7 4
Diunggah oleh
Izwan HassanDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
7 4
Diunggah oleh
Izwan HassanHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Practice Problems # 2 Solution Question 1: 1.
For each of edge, screw and mixed dislocations, cite the relationship between the direction of the applied shear stress and the direction of dislocation line motion. 2. Briefly explain why some metals (e.g. lead and tin) do not strain harden when deformed at room temperature. 3. Briefly explain why small-angle grain boundaries are not as effective in interfering with the slip process as are high-angle grain boundaries. 4. Can dispersion-strengthened materials be used at high temperature? Explain. Solution 1. edge dislocation--parallel screw dislocation--perpendicular mixed dislocation--neither parallel nor perpendicular 2. Metals such as lead and tin do not strain harden at room temperature because their recrystallization temperatures lie below room temperature (Table 7.2). 3. Small-angle grain boundaries are not as effective in interfering with the slip process as are high-angle grain boundaries because there is not as much crystallographic misalignment in the grain boundary region for small-angle, and therefore not as much change in slip direction. 4. Yes. Because the particles used in dispersion strengthening are usually inert so they dont coarsen upon heating.
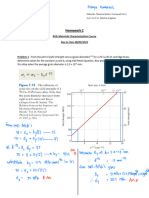
Question 2: 7.15 calister 8th A single crystal of a metal that has the FCC crystal structure is oriented such that a tensile stress is applied parallel to [110] direction. If the critical resolved shear stress for this material is 1.75 MPa, calculate the magnitude(s) of applied stress (es) necessary to cause slip to occur on the (111) plane in each of the , and directions.
Question 3: 7.24 calister 8th
The lower yield point for an iron that has an average grain diameter of 5x10-2 mm is 135 MPa (19,500 psi). At a grain diameter of 8x10-3 mm, the yield point increases to 260 MPa (37,500 psi). At what grain diameter will the lower yield point to be 205 MPa (30,000 psi)?
Question 4: A cylindrical 1040 steel rod having a minimum tensile strength of 865 MPa, a ductility of at least 10%EL, and a final diameter of 6.0mm is desired. Some 7.94mm diameter 1040 steel stock, which has been cold worked 20%, is available. Describe the procedure you would follow to obtain this material. Assume that 1040 steel experiences cracking at 40%CW. Solution
Question 5: 7.D1 calister 8th Determine whether it is possible to cold work 1040 steel so as to give a minimum Brinell hardness of 225, and at the same time have a ductility of at least 12% EL. Justify you decision.
Question 6: (a) Briefly cite the differences between recovery and recrystallization processes. (b) Explain the differences in grain structure for a metal that has been cold worked and one that has been cold worked and then recrystallized. (a)
(b) 7.35 During cold-working, the grain structure of the metal has been distorted to accommodate the
deformation. Recrystallization produces grains that are equiaxed and smaller than the parent grains.
Question 7: 7.38 calister 8th The average grain diameter for a brass material was measured as a function of time at 6500C, which is shown in the following table at two different times:
Time (min) 30 90
GrainDiameter (mm) 3.9x102 6.6x102
(a) What was the original grain diameter?
(b) What grain diameter would you predict after 150 min at 650C?
Question 8: 16.12 calister 8th .. In an aligned and continuous glass fiber-reinforced nylon 6, 6 composite, the fibers are to carry 94% of a load applied in the longitudinal direction. (a) Using the data provided, determine the volume fraction of fibers that will be required. (b) What will be the tensile strength of this composite? Assume that the matrix stress at fiber failure is 30 MPa (4350 psi).
