NCP Anxiety
Diunggah oleh
cathyDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NCP Anxiety
Diunggah oleh
cathyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
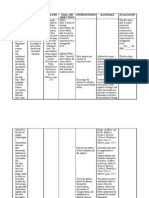
ASSESSM ENT Objectives: Suicidal behaviour Fear of being alone depression and anxiety selfdestructive feelings paranoia and
d loss of contact with real
DIAGNOSIS ANXIETY(sever e topanic) asevidenced byabuse of alcohol/other drugs andtransientpsy choticsymptom s
PLANNING
1. Limit
INTERVENTION Independent: Maintain open communication and provide consistency of care. Assess escalating anxiety and observe client contact inadequacy with reality
RATIONALE Provides for Accurate information and reduces anxiety. Underlying feelings of worthlessness, powerlessness can lead to increasing anxiety. Need for immediate gratification can lead to frustration and changes in behavior ,which may indicate loss of touch with reality May cloud symptomatology, potentiate erratic behavior, and interfere with progress therapeutic intervention
EVALUATION Client Will: Verbalize awareness of feelings of anxiety and healthy ways to deal with them. Recognize warning signs of increasing anxiety and validate perceptions before drawing conclusions. Develop and implement effective methods for decreasing anxiety. Report anxiety reduced to manageable level.
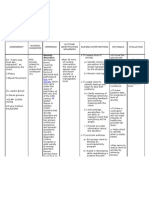
aggressive behavior; promote socially acceptable responses 2. Encourage assertive behaviors to attain sense of control.
3. Assist client
to learn healthy ways of controlling anxiety/develo ping positive self-concept.
4. Promote
Note rapid changes in behavior (e.g. ,from cooperative to angry ,demanding, argumentative). Monitor for substance use note physical symptoms of abuse (e.g., slurred speech, mood swings, dilated/requiring constricted pupils, abnormal vital signs, needle marks). Provide information in brief, clear, calm manner
development of effective coping skills.
5.
Help client learn alternate, constructive
Specific instructions and expectations about what is Use resources happening help client maintain effectively. contact with reality.
methods of interacting with others
Maintain calm, quiet, non stimulating environment.
Auditory and visual stimulation may increase labile affect and potential for acting-out Confronting misperceptions honestly, with a caring and accepting attitude, provides a therapeutic orientation to reality and preserves clients feelings of dignity and selfworth. Helps to establish a causeeffect relationship ,enhancing awareness and promoting change. Provides an understanding of the relationship between anxiety and drug use.
Correct misinterpretations of environment as expressed by the client
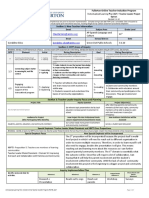
Encourage client to identify events that precipitate stress/anxious feelings Explore how client has dealt with these feelings, including times when substances were taken to relive tension, anxiety. Have client keep an anger journal Describing when anger occurs, how it is handled, and outcome insight of situation.
When reviewed periodically with primary nurse/therapist, therapeutic writing can provide into development of feelings, effectiveness of response and create opportunity to develop new coping
strategies Assist in learning to identify early warning signs that anxiety is escalating and request intervention before it becomes overwhelming. Ask client to describe events/feelings preceding, cutting or hurting self .Explore ways to relieve anxiety without selfdamaging acts. Discuss fears involving interactions with parents, spouse, children, or significant other(s). Collaborative: Administer medications as indicated: Antipsychotics, e.g., haloperidol(Haldol), to other therapeutic approaches. antidepressants A number of agents have been used with varying success to help alleviate symptoms of severe Promotes development of internal control.
Provides knowledge for adapting new effective coping skills and breaking the pattern of self-destructive acts. Knowledge of specific fear may provide insight into problem areas.
