Conlaw Outline To Memorize
Diunggah oleh
mn2218Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Conlaw Outline To Memorize
Diunggah oleh
mn2218Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Constitutional Law Outline to Memorize
MINIMAL CHECKLIST: o JR Justiciabliity Exceptions clause Who is bound o DP 2 levels: o EP Suspect class Fundamental interest Hybrid o 1st Am o If federal is there a federal power? I. Introduction A. Methods of Constit. Interpretation (Dred Scott): Interpretive Criteria - plain language o NOT always enough: bc all pp in Const. preamble shld have included slaves B didnt under Scott v. Sanford - framers intent/social beliefs o statements made in enacting the provision OR more indirect evid from soc per o (ex. some slaveh some abolit) - other clauses of Const. o more persuasive if broad & structural - precedent (prior interpetations of const.) o other laws o other cases - framers character o great men incapable of asserting principles inconsistent on which they were acting B bad reason bc good pp do bad stuff frequently - practicality o effects of the law - morality o (b judged irelev in Dred Scott) B. can DEPART from interpretive criteria IF: a. conflict of provisions b. specific intent conflicts with broad intent i. (ex. thought eq cld be est w/o desegreg schools) c. broader interpretation is imp i. (ex. eq protection clause no one thought about gender b can be logically incorporated) C. If more than interpretation of Const., source could be: a. Morally right
i. B justices all think dif thinks morally right swings throughout time ex. abortion b. Traditions/history of pp Judicial Review A. Jurisidiction issue (article 3) (1st thing to address) a. Federal law/executive action judicial rev (Marbury v. Madison) i. Who decides: judicial Review: (aka SC can review acts of Cong & void the unconst ones) 1. Art. II Sect 3 cl. 1: extends the judicial pwr to all cases & controversies arising under the cons & the laws of the US a. With such exceptionsas the Congress shall make means that Congress can take away appellate jurisdiction in some cases but it cannot create original jurisdiction (aka N orig jurisd over writ of mandam) meant to limit power 2. supremacy clause shall be the supreme law of the land; and the judges in every state shall be bound thereby: JR implicit 3. pub meaning judges nullified unconst. + Orig intent 4. practical reaons: other branches cant be impartial bc they create law/intent/courts best to protect minorities ii. Legitimacy: Act repugnant to the Const. can NOT become the law of the land BC (Marb): 1. (Supremacy clause Const. is the supreme law of the land) 2. Const purp = instruct Congr what it shld do (bad reason bc other purps) 3. written nature 4. language: a. arising under(article 3): includes const laws in list 5. paramount & renders all other conflicting laws void a. either paramount or ordinary: N ordinary bc agreed upon by 2/3 majority (B doesnt mean it overrules everything) 6. institutional competence have already interpreted, insulation from political pressure, more time to decide, balance of power
b. State court decisions/actions judicial rev (Martin v. Hunters Lessee B. Jusisticiable issue = political question doctrine C. Cases & Controversies Issue (article 3) a. Standing (whether P is proper party to bring the matter to court) IF i. Injury P proves has been/immininently will be injured ii. Causation P must allege that D is cause of harm (so decision will likely remedy) (should not give advisory opinions) (IRS case) iii. Non 3rd party UNLESS if close rltnshp/ someone that cant assert their own
rts/3rd injured party unlikely to assert 1. docs asserting patient right 2. parents of kids 3. criminal AAAAAND iv. Non generalized grievance (did we read US v. Richardson) 1. (just bc a lot of pp injured does mean generalized) 2. tax payers have standing to challenge gov expenditures as per violating establishment clause b. Ripeness i. Usu when challenge law by violating, prosecuting and arguing unconstitutional ii. If request for declar judgment ripeness issue look @ these factors to see if met: 1. Fed crt has all it needs to decide issue 2. Not better off to wait for actual violation of law c. Mootness i. If NOT live controv/ongoing inj moot case dismissed 1. Ex. if filing lawsuit ends injury moot 2. Case is only NOT dismissed IF: a. Wrong capable of repetition but will always avoid review (Roe v. Wade Roe wasnt pregnant anymore by the time the case got to SC, but court decided anyway) b. D voluntar stops activ B can resume whenev d. Political Question Doctrine i. Const violation allegations that fed courts will NOT adjudicate BC shld be left to political branches ii. Baker v. Carr TEST iii. Things that are dimissed bc political questions 1. Challenges to presidents foreign policy conduct 2. Chall to impeachment/presidential removal (Nixon v. US fed judge impeached case dismi) 3. Chall to partisan gerrymandering
