Nursing Care Plan
Diunggah oleh
Jess Fernandez BorgaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Nursing Care Plan
Diunggah oleh
Jess Fernandez BorgaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
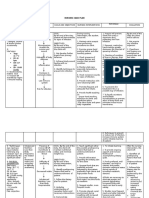
NURSING CARE PLAN
Cues and Evidences
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing Objectives
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
Subjective: Ubos lage daw iyang hemoglobin ingon ang doctor ug naa man gud pod ga gawas nga dugo diha sa iyang samad sa lagos as verbalized by the client live in partner .
Risk for infection related inadequate primary and secondary defenses (decrease hemoglobin and traumatized tissue)
LTO: At the end of 3 days the client would be able to remain free of symptoms of infection and demonstrate appropriate care of infection prone site STO: At the end of the first visit , we would be able to impart health teachings to the client and family member emphasizing the hygienic measure to prevent infection and SSx of infection of which to be aware of.
1. Observe and report sign of infection such as redness, warmth, discharge, and increase body temperature.
Objective: Restlessness Weakness Presence of dried blood on the face towel covered on her head noted V/s: Temp: 36.2 PR: 106 bpm RR: 26 cpm BP: 90/60mmHg
Prospective surveillance study for nasocomial infection on hematologyoncology units should include fever of unknown origin as the single most common and clinically important entity. Lab values are correlated with client history and provide a global view of client immune function and to develop an appropriate plan care for diagnosis. To formulate plan and nursing intervention to
Goal Fully met.
2. Note and report laboratory values.
Lab result: Hgb: 7.5g/dl Hct: 22.7 vol %
3. Observe for localized signs of infection at wounds.
prevent infection. 4. Stress proper hand hygiene by all caregiver and client. Collaborative: 1. Each client and family member the risk factors contributing to surgical wound infection, smoking and high BMI. 2. Refer client and family to social services and community resources. These are some factors associated with risk of surgical wound infections. First line defense against infections.
To obtain support in maintaining a lifestyle that increase immune function.
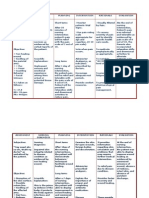
Cues and Evidences
Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing Objectives
Nursing Intervention
Rationale
Evaluation
Subjective: Dili gyud ko ganahan na mag pangarte kay tungid sa akong kahimtang As verbalized by the client
Objective: Restlessness Less eye to eye contact Facial discomfort noted V/s: Temp- 36.4 PR: 111bpm RR: 23cpm BP:90/70 mmHg
Self care deficit, dressing/grooming related discomfort and lack of motivation as manifested by inability to maintain appearance at a satisfactory level
LTO: At the end of 3 days the client would be able to dress and groom self optional potential. STO: At the end of the visit, the client would be able to maintain appearance at a satisfactory level and we methods to enhance strength during dressing and grooming.
1. Observe the client ability to dress and groom self through direct observation and noting specific deficits and their causes.
Presence of chronic diseases alter dressing routines, and understanding these routines can allow development of energy conservation method of dressing. Energy conservation increases activity tolerance and promotes self care. An established routine of walking and dressing provides a sense of normalcy and increase motivation to perform self care.
2. Plan activity to prevent fatigue while dressing and grooming.
3. Encourage client to dress appropriately for time of day. Perform dressing and grooming activities in a consistent sequence each day.
Collaborative: 1. Teach the client and family to dress the affected side first, then the unaffected side. 2. Teach the client and family to select clothes appropriate for season, temperature, and weather. Dressing the affected side first allows for easier manipulation of clothing.
Clients with altered sensation need to understand the factors that influence body temperature and the environment.
NURSING CARE PLAN
DRUG STUDY
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
indication
Side effects and Contraindications adverse effects CNS: headache CV: chest pain Dyspnea Contraindicated with allergy to acetaminophen.
Nursing Responsibilities Do not exceed the recommend ed dosage. Avoid using multiple preparations containing acetaminop hen. Carefully check the OTC products. Give drug with foods if GI upset occurs.
