Drug Study
Diunggah oleh
TeZza_Enano_2209Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Drug Study
Diunggah oleh
TeZza_Enano_2209Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
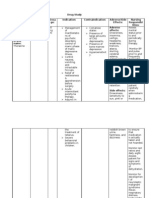
DRUG
CLASSIFICATION
ACTION
SIDE EFFECTS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
NURSING INTERVENTION
BIPERIDIN HCL tab OD
Antiparkinsonian
y Anticholinergic activity in the CNS that is believed to help normalize the hypothesized imbalance of cholinergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission in the basal ganglia
y y y y y y
Disorientation Confusion Nervousness Lightheadedness Dizziness blurred vision
y Angle-closure glaucoma y pyloric or duodenal obstruction y Use cautiously with tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias
y Take this drug exactly as prescribed y Avoid use of alcohol, sedative and OTC y Report presence of side effects
Levopromazine 100 mg OD
aliphatic phenothi azineneuroleptic d rug.
y Levomepromazine is used for the treatment of psychosis, particular those of schizophrenia, and manic phases of bipolar disorder. It should be used only with caution in the treatment of agitated depressions, as it can cause akathisia as a side effect, which could worsen the agitation.
y Dizziness, headache, nausea, anorexia, impotence
y Levomepromazi ne may increase the risk of death when used in elderly patients with dementiarelated psychosis. Because of this possible risk, levomepromazi ne should not be used in the treatment of such patients.
y Hypersensitivity. Cross-sensitivity may exist among phenothiazines. Should not be used in narrow-angle glaucoma. Should not be used in patients who have CNS depression.
Chlorpromazine 150 mg OD
FumenazolDecanoate 0.5 cc once a monrt
Antipsychotic drugs
y Acute and chronic y CNS: neuroleptic psychoses, particularly malignant syndrome, when accompanied by sedation, extrapyramidal increased reactions, tardive psychomotor activity. dyskinesia Nausea and vomiting. CV: hypotension Also used in the (increased with IM, IV) treatment of EENT: blurred vision, intractable hiccups dry eyes, lens opacities GI: constipation, dry mouth, anorexia, hepatitis, ileus GU: urinary retention Hematologic: agranulocytosis, leukopenia Skin: photosensitivity, pigment changes, rashes The exact y hypotension, mechanism of action y insomnia of flupenthixol has y headache not been y Lightheadedness established. Its y Dizziness effects resemble those of the phenothiazine, fluphenazine, in that it belongs among the antipsychotic drugs which are less likely to cause sedation and hypotension, but have greater propensity for producing extrapyramidal reactions.
Do not use in patients with known hypersensitivity to phenothiazines. Do not use in comatose states or in the presence of large amounts of central nervous system depressants (alcohol, barbiturates, narcotics, etc.). y y The maintenance therapy of chronic schizophrenic patients whose main manifestations do not include excitement, agitation or hyperactivity
Cross-sensitivity may exist among phenothiazines. Should not be used in narrowangle glaucoma. Should not be used in patients who have CNS depression.
y Flupenthixol is also contraindicated in the presence of CNS depression due to any cause, comatose states, suspected or established subcortical brain damage, blood dyscrasias, pheochromocytoma, liver damage, cerebrovascular or renal insufficiency, and severe cardiovascular disorders. It is not indicated for the management of severely agitated
Haloperidol
Antipsychotic
Completely blocks dopamine receptors to cause sedation and also causes alpha-adrenergic and anticholinergic blockade. It depresses cerebral cortex, hypothalamus and limbic system, which control activity and aggression but also cause significant extrapyramidal effects.