II. Fed. Legislative Power article 1 a) Congress auth to act a. Express/implied author Cong can act b. If law necessary & proper to carry out its auth Congr. Can enact = Necessary & Proper Clause Art 1 i. Congr can choose any means NOT expressly prohibited by Cons (McCullough v. MD 1819) c. Whats listed under Art 1 Sect 8 d. Congr can adopt any tax/spend any money for general welfare e. Can regulate commerce w/ foreign nations/Indian tribes/several states/things that have
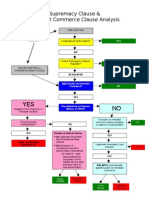
SUBSTANTIAL IMPACT ON interstate commerce Commerce Clause i. interst com ex highways, waterways, internet ii. can regulate instruments of/persons/things involved in interstate com ex. Gibbons: commerce = all forms of intercourse (radio, insurance, cattle, pp) iii. subst impact: 1. Wickard v. filburn -1942 all wheat farmers home consumption qualified as subst eff on interstate comm. 2. if nonpurely economic activ, subst effect can NOT BASED ON CUMULATIVE IMPACT a. US v. Morrison fed law re viol ag women N based on cumul impact f. NO general fed police pwr i. (but state/local govs have pol pwr to do anything not prohibited by const.) g. IF NOT granted to US/prohibited to states states & pp get those pwrs 10th amendment i. Cong CAN NOT compel state legislative/regulatory activ (B can compel via grants if conditions clear) h. Cong. Can NOT expand/create new rights Cong. can JUST prevent/fix violations of rights that crts already recog. Via NARROWLY TAILORED MEANS i. Must be proportioned/congruent to remedy proven violations ii. Burnia v. florres b) Delegation of powers: NOOO limit on Congr abil to deleg legisl pwrs
III. Fed. Exec. Pwr article 2 a) foreign policy a. Pres. has broad pwrs as com. In chief to use troops in foreign countries b) domestic affairs a. if appointment of ambassadors/fed judges/officers of US Pres alone appoints B Senate must approve nomination before takes office case b. inferior officers (cab/hired/fired by cab)/heads of deps/lwr fed courts Cong can appt AND Congr can give appt. pwrs to itself or other officers c. removal of any exec br official Pres role UNLESS removal limited by fed statute (Nixon tried to order ) i. congr can limit IF office where indep from Pres is desirable AND must be GOOD CAUSE d. Exec privil yields to imp needs for info ( N absolute) (US v. Nixon - need for Watergate tapes info @ crim trial outweights exec priv)
IV. Federalism: limits on state/local power to regulate commerce clause, preemption, interstate privileges & immunities clause a) preemption
a. const AND laws made pursuaint to it supreme law of land as per Art 6 Supremacy Cl (if confl btw fed w state/loc, preemption wins) b. if fed stat says exclusive in field express preemption c. if fed stat silent about preemption BUT fed & state mutually exclusive, st/local law interferes with fed objective, AND Congr has intent to preempt state/local laws Implied preemption d. if fed gov. activy preemption bc state can NOT tax/regulate fed gov i. McCullough v. MA state tax on US bank unconst ii. States must N put signif burden on fed activ b) if state/local laws place undue burden on interstate commerce unconst under Dormant Commerce Clause Art 4 a. burdens v. benefits : balance burdens on interstate commerce with benefits of law b. this undue burden test c. (bc const grant to fed gov to regulate state commerce) c) if state discriminates ag. citiz of other states w/ regards to privil/immuns. it gives its own citizens unconst under Priviliges & Immunities Cl Art 4 UNLESS NECESSARY to achieve imp. gov. purpose (if necessary no other less discrim altern can be achieved) a. discrimin law heavy presumption that burdens interstate commerce must show imp. purpose (only upheld with main v. taylor upheld bc envir purp) d) if state deprives ANY citiz of privil/immune. Of US citizen unconst under Priv & Imm Cl of 14th Am. a. (slaughterhouse cases early on destroyed provision BUT revised in Saenz 99 - freedom of travel as fund right & only right protected under Priv & Im cl of 14th)
