Hypo Vole Mia
Diunggah oleh
Aladil TapsiDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Hypo Vole Mia
Diunggah oleh
Aladil TapsiHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
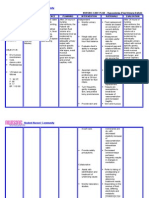
NCP - Hypovolemia (Fluid Volume Deficit)
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
SUBJECTIVE:
Deficient fluid volume may be related to active fluid loss (hemorrha ge, vomiting, gastric intubation, diarrhea, burns, wounds, fistulas).
Inadequate water intake, loss through vomiting, diarrhea, gastrointesti nal obstruction, fever or sweating, hemorrhage, burns, third space fluid shifting.
After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the Patient will maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by individually adequate urinary output with normal specific gravity, stable vital signs, moist mucous membranes, good skin turgor, and prompt capillary refill.
Independent Monitor urinary output. Weigh daily and compare with 8-hour fluid balance. Evaluate clients ability to manage own hydration Ascertain clients beverage preference s, and set up a 24hour schedule for fluid intake. Turn frequently, gently massage skin, and protect bony prominenc es.
Fluid replacement needs are based on correction of current deficits and ongoing losses. Measurement provides useful data for comparison. Impaired gag and swallow reflexes and change in level of consciousness are among the factors that affect clients ability to replace fluids orally. Relieves thirst and discomfort of dry mucous membranes and augments parenteral replacement. Tissues are susceptible to breakdown because of
After 8 hours of nursing interventions, the Patient was able to maintain fluid volume at a functional level as evidenced by individually adequate urinary output with normal specific gravity, stable vital signs, moist mucous membranes, good skin turgor, and prompt capillary refill.
Limang araw na akong nagtatae at suka (I have been
vomiting and having diarrhea for 5 days) as
verbalized by the patient.
OBJECTIVE: Dry mucous membranes Cold, clammy skin Restlessness
V/S taken as follows T: 36.5C P: 78 R: 20 BP: 120/ 80
Provide skin and mouth care.
vasoconstrictio n and increased fragility. Skin and mucous membranes are dry with decreased elasticity because of vasoconstrictio n and reduced intracellular water. Decreased cerebral tissue perfusion frequently results in changes in mentation. Refer to listing of predisposing or contributing factors to determine treatment needs. Depending on the avenue of fluid loss, differing electrolyte and metabolic imbalances may be present and require correction.
Provide safety precaution s.
Collaborative: Assist with identificati on and treatment of underlying cause. Monitor laboratory studies.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Fluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsDokumen17 halamanFluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsA.Belum ada peringkat
- 4 Phases of IV Fluid Therapy FinalDokumen29 halaman4 Phases of IV Fluid Therapy FinalLuqmanul Hakim Junaidden100% (1)
- Aguinaldo Nursing Care Plan Ulcerative ColitisDokumen3 halamanAguinaldo Nursing Care Plan Ulcerative ColitisSophia Kaye Aguinaldo100% (1)
- NCP For Nephrotic SyndromeDokumen2 halamanNCP For Nephrotic SyndromeLee Jenny100% (5)
- Risk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPDokumen2 halamanRisk For Deficient Fluid Volume Best NCPMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon83% (47)
- Defient Fluid Volume Intake and Impaired Mobility NCPDokumen6 halamanDefient Fluid Volume Intake and Impaired Mobility NCPjordan aguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Leachables Best Practice Guideline Disposable Solutions For Biomanufacturing PDFDokumen36 halamanLeachables Best Practice Guideline Disposable Solutions For Biomanufacturing PDFAziz Aditya Wiguna100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plans With Nursing DiagnosisDokumen6 halamanNursing Care Plans With Nursing DiagnosisLalaine RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- NCP & FdarDokumen3 halamanNCP & Fdarkingawesome21Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen28 halamanNursing Care PlanChristine Karen Ang Suarez67% (3)
- Co-Occurring Disorders: Substance Use and Mental HealthDokumen52 halamanCo-Occurring Disorders: Substance Use and Mental HealthElisyah MarsiahBelum ada peringkat
- Dengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDokumen1 halamanDengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume Deficitemman_abz100% (5)
