Functional Classification of Highways
Diunggah oleh
Jester AbucayDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Functional Classification of Highways
Diunggah oleh
Jester AbucayHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Functional Classification of Highways Functional Classification is the process by which streets and highways are grouped into classes,
or systems, according to the character of service they are intended to provide. There are three primary federal highway functional classifications: arterial, collector, and local roads. All streets and highways are grouped into one of these classes, depending on the character of the traffic (i.e., local or long distance) and the degree of land access that they allow. These classifications are described in Table 1. Functional System Services Provided Arterial Provides the highest level of service at the greatest speed for the longest uninterrupted distance, with some degree of access control. Collector Provides a less highly developed level of service at a lower speed for shorter distances by collecting traffic from local roads and connecting them with arterials. Local Consists of all roads not defined as arterials or collectors; primarily provides access to land with little or no through movement. Table 1: Functional Classification Systems Typically, travelers will use a combination of arterial, collector, and local roads for their trips. Each type of road has a specific purpose or function. Some provide land access to serve each end of the trip. Others provide travel mobility at varying levels, which is needed en route. The Functional Classification system can be further broken down into rural and urban classifications, and there are sub-classifications within these groupings as well. (See Exhibit 1) For more detailed information, please see Highway Functional Classification: Concepts, Criteria and Procedures. Rev. March 1989. Exhibit 1 The Transportation Planning Branch of NCDOT is responsible for the Functional Classification updates for North Carolina. The NCDOT GIS Unit prepares digital mapping. In the 17 Urbanized Areas or Metropolitan Planning Organizations (MPOs) (population >50,000) the changes were mutually established between the MPOs and the NCDOT. Of the 90 Urban Clusters within the State (population between 2500-50000), 56 were processed as Urban Clusters and the remaining UCs with population less than 5000 were processed as rural areas. Our 2005/ 2006 update was initiated due to the Decennial Census revision of Urban Area Boundary. In the May 1, 2002, Federal Register, the US Bureau of the Census issued the designations of Urbanized Areas (UZAs) and Urban Clusters (UCs) based on the 2000 Census. While the USDOT has no direct role in the designation of these areas, they are critical to the administration of the surface transportation program. Key FHWA/FTA program impacts for planning and environmental are: designation of MPOs and application of metropolitan planning requirements; designation of Transportation Management areas (TMA); application of Air Quality Conformity requirements; and, funding availability.
CHAPTER 2. INTRODUCTION TO HIGHWAY ENGINEERING NPTEL May 24, 2006 Chapter 2 Introduction to Highway Engineering 2.1 Overview Road transport is one of the most common mode of transport. Roads in the form of trackways, human pathways etc. were used even from the pre-historic times. Since then many experiments were going on to make the riding safe and comfort. Thus road construction became an inseparable part of many civilizations and empires. In this chapter we will see the di_erent generations of road and their characteristic features. Also we will discuss about the highway planning in India. 