Chapter 4 - Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output
Diunggah oleh
Kollyn MarajasDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chapter 4 - Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output
Diunggah oleh
Kollyn MarajasHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
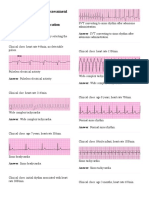
Risk for decreased cardiac output related to compression of cardiac structures due to swelling of the chest Risk for
decreased cardiac output is defined as the risk of inadequate blood pumping by the heart to meet the metabolic demands of the body. When there is a risk for decreased cardiac output, there is also a risk for the client to have tissue perfusion problems. Pnuemothorax is caused by trauma, tension or other predisposing ling disease that causes the lungs to be filled by air. In pnuemothorax, the air accumulated in the pleural cavity can cause pressure that may lead to lung collapse. That lung collapse may further put pressure in the pleural cavity that may lead to a condition called mediastinal shift. Mediastinal shift is the displacement of the central thoracic structures including the heart on one side that may be caused by compression or kinking of the great vessels and pressure from lung collapse. These dangerously impair the blood return to the heart. The latter cause a subsequent decrease in cardiac output and blood pressure. Mediastinal shift is a medical emergency and needs to be acted upon immediately. In relation to the patient, traumatic bilateral pnuemothorax accompanied by fractures in the 3rd-6th rib caused his chest to be swollen. Another cause of the chest swelling is the accumulation of air due to the puncture in both lungs. Due to the swelling and the pull of gravity, his major arteries can be impeded and may cause decrease cardiac output. There is also a great risk of him of having decreased cardiac output due to the possible mediastinal shift. To prevent the mediastinal shift, chest tube thoracostomy was done to the patient to decrease the pressure and remove the air that went in the pleural cavity of the client. Thoracentesis is also done to aspirate accumulated fluid in the pleural cavity that can prevent mediastinal shift that can
decrease the cardiac output of the client. In order to prevent hemodynamic instability, the researchers did the following intervention; 1) Assessed vital signs and note sudden change in BP. The rationale behind is that sudden severe hypotension may indicate mediastinal shift cause by the compression of the cardiac structure specifically the great vessels. 2) Assessed the swelling of the chest and assessed the feeling of tightness. The swelling of the chest due to the fractures of the client and the gravity compresses the cardiac structure that is why there a great need for assessment. The feeling of tightness may be an indication of mediastinal shift. 3) A liquid to soft diet is encouraged to decrease the workload of the heart. 4) Instructed the patient to limit activities and promote adequate rest. 5) Provided a calm environment. 6) Encourage verbalization of feelings, concerns and feeling of chest tightness. And lastly, the client was given health teaching regarding the possible complications of the illness and the activities to be avoided to avoid complications. As the result of the said interventions, the client has stable vital signs, no reports of exhaustion, no signs of further chest swelling, no severe hypotension, no severe chest tightness and verbalization of feelings and understanding was noted. The goal of the nursing diagnosis was fully met.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Anti TuberDokumen16 halamanAnti TuberpgfhgfgfBelum ada peringkat
- Peritonitis Update On Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and PDFDokumen11 halamanPeritonitis Update On Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations, and PDFAnonymous InJS6aYZ100% (1)
- Tren Tata Laksana Kanker Prostat PDFDokumen18 halamanTren Tata Laksana Kanker Prostat PDFShannia FrnsBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Education: School Contingency PlanDokumen14 halamanDepartment of Education: School Contingency PlanClerica RealingoBelum ada peringkat
- Typhoid Fever PamphletDokumen3 halamanTyphoid Fever PamphletCLaui SagibalBelum ada peringkat
- Deyo 1992Dokumen6 halamanDeyo 1992Wwwanand111Belum ada peringkat
- State of The ArtDokumen3 halamanState of The ArtArne HeyerickBelum ada peringkat
- Granulomatous Mastitis: The Histological Differentials: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleDokumen13 halamanGranulomatous Mastitis: The Histological Differentials: Click To Edit Master Subtitle StyleAsmara SyedBelum ada peringkat
- Jemds Title PDokumen1 halamanJemds Title PKriti KumariBelum ada peringkat
- The Body Nutrition PortionDokumen35 halamanThe Body Nutrition PortionHerditya putri rahmaBelum ada peringkat
- Bhopal (M.P.) : Assignment OnDokumen9 halamanBhopal (M.P.) : Assignment OnamitBelum ada peringkat
- PALS Precourse Self 2023Dokumen9 halamanPALS Precourse Self 2023Airene SibleBelum ada peringkat
- Livedoidna VaskulopatijaDokumen5 halamanLivedoidna VaskulopatijaemirkurtalicBelum ada peringkat
- E Stimation of HemoglobinDokumen13 halamanE Stimation of HemoglobinSANABelum ada peringkat
- Bola CommunityDokumen5 halamanBola CommunityOladimeji Raphael OnibonBelum ada peringkat
- Nausea and Vomitting-FonDokumen52 halamanNausea and Vomitting-FonZephas HillsBelum ada peringkat
- PathogenesisDokumen14 halamanPathogenesisIdreesBelum ada peringkat
- Homeopathy and PaediatricsDokumen15 halamanHomeopathy and PaediatricsCristinaBelum ada peringkat
- Tehnica Injectiei IM Vast Lateral Si DeltoidDokumen6 halamanTehnica Injectiei IM Vast Lateral Si DeltoidAnca NeaguBelum ada peringkat
- Lab Values: Interpreting Chemistry and Hematology For Adult PatientsDokumen36 halamanLab Values: Interpreting Chemistry and Hematology For Adult PatientsBrian Johnson100% (1)
- Food HandlersDokumen27 halamanFood HandlersNickz AgbayaniBelum ada peringkat
- Science Form 3 PPTnewDokumen9 halamanScience Form 3 PPTnewRedzuan SulaimanBelum ada peringkat
- Laryngopharyngeal Reflux and Functional Laryngeal Disorder: Perspective and Common Practice of The General GastroenterologistDokumen9 halamanLaryngopharyngeal Reflux and Functional Laryngeal Disorder: Perspective and Common Practice of The General GastroenterologistKenzi A HasyaputraBelum ada peringkat
- ترجمة 2Dokumen18 halamanترجمة 2habibBelum ada peringkat
- v20 n4Dokumen223 halamanv20 n4Sivanantham KrishnamoorthiBelum ada peringkat
- One Lung Ventilation: General Principles - UpToDateDokumen26 halamanOne Lung Ventilation: General Principles - UpToDateAna Belén Artero CastañoBelum ada peringkat
- 2011-2012 Annual Report Department of Pediatrics Saint Louis University School of MedicineDokumen131 halaman2011-2012 Annual Report Department of Pediatrics Saint Louis University School of Medicineslusompeds0% (1)
- Cloning of Hybridoma Cell Lines by Limit PDFDokumen2 halamanCloning of Hybridoma Cell Lines by Limit PDFMaha MardenliBelum ada peringkat
- Optimal Management of Collagenous Colitis A Review 021016Dokumen9 halamanOptimal Management of Collagenous Colitis A Review 021016Eliza DNBelum ada peringkat
- Review of Related LiteratureDokumen6 halamanReview of Related Literaturegilrae merlanBelum ada peringkat