y Dry mouth, salivation, hypotension, drowsiness, insomnia
y Severe toxic CNS depression or comatose states from any cause; Parkinson disease. Hypersensitivity , blood dyscrasias, coma, bone marrow depression, alcohol and barbiturate withdrawal states. Angina, epilepsy, urinary retention, narrow-angle glaucoma
y y
y y
psychotic patients, psychoneurotic patients or geriatric patients with confusion and/or agitation. As with phenothiazines, flupenthixol should not be used concomitantly with large doses of hypnotics due to the possibility of potentiation. Assess patient s disorder and mental status before drug therapy and reassesses regularly Monitor for possible adverse reactions Monitor VS during initial treatment. Check for dizziness, faintness, tachycardia Assess for constipation and urinary retention daily Assess for neuroleptic malignant syndrome Assess reflexes, gait, coordination and EPS Give oral drug in form mixed in glass
y y
y y
of juice or caffeinefree cola if hoarding is suspected; do not mix caffeine drinks, tannics and pectins give with food to decrease GI upset store in tight, lightresistant container, oral solution in amber bottle advise patient to shift positions slowly because orthostatic hypotension may occur tell patient to report adverse reaction teach patient to use good oral hygiene, frequent rinsing of mouth to prevent candidiasis. Sugarless gum may be used for dry mouth
Enano, Ma. Tezza Joy H. (3nu04)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Drug Study HaldolDokumen2 halamanDrug Study HaldolGracia EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study-Grand Case PresDokumen8 halamanDrug Study-Grand Case PresLorina Lynne ApelacioBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study and Mental Health AssessmentDokumen8 halamanDrug Study and Mental Health AssessmentVincent Quitoriano100% (1)
- Drug StudyDokumen8 halamanDrug StudyBien EstrellaBelum ada peringkat
- ZonisamideDokumen2 halamanZonisamideRo-anne AkuBelum ada peringkat
- AlprazolamDokumen3 halamanAlprazolamapi-3797941100% (1)
- Fluvoxamine MaleateDokumen3 halamanFluvoxamine MaleateHilman Fitriaji Suganda PrawiraBelum ada peringkat
- pw-Drug-Study 4Dokumen3 halamanpw-Drug-Study 4MFQ.RNBelum ada peringkat
- MultivitaminDokumen1 halamanMultivitaminKatie McPeek88% (8)
- Apixaban 5 PDFDokumen2 halamanApixaban 5 PDFWanie Al-basriBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanDrug StudyKeanu ArcillaBelum ada peringkat
- School of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeDokumen3 halamanSchool of Nursing and Midwifery: Emilio Aguinaldo CollegeMiggsBelum ada peringkat
- Mina Drug StudyDokumen7 halamanMina Drug StudyChi Chaw Giselle HilarioBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG StudyDokumen3 halamanDRUG StudyArfe BaquinquitoBelum ada peringkat
- Methylphenidate: CNS Stimulant DrugDokumen3 halamanMethylphenidate: CNS Stimulant Drugjabez100% (1)
- SeroquelDokumen2 halamanSeroqueldanaBelum ada peringkat
- CCMH Drug StudyDokumen5 halamanCCMH Drug StudyJoy JarinBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen6 halamanDrug StudySuzette Rae Tate0% (1)
- Paroxetine Wsiness, Diz ZinessDokumen3 halamanParoxetine Wsiness, Diz Zinessunkown userBelum ada peringkat
- Effectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorDokumen4 halamanEffectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorGwyn RosalesBelum ada peringkat
- NeostigmineDokumen4 halamanNeostigmineDonna Lyn B. DizonBelum ada peringkat
- Campral (Acamprosate Calcium)Dokumen1 halamanCampral (Acamprosate Calcium)E100% (1)
- Alprazolam Guide - Anxiety Drug DetailsDokumen2 halamanAlprazolam Guide - Anxiety Drug DetailsRenggaSuhardijantoBelum ada peringkat
- DRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseDokumen10 halamanDRUG STUDY - Docx Grand CaseAntonette PereyraBelum ada peringkat
- Olanzapine and Divalproex Sodium Drug InformationDokumen4 halamanOlanzapine and Divalproex Sodium Drug InformationJenny YenBelum ada peringkat
- DesyrelDokumen1 halamanDesyrelKatie McPeekBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug StudyJezen SucalitBelum ada peringkat
- Buspar (Buspirone)Dokumen1 halamanBuspar (Buspirone)EBelum ada peringkat
- Oxcarbazepine Drug DescriptionDokumen4 halamanOxcarbazepine Drug Descriptionahmad_makhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Vit B ComplexDokumen1 halamanVit B Complexpauchanmnl100% (1)
- ImipramineDokumen6 halamanImipramineMuhammed Faruk JambazBelum ada peringkat
- Mucosta film-coated tabDokumen7 halamanMucosta film-coated tabyvoniemaebruno0% (1)
- Drug Studies (Levodopa, Ropinirole, Rivastigmine Tatrate, Glucerna)Dokumen12 halamanDrug Studies (Levodopa, Ropinirole, Rivastigmine Tatrate, Glucerna)KBDBelum ada peringkat
- Pregnancy Risk Category B DIN RD TrimesterDokumen7 halamanPregnancy Risk Category B DIN RD TrimesterLheajane SocratesBelum ada peringkat
- Paxil: Generic Name: Paroxetine HydrochlorideDokumen3 halamanPaxil: Generic Name: Paroxetine Hydrochloridenasir khanBelum ada peringkat
- LansoprazoleDokumen3 halamanLansoprazoleJody FelizioBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen4 halamanDrug StudyXio PauBelum ada peringkat
- Thioridazine hydrochloride for schizophrenia treatmentDokumen1 halamanThioridazine hydrochloride for schizophrenia treatmentGritoBelum ada peringkat
- Biperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsDokumen1 halamanBiperiden Generic and Brand Names, Uses, Side EffectsMFQ.RN100% (2)
- ChlorpromazineDokumen1 halamanChlorpromazineimthebossBelum ada peringkat
- Calcitriol - Drug InformationDokumen13 halamanCalcitriol - Drug InformationNikesh DoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)Dokumen5 halamanDrug Study (Acamprosate (Campral) and Bupropion)kuro hanabusaBelum ada peringkat
- Epinephrine Drug StudyDokumen7 halamanEpinephrine Drug StudyJhoy Iris SarangayaBelum ada peringkat
- Chromium Picolinate Drug StudyDokumen1 halamanChromium Picolinate Drug StudyjoellaBelum ada peringkat
- HaloperidolDokumen2 halamanHaloperidolMikz JocomBelum ada peringkat
- Amlodipine BesylateDokumen2 halamanAmlodipine BesylateYakumaBelum ada peringkat
- Pregabalin An Anticonvulsant DrugDokumen2 halamanPregabalin An Anticonvulsant DrugmeimeiliuBelum ada peringkat
- Olmesartan Drug StudyDokumen2 halamanOlmesartan Drug StudydyndzBelum ada peringkat
- Filgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyDokumen3 halamanFilgrastim Boosts Neutrophil Recovery After ChemotherapyKyla Barrera TabungarBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen24 halamanDrug StudyMc Joewell HudencialBelum ada peringkat
- Citalopramhydrobromide CelexaDokumen3 halamanCitalopramhydrobromide CelexaKristi Wray100% (1)
- Sulfa Sal AzineDokumen2 halamanSulfa Sal Azineikke alma alukaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticDokumen2 halamanPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug StudyKristine Joy A. AniBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen7 halamanDrug StudyMariCris CaronanBelum ada peringkat
- Haloperidol Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanHaloperidol Drug StudyAysaaa DCBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study 2019Dokumen14 halamanDrug Study 2019Aubrey Unique Evangelista100% (1)
- CLOZAPINEDokumen5 halamanCLOZAPINEMar OrdanzaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen12 halamanDrug StudyMeraflor BahonsuaBelum ada peringkat
- Soumya Mary 1 Year MSC (N)Dokumen24 halamanSoumya Mary 1 Year MSC (N)Salman HabeebBelum ada peringkat