ModulusofElasticity (GPa(psi)) 72.5(10.5x106) 3.0(4.35x105) Tensile Strength (MPa(psi)) 3400(490,000) 76(11,000)
Glassfiber Nylon6,6
Note: Ans. for a) Vf = 0.39 And for b) *cl = 1344.3 MPa
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Assignment ProcessDokumen2 halamanAssignment ProcessMuhammad Nazmul Hassan KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanical Properties of Metals Chapter SolutionsDokumen14 halamanMechanical Properties of Metals Chapter SolutionsJesse McClure100% (3)
- Mechanical Properties of Metals ChapterDokumen14 halamanMechanical Properties of Metals Chaptersgarrab100% (1)
- MSE 227 Chapter 8 HWDokumen1 halamanMSE 227 Chapter 8 HWjosewilliam85Belum ada peringkat
- MECH2300 TEST 1 - Paper B AnswersDokumen8 halamanMECH2300 TEST 1 - Paper B Answersbgrin7Belum ada peringkat
- Material Science II 2011 Final Exam With AnswersDokumen9 halamanMaterial Science II 2011 Final Exam With AnswersAndre Anil GovinathanBelum ada peringkat
- Segregation Stabilizes Nanocrystalline BDokumen5 halamanSegregation Stabilizes Nanocrystalline BmehecoBelum ada peringkat
- Excersises For Essentials and Engineering of MaterialsDokumen5 halamanExcersises For Essentials and Engineering of MaterialsBraulio BolañosBelum ada peringkat
- Test 2 SolutionDokumen7 halamanTest 2 SolutionLeng ChaiBelum ada peringkat
- Lab. 2 - Strengthing Materials by Cold WorkingDokumen4 halamanLab. 2 - Strengthing Materials by Cold WorkingDonBelum ada peringkat
- TUT Physical Metallurgy Test 3: Slip Systems, Yield Strength, FractureDokumen4 halamanTUT Physical Metallurgy Test 3: Slip Systems, Yield Strength, FractureJonathan LukwichiBelum ada peringkat
- Heat-Treatment of High Carbon Steel Wire - PatentingDokumen4 halamanHeat-Treatment of High Carbon Steel Wire - Patentingعزت عبد المنعم100% (1)
- High Strength and Ductility of Nanostructured Al-Based Alloy, Prepared by High-Pressure TechniqueDokumen4 halamanHigh Strength and Ductility of Nanostructured Al-Based Alloy, Prepared by High-Pressure TechniqueviniciushiperBelum ada peringkat
- AISI 1015 Carbon Steel NitridedDokumen4 halamanAISI 1015 Carbon Steel NitridedRamil SerdanBelum ada peringkat
- CH 08Dokumen8 halamanCH 08Ingi Abdel Aziz Srag0% (1)
- ME2151Dokumen6 halamanME2151Delroy JqBelum ada peringkat
- TUGAS-03 Metlas PDFDokumen1 halamanTUGAS-03 Metlas PDFyanuarBelum ada peringkat
- TUGAS-03 MetlasDokumen1 halamanTUGAS-03 MetlasMr. Everywhere100% (1)
- 3094 HW ECBDokumen2 halaman3094 HW ECBradarskiBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Interlamellar Spacing On The Delamination of Pearlitic Steel WiresDokumen6 halamanEffect of Interlamellar Spacing On The Delamination of Pearlitic Steel WiresSmruti Ranjan PattanayakBelum ada peringkat
- Boateng, Stephanie (0377091) - ENGR3536 - Assign. 1 PDFDokumen4 halamanBoateng, Stephanie (0377091) - ENGR3536 - Assign. 1 PDFStephanie BoatengBelum ada peringkat
- HW #7Dokumen4 halamanHW #7c_sierra34Belum ada peringkat
- MECH 390 - PRACTICE 1 - FALL 2011Dokumen5 halamanMECH 390 - PRACTICE 1 - FALL 2011Abeer AlnaqbiBelum ada peringkat
- Metal Forming Processes GuideDokumen4 halamanMetal Forming Processes GuideRenaldi Khaesar KumaraBelum ada peringkat
- High-Cycle Fatigue Properties at Cryogenic Temperatures in INCONEL 718 Nickel-Based SuperalloyDokumen4 halamanHigh-Cycle Fatigue Properties at Cryogenic Temperatures in INCONEL 718 Nickel-Based SuperalloyB Bala Venkata GaneshBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Manufacturing ScienceDokumen3 halamanAdvanced Manufacturing Sciencemukesh3021Belum ada peringkat
- Assignment 2Dokumen2 halamanAssignment 2nik farisBelum ada peringkat
- SI-Kim-2002-Continuous Dynamic Recrystallization of AISI 430 Ferritic St...Dokumen7 halamanSI-Kim-2002-Continuous Dynamic Recrystallization of AISI 430 Ferritic St...鄭勝元Belum ada peringkat
