Brest Cancer
Diunggah oleh
Pankaj SachdevaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Brest Cancer
Diunggah oleh
Pankaj SachdevaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
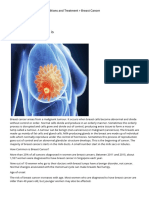
Breast cancer is the second most common cancer seen in women.
Once thought a disease of the developed countries, the incidence of breast cancer is on the rise in India as well. Breasts are designed to produce milk for the newborn baby after delivery. Breast is made up of milk glands and supporting breast tissue. Milk glands contain milk sacs, where milk is produced and milk ducts carry the milk to the nipples from where it is discharged. The breast tissue extends up to the collarbone on top and the armpits on the side. Traditionally the shape and size of the breasts are associated with femininity and any disease affecting the breasts are psychologically traumatic. [Top] What is Breast Cancer? Breast cancer is a tumor (a mass of abnormal tissue) within the breast. The majority of breast cancers begin in the milk ducts, however a small number start in the milk sacs or the lobes. Like other cancers, breast cancer if unchecked also has the ability to spread to different areas. The spread occurs mainly via the lymph ducts. [Top] Who is at risk? Breast cancer is far more common in women than in men although men can also get breast cancer. Some women are at a particularly higher risk. Age-risk of breast cancer increases with age. Family history of breast cancer i.e. women whose mother, grandmothers, aunts or sisters have developed breast cancer, are at an increased risk. Women, who previously had breast cancer, have a slightly higher chance of having breast cancer in the other breast. Women who started their periods (menarche) at an earlier age (before 12 years). Delayed childbearing, women who did not breast-feed their infants, or those who never had children. Late menopause (after 50 years) Obesity Diet rich in animal fat.
It is important to mention here that even if several risk factors are present, if does not necessarily mean that cancer will develop in these cases. It is equally important to mention that 75% of women who develop breast cancer have no known risk factors. [Top] What are the signs and symptoms of Breast Cancer? In a majority of women breast cancer is first noticed as a lump in the breast. There are other important signs and symptoms. Discharge from the nipple, particularly if blood stained. Change in shape or size of breast. Change in appearance of skin in a part of the breast. Rash on the nipples or surrounding areas.
A lump or thickening inside the breast tissue. Inversion or turning in of the nipple. Swelling on the upper arm Swelling in the armpit [Top]
How can Breast Cancer be diagnosed? Being in an area, which is easily accessible, the importance of early detection and diagnosis of breast cancer cannot be over-emphasized. Early detection and treatment can provide an almost 100% cure. Breast Self Examination (BSE) is important as it helps the patient to detect any changes occurring in her breast by herself. All women should be taught how to do a breast selfexamination. However it is reassuring to note that all lumps in the breast are not cancerous, though one must check out with the doctor, when a lump is suspected. A Mammogram is an X-ray of the breast using a specially designed machine and is very useful in early diagnosis. Besides BSE every woman over 40 years must have Physical Examination of the breast done by a doctor, as part of the annual check up program. Following a clinical examination a Biopsy is the only definite way of confirming or ruling out breast cancer in suspected cases. A piece of breast tissue is taken for testing; this can be done by inserting a needle into the Breast (FNAC-fine needle aspiration cytology), or by an operation under local or general anesthesia. A pathologist then examines the breast tissue under the microscope to check for cancer cells.
What are the treatment options for Breast Cancer? Surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy are the three options available for treating breast cancer. Often the treatment given may be a combination of 2 modalities, such as surgery followed by radiotherapy; or chemotherapy followed by surgery. Selection of the appropriate therapeutic approach depends on the location and size of the tumor, breast size, appearance on the mammogram, the extent of change in the tissues, and the preference of the patient and treating doctor. Surgery is the commonest modality of cancer treatment wherein the surgeon removes the affected tissues mostly a localized tumor. The types of surgery may vary. Mastectomy means total removal of breast tissue. Radiotherapy involves subjecting the tumor-bearing region either in part or whole to ionizing radiation using a variety of delivering systems. Chemotherapy using cytotoxic drugs capable of arresting fast growth of cancer cells. [Top] Dos and Don't - A few simple moves to help you move back to normal Dos Wear loose rubber gloves when working. Protect your arm from pinpricks, scratches, bruises, cuts or burns of any kind.