Due Process Issue 1) Is there a fundamental right under the Due Process Clause of the 14th Ammendment? a. fundamental rights are those that are: i. rooted in traditions and collective conciousness of the people (Douglas majority test for fundamental right in Griswold v. CT 1965) OOOOOR implicit in the concept of ordered liberty 1. dispute re. how broadly/narrowly we should look @ traditions 2. has there always been this right? 3. (can we call t his a free society without this right?) ii. precedent other cases have already established this/related right as a fundamental right: EST. FUNDAMENTAL RIGHTS: 1. directing upbringing of ones child 2. family planning 3. create/maintain/change family relationships (Zablocki v. Redhail 1978) 4. right to refuse ones own life-saving medical treatment
5. parental right to refuse medical treatment UNLESS life-saving 6. right to refuse involuntary medical treatment Washington v. Harper - 1990 7. not really abortion B abort specially protected right: fund rt to terminate pregnancy without undue state interference: UNDUE BURDEN TEST: weight womans rights ag. state interests & life of fetus Roe v. Wade 73 and Planned Parenthood v. Casey 92 a. 1st trimester = fundamental right and state canNOT interfere at all (so no need to even do any test) b. 2nd: apply SS health/safety of mother is CSI, so state may regulate if NTM also exist c. 3rd: fetus if viable so CSI in life of child, so state may regulate if NTM also exist AND health/life of mother is NOT @ issue 8. contraception 9. freedom of travel a. under Priv & Im clause of 14th Am Saenz case DEF NOT fundamental rights: 1. engage in homosexual sodomy (Bowers v. Hardwick 1986) 2. education (San Antonio Ind. School District v. Rodriguez 73) a. also not fund right to ensure equal financial resources devoted to each child Plyler v. Doe 82 ) 3. basic necessities of life/welfare: a. since soc/econ leg RR (Dandridge v. Williams 1970 did NOT read yet) b. If a fundamental right that does NOT re. econom regulation of social/econ matter (ec fund right exception rat rev) STRICT SCRUTINY TEST i. SS compelling state interest + narrowly tailored means 1. CSI a. Life of child (Roe v. Wade) 2. NTM a. Ex. this means MUST occur in order to further the compelling state interest b. Can we achieve csi/ends via less intrusive/restrictive alternatives? c. Are there more restrictive alternatives? i. If so yet we are not choosing the worse ones, we can argue narrowly tailored c. If NOT fundamental right rational relationship test i. RR the regulation rationally relates to a legitimate state purpose (OConnor plurality opinion in City of Akron 1983) 1. No leg state purpose (or is it csi) in mans rltnshp with a child conceived with another mans wife (Michael H. v. Gerald D. 1989) OTHER TESTS:
d. If state restrictions on womens access to abortions & non viable fetus (aka 1st/2nd trimester) can use alternative to SS undue burden test (Roe v. Wade) i. Undue burden test [a] burden may be 'undue' either because [it] is too severe OR because it lacks a legitimate, rational justification (Stevens concur in part and dissent in part in Planned Parenthood v. Casey 1992)
Equal Protection Issue 1) Whats the classification? (Whats the right structure?) a. Social/Economic regulation RR i. RR rationally related to legitimate state purpose b. gender/alienage/illegitimacy Heightened Scrutiny aka Intermediate Review i. HS substantially related to important gov. interest c. suspect classification / fundamental right eq prot SS i. eq prot SS must be NECESSARY to achieve CSI ii. suspect classfication = suspect class + factors 1. suspect class a. race b. national origin c. ethnicity 2. to prove, must show factors of discriminatory intent OR purpose (discrimin intent is only sufficient if disproportionate impact too) 3. (affirmative action is benign racial classification and is subj to strict scrutiny but race is only one factor to show csi) 2) How can we tell? a. not on face OR b. prima facie c. must be purposeful discrimination AND NOT just impact alone
Strict Interest Compelling
Intermediate Important
Rational Relationship Legitimate
Connection Classification is necessary or Use of classification substantially Rational, non arbitrary Narrowly tailored related to achievement of goals
9th amendment (just because we list certain rights does NOT mean others dont exist) substantive due process: unenumerated rights that are substantively unemerated?