2.2 History of highway engineering The history of highway enginnering gives us an idea about the roads of ancient times. Roads in Rome were constructed in a large scale and it radiated in many directions helping them in military operations. Thus they are considered to be pioneers in road construction. In this section we will see in detail about Ancient roads, Roman roads, British roads, French roads etc. 2.2.1 Ancient Roads The _rst mode of transport was by foot. These human pathways would have been developed for speci_c purposes leading to camp sites, food, streams for drinking water etc. The next major mode of transport was the use of animals for transporting both men and materials. Since these loaded animals required more horizontal and vertical clearances than the walking man, track ways emerged. The invention of wheel in Mesopotamian civilization led to the development of animal drawn vehicles. Then it became necessary that the road surface should be capable of carrying greater loads. Thus roads with harder surfaces emerged. To provide adequate strength to carry the wheels, the new ways tended to follow the sunny drier side of a path. These have led to the development of foot-paths. After the invention of wheel, animal drawn vehicles were developed and the need for hard surface road emerged. Traces of such hard roads were obtained from various ancient civilization dated as old as 3500 BC. The earliest authentic record of road was found from Assyrian empire constructed about 1900 BC. 2.2.2 Roman roads The earliest large scale road construction is attributed to Romans who constructed an extensive system of roads radiating in many directions from Rome. They were a remarkable achievement and provided travel times across Introduction to Transportation Engineering 2.1 Tom V. Mathew and K V Krishna Rao CHAPTER 2. INTRODUCTION TO HIGHWAY ENGINEERING NPTEL May 24, 2006 Large stone slabs 1015 cm thick Total thickness 0.751.2m in Lime cocrete
Figure 2:2: French roads Europe, Asia minor, and north Africa. Romans recognized that the fundamentals of good road construction were to provide good drainage, good material and good workmanship. Their roads were very durable, and some are still existing. Roman roads were always constructed on a _rm - formed subgrade strengthened where necessary with wooden piles. The roads were bordered on both sides by longitudinal drains. The next step was the construction of the agger. This was a raised formation up to a 1 meter high and 15 m wide and was constructed with materials excavated during the side drain construction. This was then topped with a sand leveling course. The agger contributed greatly to moisture control in the pavement. The pavement structure on the top of the agger varied greatly. In the case of heavy tra_c, a surface course of large 250 mm thick hexagonal ag stones were provided. A typical cross section of roman road is given in Figure 2:1 The main features of the Roman roads are that they were built straight regardless of gradient and used heavy foundation stones at the bottom. They mixed lime and volcanic puzzolana to make mortar and they added gravel to this mortar to make concrete. Thus concrete was a major Roman road making innovation. 2.2.3 French roads The next major development in the road construction occurred during the regime of Napoleon. The signi_cant contributions were given by Tresaguet in 1764 and a typical cross section of this road is given in Figure 2:2. He developed a cheaper method of construction than the lavish and locally unsuccessful revival of Roman practice. The pavement used 200 mm pieces of quarried stone of a more compact form and shaped such that they had at least one at side which was placed on a compact formation. Smaller pieces of broken stones were then compacted into the spaces between larger stones to provide a level surface. Finally the running layer was made with a layer of 25 mm sized broken stone. All this structure was placed in a trench in order to keep the running surface level with the surrounding country side. This created major drainage problems which were counteracted by making the surface as impervious as possible, cambering the surface and providing deep side ditches. He gave Introduction to Transportation Engineering 2.2 Tom V. Mathew and K V Krishna Rao CHAPTER 2. INTRODUCTION TO HIGHWAY ENGINEERING NPTEL May 24, 2006
50mm Broken Stones, 100mm thick 37.5mm Broken Stones, 100mm thick Surface Course 20mm, 50mm thick Cross slope 4.5 m Side drain Compacted Subgrade slope 1:36
