NCP-DR 1
Diunggah oleh
krayzenDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NCP-DR 1
Diunggah oleh
krayzenHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
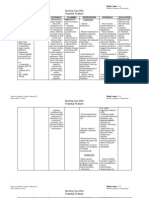
Nursing Care Plan
Cues/ Needs
Subjective: - none Objective: - dressing dry and intact -V/S taken as follows: T: 36.8 P: 81 R: 16 BP: 120/70 O2 sat: 97
Nursing Diagnosis
Risk for infection related to inadequate primary defenses secondary to surgical incision
Rationale
Goals/Desired Outcomes
STG: After 4 hours of nursing intervention, patient will be able to understand causative factors, identify signs of infection and report them to health care provider accordingly. LTG: After 2-3 days of nursing intervention, patient will achieve timely wound healing, be free of purulent drainage or erythema, be afebrile and be free of infection.
Interventions
Rationale
Evaluation
Due to an elective cesarean section, patients skin and tissue were mechanically interrupted. Thus, the wound is at risk of developing infection.
Independent: 1.)Monitor vital signs.
-To establish a baseline data. -Moist from drainage can be a source of infection.
2.)Inspect dressing and perform wound care. 3.)Monitor white blood count (WBC).
- Rising WBC indicates bodys efforts to combat pathogens; normal values: 4000 to 11,000 mm3. -These are signs of infection.
Patient is expected to be free of infection, as evidenced by normal vital signs and absence of purulent drainage from wounds, incisions, and tubes.
4.)Monitor elevated temperature, redness, swelling, increased pain, or purulent drainage at incisions. 5.)Wash hands and teach other caregivers to wash hands before contact with patient and between procedures with patient.
-Friction and running water effectively remove microorganisms from hands. Washing between procedures reduces the risk of transmitting pathogens from one area of the body to another. -Fluids promote diluted urine and frequent emptying of bladder; reducing stasis of urine, in turn, reduces risk of bladder infection or
6.)Encourage fluid intake of 2000 ml to 3000 ml of water per day (unless contraindicated).
urinary tract infection (UTI). -These measures reduce stasis of secretions in the lungs and bronchial tree. When stasis occurs, pathogens can cause upper respiratory infections, including pneumonia. -Antibiotics have bactericidal effect that combats pathogens.
7.) Encourage coughing and deep breathing; consider use of incentive spirometer.
Independent: - Administer antibiotics.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Nursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseDari EverandNursing care process in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen5 halamanNCPf_jm06_gBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts of Infection ControlDokumen53 halamanConcepts of Infection ControlBimal Dey100% (1)
- Arjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIDokumen69 halamanArjumand Zargar Anp@AARUSIMIArjumand ZargarBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts of Infection ControlDokumen53 halamanConcepts of Infection ControlPak Pandir0% (1)
- Prevention of Hospital Acquired InfectionDokumen39 halamanPrevention of Hospital Acquired Infectionbtalera80% (5)
- Week 7-8Dokumen13 halamanWeek 7-8Glaiza Dalayoan FloresBelum ada peringkat
- Appliedmicro Micro d&Amp;r AgamDokumen83 halamanAppliedmicro Micro d&Amp;r Agamjanijkson29Belum ada peringkat
- Surgical InfectionsDokumen20 halamanSurgical InfectionsDr-Mohammad Ali-Fayiz Al TamimiBelum ada peringkat
- K.Hema Anandhy, M.SC Nursing, PuducherryDokumen53 halamanK.Hema Anandhy, M.SC Nursing, PuducherryhemihemaBelum ada peringkat