Is this right implicit in ordered liberty as evidenced by our tradition? Can we call this a free society without this right Rights: 1) Is this a suspect classification? a. Gay, race, alien status b. NOT if functional, disabled, mental handicap? 2) Is there a fundamental right? a. If YES Strict Scrutiny b. If No Rational Relationship c. (if gender important ends and substantitally related means? Wat)
Freedom of Speech:
1) Is it pure speech? a) If so apply brien 2) Is it hostile audience/fighting words/threat OR some expansion of such? 3) Does it fit into illicit or illegal conduct but like the dennis exception possibly? 4) Time place & manner restriction? 5) Group libel? But probably N good law anymore 6) Should we have a new category (does pick new in Ferber & considers it in Johnson) 7) IF fail all of the other justifications: CSI + NTM
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Law School Survival Guide (Volume II of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Evidence, Constitutional Law, Criminal Law, Constitutional Criminal Procedure: Law School Survival GuidesDari EverandLaw School Survival Guide (Volume II of II) - Outlines and Case Summaries for Evidence, Constitutional Law, Criminal Law, Constitutional Criminal Procedure: Law School Survival GuidesBelum ada peringkat
- Constitutional Law - Case BriefsDokumen437 halamanConstitutional Law - Case BriefsDaenen Merrill100% (4)
- Dormant Commerce Clause - Con Law OutlineDokumen9 halamanDormant Commerce Clause - Con Law OutlineMadhulika VishwanathanBelum ada peringkat
- Chemerinsky Conlaw 1 OutlineDokumen40 halamanChemerinsky Conlaw 1 Outlinemkelly1021100% (5)
- Con Law Outline - Rules and AnalysisDokumen16 halamanCon Law Outline - Rules and Analysischampion_egy325100% (4)
- Con Law Outline (OUTLINE)Dokumen69 halamanCon Law Outline (OUTLINE)india0173Belum ada peringkat
- Devlin Con Law I 2011 - Quick Sheets For ExamDokumen5 halamanDevlin Con Law I 2011 - Quick Sheets For ExamJeremy100% (1)
- Commerce Clause TestsDokumen10 halamanCommerce Clause Testsmdaly102483Belum ada peringkat
- Con Law I Outline - WeaverDokumen62 halamanCon Law I Outline - WeaverJasonBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law Outline - Case ReferencesDokumen59 halamanCon Law Outline - Case Referenceschampion_egy325Belum ada peringkat
- CON LAW Attack OutlineDokumen42 halamanCON LAW Attack OutlineKaitlyn MakerBelum ada peringkat
- Bar Bri Con Law OutlineDokumen24 halamanBar Bri Con Law Outlinelulubelle329Belum ada peringkat
- Midterm OutlineDokumen40 halamanMidterm OutlineAlejandra Aponte100% (2)
- Elward Evidence OutlineDokumen31 halamanElward Evidence OutlineAnonymous 13FhBKlBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law Steps 01-1 (Analysis)Dokumen24 halamanCon Law Steps 01-1 (Analysis)maturity88100% (2)
- Barbri Outline - MBE-NY (2005) - Constitutional LawDokumen13 halamanBarbri Outline - MBE-NY (2005) - Constitutional Lawsab0714Belum ada peringkat
- EPC, DPC Attack PlansDokumen6 halamanEPC, DPC Attack PlansEl100% (3)
- Con Law OutlineDokumen38 halamanCon Law OutlineJohnBarkum100% (3)
- Con Law Case ChartDokumen5 halamanCon Law Case ChartBree SavageBelum ada peringkat
- Public Function Test - A Private Entity Engaging in An Activity That HasDokumen24 halamanPublic Function Test - A Private Entity Engaging in An Activity That HasNate Enzo100% (1)
- Constitutional Law Rules & FrameworksDokumen20 halamanConstitutional Law Rules & FrameworksNick Arenstein100% (1)
- One Sheet J&J (Exam Day)Dokumen3 halamanOne Sheet J&J (Exam Day)Naadia Ali-Yallah100% (1)