Patient teaching Do not take for longer than 10 days. Take the drug only for complaint s indicate; it is not an antiinflammat ory agent. Report rash, unusual bleeding or bruising, yellow of skin or eyes, changes in voiding patterns.
Generic name:
Reduces fever by acetaminophen acting (Paracetamol) directly on the hypothalamic Classification: heat Anti-pyretic regulating Analgesic center to (non-opioid) cause vasodilation Pracetamol and 500 mg tab sweating, every 4 hours which helps PRN for fever. dissipate heat. Site and mechanism of action unclear.
Analgesicantipyretic in patients with aspirin allergy, hemostatic disturbances, bleeding diatheses, upper GI disease, gouty arthritis.
Use cautiously GI: Hepatic with impaired toxicity and hepatic function, failure jaundice. chronic alcoholism and GU: acute pregnancy, kidney failure, lactation. renal tubular necrosis. Hypersensitivity: Rash, fever.
DRUG STUDY
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
indication
Side effects and adverse effects CNS: headache, dizziness
Contraindications
Nursing Responsibilities
Patient teaching
Generic name: Mefenamic Acid
Anti-pyretic Analgesic Antiinflammatory Classification: Activities Anti-pyretic related to Analgesic inhibition of Antiprostaglandin inflammatory synthesis; exact Mefenamic mechanism of Acid every 6 action area is hours RTC. not known.
Relief of moderate pain when therapy will not exceed 1 week.
Contraindicated to hypersensitivity to mefenamic GI: nausea, acid, aspirin GI pain, allergy, and as diarrhea, treatment of vomiting preoperative pain with coronary Other: artery bypass peripheral grafting. edema Use cautiously in asthmatic patient, renal or hepatic impairment, patient has a heart failure and in the pregnant and breastfeeding woman.
Give with milk or food to decrease GI upset. Monitor the level of consciousn ess.
Report any unusual happenin g.
DRUG STUDY
Name of drug
Mechanism of action
indication
Side effects and adverse effects
Contraindications
Nursing Responsibilities
Patient teaching
Generic name: Cefazolin
Treat a wide variety of bacterial Classification: infections. It Cephalosporin may also be antibiotic used before and during Cefazolin IVTT certain now ANST (-) surgeries to help prevent infections.
It will not work with viral infections. Unnecessary use or misuse of any antibiotic can lead to its decreased effectiveness.
Loss of Contraindicated appetite; mild with diarrhea; hypersensitivity nausea; of cephalosporin stomach agents. cramps; Use cautiously in vomiting. children younger than 1 month or younger than 10 years old, be cautious also to the elderly for they may be more sensitive to its effects.
any Check level Report unusual of consciousn happening. ess. Monitor vital signs.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Anti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIIIDari EverandAnti-Aging Therapeutics Volume XIIIBelum ada peringkat
- NCP HyperthermiaDokumen6 halamanNCP HyperthermiaGrax DeeBelum ada peringkat
- NCP Knowledge Deficit (FINAL)Dokumen8 halamanNCP Knowledge Deficit (FINAL)Nikki Ricafrente89% (9)
- NCPDokumen17 halamanNCPShayne Jessemae AlmarioBelum ada peringkat
- NCP and Drug StudyDokumen11 halamanNCP and Drug StudyTonio PagaoBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen5 halamanNCPSheana TmplBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Gastritis in PediaDokumen13 halamanAcute Gastritis in PediaMenchie Vivas-AlotBelum ada peringkat