Use an electric razor with a narrow head to shave as this decreases the risk of cuts and scratches. Use a thimble while stitching. Wear loose clothing and jewellery. Use insect repellant to avoid insect bites. In case you injure yourself, wash with an antiseptic solution and apply a sterile bandage.
Donts Never take injections or IV fluids or check your blood pressure or draw blood on the affected arm. Do not wear glass bangles. Do not expose the arm to excessive heat while cooking. Do not cut or pull cuticles on the affected arm.
Life after mastectomy (surgery done to remove the breast) Because of the traditional thinking that femininity is associated with presence of breasts, the surgical removal of a breast can be traumatic and requires rehabilitation measures. Detachable External Prosthesis, Silicone prosthesis and reconstructive surgery provide hope to these patients. Breast prosthesis are now available, to help patients feel as feminine as before and nobody can notice the difference. The fitting of breast prosthesis should occur approximately 6-8 weeks following mastectomy. Careful measurements help in getting a well-fitted prosthesis. When fitted correctly, the prosthesis is comfortable and looks as natural as the healthy breast. Check for the following: Does the prosthesis fill out the cup of the bra both top and bottom. Check for similarity. Place the flats of your hands on top of both your natural breast and the prosthesis and compare size and softness. Check that there is not too much fullness in the underarm extension of your breast prosthesis. You can do this by feeling with the hand, then by swinging your arms back and forth. If fullness is greater than on your other side, then try a shape with less thickness in this area. Stand upright and look in the mirror to check shape and symmetry. The form should be completely covered by the bra. To check final result put on a soft blouse or T-shirt. No difference should be noticed in either breasts.
CPAAs economical, fully washable breast prosthesis, developed specially for Indian patients by our Rehabilitation Centre, is soft and fully washable (important in view of the hot and humid climate), gives an extremely good cosmetic appearance, and costs Rs.350 to 400 (depending on size). The prosthesis is fitted at the Smt. Panadevi Dalmia Cancer Management Centre under the guidance of a sympathetic and fully qualified technician. Self-Breast Examination In the shower Raise one arm, with fingers flat, touch every part of each breast, gently feeling for a lump or thickening. Use your right hand to examine your left breast, your left hand for your right breast.
Before the mirror With arms at your sides, then raised above your head, look carefully for changes in the size, shape, and contour of each breast. Look for puckering, dimpling or changes in skin texture. Gently squeeze both nipples and look for discharge. Lying down
Place a towel or pillow under your shoulder and you right hand behind your head. Examine your right breast with your left hand.
Finger flat, press gently in small circles, starting at the outermost top edge of your breast and spiraling in towards the nipple. Examine every part of the breast. Repeat with left breast.
With your arm resting on a firm surface, use the same circular motion to examine the underarm area, this is breast tissue, too.