- Judicial Review: Marbury v. MadisonDokumen35 halamanJudicial Review: Marbury v. MadisonXi ZhaoBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law Flow ChartsDokumen6 halamanCon Law Flow ChartsBrady WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- IL Corporations Bar OutlineDokumen8 halamanIL Corporations Bar OutlineJulia NiebrzydowskiBelum ada peringkat
- Civil Procedure Outline (Detailed)Dokumen91 halamanCivil Procedure Outline (Detailed)par halBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law OutlineDokumen14 halamanCon Law Outlinetm05101Belum ada peringkat
- Dormant Commerce Clause AnalysisDokumen1 halamanDormant Commerce Clause Analysishollyhastings42100% (2)
- Con Law SkeletalDokumen20 halamanCon Law Skeletalnatashan1985Belum ada peringkat
- Con Law Skeleton OutlineDokumen36 halamanCon Law Skeleton OutlineRebekahBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law Essay Tips StudicataDokumen16 halamanCon Law Essay Tips StudicataMacKenzie LeonardBelum ada peringkat
- Chemerinsky Points 01Dokumen12 halamanChemerinsky Points 01Jared DerringerBelum ada peringkat
- Leg Reg FinalDokumen2 halamanLeg Reg Finalnamratha minupuri50% (2)
- Con Law I Final Cheat SheetDokumen3 halamanCon Law I Final Cheat SheetKathryn CzekalskiBelum ada peringkat
- MPRE OutlineDokumen14 halamanMPRE Outlineesquire1010Belum ada peringkat
- Best - Con Law I Outline Vandevelde - NBDokumen22 halamanBest - Con Law I Outline Vandevelde - NBHaifa NeshBelum ada peringkat
- Leg Reg Outline SheetDokumen3 halamanLeg Reg Outline Sheetdp714100% (1)
- MBE-Criminal Procedure OutlineDokumen16 halamanMBE-Criminal Procedure OutlineYerinBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law 1 Attack OutlineDokumen6 halamanCon Law 1 Attack Outlinemkelly2109Belum ada peringkat
- Con Law II OutlineDokumen59 halamanCon Law II OutlineHenry ManBelum ada peringkat
- State ActionsDokumen1 halamanState ActionsKatie Lee WrightBelum ada peringkat
- Motion To Proceed Pro SeDokumen3 halamanMotion To Proceed Pro SeThomas MatesBelum ada peringkat
- Realproperty OpeningpsDokumen6 halamanRealproperty OpeningpsKellyMacDevittBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law II OutlineDokumen29 halamanCon Law II OutlineLangdon SouthworthBelum ada peringkat
- Constitutional Law - Opening Paragraphs (1) Standing: TH TH THDokumen2 halamanConstitutional Law - Opening Paragraphs (1) Standing: TH TH THLaura SkaarBelum ada peringkat
- Legislative and Regulatory State Attack OutlineDokumen12 halamanLegislative and Regulatory State Attack OutlinemyerscaBelum ada peringkat
- LH Admin Attack OutlineDokumen9 halamanLH Admin Attack OutlineDave Leslie100% (1)
- Con Law PracticeDokumen10 halamanCon Law PracticeNick ArensteinBelum ada peringkat
- Free Exercise ChartDokumen2 halamanFree Exercise ChartcrkatzBelum ada peringkat
- CH 2 NOTES ChemerinskyDokumen33 halamanCH 2 NOTES ChemerinskyNana Mireku-BoatengBelum ada peringkat
- C L B R O: I. The Federal Judicial Power A. Cases and ControversiesDokumen15 halamanC L B R O: I. The Federal Judicial Power A. Cases and Controversiesmarciagray15514Belum ada peringkat
- Con Law OutlineDokumen22 halamanCon Law OutlineslavichorseBelum ada peringkat
- FL Con Law OutlineDokumen28 halamanFL Con Law OutlineassiramufBelum ada peringkat
- Constitutional Law Essay GuideDokumen2 halamanConstitutional Law Essay Guidesuperxl2009Belum ada peringkat
- Conlaw Rights Outline - CODY HOCKDokumen49 halamanConlaw Rights Outline - CODY HOCKNoah Jacoby LewisBelum ada peringkat
- Good Con Law OutlineDokumen91 halamanGood Con Law OutlineJordan WoodsBelum ada peringkat
- Different Classes of Scrutiny TestDokumen2 halamanDifferent Classes of Scrutiny Testarellano lawschool100% (1)