May help reduce anxiety, hostility, ideas of thiothixine(Navane),thiori dazine(Mellaril);reference,ill usions,increasingreceptivenes s
depression
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- NCP - AnxietyDokumen2 halamanNCP - AnxietyTarquin TomadaBelum ada peringkat
- Anxiety NCPDokumen3 halamanAnxiety NCPJulibeth Subong Dominguez50% (2)
- NCP Ineffective CopingDokumen3 halamanNCP Ineffective CopingAqua RentoBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Social Interaction Related To Fear of Being Scrutinized and Embarrassed by OthersDokumen9 halamanImpaired Social Interaction Related To Fear of Being Scrutinized and Embarrassed by Othersnathalie cotengBelum ada peringkat
- NCP AnxietyDokumen2 halamanNCP Anxietyjae_lee_730% (1)
- Anxiety NCPDokumen2 halamanAnxiety NCPTrinitine Poblete87% (70)
- NCPDokumen8 halamanNCPTrixia Diaz67% (3)
- Anxiety NCPDokumen1 halamanAnxiety NCPJamaica AbalosBelum ada peringkat
- Edited NCP AnxietyDokumen6 halamanEdited NCP AnxietyJerwelyn Joy100% (6)
- Anxiety NCPDokumen4 halamanAnxiety NCPRey Tommy NaponeBelum ada peringkat
- NCP AnxietyDokumen1 halamanNCP AnxietyLeanie Louise50% (8)
- Knowledge DeficitDokumen3 halamanKnowledge DeficitInigo Miguel DulayBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Self HarmDokumen1 halamanNCP Self HarmJoshua ArevaloBelum ada peringkat
- NCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesDokumen1 halamanNCP DisturbedThoughtProcessesJoan KarlaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Anxiety (Mild)Dokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan Nursing Diagnosis Anxiety (Mild)yvenette_kris871881% (27)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen3 halamanDecreased Cardiac OutputTiffany Mathis100% (1)
- NCP FearDokumen3 halamanNCP FearKristian Urcia Serrano100% (6)
- NCP AnxietyDokumen2 halamanNCP AnxietyVanessa SumalbagBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - AnxietyDokumen1 halamanNCP - AnxietyNovie Carla100% (1)
- Bipolar NCPDokumen2 halamanBipolar NCPGenevieve VLs100% (1)
- ND - Risk For SuicideDokumen3 halamanND - Risk For SuicideHu Dawi100% (2)
- Self Care NCPDokumen2 halamanSelf Care NCPMick De Leon100% (3)
- NCPDokumen3 halamanNCPChrisTine M. MoralesBelum ada peringkat
- Ncp-Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsDokumen3 halamanNcp-Imbalanced Nutrition Less Than Body RequirementsAllan Maglente63% (8)
- BPD NCP 1Dokumen4 halamanBPD NCP 1Jordz PlaciBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDokumen3 halamanNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP FearDokumen3 halamanNCP Fearエド パジャロン100% (1)
- NCP DepressionDokumen2 halamanNCP Depressionhollymadison80% (5)
- NCP MiDokumen4 halamanNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Everyone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDokumen4 halamanEveryone Would Be Better Off Without Me" As Verbalized by The PatientDanica Kate GalleonBelum ada peringkat
- Bipolar NCPDokumen2 halamanBipolar NCPweehdinga89% (9)
- NCPDokumen7 halamanNCPJo Chiko FlorendoBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDokumen3 halamanActivity Intolerance Related To Decrease Blood FlowDarkCeades100% (3)
- Disturbed Sensory PerceptionDokumen2 halamanDisturbed Sensory Perceptionsuper ahga-once0% (1)
- Care Plan 27Dokumen10 halamanCare Plan 27Oroma TobiasBelum ada peringkat
- Activity IntoleranceDokumen1 halamanActivity IntoleranceJoshua D. Garcia100% (1)
- NCP Activity IntoleranceDokumen5 halamanNCP Activity IntoleranceRea HashimBelum ada peringkat
