pythagorean Theorem, Its Proofs and ApplicationsDokumen5 halamanExplain The Pythagorean Theorem, Its Proofs and ApplicationsMichael OmolloBelum ada peringkat
- Measuring focal length and refraction of lightDokumen5 halamanMeasuring focal length and refraction of lighthridyanshi vigBelum ada peringkat
- Perimeter and Area On A Line SegmentDokumen15 halamanPerimeter and Area On A Line Segmentdbrizzolara191Belum ada peringkat
- First Terms Questions For XIDokumen9 halamanFirst Terms Questions For XIIkshya kcBelum ada peringkat
- Developing Concepts in Linear Algebra and Analytic Geometry by The Integration of DGS and CASDokumen10 halamanDeveloping Concepts in Linear Algebra and Analytic Geometry by The Integration of DGS and CASASPERPHYSBelum ada peringkat
- Math 5 Module 4 NewDokumen7 halamanMath 5 Module 4 NewJonwille Mark CastroBelum ada peringkat
- ELECTIVE-MATHEMATICS-10-Module-3 Analytic ProofsDokumen21 halamanELECTIVE-MATHEMATICS-10-Module-3 Analytic ProofsFVERON, JESSICA FABELLOREBelum ada peringkat
- GED 102 Week 5 Lessons on Geometry, Trigonometry, and Algebra ApplicationsDokumen6 halamanGED 102 Week 5 Lessons on Geometry, Trigonometry, and Algebra ApplicationsVince GonzalvoBelum ada peringkat
- Yearly Plan Mathematics T 2013Dokumen22 halamanYearly Plan Mathematics T 2013Tan Chin HuatBelum ada peringkat
- Lec Week1Dokumen3 halamanLec Week1Milos StamatovicBelum ada peringkat
- GED102 Week 5 WGN - ANTEDokumen5 halamanGED102 Week 5 WGN - ANTEArsen Rae M. ANTEBelum ada peringkat
- Precalculus Daily Lesson LogDokumen6 halamanPrecalculus Daily Lesson Logjun del rosarioBelum ada peringkat
- Relationship between temperature and bounce heightDokumen6 halamanRelationship between temperature and bounce heightaftabBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching of SpaceDokumen5 halamanTeaching of SpaceHaniza HossenBelum ada peringkat
- Arizona Mathematics Standards GeometryDokumen9 halamanArizona Mathematics Standards GeometryLuke ThorneBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry, Trigonometry, Mensuration, Area, Volume, Perimeter (Part 3 of 3) For UPSC Combined Defense Service Exam MrunalDokumen15 halamanGeometry, Trigonometry, Mensuration, Area, Volume, Perimeter (Part 3 of 3) For UPSC Combined Defense Service Exam Mrunalkirtivardhan1989Belum ada peringkat
- Learning Module For General Physics 1/ 12/quarter 1 Title: Kinematics (Motion in 2 Dimensions)Dokumen20 halamanLearning Module For General Physics 1/ 12/quarter 1 Title: Kinematics (Motion in 2 Dimensions)GR MacopiaBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra - CommonCoreStandardsDokumen6 halamanAlgebra - CommonCoreStandardsratliffjBelum ada peringkat
- Shape and SpaceDokumen7 halamanShape and Spaceapi-65563698Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Form 1 & 2 Short Simple Notes by Kelvin 3E/2018Dokumen4 halamanMathematics Form 1 & 2 Short Simple Notes by Kelvin 3E/2018Kelvin100% (1)
- PNU-NCTE Distance Formula Lesson PlanDokumen4 halamanPNU-NCTE Distance Formula Lesson PlanLyn Macabulit100% (1)
- Hong Kong Community College SEHH2315 Survey Adjustment 2020/2021 Semester 2 Take Home Assignment 2Dokumen5 halamanHong Kong Community College SEHH2315 Survey Adjustment 2020/2021 Semester 2 Take Home Assignment 2muhammad saadBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Unit7Dokumen45 halaman8 Unit7HEXAGON ProductionBelum ada peringkat
- 2015 Scheme of Work Add Maths F5Dokumen9 halaman2015 Scheme of Work Add Maths F5nurizwahrazakBelum ada peringkat
- MATH_1330Dokumen2 halamanMATH_1330Siddharth VBelum ada peringkat
- Addis Ababa University Physics WorksheetDokumen9 halamanAddis Ababa University Physics WorksheetNahi ManBelum ada peringkat
- Stem Physics 1 Q1 WK1 M3 PDFDokumen20 halamanStem Physics 1 Q1 WK1 M3 PDFJoiemmy Sumedca Bawengan GayudanBelum ada peringkat
- 8th Grade Dilation Investigation With Answers 8.3ABC PDFDokumen15 halaman8th Grade Dilation Investigation With Answers 8.3ABC PDFDaisy beBelum ada peringkat
- Geom82015 ExamDokumen28 halamanGeom82015 ExamBenjaminAgalliuBelum ada peringkat
- Phy XI Term 1 Set A 080Dokumen5 halamanPhy XI Term 1 Set A 080aayankc9841Belum ada peringkat