Figure 2:3: British roads much importance for drainage. He also enunciated the necessity for continuous organized maintenance, instead of intermittent repairs if the roads were to be kept usable all times. For this he divided the roads between villages into sections of such length that an entire road could be covered by maintenance men living nearby. 2.2.4 British roads The British government also gave importance to road construction. The British engineer John Macadam introduced what can be considered as the _rst scienti_c road construction method. Stone size was an important element of Macadam recipe. By empirical observation of many roads,he came to realize that 250 mm layers of well compacted broken angular stone would provide the same strength and sti_ness and a better running surface than an expensive pavement founded on large stone blocks. Thus he introduced an economical method of road construction. The mechanical interlock between the individual stone pieces provided strength and sti_ness to the course. But the inter particle friction abraded the sharp interlocking faces and partly destroy the e_ectiveness of the course. This e_ect was overcome by introducing good quality interstitial _ner material to produce a wellgraded mix. Such mixes also proved less permeable and easier to compact. A typical cross section of British roads is given in Figure 2:3. 2.2.5 Modern roads The modern roads by and large follow Macadam's construction method. Use of bituminous concrete and cement concrete are the most important developments. Various advanced and cost-e_ective construction technologies are used. Development of new equipments help in the faster construction of roads. Many easily and locally available materials are tested in the laboratories and then implemented on roads for making economical and durable pavements. Scope of transportation system has developed very largely. Population of the country is increasing day by day. The life style of people began to change. The need for travel to various places at faster speeds also increased. This increasing demand led to the emergence of other modes of transportation like railways and travel by air. While the above development in public transport sector was taking place,the development in private transport was at a much faster rate mainly because of its advantages like accessibility, privacy, exibility, convenience and comfort. This led to the increase in vehicular tra_c especially in private transport network. Thus road space available was becoming insu_cient to meet the growing demand of tra_c and congestion started. In addition, chances for accidents also increased. This has led to the increased attention towards control of vehicles so Introduction to Transportation Engineering 2.3 Tom V. Mathew and K V Krishna Rao CHAPTER 2. INTRODUCTION TO HIGHWAY ENGINEERING NPTEL May 24, 2006 that the transport infrastructure was optimally used. Various control measures like tra_c signals, providing roundabouts and medians, limiting the speed of vehicle at speci_c zones etc. were implemented. With the advancement of better roads and e_cient control, more and more investments were made in the
road sector especially after the World wars. These were large projects requiring large investment. For optimal utilization of funds, one should know the travel pattern and travel behavior. This has led to the emergence of transportation planning and demand management. 2.3 Highway planning in India Excavations in the sites of Indus valley, Mohenjo-dero and Harappan civilizations revealed the existence of planned roads in India as old as 2500-3500 BC. The Mauryan kings also built very good roads. Ancient books like Arthashastra written by Kautilya, a great administrator of the Mauryan times, contained rules for regulating tra_c, depths of roads for various purposes, and punishments for obstructing tra_c. During the time of Mughal period, roads in India were greatly improved. Roads linking North-West and the Eastern areas through gangetic plains were built during this time. After the fall of the Mughals and at the beginning of British rule, many existing roads were improved. The construction of Grand-Trunk road connecting North and South is a major contribution of the British. However, the focus was later shifted to railways, except for feeder roads to important stations. 