This self-examination is not a substitute for periodic examination by qualified physician. For a free brochure on the correct procedure for conducting a Self Breast Examination, contact us.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Breast Cancer Prevention: Steps to Protect Your Health: Course, #5Dari EverandBreast Cancer Prevention: Steps to Protect Your Health: Course, #5Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Information About Breast CancerDokumen13 halamanBasic Information About Breast CancerCarlo RomanBelum ada peringkat
- Guide To Breast Self ExamsDokumen7 halamanGuide To Breast Self Examsaamer_rasheed1571Belum ada peringkat
- Breast CancerDokumen7 halamanBreast CancerLea Tabo MelchorBelum ada peringkat
- What you need to know about breast cancerDokumen9 halamanWhat you need to know about breast cancerIrfan AhmadBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Health Begins With You: What You Need To Know About Breast CancerDokumen41 halamanBreast Health Begins With You: What You Need To Know About Breast CancerSaima HaiderBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study 1Dokumen9 halamanCase Study 1Mark SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer - DZMEDokumen6 halamanBreast Cancer - DZMEMarife CompraBelum ada peringkat
- Article WKPDokumen2 halamanArticle WKPAnonymous QNd289iGPBelum ada peringkat
- Mastectomy Power PointDokumen63 halamanMastectomy Power PointokaciaBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation Medical TerminologyDokumen26 halamanPresentation Medical TerminologySunaina BhartiBelum ada peringkat
- Know Your Melon: A Breast Cancer Awareness CampaignDokumen3 halamanKnow Your Melon: A Breast Cancer Awareness CampaignRaffy John BinbinBelum ada peringkat
- Corpus Uteri Cancer Factsheet: What Is The Uterus? What Is The Uterus? What Is The Uterus? What Is The Uterus?Dokumen4 halamanCorpus Uteri Cancer Factsheet: What Is The Uterus? What Is The Uterus? What Is The Uterus? What Is The Uterus?Dhyc DhincaBelum ada peringkat
- Self Breast ExaminationDokumen11 halamanSelf Breast ExaminationJairene Dave Martinez Cambalon100% (2)
- Breast Cancer Facts and TypesDokumen20 halamanBreast Cancer Facts and Typesagnesia lissaBelum ada peringkat
- Adewumi Precious Olusola 1808001031Dokumen13 halamanAdewumi Precious Olusola 1808001031Adewumi preciousBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Health Begins With You: A Guide to Breast Cancer AwarenessDokumen41 halamanBreast Health Begins With You: A Guide to Breast Cancer AwarenessEsa OraBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Self ExaminationDokumen18 halamanBreast Self ExaminationjenrastaBelum ada peringkat
- WOMEN'S HEALTH 2019with VIDEODokumen73 halamanWOMEN'S HEALTH 2019with VIDEOAurora Doris BatagaBelum ada peringkat
- Breast CancerDokumen24 halamanBreast Cancerbkbaljeet116131Belum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer Stages & Treatment Options in 40 CharactersDokumen43 halamanBreast Cancer Stages & Treatment Options in 40 CharactersArchana VermaBelum ada peringkat
- Breast CancerDokumen50 halamanBreast CancerZainab Idrees- F2FBelum ada peringkat
- Breast CancerDokumen4 halamanBreast Cancersina bayat shahbaziBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Self ExamDokumen6 halamanBreast Self ExamZeljnaznanjaBelum ada peringkat
- Breast CancerDokumen8 halamanBreast CancerJeyser T. Gamutia100% (1)
- Breast Cancer: Prepared By: Dipti PunjalDokumen52 halamanBreast Cancer: Prepared By: Dipti PunjalDiptiBelum ada peringkat
- Malignancies of The Female Reproductive SystemDokumen61 halamanMalignancies of The Female Reproductive SystemMakanjuola Osuolale John50% (2)
- Breast Cancer: Key Facts for Medical StudentsDokumen60 halamanBreast Cancer: Key Facts for Medical StudentsPanuta AndrianBelum ada peringkat
- Dian Pratiwi Abdullah K11115309: Created byDokumen11 halamanDian Pratiwi Abdullah K11115309: Created bydian pratiwiBelum ada peringkat