- Projectile Motion Components PriceDokumen5 halamanProjectile Motion Components PriceDhara Patel100% (1)
- A Geometrical Derivation of The Three Trigonometric IdentitiesDokumen8 halamanA Geometrical Derivation of The Three Trigonometric IdentitiesCharlston ChavezBelum ada peringkat
- CO Math10 Q2 Module6Dokumen22 halamanCO Math10 Q2 Module6j.yukii0014Belum ada peringkat
- Field 2 PowerpointDokumen61 halamanField 2 Powerpointapi-219074785Belum ada peringkat
- Mathematics: A. Statistics at A GlanceDokumen32 halamanMathematics: A. Statistics at A GlanceAruna VijayanBelum ada peringkat
- Physics-experiment 1-lab-reportDokumen8 halamanPhysics-experiment 1-lab-reportgacc4sitesBelum ada peringkat
- Study Material Term Ii: Class - Ix Subject: MathematicsDokumen49 halamanStudy Material Term Ii: Class - Ix Subject: MathematicsCHIRAG MATTABelum ada peringkat
- Translation Transformation Lesson Plan For Module 4 For Fourth Form MathematicsDokumen8 halamanTranslation Transformation Lesson Plan For Module 4 For Fourth Form MathematicsChet Jerry AckBelum ada peringkat
- Math Lesson on Triangle Congruence PostulatesDokumen6 halamanMath Lesson on Triangle Congruence PostulatesLESTER PARADILLOBelum ada peringkat
- Coimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit: State Examinations CommissionDokumen20 halamanCoimisiún Na Scrúduithe Stáit: State Examinations Commissionfrank mutaleBelum ada peringkat
- 4.4.4 Test (TST) - Trigonometry (Test)Dokumen11 halaman4.4.4 Test (TST) - Trigonometry (Test)Charlotte Hargrove100% (1)
- Geometry - Angle PropertiesDokumen14 halamanGeometry - Angle PropertiesAnthony Benson100% (1)
- Gini Index Student HandoutDokumen8 halamanGini Index Student HandoutNicholas Yates100% (1)
- Phi ProjectDokumen4 halamanPhi ProjectNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2T4QuizP3 6 7 8 9Dokumen3 halamanA2T4QuizP3 6 7 8 9Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TQuizP1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6Dokumen2 halamanA2TQuizP1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- Green Eggs & Catch: The RulesDokumen4 halamanGreen Eggs & Catch: The RulesNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TQuiz9 10 11 12 13 15 16 17 A2 A3 A4 A5Dokumen4 halamanA2TQuiz9 10 11 12 13 15 16 17 A2 A3 A4 A5Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- Big Picture Ideas in A2TDokumen1 halamanBig Picture Ideas in A2TNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- STEM AnnualChallenge2011Dokumen4 halamanSTEM AnnualChallenge2011Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- Bridge GeometryDokumen1 halamanBridge GeometryNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2T4QuizP5 P6 1 2 A1Dokumen3 halamanA2T4QuizP5 P6 1 2 A1Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TQuizP3 P5 1 2 3 5 6 A1Dokumen2 halamanA2TQuizP3 P5 1 2 3 5 6 A1Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- Mr. Yates: 270° Coordinates: (,) 105° Coordinates: (,) A Graph: B GraphDokumen3 halamanMr. Yates: 270° Coordinates: (,) 105° Coordinates: (,) A Graph: B GraphNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TQuiz7 8 9 10 11 12Dokumen2 halamanA2TQuiz7 8 9 10 11 12Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TQuizP1 P2 3 4 5 6Dokumen2 halamanA2TQuizP1 P2 3 4 5 6Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2T4QuizP1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6Dokumen3 halamanA2T4QuizP1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2T Final Exam 11 FormulaeDokumen2 halamanA2T Final Exam 11 FormulaeNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- Mr. Yates: Lgebra With RigonometryDokumen3 halamanMr. Yates: Lgebra With RigonometryNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TQuiz7 8 9 10 11 12Dokumen2 halamanA2TQuiz7 8 9 10 11 12Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- Mr. Yates: Lgebra With RigonometryDokumen3 halamanMr. Yates: Lgebra With RigonometryNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2T4Quiz1 2 3 4 5Dokumen3 halamanA2T4Quiz1 2 3 4 5Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TSkillsHandout SkillsGradingDokumen2 halamanA2TSkillsHandout SkillsGradingNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2T4MiniQuiz10 11Dokumen1 halamanA2T4MiniQuiz10 11Nicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TSkillsHandout Algebra P+ADokumen1 halamanA2TSkillsHandout Algebra P+ANicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- Algebra 2 With Trigonometry SyllabusDokumen3 halamanAlgebra 2 With Trigonometry SyllabusNicholas Yates0% (1)