2.3.1 Modern developments The _rst World war period and that immediately following it found a rapid growth in motor transport. So need for better roads became a necessity. For that, the Government of India appointed a committee called Road development Committee with Mr.M.R. Jayakar as the chairman. This committee came to be known as Jayakar committee. Jayakar Committee In 1927 Jayakar committee for Indian road development was appointed. The major recommendations and the resulting implementations were: _ Committee found that the road development of the country has become beyond the capacity of local governments and suggested that Central government should take the proper charge considering it as a matter of national interest. _ They gave more stress on long term planning programme, for a period of 20 years (hence called twenty year plan) that is to formulate plans and implement those plans with in the next 20 years. _ One of the recommendations was the holding of periodic road conferences to discuss about road construction and development. This paved the way for the establishment of a semi-o_cial technical body called Indian Road Congress (IRC) in 1934 _ The committee suggested imposition of additional taxation on motor transport which includes duty on motor spirit, vehicle taxation, license fees for vehicles plying for hire. This led to the introduction of a development fund called Central road fund in 1929. This fund was intended for road development. Introduction to Transportation Engineering 2.4 Tom V. Mathew and K V Krishna Rao CHAPTER 2. INTRODUCTION TO HIGHWAY ENGINEERING NPTEL May 24, 2006 _ A dedicated research organization should be constituted to carry out research and development work. This resulted in the formation of Central Road Research Institute (CRRI) in 1950. Nagpur road congress 1943 The second World War saw a rapid growth in road tra_c and this led to the deterioration in the condition of roads. To discuss about improving the condition of roads, the government convened a conference of chief engineers of provinces at Nagpur in 1943. The result of the conference is famous as the Nagpur plan. _ A twenty year development programme for the period (1943-1963) was _nalized. It was the _rst attempt to prepare a co-ordinated road development programme in a planned manner. _ The roads were divided into four classes: { National highways which would pass through states, and places having national importance for
strategic, administrative and other purposes. { State highways which would be the other main roads of a state. { District roads which would take tra_c from the main roads to the interior of the district . According to the importance, some are considered as major district roads and the remaining as other district roads. { Village roads which would link the villages to the road system. _ The committee planned to construct 2 lakh kms of road across the country within 20 years. _ They recommended the construction of star and grid pattern of roads throughout the country. _ One of the objective was that the road length should be increased so as to give a road density of 16kms per 100 sq.km Bombay road congress 1961 The length of roads envisaged under the Nagpur plan was achieved by the end of it, but the road system was de_cient in many respects. The changed economic, industrial and agricultural conditions in the country warranted a review of the Nagpur plan. Accordingly a 20-year plan was drafted by the Roads wing of Government of India, which is popularly known as the Bombay plan. The highlights of the plan were: _ It was the second 20 year road plan (1961-1981) _ The total road length targeted to construct was about 10 lakhs. _ Rural roads were given speci_c attention. Scienti_c methods of construction was proposed for the rural roads. The necessary technical advice to the Panchayaths should be given by State PWD's. _ They suggested that the length of the road should be increased so as to give a road density of 32kms/100 sq.km _ The construction