Obstacles
Diunggah oleh
Syed MehtajDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Obstacles
Diunggah oleh
Syed MehtajHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
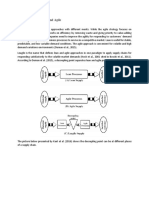
CHALLENGES AND OBSTACLES OF SUPPLY CHAIN INTEGRATION Supply chain management (SCM) executives face unique challenges, with
respect to integrating supply chain-specific strategies with the overall corporate business strategy. The general understanding of the business environment in most industries is that competition has increased and the conditions under which business is made are more turbulent. The challenges are from three perspectives: Technical perspective. Managerial perspective . Relationships perspective . Transaction Costs From inside the organization the decision to outsource business processes and create a supply chain outside of the organization is clearly one that requires an assessment of where the boundary of the organization should reside. As such, an economic assessment is required of the various merits of integration versus market provision. Thus, the decision is based on a transaction costs approach where there is an examination of the comparative costs of planning, adapting and monitoring task completion under alternative governance structures . The outsourcing decision is focused primarily on the management of recurrent transactions; the key dimensions of this context are the uncertainty and asset specificity germane to the transaction. Since these dimensions will vary, this creates a variety of contexts and the result will be diversity within governance structures. Strategy and planning If supply chain management is to be considered an essential component of long-term business competitiveness, it is sensible to consider how it relates to strategy theory and concepts. An effective supply chain must be able to cope with uncertainty; it follows that it must also be flexible. Therefore, supply chain management will be one of the organizational processes, or
functions, that are a key to strategic success if an organization is to achieve its mission in an adaptive and changing environment. Customer order management Customers expectations are evolving toward greater levels of service and response with higher degrees of product and service customization. Value chain partners (suppliers, service providers) integrated to provide differentiated customer segment product/service bundling and superior customer service levels. Increased profitability (increased revenue and reduced cost) is the top driver of customer order management performance. This centered attention on profitability is probably resulting from the economic market conditions of the past few years, but may be a short-term view. Customer responsiveness leads to customer retention and revenue growth. Logistic management The more complex the supply chain, the more difficult it becomes for companies to answer basic questions, such as which crude should they purchase and how should they transport it? Which facilities should process it? What will the best product slate be? Which components should they buy and which should they make? In many cases, different departments or divisions within a company trade, supply chain planning, operations and blending to name a few have a hand in these decisions, but communication among these entities is not always clear or consistent, and each may optimize to their own objectives without regard for others Manage operation flexibility Switching costs and Coordination costs are a barrier to operating flexibility. Switching costs can be reduced if all SC partners standardizing their products and processes globally which is seems to be challenge. Coordination costs can be significant for global integration of cross-functional supply chain processes. A well-structured global demand forecasting and planning process is an important mechanism for global coordination across functions. Regional representation to ensure all relevant input is considered is also important. A globally integrated process with regional representation requires costly resources, information infrastructure, and travel.
Globally integrated information systems are critical to reduce the cost of communications and to make relevant information readily accessible or to reduce coordination costs. Setting up standards of trade For SMEs and their suppliers, the high cost of technology is exacerbated by the lack of a widely accepted international electronic information standards governing the financial supply chain. The solution is a standard mechanism for communications protocols, rather than many standards. Several organizations have made some headway towards creating such standards, but there are no comprehensive and internally consistent open standards now, which is why automating the supply chain is so costly. Procurement management The challenge here is how to manage the complexity of the procurement process, and establishing a strong procurement infrastructure to execute on strategic supply initiatives, using an empowered organization structure, fully integrated to the stakeholder and finance organization. People training and development was the key challenge for procurement organizations, includes skill development; the right recruiting and retention practices, and career paths in other functions outside of procurement. Enterprise integration Enterprise integration needs to be planned, yet the planning cannot be precise, as business processes and facilitating technologies will change, creating different needs and different potential solutions. The reference architecture efforts mentioned define methodologies for building integrated architectures. The problem of integration is exacerbated by the limits of human cognition, by behavioral issues, by the difficulty of aligning the goals of individuals with organizational units, and by the relentless need for faster change. Application Integration ERP systems achieve application integration because ERP vendor-developed applications that perform common business functions are united through a common database (also providing