- Risk For InjuryDokumen2 halamanRisk For InjuryRo-anne AkuBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Set 1Dokumen18 halamanNCP Set 1Augene Toribio50% (2)
- Problem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentDokumen2 halamanProblem Nursing Diagnosis Outcome Plan Intervention Evaluation Subjective Data: "Masakit Po Yung Sa Short Term: IndependentkyawBelum ada peringkat
- Casilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Dokumen3 halamanCasilan Ynalie S BSN 2-2Ynalie Casilan100% (1)
- NCP Acute PainDokumen4 halamanNCP Acute PainSj 斗力上Belum ada peringkat
- SAMPLE NCP For Angina PectorisDokumen3 halamanSAMPLE NCP For Angina Pectorisseanne_may100% (4)
- NCP Nursing Care Plan For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDSDokumen6 halamanNCP Nursing Care Plan For Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome ARDSTina Larsen100% (4)
- NCP Imbalanced NutritionDokumen2 halamanNCP Imbalanced Nutritioncj_080882% (22)
- CBT For PsychosisDokumen21 halamanCBT For PsychosisjigishazopeBelum ada peringkat
- 10 - Cognitive TherapyDokumen32 halaman10 - Cognitive TherapymartinjeanellBelum ada peringkat
- Psychoanalysis View of Human NatureDokumen27 halamanPsychoanalysis View of Human NatureHollis VilagosBelum ada peringkat
- Counseling and Psychotherapy-1Dokumen40 halamanCounseling and Psychotherapy-1Sara Kaleem100% (1)
- Factors Affecting Health and IllnessDokumen13 halamanFactors Affecting Health and IllnessEduard100% (4)
- Principles of Mental Health NursingDokumen26 halamanPrinciples of Mental Health NursingHardeep KaurBelum ada peringkat
- Adigrat UniversityDokumen16 halamanAdigrat UniversityabrihamBelum ada peringkat
- Lec 4 Three Phases of Nurse-Client Relationship (Psychiatric Nursing)Dokumen10 halamanLec 4 Three Phases of Nurse-Client Relationship (Psychiatric Nursing)imafashionistaBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 117 - Nurse Patient Interaction - April 2021Dokumen58 halamanNCM 117 - Nurse Patient Interaction - April 2021kimberly dedaseBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Psy NotesDokumen8 halaman12 Psy NotesAziyaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care and Management of Client With SchizophreniaDokumen29 halamanNursing Care and Management of Client With SchizophreniaMaizatul Akmar IbrahimBelum ada peringkat
- psy-TREATMENT PLANDokumen3 halamanpsy-TREATMENT PLANWil SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 6 B Therapeutic Relationship-1Dokumen36 halamanUnit 6 B Therapeutic Relationship-1Nayel ZeeshanBelum ada peringkat
- Rational Emotive Behavioral Therapy: Josemon P.George V Mba (PT)Dokumen27 halamanRational Emotive Behavioral Therapy: Josemon P.George V Mba (PT)Josemon George ParanilamBelum ada peringkat
- DLL in Eng10 3rd QuarterDokumen29 halamanDLL in Eng10 3rd QuarterDonna Toroba100% (3)
- M C M C M C: Super Minds Lesson 2Dokumen3 halamanM C M C M C: Super Minds Lesson 2Shamalaa RushaBelum ada peringkat
- 01 GrammarOnlinePrintable PDFDokumen81 halaman01 GrammarOnlinePrintable PDFSusana GarridoBelum ada peringkat
- Module 1 Lesson 1 Introduction To Materials DevelopmentDokumen17 halamanModule 1 Lesson 1 Introduction To Materials DevelopmentEric Cabrera100% (1)
- Center-Based Eccd PROGRAM Conducted in An Alternative Venue (CBPAV)Dokumen24 halamanCenter-Based Eccd PROGRAM Conducted in An Alternative Venue (CBPAV)GenderAnd Development Mabalacat100% (5)
- Blue & Black Artificial Intelligence Vocabulary Memory Game FlashcardsDokumen3 halamanBlue & Black Artificial Intelligence Vocabulary Memory Game FlashcardsAndreeOlmosBelum ada peringkat