of 1600 km of expressways was also then included in the plan. Introduction to Transportation Engineering 2.5 Tom V. Mathew and K V Krishna Rao CHAPTER 2. INTRODUCTION TO HIGHWAY ENGINEERING NPTEL May 24, 2006 Lucknow road congress 1984 This plan has been prepared keeping in view the growth pattern envisaged in various _elds by the turn of the century. Some of the salient features of this plan are as given below: _ This was the third 20 year road plan (1981-2001). It is also called Lucknow road plan. _ It aimed at constructing a road length of 12 lakh kilometres by the year 1981 resulting in a road density of 82kms/100 sq.km _ The plan has set the target length of NH to be completed by the end of seventh, eighth and ninth _ve year plan periods. _ It aims at improving the transportation facilities in villages, towns etc. such that no part of country is farther than 50 km from NH. _ One of the goals contained in the plan was that expressways should be constructed on major tra_c corridors to provide speedy travel. _ Energy conservation, environmental quality of roads and road safety measures were also given due importance in this plan. 2.4 Summary This lecture cover a brief history of highway engineering, highlighting the developments of road construction. Signi_cant among them are Roman, French, and British roads. British road construction practice developed by Macadam is the most scienti_c and the present day roads follows this pattern. The highway development and classi_cation of Indian roads are also discussed. The major classes of roads include National Highway, State highway, District roads, and Village roads. Finally, issues in highway alignment are discussed.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Highway HistoryDokumen3 halamanHighway HistoryCHARLES MAINABelum ada peringkat
- CE 518 NotepdfDokumen56 halamanCE 518 NotepdfVictor Musa OgimaBelum ada peringkat
- Nptel ceTEI L02 PDFDokumen7 halamanNptel ceTEI L02 PDFdkavitiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1Dokumen8 halamanChapter 1Anirudh AnirudhpBelum ada peringkat
- Unit I Highway Planning and AlignmentDokumen29 halamanUnit I Highway Planning and AlignmentKandasamy AsohanBelum ada peringkat
- Highway Engineering Interview QuestionsDokumen6 halamanHighway Engineering Interview Questionsmosammat sumaBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 (INTRODUCTION OF HIGHWAY ENGINEERING) - JLN RayaDokumen21 halamanUnit 1 (INTRODUCTION OF HIGHWAY ENGINEERING) - JLN RayaZara Nabilah83% (6)
- 2017 Highway EngineeringDokumen212 halaman2017 Highway EngineeringChristopher Joshua MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Highway Engineering 1 PDF FreeDokumen212 halamanHighway Engineering 1 PDF FreeMarjon MamangunBelum ada peringkat
- Highway and Transportation Notes 1Dokumen79 halamanHighway and Transportation Notes 1dody freestyleBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 1 IntroductionDokumen12 halamanCHAPTER 1 IntroductionMul'ataa Vission AbdiisaaBelum ada peringkat
- 2 History of Highway EngineeringDokumen16 halaman2 History of Highway EngineeringSanderson BautistaBelum ada peringkat
- Highways Module 1Dokumen7 halamanHighways Module 1Eugene TongolBelum ada peringkat
- Highway Engineering 1Dokumen212 halamanHighway Engineering 1Agerico Funelas100% (1)
- Equipments, Methods, and Innovative Practices in Road Construction and MaintenanceDokumen16 halamanEquipments, Methods, and Innovative Practices in Road Construction and MaintenanceLoveLee Aquino NievesBelum ada peringkat
- He NotesDokumen207 halamanHe NotesPG - ARMY f fBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Introduction To Highway EngineeringDokumen19 halaman1 Introduction To Highway EngineeringLynas Beh TahanBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Highway EngineeringDokumen15 halamanWhat Is Highway EngineeringSyazwi Akram Ab RazakBelum ada peringkat
- Welcome: Highway Engineering Code No. (CM 304)Dokumen16 halamanWelcome: Highway Engineering Code No. (CM 304)narasimhanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 (Development of Roads and Highway) PDFDokumen4 halamanLecture 1 (Development of Roads and Highway) PDFمصطفى عليBelum ada peringkat
