Why It Can Be Useful
Diunggah oleh
api-3742014Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Why It Can Be Useful
Diunggah oleh
api-3742014Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
64
Why it can be useful
to attract the enemy:
leading mosquitoes
around by the nose
Mosquitoes as disease vectors
A little more than a hun- on of a selection of viruses
dred years have passed transmitted to humans by
since mosquitoes were mosquitoes. For some of
found not just to be an the pathogens transmitted
irritating pest – they can by mosquitoes, such as
actually be deadly. In India malaria or dengue fever,
in 1897, a British army we have still yet to find an
doctor, Ronald Ross, con- effective vaccine or
firmed the hypothesis that method for warding off
malaria was borne by the disease. All too often, the
Anopheles mosquito. Three only things standing in the
years later, in October way of widespread vacci-
1900, a working group led nation programs are
by his American colleague, Fig. 1: Aedes aegypti, vector of yellow fever and dengue. poverty and over-populati-
(Source: E A Goeldi (1905) Os Mosquitoes no Pará.)
Walter Reed, confirmed on. Sudden outbreaks can
the role played by another even catch well-prepared
Mosquito Control
mosquito species – Aedes health programs off guard.
aegypti (fig. 1), in trans- Sometimes mosquitoes
mitting the yellow fever wreak havoc in places
pathogen. where people otherwise
only consider them to be
But things did not stop an irritating pest, as was
there: as time went by the case in the US when it
mosquitoes turned out to was struck by West Nile
be vectors of a broad spec- Fig. 2: The distribution of the main mosquito-borne viral diseases fever. This particular
trum of diseases. Tab. 1 affecting man. DEN: Dengue Fever, EEE: Eastern Equine Encepha- disease is also transmitted
litis, JE: Japanese Encephalitis, LAC: La Crosse Encephalitis, MVE:
shows the most important Murray Valley Encephalitis, SLE: St Louis Encephalitis, VEE: Vene-
by mosquitoes, and is
mosquito-borne diseases zuelan Equine Encephalitis, WEE: Western Equine Encephalitis, most common in birds.
worldwide. Fig. 2 shows WNV: West Nile Virus, YF: Yellow Fever. Derived from various But by changing its host it
sources
the approximate distributi- can also transfer itself to
Mosquito Control 65
tored in a number of ways. One is to
Disease Cases / Year Deaths / Year
examine the biotopes and waters
Malaria 300.000.000 1.000.000 populated by larvae, pupae and eggs
Yellow Fever 200.000 30.000 (fig. 3). One drawback with this
method is that you already have to
Dengue Fever/
know where the breeding grounds
Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever 20.000.000 24.000
are (or look for them), and the ana-
Japanese Encephalitis 50.000 15.000 lysis requires specialist knowledge.
Lymphatic Filariasis Another approach is to try and catch
(Elephantiasis) 120.000.000 -
adult mosquitoes. But using cap-
Tab. 1: The currently most important diseases transmitted by mosquitoes. Sources: World
Health Organization (www.who.int) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
turing devices in large areas is costly
in the US (www.cdc.gov) and findings are not representative:
so far, you can only use generic baits
people. Once considered only an dengue; despite intensive efforts to such as lights and carbon dioxide.
„old-world“ virus, West Nile first treat and eradicate these diseases, For this reason, to gather sufficiently
appeared in America in 1999, when infection levels continue to rise. representative samples of the
it was discovered in the corpses of Worldwide, more than 500 million overall mosquito population for
dead birds. But soon it claimed its people are infected every year by health assessment reasons, scientists
first human victims. In its first year, diseases passed on by mosquitoes. often still turn to volunteers –
the epidemic boasted 62 seriously The damage this inflicts on coun- human guinea-pigs, who catch
ill and 7 deaths. In the following 2 tries’ economies is put in the tens approaching mosquitoes and count
years, serious infections numbered of billions. them. The ethics of this technique
21 and 66 respectively, there were are somewhat dubious due to the
2 deaths and then 9. In 2002 the The role of efficient risk of infection. It is also unreliable
number of reported cases rose to monitoring systems (mosquito catcher motivation varies
4156, with 284 deaths. By 2003 as There are a number of ways to wage widely). And it is expensive. Much
many as 9858 instances of the wholesale war on mosquitoes. The better solutions would be to find
disease were counted in 40 States, most common technique is to use simple, inexpensive, highly targeted
with 262 deaths. (Source: Centers chemical and biological insecticides, traps for adult mosquitoes which are
for Disease Control and Preventi- or destroy the waters in which they as appealing as human hosts or the
on, USA, www.cdc.gov.) lay their eggs. But the ecological natural breeding grounds. Another
side-effects, the often astronomical significant advantage associated with
Whether a mosquito has the po- costs involved and the danger of the the capturing of adult mosquitoes is
tential to transmit disease, and mosquito developing insecticide that these can then be examined
which diseases it can transmit, using molecular biological testing to
depend primarily on its preferred ascertain whether they are already
host. Some mosquito species do infected with pathogens.