- Kanker PayudaraDokumen11 halamanKanker PayudaracahyaaBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Self ExaminationDokumen8 halamanBreast Self ExaminationashBelum ada peringkat
- Fast Facts On Breast CancerDokumen8 halamanFast Facts On Breast CancerTety KarmilaBelum ada peringkat
- Breast LeafletDokumen6 halamanBreast LeafletcilengsaiBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Self Examination1Dokumen17 halamanBreast Self Examination1lolabayBelum ada peringkat
- 3.1 Breast CancerDokumen46 halaman3.1 Breast CancerNur AinaaBelum ada peringkat
- Things You Should Know: Breast CancerDokumen2 halamanThings You Should Know: Breast CancerLea Tabo MelchorBelum ada peringkat
- Stages of Breast CancerDokumen19 halamanStages of Breast CancerOktovianus PalulluBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Tumors.Dokumen23 halamanBreast Tumors.jabarinjamalsajaBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Self ExaminationDokumen4 halamanBreast Self ExaminationRohini RaiBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Self-Examination: A Presentation By: Uckjin, Heather, and YajjayraDokumen28 halamanBreast Self-Examination: A Presentation By: Uckjin, Heather, and YajjayraHeather SeymourBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Self Examination 1!Dokumen22 halamanBreast Self Examination 1!Soma Al-mutairi79% (14)
- Breast Asymmetry 0441Dokumen8 halamanBreast Asymmetry 0441VitaPuspitaSariBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Two (Breast Cancer)Dokumen7 halamanAssignment Two (Breast Cancer)Arisha NicholsBelum ada peringkat
- Become Familiar With Your Breasts Through Breast Self-Exam For Breast AwarenessDokumen3 halamanBecome Familiar With Your Breasts Through Breast Self-Exam For Breast AwarenessApple Jenn TempladoBelum ada peringkat
- Breast CancerDokumen16 halamanBreast CancerRiya potbhareBelum ada peringkat
- Breast CancerDokumen43 halamanBreast CancerNinz Taruc100% (1)
- Breast CancerDokumen7 halamanBreast CancerMary Jane TiangsonBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer: Symptoms, Types, Risk Factors, Stages, and TreatmentDokumen13 halamanBreast Cancer: Symptoms, Types, Risk Factors, Stages, and TreatmentMarde Cabucos Phillip BonachitaBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer Gene Therapy 1Dokumen23 halamanBreast Cancer Gene Therapy 1EINSTEIN2DBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer Detection and Treatment GuideDokumen35 halamanBreast Cancer Detection and Treatment GuidePrima MedikaBelum ada peringkat
- FMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFDokumen17 halamanFMS 1 - Week 7 Tutorial 1 LO PDFAprillia AlmaasBelum ada peringkat
- Breast CancerDokumen8 halamanBreast CancerHareem AliBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer PresentationDokumen48 halamanBreast Cancer Presentationvanessa91% (11)
- Think Pink 2013Dokumen4 halamanThink Pink 2013Messenger Post MediaBelum ada peringkat
- Municipal Health Office of Palompon CelebratesDokumen35 halamanMunicipal Health Office of Palompon CelebratesSophie Rose V R-zBelum ada peringkat
- BWC Lecture DR Filipinas RojoDokumen148 halamanBWC Lecture DR Filipinas RojoHyperalex1987Belum ada peringkat
- 1.page de Garde 2Dokumen8 halaman1.page de Garde 2Lu SuznBelum ada peringkat
- Mastectomy Final!Dokumen5 halamanMastectomy Final!Nilreb SamonteBelum ada peringkat
- Album de InglesDokumen8 halamanAlbum de Ingles夢於נмᷓBelum ada peringkat
- Refrat Onko RevDokumen4 halamanRefrat Onko RevYusuf Arif SalamBelum ada peringkat
- Entrepreneurship Project On Jam, Jelly & PicklesDokumen24 halamanEntrepreneurship Project On Jam, Jelly & Picklesashish karshinkarBelum ada peringkat
- Ultrasonic Weld Examination ProcedureDokumen16 halamanUltrasonic Weld Examination ProcedureramalingamBelum ada peringkat