- NCP GCP FinalDokumen15 halamanNCP GCP FinalssilvozaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP and DrugsDokumen13 halamanNCP and DrugsApRil ANn ChUa BingcangBelum ada peringkat
- Acute GastritisDokumen14 halamanAcute GastritisMenchie Vivas-AlotBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlansDokumen7 halamanNursing Care PlansNicholaiCabadduBelum ada peringkat
- CS URTIs BSN3AG3Dokumen21 halamanCS URTIs BSN3AG3GLORY MI SHANLEY CARUMBABelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen6 halamanNCPAngelaTrinidadBelum ada peringkat
- Myocardial InfarctionDokumen5 halamanMyocardial InfarctionDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP and Drug Study For Case in SleDokumen34 halamanNCP and Drug Study For Case in SlePaolo Vittorio Perdigueros GonzalesBelum ada peringkat
- Diagno SIS Planni NG Intervention Rationale Evaluati ONDokumen3 halamanDiagno SIS Planni NG Intervention Rationale Evaluati ONAnn Nicole G. NeriBelum ada peringkat
- The Use of ThrombolyticsDokumen9 halamanThe Use of ThrombolyticsNestleBelum ada peringkat
- Guillain Barre SyndromeDokumen21 halamanGuillain Barre Syndromebasinang_jangilBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen10 halamanNCPannamargie07Belum ada peringkat
- Ncar (Sr. Nerlyn)Dokumen9 halamanNcar (Sr. Nerlyn)nerlynBelum ada peringkat
- CASE ANALYSIS IMMUNITY (Operaña, Ellayza)Dokumen5 halamanCASE ANALYSIS IMMUNITY (Operaña, Ellayza)OPERAñA ELLAYZA RB DECANOBelum ada peringkat
- AssessmentDokumen4 halamanAssessmentJhaypee SorianoBelum ada peringkat
- Caring For Children Receiving Chemotherapy, Antimicrobial Therapy and Long-Term Insulin TherapyDokumen34 halamanCaring For Children Receiving Chemotherapy, Antimicrobial Therapy and Long-Term Insulin TherapyRubinaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For OsteomyleitisDokumen5 halamanNCP For OsteomyleitisAyaBasilioBelum ada peringkat
- PlateletDokumen16 halamanPlateletArgene Rose MilletBelum ada peringkat
- Drug StudyDokumen17 halamanDrug Studyjlg513Belum ada peringkat
- Dec 21 23 Case Study ModuleDokumen7 halamanDec 21 23 Case Study ModuleKristian Karl Bautista Kiw-isBelum ada peringkat
- Laryngeal Cancer - DanDokumen12 halamanLaryngeal Cancer - DanRoldan VidadBelum ada peringkat
- Gnur 405 SuzyDokumen6 halamanGnur 405 SuzySeth MensahBelum ada peringkat
- Cap NCPDokumen6 halamanCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- DocxDokumen7 halamanDocxShannon GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansDokumen19 halaman5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansRoanna Alyssa Sy Jimenez75% (4)
- DischargeDokumen49 halamanDischargejonel_amarilleBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen10 halamanNursing Care PlanSittie Rohaina SabanBelum ada peringkat
- HEMATOLOGICAL CONDITIONS Answers Theory 2Dokumen14 halamanHEMATOLOGICAL CONDITIONS Answers Theory 2CJ RelleveBelum ada peringkat
- Subjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. ObjectiveDokumen4 halamanSubjective: "Nahihirapan Ako Huminga" As Verbalized by The Patient. Objectivechaoz09Belum ada peringkat
- NURSING CARE PLAN On LeptospirosisDokumen8 halamanNURSING CARE PLAN On LeptospirosisRosalie Valdez Espiritu71% (7)
- Cardiovascular Drug ProjectDokumen3 halamanCardiovascular Drug ProjectHannaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study QiDokumen7 halamanDrug Study QiJeremiah Mauricio100% (1)
- NCP Laryngeal CancerDokumen10 halamanNCP Laryngeal CancerAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (2)