- Presentation17 Hardening or Strenghening PDFDokumen23 halamanPresentation17 Hardening or Strenghening PDFMahadi HasanBelum ada peringkat
- Improvement of Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) Resistance of A 7150 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy byDokumen5 halamanImprovement of Stress Corrosion Cracking (SCC) Resistance of A 7150 Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy bySundaraPandiyanBelum ada peringkat
- Casting tools and processes explainedDokumen9 halamanCasting tools and processes explainedEswaran ManakorBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Science AssignmentsDokumen1 halamanMaterials Science AssignmentsGajanan SawantBelum ada peringkat
- Brass AnnealingDokumen11 halamanBrass AnnealingChristos KalavrytinosBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment No. 1 Materials Science and MetallurgyDokumen2 halamanAssignment No. 1 Materials Science and MetallurgySamruddhi MirganeBelum ada peringkat
- ESS352024 Prob 1Dokumen2 halamanESS352024 Prob 1潘詩媛Belum ada peringkat
- HW1 Solutions S14 MAE 3344Dokumen4 halamanHW1 Solutions S14 MAE 3344trapstar15Belum ada peringkat
- Tính chất Vật liệu Bài tậpDokumen26 halamanTính chất Vật liệu Bài tậpHoàng BeeBelum ada peringkat
- Homework#6 F14 - M E 311Dokumen1 halamanHomework#6 F14 - M E 311Jeremy PriestBelum ada peringkat
- 2022-Dec ME-312 53Dokumen2 halaman2022-Dec ME-312 53Aakash TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Effects of FSW Parameters on Microstructures and Properties of Brass JointsDokumen4 halamanEffects of FSW Parameters on Microstructures and Properties of Brass JointsAdi PriyantoBelum ada peringkat
- APSC 278 Midterm Feb 13 2013 SolutionsDokumen9 halamanAPSC 278 Midterm Feb 13 2013 SolutionsykfungBelum ada peringkat
- Cold WorkingDokumen7 halamanCold WorkingShahir Afif IslamBelum ada peringkat
- Properties of ElectrodepositsDokumen27 halamanProperties of Electrodepositsjvo917Belum ada peringkat
- RVIE - MC - Homework 2 - PichayaDokumen7 halamanRVIE - MC - Homework 2 - Pichayapichaya kumarnsitBelum ada peringkat
- InTech-Recrystallization of Dispersion Strengthened Copper AlloysDokumen21 halamanInTech-Recrystallization of Dispersion Strengthened Copper AlloysbinkinBelum ada peringkat
- Kuliah Ke-9 Strengthening MechanismDokumen48 halamanKuliah Ke-9 Strengthening MechanismNixonBelum ada peringkat
- High-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of Type 316L Stainless SteelDokumen9 halamanHigh-Cycle Fatigue Behavior of Type 316L Stainless SteelDeva RajBelum ada peringkat
- Liu 2016Dokumen8 halamanLiu 2016Adisya Yuliasari RohimanBelum ada peringkat
- Finite Element Modelling of Concurrent Deformation and Transformation in Metastable SteelsDokumen13 halamanFinite Element Modelling of Concurrent Deformation and Transformation in Metastable Steelsklomps_jrBelum ada peringkat
- Wear Behavior of 100cr6-PolatDokumen6 halamanWear Behavior of 100cr6-PolatAntonioBelum ada peringkat
- Study The Mechanical Properties and Numerical Evaluation of Friction Stir Processing (FSP) For 6061-T6 Aluminum AlloysDokumen10 halamanStudy The Mechanical Properties and Numerical Evaluation of Friction Stir Processing (FSP) For 6061-T6 Aluminum AlloysayadBelum ada peringkat
- Problems 4012 PDFDokumen8 halamanProblems 4012 PDFjonthemesBelum ada peringkat
- Rolling 1Dokumen142 halamanRolling 1atul bartyBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of Heat and Surface Treatment PDFDokumen45 halamanIntroduction of Heat and Surface Treatment PDFScott BakerBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Tempering Pass On HSLA-80 Steel HAZ MicrostructuresDokumen8 halamanEffect of Tempering Pass On HSLA-80 Steel HAZ MicrostructuresElias KapaBelum ada peringkat