not really care who their host is,
they tap into the first vertebrate Tempting aroma cocktails
they can find. These are the ones Scientists at the Institute of Zool-
most likely to transfer diseases ogy at the University of Regensburg
from one type of host to another, (Germany) have now joined forces
as was the case with the West Nile Fig. 3: Monitoring of mosquito populati- with the University of Minas
fever virus. We face more serious ons: the hunt in Brazil for water recept- Gerais in Belo Horizonte (Brazil)
problems with the mosquito spe- acles infested by eggs, larvae or pupae to pool research findings and
(photo: Á.E. Eiras, University of Minas
cies that prefer humans or will only Gerais, Belo Horizonte, Brazil.)
develop new types of monitoring
seek out humans for a tasty top-up systems. The aim is to fight diseases-
of blood – even if they could resistance make it increasingly transmitting mosquitoes more effi-
actually turn to other hosts. It is essential for us to simply become ciently. The Regensburg resear-
mainly this selective type of beha- more efficient at what we do. chers identified the types of aroma
viour that causes the rapid prolife- mosquitoes recognise on human
ration of epidemics. Some of the A key issue in combating mosquito- beings and how they actually zoom
best known cases of this were with borne disease is therefore how in on them. Their colleagues in
Anopheles gambiae, the mosquito quickly we identify rapidly devel- Brazil investigated the aromas used
transmitting malaria, or Aedes aegypti, oping mosquito hot-spots. Pockets of by pregnant mosquitoes to find a
the transmitter of yellow fever and dangerous mosquitoes can be moni- suitable place to lay their eggs.
66 Mosquito Control
different types of hairs, distin-
guished by morphological features.
Generally, each contains characte-
ristic sets of sensory cells. In total,
each antenna boast more than 2000
olfactory cells on around 1000
scent-detecting hairs. You can
record the neuronal activity of indi-
vidual hairs by using electrophysio-
logical techniques, measuring how
they react to scents. Depending on
the stimulus, the olfactory cells res-
pond by increasing or inhibiting
neuronal activity. It is not until in-
sects start recognising patterns of
activity across many cells that they
can piece together the properties
of individual scent stimuli, as well
as their concentration and duration.
To break down the parts of the
human bouquet with the most
appeal, scientists isolated aromatic
components on human skin and
measured their electrophysiological
effects, as well their effect in attrac-
ting mosquitoes in behavioural
assays. According to their findings,
only certain aromas are needed to
identify the right host. But when
they examined each component in
isolation they hardly had any effect.
It is only when they are brought
together in certain combinations
that the attractiveness of each
aroma unfolds, tempting the mos-
quito in a similar fashion to their
natural host. So mosquitoes re-
Fig. 4: Images of a yellow fever mosquito (Aedes aegypti) taken with a scanning electron cognise their favourite hosts by their
microscope. A) head with antennae, proboscis with stylet and sheath, and two palps
(paired extensions at the base of the proboscis). B) A segment of the antenna with characteristic aroma patterns. This
olfactory hairs containing the olfactory cells. C) Tip of the stylet which is injected into the aroma cocktail has been registered
skin of the host to feed on blood. (Images: A. Kühn, University of Regensburg) for patent. The substances involved
have no adverse effects on health,
Both baited cocktails are now being who roam around looking for are easy to handle and economical,
introduced to improved monitor human hosts. side-stepping expensive carbon
systems, making it easier to track dioxides used to date. Laboratory
and influence mosquito population As with all insects, mosquitoes and field testing shows that they
developments quickly, economi- mainly pick up smells with their can entice several species of mos-
cally and accurately. antennae. Under the microscope quito attracted to humans.