data integration one of the selling points of ERP systems.) The integration of the functional applications implies also that integration at the next layer, business processes, is achieved. However a major issue with ERP systems is that they fail to bridge the gap between the application and process layers in a flexible fashion. To reach the application integration firms must break down complex processing; to cope with application integration they must support interactive process. Finally Applications must integrate with the business processes. Extranet adapting challenges There are several issues to consider while adopting extranet as a facility of SC integration. A firm must be committed to using the system, as phone, fax, and written record, (instead relying on the automated supply chain system) and it influences the firm's processes as well. Costs of implementation, Loss of Trust, Unable to Adapt to Change, Losing the Inimitability of Product, Unnecessary Liability, Lack of Security, Uneven Partner benefit,Increased Independences,Keeping Up With the change in Expectations. Business process integration External process integration, which is called value chain coordination, is the focus of modern supply chain management. The E-commerce helps organizations to be able to connect its internal processes with its stakeholder. The challenge in business process improvement is the processes must be coordinate between all firms in the vale chain to achieve improve performance and service. Integrated must happen between decision making and business process layers which is occurs whenever human operator (or software agent) makes a decision that change the flow of work through a process. Culture and Change The accumulated history of relationships and experience, within and between organizations, will provide part of the context within which the inter-organizational activities are enacted. If there is a drive to closer relations within supply chains, this will involve the replacement of
existing governance structures and will challenge existing supply chain behaviors associated with traditional bid-buy relations. Supplier competence requirements If customers are moving to fewer suppliers, and investing in strategically important supply chain relations, then SME suppliers that cannot make themselves attractive purely through economies of scale and scope must increase their asset specificity and decrease uncertainty. This requires the suppliers to respond to the changing context and develop stronger relational and organizational competences. Since issues of quality and performance are the baseline measure for the customer-supplier interaction, any existing competences must support the achievement of this standard. It is the capabilities that create differentiation that will be a key. Globalization How to cut costs and grow simultaneously? Senior executives now understand that they can t just focus on supply chain operations to create efficiencies. The challenge is to integrate supply chain execution with the overall corporate business strategy, and to use the supply chain as a catalyst for business transformation or business reinvention. Data and information integration Information integration refers to the sharing of information among members of the supply chain. The ability to seamlessly connect with customers, partners, and co-workers is vital for success. The ability to map between different formats is mission-critical. This includes any type of data that could influence the actions and performance of other members of the supply chain. The meaning of all data items must be understood and the same data item must have the same definition across multiple applications both within and outside the firm. To make the integration process worth the effort, the data must be of high quality - timely, accurate and relevant.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Kunst CaseDokumen11 halamanKunst CaseSyed MehtajBelum ada peringkat
- Ratios 2Dokumen7 halamanRatios 2Syed MehtajBelum ada peringkat
- Summers ReportDokumen17 halamanSummers ReportSyed MehtajBelum ada peringkat
- Publication: The Economic Times Mumbai Date: Jan 19, 2011 Section: Brand Equity : 27Dokumen86 halamanPublication: The Economic Times Mumbai Date: Jan 19, 2011 Section: Brand Equity : 27Syed Mehtaj100% (1)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Chapter-Iv Data Analysis and InterpretationDokumen58 halamanChapter-Iv Data Analysis and InterpretationeswariBelum ada peringkat
- 24oct2016 OlamAcquiresSchluterDokumen2 halaman24oct2016 OlamAcquiresSchluteruntuk download100% (1)
- Gent's ParlourDokumen33 halamanGent's ParlourNiloy Abu NaserBelum ada peringkat
- GapDokumen12 halamanGapRubaiat HishamBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamentals of Process Intensification: A Process Systems Engineering ViewDokumen28 halamanFundamentals of Process Intensification: A Process Systems Engineering Viewkumar_chemicalBelum ada peringkat
- Journal Pre-Proof: Cleaner Engineering and TechnologyDokumen43 halamanJournal Pre-Proof: Cleaner Engineering and TechnologyMaharsiwi Diah Chandra DewiBelum ada peringkat
- Fluor Upfront BrochureDokumen8 halamanFluor Upfront BrochureRiccardo GastaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Zara Agile Supply ChainDokumen3 halamanZara Agile Supply ChainBilal ManzoorBelum ada peringkat
- Bharathi AssociatesDokumen8 halamanBharathi AssociatesMeghana Cd100% (2)
- Purchasing and Procurement StrategyDokumen3 halamanPurchasing and Procurement StrategyMoccha Ling100% (1)
- Lifting GuideDokumen59 halamanLifting GuideAnandababuBelum ada peringkat
- Powerpoint Presentation To Accompany Heizer and Render Operations Management, 10E Principles of Operations Management, 8EDokumen40 halamanPowerpoint Presentation To Accompany Heizer and Render Operations Management, 10E Principles of Operations Management, 8EArie ArganthaBelum ada peringkat
- APM - Strategic Planning and Control: Rational Model / Mission / MendelowDokumen3 halamanAPM - Strategic Planning and Control: Rational Model / Mission / Mendelowtaxathon thaneBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Procurement ManagementDokumen21 halamanChapter 1 - Introduction To Procurement ManagementLinh LilinBelum ada peringkat
- India Edition Chapter 22Dokumen9 halamanIndia Edition Chapter 22Moidin AfsanBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 2Dokumen44 halamanPaper 2AMLFajardoBelum ada peringkat
- Pub100311 PDFDokumen347 halamanPub100311 PDFHr MattBelum ada peringkat
- Subject Name BLG 20203 Logistics Management Final ProjectDokumen36 halamanSubject Name BLG 20203 Logistics Management Final ProjectYagentiran Repsol100% (1)
- Freepdf Iiav7ce Part3Dokumen284 halamanFreepdf Iiav7ce Part3msoodBelum ada peringkat
- AppleDokumen3 halamanAppleNavi S0% (1)
- CH 01 EOC SolutionsDokumen2 halamanCH 01 EOC SolutionsNgọc MaiBelum ada peringkat
- Key Account ManagementDokumen61 halamanKey Account ManagementPreticia Christian100% (1)
- Lean or Agile or Lean and AgileDokumen3 halamanLean or Agile or Lean and AgileHakanBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology Business PlanDokumen42 halamanInformation Technology Business Planseju078967% (3)
- Case Study On Apple's Supply ChainDokumen6 halamanCase Study On Apple's Supply ChainVaibhav SinghBelum ada peringkat
- BPMLDokumen28 halamanBPMLMakeesh Narayan100% (1)
- The Nature of An External AuditDokumen5 halamanThe Nature of An External AuditCamille100% (1)
- OMDokumen5 halamanOMMihiret GirmaBelum ada peringkat
- Competency Framework BookletDokumen24 halamanCompetency Framework BookletCompguru100% (3)
- Operations Management: Managing Business Operations - . - Manufacturing Distribution Transportation ServicesDokumen20 halamanOperations Management: Managing Business Operations - . - Manufacturing Distribution Transportation ServicesHuong LanBelum ada peringkat