- Transportation Engineering NotesDokumen19 halamanTransportation Engineering NotesMahesh Ramteke100% (1)
- CE43-A/B Principles of Transportation: Instructor: Engr. Giovanni B. Narciso, M'ENG. (CE), Mat'l. Eng'rDokumen55 halamanCE43-A/B Principles of Transportation: Instructor: Engr. Giovanni B. Narciso, M'ENG. (CE), Mat'l. Eng'rMoira Elizabeth SyBelum ada peringkat
- M.Tech Assignment Report: Under Lying Foundation."Dokumen58 halamanM.Tech Assignment Report: Under Lying Foundation."Harsh DeepBelum ada peringkat
- Transportation SystemDokumen3 halamanTransportation SystemEdis HrnjicaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Transportation Planning and Engineering: Components of Transportation SystemDokumen22 halamanIntroduction To Transportation Planning and Engineering: Components of Transportation SystemJudd Cortez100% (1)
- Hre Research#1Dokumen3 halamanHre Research#1Nivea ZuniegaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Highway & Traffic: Topic 1Dokumen75 halamanIntroduction To Highway & Traffic: Topic 1Nur ShazrinBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Highway Engineering: 1. Importance of TransportationDokumen7 halamanIntroduction To Highway Engineering: 1. Importance of TransportationFrancis AguisandaBelum ada peringkat
- Module 2 Highway Development and Planning Reviewer Partialy FinishedDokumen8 halamanModule 2 Highway Development and Planning Reviewer Partialy FinisheddenzzaidBelum ada peringkat
- Trésaguet RoadsDokumen2 halamanTrésaguet Roadsstacy basalanBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Tunnels and GeologyDokumen7 halaman12 Tunnels and Geology22100204Belum ada peringkat
- Highway and RailroadsDokumen2 halamanHighway and RailroadsWendelyn P. GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- Batch-19 Rigid PavementDokumen48 halamanBatch-19 Rigid PavementShiva ShankarBelum ada peringkat
- Transportation Engineering NotesDokumen110 halamanTransportation Engineering NotesrpsirBelum ada peringkat
- Rigid Pavement Thesis - 2Dokumen12 halamanRigid Pavement Thesis - 2san htet aung100% (1)
- Unit 2Dokumen22 halamanUnit 2tausifr535Belum ada peringkat
- Unit - I TransportationDokumen90 halamanUnit - I TransportationSunil PadmanabhamBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Highway Engineering & Railroad EngineeringDokumen44 halamanIntroduction To Highway Engineering & Railroad EngineeringKyle Ydle Vinne RespicioBelum ada peringkat
- History of Highway Engineering Ancient Roads by FootDokumen6 halamanHistory of Highway Engineering Ancient Roads by FootCristina Mauren P. PajesBelum ada peringkat
- History of PavementDokumen8 halamanHistory of PavementPradip SarkerBelum ada peringkat
- HE Unit 1Dokumen20 halamanHE Unit 1isvaryaBelum ada peringkat
- The Importance of Compaction From An Historical Perspective: Lucas.e@uwp - Co.zaDokumen10 halamanThe Importance of Compaction From An Historical Perspective: Lucas.e@uwp - Co.zaYakkoBelum ada peringkat
- Pavement Engineering Lec-1Dokumen16 halamanPavement Engineering Lec-1Aqib HussainBelum ada peringkat
- Transportation Engineering - I - CHAPTER-1Dokumen11 halamanTransportation Engineering - I - CHAPTER-1rpsirBelum ada peringkat
- History of Road1Dokumen10 halamanHistory of Road1Heart HackerBelum ada peringkat
- 02 Historical BackgroundDokumen33 halaman02 Historical BackgroundShikha Mrunal MeshramBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Highway Engineering: 2.2.1 Ancient RoadsDokumen3 halamanIntroduction To Highway Engineering: 2.2.1 Ancient RoadsSaoirseBelum ada peringkat
- Transportation Engineering-I PDFDokumen89 halamanTransportation Engineering-I PDFAnonymous BC0yu9HHHBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 1 (Road Construction Development)Dokumen18 halamanLecture 1 (Road Construction Development)Moneer MohamedBelum ada peringkat
- CHAPTER 1 NotesDokumen4 halamanCHAPTER 1 NotesSunflowerBelum ada peringkat
- Roman Construction MethodsDokumen54 halamanRoman Construction MethodsAnonymous MklNL77Belum ada peringkat
- What Is Road?Dokumen12 halamanWhat Is Road?Edmar TabinasBelum ada peringkat