- Case Study Chapter 33Dokumen3 halamanCase Study Chapter 33Anjae GariandoBelum ada peringkat
- Study File ImportantDokumen12 halamanStudy File Importantsami khanBelum ada peringkat
- NCPPPPDokumen6 halamanNCPPPPIvan Liquiran AvenadoBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen7 halamanNCPLouis RoderosBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea Drug StudyDokumen12 halamanDiarrhea Drug StudyCeelin Robles0% (1)
- Maternal ATIDokumen6 halamanMaternal ATIGeorgeBelum ada peringkat
- NCMB 312 MS RLE WEEK 15 Concept Mapping GI BleedingDokumen2 halamanNCMB 312 MS RLE WEEK 15 Concept Mapping GI BleedinggabbyBelum ada peringkat
- Integrated Process NP AnalysisDokumen146 halamanIntegrated Process NP AnalysisDonaJeanBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical NCPDokumen6 halamanSurgical NCPAreeya SushmitaBelum ada peringkat
- Preassignment Work-Careplan #2Dokumen30 halamanPreassignment Work-Careplan #2djbhetaBelum ada peringkat
- ReportDokumen4 halamanReportKyle DapulagBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen8 halamanNCPJose Benit DelacruzBelum ada peringkat
- Ugib NCPDokumen5 halamanUgib NCPJhuRise Ann Mangana100% (1)
- KETOROLACDokumen7 halamanKETOROLACtalitha kumiBelum ada peringkat
- Tablet Paracetamol: Phenobarb, Liver Enzyme Inducers, HepatotoxicDokumen19 halamanTablet Paracetamol: Phenobarb, Liver Enzyme Inducers, Hepatotoxicnafahmi2Belum ada peringkat
- Concept Map Care PlanDokumen5 halamanConcept Map Care Planapi-252910411Belum ada peringkat
- Gastroenterology Hospital Handbook Volume 2: Volume, #2Dari EverandGastroenterology Hospital Handbook Volume 2: Volume, #2Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Assessment, Nursing Interventions GuideDari EverandNursing Care Plans: Nursing Diagnosis and Assessment, Nursing Interventions GuidePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (4)
- Question 2 FundamentalsDokumen7 halamanQuestion 2 FundamentalsJess Fernandez BorgaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample QuestionareDokumen4 halamanSample QuestionareJess Fernandez BorgaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Practice I-AnswerDokumen9 halamanNursing Practice I-AnswerJess Fernandez BorgaBelum ada peringkat
- Sample QuestionnaireDokumen10 halamanSample QuestionnaireJess Fernandez BorgaBelum ada peringkat
- Medical Surgical Nursing With MnemonicsDokumen110 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing With MnemonicsJerome F. Adorable, RN92% (76)
- Medical Surgical Nursing With MnemonicsDokumen110 halamanMedical Surgical Nursing With MnemonicsJerome F. Adorable, RN92% (76)
- Practice Test Pediatric Nursing 100 ItemsDokumen17 halamanPractice Test Pediatric Nursing 100 ItemsPaul Christian P. Santos, RN94% (87)
- Hyperparathyroidism: Diabetes Incipidus Lab Test and DiagnosticDokumen3 halamanHyperparathyroidism: Diabetes Incipidus Lab Test and DiagnosticJess Fernandez BorgaBelum ada peringkat
- PsychodramaDokumen5 halamanPsychodramaAkhila R KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Materials Today: Proceedings: Ashish Malik, Shivam KohliDokumen7 halamanMaterials Today: Proceedings: Ashish Malik, Shivam KohliSenthil KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Von Willebrand Disease in WomenDokumen0 halamanVon Willebrand Disease in WomenMarios SkarmoutsosBelum ada peringkat
- Flaxseed Paper PublishedDokumen4 halamanFlaxseed Paper PublishedValentina GarzonBelum ada peringkat