- Outline Contracts Knapp SP 02Dokumen103 halamanOutline Contracts Knapp SP 02adlahc1234567100% (1)
- Con Law ChecklistDokumen1 halamanCon Law ChecklistekfloydBelum ada peringkat
- Chevron Step 0: (If No Apply Statute) (If Yes Chevron 2a)Dokumen2 halamanChevron Step 0: (If No Apply Statute) (If Yes Chevron 2a)GeneTeam100% (1)
- Con Law Short OutlineDokumen17 halamanCon Law Short OutlineJennifer IsaacsBelum ada peringkat
- Constitutional Law 2 Course Outline (Syllabus) John Wesley School of Law and GovernanceDokumen17 halamanConstitutional Law 2 Course Outline (Syllabus) John Wesley School of Law and GovernanceHanabishi RekkaBelum ada peringkat
- Professional Responsibility OutlineDokumen38 halamanProfessional Responsibility Outlineprentice brown50% (2)
- Plessy v. Ferguson 1896Dokumen2 halamanPlessy v. Ferguson 1896Stephanie Dyson100% (1)
- Civil Procedure OutlineDokumen7 halamanCivil Procedure OutlinePatrick WeaverBelum ada peringkat
- James v. USDokumen2 halamanJames v. USCarlo PajoBelum ada peringkat
- Griswold Vs ConnecticutDokumen2 halamanGriswold Vs ConnecticutRelmie TaasanBelum ada peringkat
- Constitutional Law OutlineDokumen16 halamanConstitutional Law OutlineStephanieIjomaBelum ada peringkat
- Constitutional Law I Funk 2005docDokumen24 halamanConstitutional Law I Funk 2005docLaura SkaarBelum ada peringkat
- Outline Without CasesDokumen38 halamanOutline Without CasesLeah PybasBelum ada peringkat
- Orozco V Texas 394 US 324 (1969) Justice Black: Petitioner: Reyes Arias OrozcoDokumen1 halamanOrozco V Texas 394 US 324 (1969) Justice Black: Petitioner: Reyes Arias OrozcoAnonymous hS0s2moBelum ada peringkat
- SCHENCK Vs USADokumen3 halamanSCHENCK Vs USADanny QuioyoBelum ada peringkat
- United States v. Tunstalle, 4th Cir. (2009)Dokumen3 halamanUnited States v. Tunstalle, 4th Cir. (2009)Scribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Kirtland Local Schools FFRF LetterDokumen4 halamanKirtland Local Schools FFRF LetterWKYC.comBelum ada peringkat
- Plessy v. Fergusun, 163 US 537Dokumen1 halamanPlessy v. Fergusun, 163 US 537Dominique VasalloBelum ada peringkat
- Constitutional Law - OutlineDokumen3 halamanConstitutional Law - OutlineMissPardisBelum ada peringkat
- Goldberg V KellyDokumen1 halamanGoldberg V KellyLiz BallesterosBelum ada peringkat
- 2022.Consti2.Syllabus and List of Cases - Modules 2-13Dokumen16 halaman2022.Consti2.Syllabus and List of Cases - Modules 2-13jem laurenteBelum ada peringkat
- U S Marshall Rich Tracy LetterDokumen1 halamanU S Marshall Rich Tracy LetterRoy WardenBelum ada peringkat
- Baker V Carr Key Cases Congressional Districting v.3 (07-03)Dokumen7 halamanBaker V Carr Key Cases Congressional Districting v.3 (07-03)TanmayBangaloreBelum ada peringkat
- Supreme Court Case StudyDokumen3 halamanSupreme Court Case StudyJack GillBelum ada peringkat
- Con Law OutlineDokumen44 halamanCon Law Outlinemsegarra88Belum ada peringkat
- United States v. Eric Orlando Reese, 397 F.3d 1337, 11th Cir. (2005)Dokumen2 halamanUnited States v. Eric Orlando Reese, 397 F.3d 1337, 11th Cir. (2005)Scribd Government DocsBelum ada peringkat
- Case Briefing TemplateDokumen2 halamanCase Briefing Templatenguyen duongBelum ada peringkat
- Bill of RightsDokumen2 halamanBill of RightsnlepasanaBelum ada peringkat
- McCulloch v. MarylandDokumen7 halamanMcCulloch v. MarylandJulian SerranoBelum ada peringkat
- Court Case Artifact 1Dokumen3 halamanCourt Case Artifact 1api-458486566Belum ada peringkat
- Ginsberg Vs New York Freedom of SpeechDokumen2 halamanGinsberg Vs New York Freedom of SpeechCharlie BartolomeBelum ada peringkat