you can make out elongated
How mosquitoes spot their mechano-sensitive bristles and How mosquitoes decide
hosts short olfactory hairs (sensillae) where to lay their eggs
Workers in the Regensburg labora- covering the whole antenna (fig. 4). On the other side of the Atlantic,
tory focussed primarily on odours Tiny pores on the outside of each colleagues in Brazil tackled the
emitted by the human body. These hair allow scents to pass through to problem from a different angle,
are attractive to female mosquitoes the sensory cells inside. There are putting the particularly malicious
Mosquito Control 67
dengue and yellow fever mosqui- ded by humans to bring their Innovative monitoring
toes under the microscope. They young into the world; they are systems for combating
were interested in female mosqui- quite happy to use even small disease
toes after they had sucked blood quantities of water, in discarded If used in the right trap, both
from humans. After an incubation plastic beakers, bottles, broken aroma cocktails can significantly
period lasting several days, the drainpipes, tyres left out in the improve the efficiency of monito-
female mosquito goes on the hunt open, plants using hydroponic ring systems. The synthetic host
for a suitable place to lay its eggs. (soil-less) growing media, watering aroma works particularly well in a
cans, rainwater collection tubs, etc. special ventilator trap (also devel-
We mainly still have the Aedes oped in Regensburg and currently
aegypti mosquito to thank for pas- Mosquitoes go about identifying being patented) which optimises
sing on yellow fever and dengue. good oviposition sites the same the emission of odours. By way of
But we have also had to start loo- way they look for a host – by contrast, the oviposition attractant
king out for its close relative, the using their sense of smell. Water requires a plastic container filled
Asian Tiger Mosquito, Aedes albo- rich in the nutrients needed by with water, coated on the inside
pictus, which has joined its cousin mosquito larvae has a distinctive with a special adhesive which grabs
in spreading these diseases world- smell, so this is what mosquitoes onto the mosquitoes. This captu-
wide – and not only in tropical and look for to lay their eggs in. In the ring device is also registered for
sub-tropical regions, since they can laboratory in Belo Horizonte, patent and is highly economical to
also survive at cooler latitudes: in scientists therefore started by produce. Outdoor testing in Brazil
shows that the best strategy to
monitor mosquitoes is to use both
systems together.
The ventilator trap uses a synthetic
human odour. It is a highly sensi-
tive monitoring system and can
capture up to ten times more mos-
quitoes per day than the oviposition
trap. The latter offers significant
cost benefits and, unlike the venti-
lator trap, does not need power.
Fig. 5: Development of a synthetic oviposition attractant. Left: The schematic output of a The straightforward oviposition
combined gas chromatography and electrophysiological measurement device. Electrical trap can be used for on-going
nerve signals are taken from the antenna of a pregnant yellow fever mosquito positio- monitoring purposes across wide
ned directly at exit of a gas chromatograph. The gas chromatogram is shown in red
(GC), the electrophysiological responses are in white (EAG). Peaks can be seen on the EAG areas. The ventilator trap can be
curve only when certain substances are emitted from the GC. Middle: A comparison of used on a more targeted basis in
synthetic and natural attractants in release and capture testing. Right: The stability of mosquito hot spots when you need
the synthetic oviposition attractant . (Á E Eiras, University of Minas Gerais, Belo Horizon-
te, Brazil)
to find out the precise density of
the mosquito population quickly.