- Roads Construction InsuranceDokumen48 halamanRoads Construction InsurancevojislavsBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - 1Dokumen68 halamanUnit - 1Anshul TiwariBelum ada peringkat
- Highway and Traffic EngineeringDokumen49 halamanHighway and Traffic EngineeringNoorAzalinaShafika74% (23)
- Module 1-3Dokumen6 halamanModule 1-3HONEY LYN GUTIERREZBelum ada peringkat
- 1-Ce103-1 Introduction To Highway and Railroad EngineeringDokumen25 halaman1-Ce103-1 Introduction To Highway and Railroad EngineeringUnesca TeeBelum ada peringkat
- Deconstructing the High Line: Postindustrial Urbanism and the Rise of the Elevated ParkDari EverandDeconstructing the High Line: Postindustrial Urbanism and the Rise of the Elevated ParkPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1)
- Portals 0 Files PDF 318-Example-1 RF R1Dokumen11 halamanPortals 0 Files PDF 318-Example-1 RF R1Adil Rasheed KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Topic12 SeismicDesignofMasonryStructuresHandoutsDokumen23 halamanTopic12 SeismicDesignofMasonryStructuresHandoutsjh50000Belum ada peringkat
- STM Ec2Dokumen39 halamanSTM Ec2Vincenzo MondelliBelum ada peringkat
- Surcharges Per CaltransDokumen11 halamanSurcharges Per CaltransManav SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- STM Model 3Dokumen6 halamanSTM Model 3Jester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- Wind Loads Per ASCE 7-02Dokumen2 halamanWind Loads Per ASCE 7-02Jester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- 2008 SC Paper 2GreenWinarta 13dec07 PDFDokumen9 halaman2008 SC Paper 2GreenWinarta 13dec07 PDFJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- CMU Block Dimensions: # Blocks Dist (In) Dist (Ft-In) # Blocks Dist (In) Dist (Ft-In)Dokumen1 halamanCMU Block Dimensions: # Blocks Dist (In) Dist (Ft-In) # Blocks Dist (In) Dist (Ft-In)Jester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- WIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Wall Components and Cladding: Input DataDokumen3 halamanWIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Wall Components and Cladding: Input DataJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- IBC2009 Equivalent Static Seismic Loading PDFDokumen1 halamanIBC2009 Equivalent Static Seismic Loading PDFJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- SAMPLE HILTI SolutionDokumen6 halamanSAMPLE HILTI SolutionJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- WIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Wall Components and Cladding: Input DataDokumen3 halamanWIND LOADING ANALYSIS - Wall Components and Cladding: Input DataJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- Allowable Stress Design: BD A E E NDokumen14 halamanAllowable Stress Design: BD A E E NyhproBelum ada peringkat
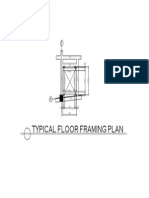
- Typical FramingDokumen1 halamanTypical FramingJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- Foundation Analysis and DesignDokumen32 halamanFoundation Analysis and DesignvbisketiBelum ada peringkat
- CMU Wall (Out of Plane) MN Calculations: MN ( (D - ( (As Fy) / .85 / F'C / B / 2) ) As Fy)Dokumen5 halamanCMU Wall (Out of Plane) MN Calculations: MN ( (D - ( (As Fy) / .85 / F'C / B / 2) ) As Fy)Jester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- Ncees Form PDFDokumen1 halamanNcees Form PDFJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- Special Moment Resisting FrameDokumen1 halamanSpecial Moment Resisting FrameJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- How To Design A Singly Reinforced Concrete BeamDokumen5 halamanHow To Design A Singly Reinforced Concrete BeamPreston Varghese0% (1)
- CMO 29 s2007 - Annex III BSCE Course Specs PDFDokumen74 halamanCMO 29 s2007 - Annex III BSCE Course Specs PDFJester Abucay100% (6)
- Distribution of Story ShearDokumen13 halamanDistribution of Story ShearJester Abucay100% (1)
- Two Way Slab ExampleDokumen14 halamanTwo Way Slab ExampleKryle Dayle VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- CL OsaDokumen1 halamanCL OsaJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- Wind Pressure CalculationDokumen8 halamanWind Pressure CalculationJester AbucayBelum ada peringkat