- SAMPLE NCP For Diabetes InsipidusDokumen3 halamanSAMPLE NCP For Diabetes InsipidusClancy Anne Garcia Naval50% (2)
- The 12 Essentials of Quality Management in Laboratory EnvironmentsDokumen5 halamanThe 12 Essentials of Quality Management in Laboratory EnvironmentsKristine Randall D. Tandoc100% (3)
- Case Study of Children With Special NeedsDokumen21 halamanCase Study of Children With Special NeedsGrf Trust83% (69)
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDokumen2 halamanNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen14 halamanNCPclaidelynBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusDokumen5 halaman3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusAnnisa Silvera II50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Fluid Volume DeficitDokumen2 halamanNursing Care Plan Fluid Volume DeficitXtinego89% (9)
- Amoebiasis NCPDokumen3 halamanAmoebiasis NCPRellie CastroBelum ada peringkat
- AnxolamDokumen38 halamanAnxolammanjitdeshmukh2Belum ada peringkat
- Risk For DehydrationDokumen2 halamanRisk For DehydrationJahne CM80% (5)
- Lanjutan NCP DMDokumen14 halamanLanjutan NCP DMVera Andri YaniBelum ada peringkat
- SbarDokumen3 halamanSbarCharlie65129Belum ada peringkat
- Anima: Beyond Fantasy Character SheetDokumen4 halamanAnima: Beyond Fantasy Character SheetTristan TaksonBelum ada peringkat
- NCP For DehydrationDokumen3 halamanNCP For Dehydrationpeter_degamo200025% (4)
- Nursing Students Peritonitis Care PlanDokumen2 halamanNursing Students Peritonitis Care PlanJide Manuel100% (1)
- Actual Nursing Care Plan 2Dokumen16 halamanActual Nursing Care Plan 2Alyanna Evangelista100% (2)
- Jil 1Dokumen1 halamanJil 1Jillybanie LigsayBelum ada peringkat
- Deficit) 1Dokumen2 halamanDeficit) 1Richard AcibarBelum ada peringkat
- Hypovolemia (Fluid Deficit)Dokumen2 halamanHypovolemia (Fluid Deficit)Lyn Reyes100% (1)
- Deficit)Dokumen2 halamanDeficit)Lee DeeBelum ada peringkat
- Deficit)Dokumen2 halamanDeficit)goldenboyjBelum ada peringkat
- NCP 1Dokumen3 halamanNCP 1kat2111993Belum ada peringkat
- Aguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningDokumen9 halamanAguinaldo, Sophia Kaye M. Nursing Care Plan On Problem-Based LearningSophia Kaye AguinaldoBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Volume DeficitDokumen3 halamanFluid Volume DeficitDan Gerald Alcido SalungaBelum ada peringkat
- Deficient Fluid VolumeDokumen1 halamanDeficient Fluid VolumeSheila ErpeloBelum ada peringkat
- NCP RiskDokumen3 halamanNCP RiskMaricar Azolae MascualBelum ada peringkat
- PeritonitisDokumen6 halamanPeritonitisDiane ArgoteBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment: N/a Diagnosis: Risk For Fluid Volume Excess Related To Compromise Renal Function Planning: Within 8 Hours of Effective Nursing Intervention, Patient Will Be Able ToDokumen4 halamanAssessment: N/a Diagnosis: Risk For Fluid Volume Excess Related To Compromise Renal Function Planning: Within 8 Hours of Effective Nursing Intervention, Patient Will Be Able Tomichael_jesus_8Belum ada peringkat
- Acute Gastroentiritis (NCP)Dokumen3 halamanAcute Gastroentiritis (NCP)April ParanganBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan3Dokumen6 halamanNursing Care Plan3Kristine Artes AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokumen9 halamanNursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationJezza Sanchez-Rellita VillariasBelum ada peringkat
- NCP FVDDokumen2 halamanNCP FVDMarlon AnryBelum ada peringkat
- NCPDokumen3 halamanNCPMhizakie Dave Rommel FranciscoBelum ada peringkat
- Lethargic Weakness Decreased Performance: Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanLethargic Weakness Decreased Performance: Nursing Care PlanZhayree R.Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Management: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDokumen2 halamanNursing Management: Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationSunshine JaranillaBelum ada peringkat
- Manajemen Cairan: Nazir/Mohan/NasrulDokumen18 halamanManajemen Cairan: Nazir/Mohan/NasrulThegreat Mokz Mokz ThegreatBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Fluid Volume DeficitDokumen2 halamanNCP - Fluid Volume DeficitPatrice LimBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Nephrotic SyndromeDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan Nephrotic SyndromeJhusmin BambicoBelum ada peringkat