- Library Dissertation in Community DentistryDokumen9 halamanLibrary Dissertation in Community DentistryPayForPaperCanada100% (1)
- 9600 DocumentDokumen174 halaman9600 Documentthom38% (13)
- Air Wellness QRSDokumen2 halamanAir Wellness QRSapi-3743459Belum ada peringkat
- Parts of ShipDokumen6 halamanParts of ShipJaime RodriguesBelum ada peringkat
- India - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen40 halamanIndia - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPrashanth KrishBelum ada peringkat
- TILE QUOTEDokumen3 halamanTILE QUOTEHarsh SathvaraBelum ada peringkat
- LSUBL6432ADokumen4 halamanLSUBL6432ATotoxaHCBelum ada peringkat
- ROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDokumen20 halamanROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDan George IIIBelum ada peringkat
- EP - EngineDokumen4 halamanEP - EngineAkhmad HasimBelum ada peringkat
- The Impact of Employees' Commitment Towards Food Safety at Ayana Resort, BaliDokumen58 halamanThe Impact of Employees' Commitment Towards Food Safety at Ayana Resort, Balirachelle agathaBelum ada peringkat
- Stability Calculation of Embedded Bolts For Drop Arm Arrangement For ACC Location Inside TunnelDokumen7 halamanStability Calculation of Embedded Bolts For Drop Arm Arrangement For ACC Location Inside TunnelSamwailBelum ada peringkat
- Essentials For Professionals: Road Surveys Using SmartphonesDokumen25 halamanEssentials For Professionals: Road Surveys Using SmartphonesDoly ManurungBelum ada peringkat
- Flexibility Personal ProjectDokumen34 halamanFlexibility Personal Projectapi-267428952100% (1)
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDokumen24 halamanPeptic Ulcer Disease: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentOktaviana Sari Dewi100% (1)
- Effect of Some Algal Filtrates and Chemical Inducers On Root-Rot Incidence of Faba BeanDokumen7 halamanEffect of Some Algal Filtrates and Chemical Inducers On Root-Rot Incidence of Faba BeanJuniper PublishersBelum ada peringkat
- B. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADDokumen25 halamanB. Pharmacy 2nd Year Subjects Syllabus PDF B Pharm Second Year 3 4 Semester PDF DOWNLOADarshad alamBelum ada peringkat
- Motor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor ConnectionsDokumen1 halamanMotor Wiring Diagram: D.C. Motor Connectionsczds6594Belum ada peringkat
- CAT Ground Engaging ToolsDokumen35 halamanCAT Ground Engaging ToolsJimmy Nuñez VarasBelum ada peringkat
- Phenomenological of in Church and TV WorshipDokumen18 halamanPhenomenological of in Church and TV WorshipCindy TirtaBelum ada peringkat
- Sto - Cristo Proper Integrated School 1 Grading Grade 9 Science Table of SpecializationDokumen2 halamanSto - Cristo Proper Integrated School 1 Grading Grade 9 Science Table of Specializationinah jessica valerianoBelum ada peringkat
- Who will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisDokumen12 halamanWho will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisbhasker sharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Revolutionizing Energy Harvesting Harnessing Ambient Solar Energy For Enhanced Electric Power GenerationDokumen14 halamanRevolutionizing Energy Harvesting Harnessing Ambient Solar Energy For Enhanced Electric Power GenerationKIU PUBLICATION AND EXTENSIONBelum ada peringkat
- Conjoint Analysis Basic PrincipleDokumen16 halamanConjoint Analysis Basic PrinciplePAglu JohnBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacokinetics and Drug EffectsDokumen11 halamanPharmacokinetics and Drug Effectsmanilyn dacoBelum ada peringkat
- An Online ECG QRS Detection TechniqueDokumen6 halamanAn Online ECG QRS Detection TechniqueIDESBelum ada peringkat
- IEEE T&D Insulators 101 Design CriteriaDokumen84 halamanIEEE T&D Insulators 101 Design Criteriasachin HUBelum ada peringkat
- DNB Paper - IDokumen7 halamanDNB Paper - Isushil chaudhari100% (7)
- Taking Back SundayDokumen9 halamanTaking Back SundayBlack CrowBelum ada peringkat