Europe, the Asian Tiger Mosquito examining the behaviour of preg-
has already reached Greece, the nant mosquitoes to see which blends To process data gathered by the
Balkans, northern Italy and southern of water and nutrients they found traps as quickly as possible, it is
France. In the US, this species was most attractive. They then used a transferred to a so-called GIS
first documented in Texas in 1985 combined gas chromatography and (geographical information system)
and is currently established in more electrophysiological measuring de- using a standard electronic data-
than 25 states. vice to identify which substances set gathering system. This makes it
off a reaction in the antennae. In a possible to identify high-risk areas
One thing both species have in sequence of experiments they then quickly and accurately and make
common is the way they lay their observed mosquito behaviour to highly localised battle plans. You
eggs. Originally, both mosquitoes work out the ideal mixture to attract can then use the ventilator traps to
used natural water retaining cavities their attention ( fig. 5). In field assess how successful each cam-
in tree holes and herbaceous plants testing, this mixture was found to be paign was. After a series of success
as a breeding ground. But in an just as effective as their natural bree- studies in Belo Horizonte, scien-
urban environment, there are also ding grounds and it has now been tists are currently carrying out
plenty of attractive locations provi- registered for patents. broad-scale tests in Brazilian cities
68 Mosquito Control
on an early warning system de- relatively small amounts of money the current capturing device and
signed to pinpoint dengue fever, – can help us move a significant scientists’ experience in the devel-
using the same type of technology. way forward in the battle against opment process, a number of dif-
Further testing is in the pipeline disease. ferent types of trap are being devel-
later in the year in North America, oped for launching on consumer
Europe, Africa and Asia. These New products in the fight markets. Each will be targeted at
against mosquitoes –
tests will be looking at the first in business and consumer different price segments and sub-
batch of a new type of monitoring markets markets. From straightforward ad-
trap. Highly effective lures and mosquito hesive traps with time-release aro-
traps are not only useful instruments mas, to high performance devices
To update, refine and market the in the battle against disease. They for professional mosquito hunters
new capturing devices efficiently, can prove interesting to anybody in hotel grounds and parks, the new
two university spin-off companies trying to shoo away the irritating technology opens up completely
were set up at the beginning of airborne pest without damaging the new avenues in capturing unwan-
2003 – one in Belo Horizonte, the environment. In the United States ted mosquitoes – without dam-
other in Regensburg, and each lin- in particular, there have been a aging the environment, when and
ked up commercially to the other. variety of mosquito traps launched where it is needed.
The Brazilian company, Ecovec in recent years, targeted at the con-
Ltda focuses on the public health sumer market. Apart from a num-
sector in South America; the Ger- ber of totally ineffective electro-
man company, BioGents GmbH, cution devices with light sources,
manages Europe, North America, most consumers plump for traps
Asia and the remaining internatio- using propane gas to attract mos-
nal markets. The combination of quitoes by generating carbon di-
laboratory and outdoor testing, the oxide, heat and moisture. These
complementary blend of expertise traps cost anywhere between 300
provided by the two research and 1300 US dollars; last year the
teams, and their tried-and-tested US market for such capturing de-
ability to work together closely vices was worth 650 million dollars.
(despite the long distances in- The consumer can clearly see the
volved) point to a promising future benefit of the methods used by
for the joint venture. these inventions: to catch the little
bloodsuckers before they sting you,
It is also a good example of an thus helping control the overall
attractive and inexpensive alterna- population.
tive to the types of preventative Contact:
medicines used in vaccination pro- As with the monitoring trap descri- Dr. Andreas Rose
grams, or the proposed release of bed above, these traps use carbon
genetically engineered vectors. For dioxide and other more generic
decades, bodies have channelled lures, mainly because there are no
colossal research funds into the alternatives. As a result, the initial
development of vaccinations to outlay and running costs are high.
fight malaria and dengue. We have They are also limited to areas out-
still yet to find one that works. In side the home because they use Dr. Martin Geier
recent years, we have also wit- explosive and poisonous gases. In
nessed intensified efforts to find a laboratory settings and outdoor
solution for combating these di- testing, scientists have found that