- Site SafetyDokumen28 halamanSite SafetyMandhar MandhariBelum ada peringkat
- White Topping Sub Seminar (1) InchDokumen24 halamanWhite Topping Sub Seminar (1) InchZuheb AktherBelum ada peringkat
- Saket District CenterDokumen18 halamanSaket District CenterRohit Tangri100% (2)
- Class X Pre Board (SET-1)Dokumen4 halamanClass X Pre Board (SET-1)Manoj SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- ECE Regulation No 055 Rev 01Dokumen81 halamanECE Regulation No 055 Rev 01Zo StevanovicBelum ada peringkat
- Ananin Ami Management PlanDokumen44 halamanAnanin Ami Management PlanTaşkın GedikBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 3 Characteristics of Driver, The Pedestrian, The Vehicle, and The RoadDokumen96 halamanChapter 3 Characteristics of Driver, The Pedestrian, The Vehicle, and The RoadArinata CahyadiBelum ada peringkat
- TRL 611 - Ground Investigation and Ground Investigation and Road PavementDokumen54 halamanTRL 611 - Ground Investigation and Ground Investigation and Road PavementAu Yong Thean SengBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Rates As Per SOR 2018-19 Escalation @5% For FY 2019-20 Unit Adopted Rate SL - No. Description of Machine Activity Output of Machine OutputDokumen4 halamanBasic Rates As Per SOR 2018-19 Escalation @5% For FY 2019-20 Unit Adopted Rate SL - No. Description of Machine Activity Output of Machine Outputanon_789699787Belum ada peringkat
- Maitreyi.Y 12Ar60R21 - R. Iswarya 12Ar60R20 - Shafiqur RAHMAN 12AR60R19Dokumen45 halamanMaitreyi.Y 12Ar60R21 - R. Iswarya 12Ar60R20 - Shafiqur RAHMAN 12AR60R19Manasi Pundlik ChaudhariBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of BridgesDokumen10 halamanClassification of BridgesABHISHEK NAVGIREBelum ada peringkat
- Rem 6Dokumen42 halamanRem 6Sandeep ArikilaBelum ada peringkat
- M.E ReviewerDokumen14 halamanM.E ReviewerAlvin TusiBelum ada peringkat
- Perubahan Nilai Ekivalensi Mobil Penumpang Akibat Perubahan Karakteristik Operasional Kendaraan Di Jalan Kota SemarangDokumen8 halamanPerubahan Nilai Ekivalensi Mobil Penumpang Akibat Perubahan Karakteristik Operasional Kendaraan Di Jalan Kota SemarangBisnisku BerkahBelum ada peringkat
- Buying Alcohol in Oman - (MM) Muscat MutteringsDokumen7 halamanBuying Alcohol in Oman - (MM) Muscat Mutteringsjyothis_joy8315Belum ada peringkat
- Freightliner Coronado SD: SectionDokumen25 halamanFreightliner Coronado SD: SectionduongpnBelum ada peringkat
- International Transport PPT SummaryDokumen33 halamanInternational Transport PPT SummaryBrenda Spiridon100% (1)
- A Summary of DRAFT Master PlanDokumen16 halamanA Summary of DRAFT Master Planakhilchibber100% (1)
- QIP-123 Heavy Duty MixesDokumen44 halamanQIP-123 Heavy Duty Mixesਸੁਖਬੀਰ ਸਿੰਘ ਮਾਂਗਟBelum ada peringkat
- Materials & Workmanship Specification For C& S Works (A6)Dokumen626 halamanMaterials & Workmanship Specification For C& S Works (A6)Anonymous 40pygqBelum ada peringkat
- Method Statement For Production and Laying of Cement Concrete Kerb and Kerb With ChannelDokumen5 halamanMethod Statement For Production and Laying of Cement Concrete Kerb and Kerb With ChannelKeerti Bongu100% (1)
- Sound Transit - Link 1 Line Fall 2021 ScheduleDokumen8 halamanSound Transit - Link 1 Line Fall 2021 ScheduleThe UrbanistBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1 PDFDokumen9 halamanAssignment 1 PDFAnubhav AroraBelum ada peringkat
- Citizen Charter DTCDokumen8 halamanCitizen Charter DTCkushiBelum ada peringkat
- CE-461 Runway Geometric DesignDokumen31 halamanCE-461 Runway Geometric DesignShubham Bansal83% (6)
- Maryboroughbustimetable PDFDokumen6 halamanMaryboroughbustimetable PDFAnonymous zNdbKT993YBelum ada peringkat
- Off Road Driving PDFDokumen7 halamanOff Road Driving PDFsleepyninjitsuBelum ada peringkat
- Draft Gravel GuidelinesDokumen9 halamanDraft Gravel Guidelinesjohn_d_thirdBelum ada peringkat
- T2 VW Touareg BrochureDokumen10 halamanT2 VW Touareg BrochureJohn BandaBelum ada peringkat
- Getting Directions 02 Fun Activities Games Games Icebreakers Picture Des 79133Dokumen11 halamanGetting Directions 02 Fun Activities Games Games Icebreakers Picture Des 79133mustiBelum ada peringkat