- G1 CurvedDokumen16 halamanG1 CurvedElbert Ryan OcampoBelum ada peringkat
- XII Biology Practicals 2020-21 Without ReadingDokumen32 halamanXII Biology Practicals 2020-21 Without ReadingStylish HeroBelum ada peringkat
- Life Everlasting 2021001Dokumen11 halamanLife Everlasting 2021001realangelinemylee2020721001Belum ada peringkat
- Rev C Diagnostic Repair Manual AC Evolution 1.0 2.0 50 60 HZDokumen254 halamanRev C Diagnostic Repair Manual AC Evolution 1.0 2.0 50 60 HZVariACK100% (1)
- Permatex, Inc - Ultra Gasket Sealant 1ozDokumen3 halamanPermatex, Inc - Ultra Gasket Sealant 1ozjaredf@jfelectric.comBelum ada peringkat
- TMP DEDADokumen8 halamanTMP DEDAFrontiersBelum ada peringkat
- Research Article Effects of PH On The Shape of Alginate Particles and Its Release BehaviorDokumen10 halamanResearch Article Effects of PH On The Shape of Alginate Particles and Its Release BehaviorAmalia HanifaBelum ada peringkat
- Principles in Biochemistry (SBK3013)Dokumen3 halamanPrinciples in Biochemistry (SBK3013)Leena MuniandyBelum ada peringkat
- Finding Clara: Establishing The Biographical Details of Clara Peeters (Ca. 1587-After 1636)Dokumen15 halamanFinding Clara: Establishing The Biographical Details of Clara Peeters (Ca. 1587-After 1636)victoriagalapedroBelum ada peringkat
- 7-13-1996 Joel Nance MDDokumen3 halaman7-13-1996 Joel Nance MDAnother AnonymomsBelum ada peringkat
- African Traditional Medicine A PrimerDokumen5 halamanAfrican Traditional Medicine A PrimerEditor IJTSRDBelum ada peringkat
- LUBRICANTCOOLANT Answer With ReflectionDokumen5 halamanLUBRICANTCOOLANT Answer With ReflectionCharles Vincent PaniamoganBelum ada peringkat
- The Man S Bible 50 Essential Tips For Success With Your Mind Body and WomenDokumen155 halamanThe Man S Bible 50 Essential Tips For Success With Your Mind Body and WomenDonStemple100% (4)
- Textile Chemical Brochure 8.6.22 - 031Dokumen1 halamanTextile Chemical Brochure 8.6.22 - 031NIKESH PRAKASHBelum ada peringkat
- Monthly Hse Report Nhai Org inDokumen12 halamanMonthly Hse Report Nhai Org inPhilip S. GongarBelum ada peringkat
- Aahaa Puttu Flour ProjectDokumen53 halamanAahaa Puttu Flour ProjectApple ComputersBelum ada peringkat
- Chan vs. ChanDokumen2 halamanChan vs. ChanMmm GggBelum ada peringkat
- Guide For Visual Inspection of Structural Concrete Building ComponentsDokumen76 halamanGuide For Visual Inspection of Structural Concrete Building ComponentsMazin AlwashBelum ada peringkat
- Di SilvioDokumen47 halamanDi SilviomaryroseengBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Anatomy and Physiology ReviewDokumen20 halamanBlood Anatomy and Physiology ReviewStacey CamilleBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 - Alkanes PDFDokumen54 halamanChapter 2 - Alkanes PDFSITI NUR ALISSA BINTI AHMAD RASMANBelum ada peringkat
- Lending Policies of Indian BanksDokumen47 halamanLending Policies of Indian BanksProf Dr Chowdari Prasad80% (5)
- Acc030 Financial Statement & Income Statement FormatDokumen2 halamanAcc030 Financial Statement & Income Statement FormatAqilahBelum ada peringkat
- KQ2H M1 InchDokumen5 halamanKQ2H M1 Inch林林爸爸Belum ada peringkat
- Clinical Crown Lengthening in The Esthetic Zone2028Dokumen12 halamanClinical Crown Lengthening in The Esthetic Zone2028AchyutSinhaBelum ada peringkat
- Arcelor Mittal Operations: Operational Area Is Sub-Divided Into 4 PartsDokumen5 halamanArcelor Mittal Operations: Operational Area Is Sub-Divided Into 4 Partsarpit agrawalBelum ada peringkat