seases with genetically engineered the mosquito capturing device
mosquitoes. This has been a simi- from Regensburg with the human
lar drain on technology research aroma frequently outperforms – or
funding, even though many experts at least matches – propane gas dri-
BioGents GmbH
have expressed their doubts about ven traps. With the new lure, the
the technology. This contrasts to manufacturing costs of capturing Universitätsstraße 31
targeted research in the field of devices can be slashed to one tenth D-93053 Regensburg/Germany
chemical ecology and the sensory of current levels. They are also Tel./Fax +49 (0)941 / 943 3064
biogents@biogents.com
ecology of mosquitoes, which – for much easier to handle. Based on
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Id Tables - AdultDokumen8 halamanId Tables - Adultapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Why Is Agricultural Biotechnology An Important Development and Human Rights Issue For WomenDokumen4 halamanWhy Is Agricultural Biotechnology An Important Development and Human Rights Issue For Womenapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Change The NameDokumen12 halamanChange The Nameapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- West Nile Virus, Mosquitoes and PesticidesDokumen6 halamanWest Nile Virus, Mosquitoes and Pesticidesapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- When Are Ant-Attractant Devices A Worthwhile InvestmentDokumen9 halamanWhen Are Ant-Attractant Devices A Worthwhile Investmentapi-3742014100% (1)
- A Pictorial Key For The Identification of The MosquitoesDokumen12 halamanA Pictorial Key For The Identification of The Mosquitoesapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- When Developmental Pathways DivergeDokumen4 halamanWhen Developmental Pathways Divergeapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Volatile Foraging Kairomones in The Littoral ZoneDokumen13 halamanVolatile Foraging Kairomones in The Littoral Zoneapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Use of Baits and Preservatives in Pitfall TrapsDokumen8 halamanThe Use of Baits and Preservatives in Pitfall Trapsapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- V-Atpase Location in Human Eccrine Sweat GlandsDokumen1 halamanV-Atpase Location in Human Eccrine Sweat Glandsapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Volatile Organic Compounds As Signals in A Plant-Herbivore SystemDokumen18 halamanVolatile Organic Compounds As Signals in A Plant-Herbivore Systemapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Use of Solid Phase Micro Extraction (SPME) Devices in Analysis ForDokumen8 halamanThe Use of Solid Phase Micro Extraction (SPME) Devices in Analysis Forapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Trapping of The Malaria Vector Anopheles Gambiae WithDokumen8 halamanTrapping of The Malaria Vector Anopheles Gambiae Withapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Visual and Olfactory Disruption of Orientation by The Western Pine Beetle ToDokumen5 halamanVisual and Olfactory Disruption of Orientation by The Western Pine Beetle Toapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Trapping cDNAs Encoding Secreted Proteins From The SalivaryDokumen6 halamanTrapping cDNAs Encoding Secreted Proteins From The Salivaryapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Releaser Effects of The Tergal Gland SecretionDokumen9 halamanThe Releaser Effects of The Tergal Gland Secretionapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Thermal and Sweating Responses in Normal and Atopic SubjectsDokumen6 halamanThermal and Sweating Responses in Normal and Atopic Subjectsapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Skin As Interface in The Transmission ofDokumen11 halamanThe Skin As Interface in The Transmission ofapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Diversity of Microorganisms Associated With AcromyrmexDokumen11 halamanThe Diversity of Microorganisms Associated With Acromyrmexapi-3742014100% (1)
- The Role of Male Disease Susceptibility in TheDokumen5 halamanThe Role of Male Disease Susceptibility in Theapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Response of The Blood-Sucking Bug Triatoma Infestans To Carbon DioxideDokumen11 halamanThe Response of The Blood-Sucking Bug Triatoma Infestans To Carbon Dioxideapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Composition of Sweat, With SpecialDokumen12 halamanThe Composition of Sweat, With Specialapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Insect Attractant 1-Octen-3-Ol Is The Natural Ligand ofDokumen6 halamanThe Insect Attractant 1-Octen-3-Ol Is The Natural Ligand ofapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Reproducibility of Closed-Pouch Sweat CollectionDokumen4 halamanThe Reproducibility of Closed-Pouch Sweat Collectionapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Market For Pre - and Probiotic IngredientsDokumen11 halamanThe Market For Pre - and Probiotic Ingredientsapi-3742014100% (1)