- Dilemma Ethics Relate To NursingDokumen5 halamanDilemma Ethics Relate To NursingMaulina AyuBelum ada peringkat
- Space in Electroacoustic Music Composition Performance and Perception of Musical Space - Frank Ekeberg Henriksen - 2002Dokumen165 halamanSpace in Electroacoustic Music Composition Performance and Perception of Musical Space - Frank Ekeberg Henriksen - 2002Rfl Brnb GrcBelum ada peringkat
- Letter To The Editor: Relevance Research: The Missing Perspective(s) : "Non-Relevance" and "Epistemological Relevance"Dokumen3 halamanLetter To The Editor: Relevance Research: The Missing Perspective(s) : "Non-Relevance" and "Epistemological Relevance"davidrojasvBelum ada peringkat
- Taboo Conversation Topics - ListeningDokumen7 halamanTaboo Conversation Topics - Listeningmaithiquy_861634688Belum ada peringkat
- CH 3 Present Perfect Vs Present Perfect ContinuousDokumen28 halamanCH 3 Present Perfect Vs Present Perfect ContinuousIndra WijayaBelum ada peringkat
- Thesis 6 Live Experiences of Senior High School Students in Mathematics inDokumen29 halamanThesis 6 Live Experiences of Senior High School Students in Mathematics inShiela Mae BasilioBelum ada peringkat
- Briere & Scott CH 6 - DISTRESS REDUCTION AND AFFECT REGULATION TRAININGDokumen14 halamanBriere & Scott CH 6 - DISTRESS REDUCTION AND AFFECT REGULATION TRAININGEmma WrigleyBelum ada peringkat
- Detailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Continuation of Previous DLPDokumen6 halamanDetailed Lesson Plan (DLP) Format: Continuation of Previous DLPOrlando Mecayer MagcalasBelum ada peringkat
- Syllabus Intro To BusinessDokumen2 halamanSyllabus Intro To Businessapi-258404762Belum ada peringkat
- Difference Between Ability and SkillDokumen7 halamanDifference Between Ability and SkilldanaBelum ada peringkat
- NCM 107Dokumen264 halamanNCM 107Jyra Mae TaganasBelum ada peringkat
- Report of Business Ethics On: "Ethical Relativism"Dokumen49 halamanReport of Business Ethics On: "Ethical Relativism"Sadia AminBelum ada peringkat
- Kuhlmann - Introduction To Computational Linguistics (Slides) (2015)Dokumen66 halamanKuhlmann - Introduction To Computational Linguistics (Slides) (2015)JoeJune100% (1)
- The Importance of Value Education For Children NationDokumen6 halamanThe Importance of Value Education For Children NationInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyBelum ada peringkat
- IELTS Academic Writing Task 1: How To Describe A GraphDokumen9 halamanIELTS Academic Writing Task 1: How To Describe A Graphakhilesh sahooBelum ada peringkat
- A16 02 Hanegraaf Problem of Post GosticismDokumen40 halamanA16 02 Hanegraaf Problem of Post GosticismCaz ZórdicBelum ada peringkat
- Very Rigorous Method of Cheating The SystemDokumen4 halamanVery Rigorous Method of Cheating The SystembeappyBelum ada peringkat
- My Portfolio in Ed TechDokumen37 halamanMy Portfolio in Ed TechAntonio DelgadoBelum ada peringkat
- 1 - H7GD Ia 12Dokumen3 halaman1 - H7GD Ia 12Sarah mae EmbalsadoBelum ada peringkat
- Development of School Based Remedial Reading ProgramDokumen87 halamanDevelopment of School Based Remedial Reading ProgramMARYNILLE JOY DELA CRUZBelum ada peringkat
- A1006770035 - 25684 - 13 - 2021 - Ca1 Soc 111Dokumen5 halamanA1006770035 - 25684 - 13 - 2021 - Ca1 Soc 111Naikoo DanishBelum ada peringkat
- People Selection Process Toyota StyleDokumen5 halamanPeople Selection Process Toyota StyleRamyata Mahajan0% (1)
- Parts of Speech in FrenchDokumen3 halamanParts of Speech in FrenchApeuDerropBelum ada peringkat
- Ilp FullertonDokumen3 halamanIlp Fullertonapi-467608657Belum ada peringkat