- A2TSkillsHandout Analysis P+ADokumen1 halamanA2TSkillsHandout Analysis P+ANicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- POE FMP The Paper Tower BlankDokumen1 halamanPOE FMP The Paper Tower BlankNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TSkillsHandout AllDokumen4 halamanA2TSkillsHandout AllNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TSkillsHandout Analysis CoreDokumen1 halamanA2TSkillsHandout Analysis CoreNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- A2TSkillsHandout Algebra CoreDokumen1 halamanA2TSkillsHandout Algebra CoreNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- WindmillDokumen1 halamanWindmillNicholas YatesBelum ada peringkat
- 12.area Related To Circles Important QuestionsDokumen7 halaman12.area Related To Circles Important QuestionsPreetham MBelum ada peringkat
- Math DaremDokumen39 halamanMath DaremAaron EstacionBelum ada peringkat
- Final - Math 9 - Q3 - Module 3Dokumen10 halamanFinal - Math 9 - Q3 - Module 3Yeoj ParasBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics Ages 5 To 6 PDFDokumen191 halamanMathematics Ages 5 To 6 PDFBrankoBelum ada peringkat
- Planar Graphs and Nonplanar Graphs DefinedDokumen29 halamanPlanar Graphs and Nonplanar Graphs DefineddangreglongBelum ada peringkat
- JBMO ShortLists-2001Dokumen2 halamanJBMO ShortLists-2001OklaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Properties of Circles II (Q)Dokumen34 halamanBasic Properties of Circles II (Q)Hoi Yee Karis LauBelum ada peringkat
- KSF 2013 Junior Math ProblemsDokumen6 halamanKSF 2013 Junior Math ProblemsJohnvic AdiqueBelum ada peringkat
- An Application of The Generalization of Ceva's TheoremDokumen3 halamanAn Application of The Generalization of Ceva's TheoremDon HassBelum ada peringkat
- Theorems in Plane Geometry Sec21Dokumen10 halamanTheorems in Plane Geometry Sec21LaiBelum ada peringkat
- Math-Data-Bank-Grade 1 - SGAESDokumen16 halamanMath-Data-Bank-Grade 1 - SGAESMaria Elaine De CastroBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 10 (9) Workbook AnswersDokumen7 halamanChapter 10 (9) Workbook Answers최재헌Belum ada peringkat
- Perimeter, Area and Volume of Regular ShapesDokumen6 halamanPerimeter, Area and Volume of Regular ShapesMohsin Raza MaitlaBelum ada peringkat
- Gmat 1 PDFDokumen6 halamanGmat 1 PDFSharanya IyerBelum ada peringkat
- Isometric Projection Problems & SolutionsDokumen11 halamanIsometric Projection Problems & SolutionsKATTA NARENDRA BABUBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics: Resource Pack Grade 10 Term 2Dokumen42 halamanMathematics: Resource Pack Grade 10 Term 2Excellent Gumede100% (1)
- Ncert Solutions Class 9 Math Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals Ex 8 1Dokumen18 halamanNcert Solutions Class 9 Math Chapter 8 Quadrilaterals Ex 8 1NGlobal ConsultantsBelum ada peringkat
- Solution of Triangle: Sine RuleDokumen41 halamanSolution of Triangle: Sine RuleMuraliBelum ada peringkat
- Third Space Learning Area of A Triangle 12absinc GCSE Worksheet 1Dokumen12 halamanThird Space Learning Area of A Triangle 12absinc GCSE Worksheet 1Lisandra SantosBelum ada peringkat
- HKMO1992heatans PDFDokumen11 halamanHKMO1992heatans PDFChai Usajai UsajaiBelum ada peringkat
- Integral Calculus Part 1Dokumen12 halamanIntegral Calculus Part 1Maria Lourven AbrahamBelum ada peringkat
- Perimeter and Area WorksheetsDokumen2 halamanPerimeter and Area WorksheetsFlute In our BLOODBelum ada peringkat
- Bum2123 Applied Calculus S2 0818Dokumen6 halamanBum2123 Applied Calculus S2 0818Deisigan ManiBelum ada peringkat
- Namma Kalvi 4th Maths, Science and Social Science Book EM Term 1Dokumen160 halamanNamma Kalvi 4th Maths, Science and Social Science Book EM Term 1Priya DharshiniBelum ada peringkat