- Deficient Fluid Volume R/T - Active Fluid Volume Loss - Failure of Regulatory MechanismsDokumen2 halamanDeficient Fluid Volume R/T - Active Fluid Volume Loss - Failure of Regulatory MechanismskarenbelnasBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study 2Dokumen7 halamanDrug Study 2Jediale CarcelerBelum ada peringkat
- Sample NCP Table With Sample Priorotization and Justification of ProblemsDokumen8 halamanSample NCP Table With Sample Priorotization and Justification of ProblemsCharm TanyaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP DeficientDokumen3 halamanNCP DeficientFRANCISCO, QUENNIE MARIE D.Belum ada peringkat
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDokumen3 halamanCues Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationVher SisonBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaDokumen2 halamanFluid Volume Loss NCP - PediaAdrian MallarBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing DiagnosisDokumen4 halamanNursing DiagnosisMavy AndresBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care PlanDokumen2 halamanNursing Care PlanTetszkie Reganit BuezaBelum ada peringkat
- Intravenous Fluid CrystalloidsDokumen34 halamanIntravenous Fluid CrystalloidsDebashish PaulBelum ada peringkat
- NCP CSDokumen7 halamanNCP CSTwobee Kriz LeghidBelum ada peringkat
- Rules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesDari EverandRules and Directions for the Employment of Injections in Various DiseasesBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Simulation Exercises As A Patient Safety Strategy PDFDokumen9 halaman10 Simulation Exercises As A Patient Safety Strategy PDFAmanda DavisBelum ada peringkat
- ZAMPHIA 2021 Summary Sheet December 2022Dokumen5 halamanZAMPHIA 2021 Summary Sheet December 2022Douglas ChiwoyaBelum ada peringkat
- Research Presentation g2Dokumen15 halamanResearch Presentation g2Alexa AlcantaraBelum ada peringkat
- Detection of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus Species From Clinical SamplesDokumen6 halamanDetection of Methicillin Resistance in Staphylococcus Species From Clinical SamplesOpenaccess Research paperBelum ada peringkat
- Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) Initial Competency Assessment and ValidationDokumen2 halamanContinuous Renal Replacement Therapy (CRRT) Initial Competency Assessment and Validationalex100% (1)
- Practice Station History Breathless 1Dokumen8 halamanPractice Station History Breathless 1Wenbin GuoBelum ada peringkat
- Gastroschisis Is A Congenital Anterior Abdominal Wall DefectDokumen1 halamanGastroschisis Is A Congenital Anterior Abdominal Wall DefectMomogi ForeverhappyBelum ada peringkat
- Vasculitis SyndromesDokumen56 halamanVasculitis SyndromesHengki Permana PutraBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDokumen16 halamanUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenPraluki HerliawanBelum ada peringkat
- Kode Icd 10Dokumen38 halamanKode Icd 10interna squardBelum ada peringkat
- MSDS Serat Kaca PDFDokumen11 halamanMSDS Serat Kaca PDFGita AzhariBelum ada peringkat
- Fispq Pta - Pqs EnglishDokumen11 halamanFispq Pta - Pqs EnglishRisad She NappholeontBelum ada peringkat
- CNA Body Mechanics Bed Making Comfort CareDokumen32 halamanCNA Body Mechanics Bed Making Comfort CareFaith VaughnBelum ada peringkat
- Alimentos PH Urinario GatosDokumen4 halamanAlimentos PH Urinario GatosLarissa VianaBelum ada peringkat
- Purine Rich FoodDokumen3 halamanPurine Rich Foodttstanescu4506Belum ada peringkat
- ROTC ReviewerDokumen6 halamanROTC ReviewerJenelyn BorbonBelum ada peringkat
- Ethics, Privacy, and SecurityDokumen10 halamanEthics, Privacy, and SecuritySittie Aina Munder100% (1)
- Rallygram 2022 FinalDokumen4 halamanRallygram 2022 Finalapi-654829982Belum ada peringkat
- Guide To Application For Registration of Medicinal Products - 4th EditiDokumen142 halamanGuide To Application For Registration of Medicinal Products - 4th EditiKdp03Belum ada peringkat
- Nursing Assessment CH 16studentsnotesDokumen25 halamanNursing Assessment CH 16studentsnotesAshley H Locklear0% (1)
- Organic Anti-Aging Blend Essential Oil (100 Pure - USDA Certified Organic) Best Therapeutic Grade Essential Oil - 1Dokumen1 halamanOrganic Anti-Aging Blend Essential Oil (100 Pure - USDA Certified Organic) Best Therapeutic Grade Essential Oil - 1Leandro LucatoBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation in ApheresisDokumen5 halamanCalculation in Apheresismilica cucuzBelum ada peringkat
- Vademecum Eiffel 2019 en PDFDokumen8 halamanVademecum Eiffel 2019 en PDFMais OmarBelum ada peringkat