- HW#1 Mse104Dokumen2 halamanHW#1 Mse104Dendi ZezimaBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Materials Questions and AnswersDokumen4 halamanEngineering Materials Questions and AnswersEmıły WınıfredBelum ada peringkat
- Friction Stir Welding of High Strength 7XXX Aluminum AlloysDari EverandFriction Stir Welding of High Strength 7XXX Aluminum AlloysBelum ada peringkat
- Class XII PHY - EDDokumen7 halamanClass XII PHY - EDsampoornaswayamBelum ada peringkat
- Complex Number Exercise Book PDFDokumen26 halamanComplex Number Exercise Book PDFRitik KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Name CompilationDokumen490 halamanName CompilationMark Taylor100% (1)
- DGS PBDokumen103 halamanDGS PBibraheemBelum ada peringkat
- Osmaan Shamsiddeen: Work History Personal InfoDokumen1 halamanOsmaan Shamsiddeen: Work History Personal InfoOsmaan ShamsiddeenBelum ada peringkat
- ACE Personal Trainer Manual Chapter 13Dokumen59 halamanACE Personal Trainer Manual Chapter 13Đạt NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Deflected Profile of A BeamDokumen2 halamanDeflected Profile of A BeamPasindu MalithBelum ada peringkat
- Sales & Distribution Management Presentation NewDokumen35 halamanSales & Distribution Management Presentation NewVivek Sinha0% (1)
- Assignment of English Spesialization Biography of B. J. HabibieDokumen3 halamanAssignment of English Spesialization Biography of B. J. HabibieFikri FauzanBelum ada peringkat
- All About Mahalaya PakshamDokumen27 halamanAll About Mahalaya Pakshamaade100% (1)
- Worldcom, Inc.: Corporate Bond Issuance: CompanyDokumen14 halamanWorldcom, Inc.: Corporate Bond Issuance: CompanyLe Nguyen Thu UyenBelum ada peringkat
- The Grand Landscape - Ian PlantDokumen145 halamanThe Grand Landscape - Ian PlantJohanny Bravo100% (1)
- Validate Analytical MethodsDokumen9 halamanValidate Analytical MethodsFernando Silva BetimBelum ada peringkat
- Activity 1.docx AjDokumen2 halamanActivity 1.docx AjMaya BabaoBelum ada peringkat
- Neotextil 8: Installation and Activation GuideDokumen21 halamanNeotextil 8: Installation and Activation GuideRamesh PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Work of Juan TamarizDokumen6 halamanWork of Juan Tamarizmrbookman3Belum ada peringkat
- Development of Overall Audit StrategyDokumen4 halamanDevelopment of Overall Audit StrategyPhrexilyn PajarilloBelum ada peringkat
- Hrm-Group 1 - Naturals Ice Cream FinalDokumen23 halamanHrm-Group 1 - Naturals Ice Cream FinalHarsh parasher (PGDM 17-19)Belum ada peringkat
- Silver Bells Convent School Annual Examination 2021-22: Duration:2hours Subject: Science M. M.: 40 Class: IXDokumen2 halamanSilver Bells Convent School Annual Examination 2021-22: Duration:2hours Subject: Science M. M.: 40 Class: IXAnkit SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Monroes Motivated Sequence LessonDokumen3 halamanMonroes Motivated Sequence Lessonapi-257123630Belum ada peringkat
- Green Schools Project LAC PlanDokumen2 halamanGreen Schools Project LAC PlanJolly Mar Tabbaban Mangilaya100% (1)
- Heat Transfer DoeDokumen32 halamanHeat Transfer DoeArt RmbdBelum ada peringkat
- System ThinkingDokumen18 halamanSystem Thinkingpptam50% (2)
- 9th Science Term 3 Model Question Paper English MediumDokumen3 halaman9th Science Term 3 Model Question Paper English MediumStalin JesudossBelum ada peringkat
- Frusciante InterviewsDokumen21 halamanFrusciante Interviewslukiguitar100% (1)
- BiotinDokumen10 halamanBiotinMohamed Aslam ABelum ada peringkat
- Your IndiGo Itinerary July - SN9NVMDokumen5 halamanYour IndiGo Itinerary July - SN9NVMaagama gurukulBelum ada peringkat
- DECIDE ChecklistDokumen2 halamanDECIDE ChecklistGuilioBelum ada peringkat
- Paul of Aegina LaminectomyDokumen9 halamanPaul of Aegina LaminectomypepepartaolaBelum ada peringkat
- Anxiety Free - Stop Worrying and - McKeown, PatrickDokumen237 halamanAnxiety Free - Stop Worrying and - McKeown, PatrickLoboCamon100% (1)