- Needle Stick InjuryDokumen6 halamanNeedle Stick InjuryNikitaBelum ada peringkat
- A Study On Knowledge and Practice of Nursing Staff Towards Infection Control MeasuresDokumen17 halamanA Study On Knowledge and Practice of Nursing Staff Towards Infection Control MeasuresPriyanka SatalkarBelum ada peringkat
- Prevention of IV Therapy Related Infections (1) 2Dokumen14 halamanPrevention of IV Therapy Related Infections (1) 29kjsntkrzcBelum ada peringkat
- اساسياات تمريضDokumen33 halamanاساسياات تمريضHasan A AsFourBelum ada peringkat
- Postoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres orDokumen6 halamanPostoperative Nursing Care Plan For Cesarian Section Patient Case Pres orLoren EstefanBelum ada peringkat
- Infections in ICUDokumen7 halamanInfections in ICUNikolay ToméBelum ada peringkat
- Infection ControlDokumen16 halamanInfection ControlMohamed AbdelkaderBelum ada peringkat
- Seminar ON: Infection Prevention (Including Hiv) and Standard Safety Measures, Bio - Medical Waste ManagementDokumen24 halamanSeminar ON: Infection Prevention (Including Hiv) and Standard Safety Measures, Bio - Medical Waste ManagementTHONDYNALUBelum ada peringkat
- Asepsis and Infection ControlDokumen46 halamanAsepsis and Infection ControlecocafephBelum ada peringkat
- Unit - Two - Infection Control - Universal PrecautionsDokumen31 halamanUnit - Two - Infection Control - Universal Precautionsvirtus_kuwaitBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts of Infection ControlDokumen53 halamanConcepts of Infection ControlMarcus PorterBelum ada peringkat
- LEARNING OBJECT-WPS OfficeDokumen11 halamanLEARNING OBJECT-WPS OfficeDanielle TengBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Case Study on AppendicitisDokumen19 halamanPatient Case Study on Appendicitisfarzaneh yeganehBelum ada peringkat
- Needle Prick InjuryDokumen20 halamanNeedle Prick InjuryThirugnanaThiruBelum ada peringkat
- All Short Notes of ICDokumen30 halamanAll Short Notes of ICaarti HingeBelum ada peringkat
- How Is A Wound Infection Treated?Dokumen5 halamanHow Is A Wound Infection Treated?Haider JulailiBelum ada peringkat
- Signs and Treatment of Wound InfectionsDokumen5 halamanSigns and Treatment of Wound InfectionsHaider JulailiBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Safety: Infection Control EssentialsDokumen38 halamanPatient Safety: Infection Control EssentialsSushant SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- NeutrotoppppcDokumen10 halamanNeutrotoppppcapi-255084253Belum ada peringkat
- Managing Peptic Ulcer Bleeding and ComplicationsDokumen320 halamanManaging Peptic Ulcer Bleeding and ComplicationsShivam AgarwalBelum ada peringkat
- Edison College Nursing Program Infection Risk PlanDokumen3 halamanEdison College Nursing Program Infection Risk PlanBrian Bracher93% (43)
- 8 Pencegahan InfeksiDokumen47 halaman8 Pencegahan InfeksiEry SuryatinBelum ada peringkat
- Infection Control Policies and ProceduresDokumen9 halamanInfection Control Policies and ProceduresKelly J WilsonBelum ada peringkat
- Hospital Infection (Laundry) PDFDokumen39 halamanHospital Infection (Laundry) PDFSumantri KasmadiBelum ada peringkat
- MAS110 - Week 1 - Infection Control Worksheet 2Dokumen4 halamanMAS110 - Week 1 - Infection Control Worksheet 2geonikawilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- Needle Sticks Sharps Injuries: FactsDokumen31 halamanNeedle Sticks Sharps Injuries: FactsDr. Ashish Jawarkar67% (3)
- INFECTION PREVENTION BMW MANAGEMENTDokumen9 halamanINFECTION PREVENTION BMW MANAGEMENTDipti PunjalBelum ada peringkat