- Immaculate Conception School of Guiuan, IncDokumen6 halamanImmaculate Conception School of Guiuan, IncJessa mae macasojotBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Maths 01Dokumen5 halamanActivity Maths 01Dr Shyam Sundar AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- 1qp Class Ix MathematicsDokumen9 halaman1qp Class Ix MathematicsMisbah unnisa JafferBelum ada peringkat
- Intersection of Two SurfacesDokumen20 halamanIntersection of Two SurfacesSbs Smrt LtaBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 3 Triangle CongruenceDokumen28 halamanMathematics: Quarter 3 - Module 3 Triangle CongruenceraymondBelum ada peringkat
- DEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES AND SOLIDS WITH CUTOUTSDokumen7 halamanDEVELOPMENT OF SURFACES AND SOLIDS WITH CUTOUTSNagaraj MuniyandiBelum ada peringkat
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormDari EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (5)
- Quantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsDari EverandQuantum Physics: A Beginners Guide to How Quantum Physics Affects Everything around UsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (2)
- Mental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorDari EverandMental Math Secrets - How To Be a Human CalculatorPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Mathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingDari EverandMathematical Mindsets: Unleashing Students' Potential through Creative Math, Inspiring Messages and Innovative TeachingPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (21)
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra For DummiesDari EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra For DummiesPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (6)
- Build a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Dari EverandBuild a Mathematical Mind - Even If You Think You Can't Have One: Become a Pattern Detective. Boost Your Critical and Logical Thinking Skills.Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Making and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenDari EverandMaking and Tinkering With STEM: Solving Design Challenges With Young ChildrenBelum ada peringkat
- Strategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceDari EverandStrategies for Problem Solving: Equip Kids to Solve Math Problems With ConfidenceBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticeDari EverandBasic Math & Pre-Algebra Workbook For Dummies with Online PracticePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Calculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusDari EverandCalculus Made Easy: Being a Very-Simplest Introduction to Those Beautiful Methods of Reckoning Which are Generally Called by the Terrifying Names of the Differential Calculus and the Integral CalculusPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDari EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (8)
- Math Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsDari EverandMath Magic: How To Master Everyday Math ProblemsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (15)
- Psychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideDari EverandPsychology Behind Mathematics - The Comprehensive GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Pre-Calculus Workbook For DummiesDari EverandPre-Calculus Workbook For DummiesPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (2)
- Mental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Dari EverandMental Math: How to Develop a Mind for Numbers, Rapid Calculations and Creative Math Tricks (Including Special Speed Math for SAT, GMAT and GRE Students)Belum ada peringkat
- A Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormDari EverandA Mathematician's Lament: How School Cheats Us Out of Our Most Fascinating and Imaginative Art FormPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (20)
- Limitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersDari EverandLimitless Mind: Learn, Lead, and Live Without BarriersPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (6)
- How Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsDari EverandHow Math Explains the World: A Guide to the Power of Numbers, from Car Repair to Modern PhysicsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (9)