- The Iron Content of Sweat in Normal AdultsDokumen5 halamanThe Iron Content of Sweat in Normal Adultsapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The Effect of Sodium Balance On Sweat Sodium SecretionDokumen6 halamanThe Effect of Sodium Balance On Sweat Sodium Secretionapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Tendency To Being Bitten by Insects AmongDokumen2 halamanTendency To Being Bitten by Insects Amongapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- The DAF-7 TGF - Signaling PathwayDokumen13 halamanThe DAF-7 TGF - Signaling Pathwayapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Systemic Inflammatory Mediators and Cystic Fibrosis GenotypeDokumen4 halamanSystemic Inflammatory Mediators and Cystic Fibrosis Genotypeapi-3742014Belum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Nowledge, Attitude, and Practices Related To Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in An Endemic Focus of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis, Outhern RanDokumen4 halamanNowledge, Attitude, and Practices Related To Cutaneous Leishmaniasis in An Endemic Focus of Cutaneous Leishmaniasis, Outhern RanDani Yitu MedanituBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines For Surgery in The HIV Patient: Samuel Smit, MB CHB, M Med (Surg)Dokumen8 halamanGuidelines For Surgery in The HIV Patient: Samuel Smit, MB CHB, M Med (Surg)Afkar30Belum ada peringkat
- Andria - Pragholapati@upi - Edu: Covid-19 Impact On StudentsDokumen3 halamanAndria - Pragholapati@upi - Edu: Covid-19 Impact On StudentsJeremyBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatrics InfectionDokumen75 halamanPediatrics InfectionHikufe JesayaBelum ada peringkat
- State wise quarantine rules customer guideDokumen22 halamanState wise quarantine rules customer guidevatsalya12345Belum ada peringkat
- CESTODESDokumen1 halamanCESTODESCarlo Domingo LadieroBelum ada peringkat
- HCM 2337 Vector, Vermin and Rodent ControlDokumen13 halamanHCM 2337 Vector, Vermin and Rodent ControlMokua FedinardBelum ada peringkat
- 14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsDokumen26 halaman14 Amazing Natural Antibiotics Mechanisms & Side EffectsGuillermoBelum ada peringkat
- Swab Guide: Chlamydia and N. Gonorrhoeae TestingDokumen2 halamanSwab Guide: Chlamydia and N. Gonorrhoeae TestingFlor OMBelum ada peringkat
- Epstein-Barr Virus Infections in PatientsDokumen3 halamanEpstein-Barr Virus Infections in PatientsFilipos ConstantinBelum ada peringkat
- Hiv and AidsDokumen2 halamanHiv and Aidsbelinda ashlynBelum ada peringkat
- Swab ResultDokumen1 halamanSwab ResultPrince Calimbo VillaBelum ada peringkat
- In The Past1 4 Da S, Did You Have Any of Thefollowing:: SheetDokumen1 halamanIn The Past1 4 Da S, Did You Have Any of Thefollowing:: SheetLeoni FrancBelum ada peringkat
- Comment: Two Years of COVID-19 in Africa: Lessons For The WorldDokumen4 halamanComment: Two Years of COVID-19 in Africa: Lessons For The Worldotis2ke9588Belum ada peringkat
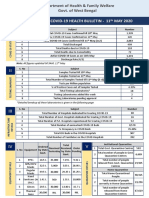
- West Bengal COVID-19 health bulletin updatesDokumen4 halamanWest Bengal COVID-19 health bulletin updatesSoham SarangiBelum ada peringkat
- Mojbm 03 00082Dokumen5 halamanMojbm 03 00082Sohrab RohaneBelum ada peringkat
- TuberculosisDokumen28 halamanTuberculosisbuddysmbdBelum ada peringkat
- H I. V. Concept of Elimination of Mother To Child Transmission (Emtct)Dokumen12 halamanH I. V. Concept of Elimination of Mother To Child Transmission (Emtct)Salihu MustaphaBelum ada peringkat
- Smallpox Was AnDokumen41 halamanSmallpox Was AnClars storyBelum ada peringkat
- Master Organism Com Commensals ListsDokumen598 halamanMaster Organism Com Commensals ListsEdbert LiangBelum ada peringkat
- Wild and Vaccine Derived Poliovirus Circulation and Implications For Polio EradicationDokumen7 halamanWild and Vaccine Derived Poliovirus Circulation and Implications For Polio Eradicationmuhfajar1_42539617Belum ada peringkat
- Emergency Management Plan Acute Infectious Disease - COVID-19Dokumen26 halamanEmergency Management Plan Acute Infectious Disease - COVID-19Keroy AganzeBelum ada peringkat
- Mycology NotesDokumen3 halamanMycology NotesVincent MarfinBelum ada peringkat
- Daftar PustakaDokumen8 halamanDaftar PustakaFathnur SaniBelum ada peringkat
- Avian Influenza (Highly Pathogenic) : Fowl Plague, Fowl Pest, Brunswick Bird Plague, Fowl Disease, Fowl or Bird GrippeDokumen23 halamanAvian Influenza (Highly Pathogenic) : Fowl Plague, Fowl Pest, Brunswick Bird Plague, Fowl Disease, Fowl or Bird Grippehericonan9Belum ada peringkat
- R 3205 - Avian InfluenzaDokumen5 halamanR 3205 - Avian InfluenzaNontacha NanBelum ada peringkat
- DCR 's-4 AprilDokumen33 halamanDCR 's-4 AprilVidya BudihalBelum ada peringkat
- Maklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsDokumen2 halamanMaklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination Detailsbd sinarbarakahBelum ada peringkat
- Department of Haematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodDokumen5 halamanDepartment of Haematology Test Name Result Unit Bio. Ref. Range MethodSunil KhandekarBelum ada peringkat
- Microbiology TablesDokumen19 halamanMicrobiology TablesRebecca MarshallBelum ada peringkat