- PrintDokumen2 halamanPrintJermaine RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- Quality & Safety Issues in BMW Quality & Accreditation Standards Bio Medical Waste Handlers SafetyDokumen12 halamanQuality & Safety Issues in BMW Quality & Accreditation Standards Bio Medical Waste Handlers SafetyParth SoniBelum ada peringkat
- Infection and Prevention Control-2Dokumen14 halamanInfection and Prevention Control-2NIKHIL RAJBelum ada peringkat
- Final Health Care Associated InfectionDokumen23 halamanFinal Health Care Associated Infectionramanand chaudharyBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 08Dokumen10 halamanChapter 08Sachin MadhukarBelum ada peringkat
- Definition of InfectionDokumen27 halamanDefinition of InfectionRenit AntoBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan (Risk For Infection) CVADokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan (Risk For Infection) CVAawesomedawn50% (4)
- Chapter 12 Healthcare EpidemiologyDokumen10 halamanChapter 12 Healthcare EpidemiologyRegiena Tamargo100% (1)
- Infection Control For Every OneDokumen79 halamanInfection Control For Every Onetummalapalli venkateswara raoBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical Site Infections (SSI) : Dr. Mahmud Ul Alam Mondal (Saikat)Dokumen42 halamanSurgical Site Infections (SSI) : Dr. Mahmud Ul Alam Mondal (Saikat)মাহমুদ সৈকতBelum ada peringkat
- MED SURG III- Food for thought reviewDokumen24 halamanMED SURG III- Food for thought reviewHannah PerkinsBelum ada peringkat
- Output 1 InfectionDokumen13 halamanOutput 1 InfectionallanrnmanalotoBelum ada peringkat
- Hand Hygiene An Evidence-Based Review For SurgeonsDokumen13 halamanHand Hygiene An Evidence-Based Review For Surgeonsulul_sasafBelum ada peringkat
- Epidemiology & Surveillance of HAIDokumen46 halamanEpidemiology & Surveillance of HAIAkhilesh BabuBelum ada peringkat
- Epidemiology & Surveillance of HAIDokumen46 halamanEpidemiology & Surveillance of HAIAkhilesh BabuBelum ada peringkat
- Mc3g5report Bsn1aDokumen58 halamanMc3g5report Bsn1aJhon Mhark GarinBelum ada peringkat
- Universal Precaution by FithriDokumen62 halamanUniversal Precaution by FithriFithriKurniatiBelum ada peringkat
- Universal Precautions Quiz 14 15Dokumen8 halamanUniversal Precautions Quiz 14 15O.r. CadzBelum ada peringkat
- Nosocomial Infection and Surgical Site InfectionDokumen48 halamanNosocomial Infection and Surgical Site InfectionFranz BalponBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Safety: Key ConsiderationsDokumen46 halamanPatient Safety: Key ConsiderationsCalvin Chowder WittelsbachBelum ada peringkat
- Hand Hygiene Reduces Hospital InfectionsDokumen48 halamanHand Hygiene Reduces Hospital Infectionszing65Belum ada peringkat
- Controls for Biological HazardsDokumen4 halamanControls for Biological HazardsAbhijeet SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Rational - Use - of - Antibiotics - For - Surgical - Infections - PahmiismifritaDokumen41 halamanRational - Use - of - Antibiotics - For - Surgical - Infections - PahmiismifritaAndikaChandraBelum ada peringkat
- Pneumonia RFIDokumen3 halamanPneumonia RFIkrayzenBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Vaginal PainDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan for Acute Vaginal Painkrayzen100% (1)
- Drug Study OophorectomyDokumen4 halamanDrug Study OophorectomykrayzenBelum ada peringkat
- NCP FeverDokumen3 halamanNCP Feversinister1785% (48)
- Ncp-Impaiered Skin IntegrityDokumen1 halamanNcp-Impaiered Skin Integritykrayzen100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Vaginal PainDokumen1 halamanNursing Care Plan for Acute Vaginal Painkrayzen100% (1)
- NCP Dengue 2Dokumen4 halamanNCP Dengue 2krayzenBelum ada peringkat
- NP OophorectomyDokumen15 halamanNP OophorectomykrayzenBelum ada peringkat