Anatomy: Subject: Done By: Doctor: Date
Diunggah oleh
nida3mk7446Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Anatomy: Subject: Done By: Doctor: Date
Diunggah oleh
nida3mk7446Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
System:
15 / 56 10 / 24
Sub-system: Price: 20
Anatomy
Subject: Done by: Doctor: Date:
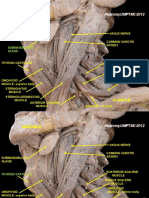
Muscles of the Lower Limb (2)
Doaa' Rawwad
Rashed Jomard Sunday, 25/9/2011
Anatomy Lecture 10/ MSS 2011-9-25 / Sunday
Muscles of the thigh
Please refer to the book and to the mind maps while reading this lecture.
The anterior group of muscles (continued):
The Dr continued what he had started in the previous lecture: Also in the anterior part of the thigh we have another landmark, this landmark is what we call the femoral triangle. Here are the edges of this triangle: - The inguinal ligament - The lateral border of adductor longus - The medial border of Sartorius
The Dr is drawing on the projector: This is the place where you see the femoral canal and we have inside the femoral sheath, we have the femoral vein and the femoral artery, and then outside the sheath we have the femoral nerve. If we want to look for this muscle which is the Iliopsoas or this muscle which is the pectineus you can't see them because they are covered with the neurovascular bundle...
The psoas minor muscle is not constant; you see it in some people and you don't see it in others but you see the psoas major is arising from 15 points; 5 slips and each slip has 3 poinsts of attachment. then this muscle - psoas major- comes down and meets the iliacus muscle which arises from the iliac fossa, and these two muscles join to form one tendon (the same arrangement as that of the quadriceps tendon), and then it will be the iliopsoas muscle, and it is inserted into the lesser trochanter, and it is one of the great flexors of the hip. Now we have an idea about the anterior group of muscles... and here is a quick idea about medial group of muscles.
The medial group of muscles:
The medial group of thigh muscles are named as adductors of the thigh at the hip joint. 1. Pectineus muscle: It originates from superior ramus of pubis, going down and lateral, and then it is attached to the upper part of linea aspera. The pectenius is a "funny!!" muscle some people say it is two muscles because it has a double nerve supply; the femoral nerve and the obturator nerve. 2. Adductor longus: It is just inferior to the pectineus. 3. Adductor brevis: It is posterior to the adductor longus. 4. Adductor magnus: If we remove the two muscles above we will see this muscle (deep to adductor longus and brevis), which is the biggest adductor . It inserts into linea aspera, and it has holes in it. Anterior to these holes we have the profunda femoris artery, and through these holes it sends branches into the posterior group of muscles. 5. gracilis: it is the most medial one
These are the medial group of muscles and they have their own nerve supply which is the obturator nerve, this muscle here -which is the adductor magnus- it has a double nerve supply; the obturator and the sciatic from posterior.
The posterior group of thigh muscles (flexors):
They are called the hamstrings, and they include 3 muscles: 1. biceps femoris : This muscle has two heads; The long head originates from the ischial tuberosity. The short head comes from the posterior part of the femur; linea aspera. We call it biceps femoris to differentiate it from biceps brachialis. Then the two heads come down and insert into the lateral part of the leg; the head of fibula . One year we had this question: - The action of which muscle becomes very painful if we have fracture of the upper end of fibula? You see muscles have attachments; origin and insertion. If you fracture the origin, then the action of this muscle becomes painful! Not weak, but painful. For example, the deltoid muscle is attaches to the clavicle acromion process and spine of the scapula. So if the clavicle is fractured, you should know that any movement of the shoulder will be very painful, so you shouldnt ask the patient to do abduction, it's painful!! He can't do such movements not because the muscle is paralyzed, but because the movement is painful. What happens if the ischial tuberosity is fractured? Then most of the muscles of the thigh will not function because the functioning is painful. So if youre kidding with your friend, and you tell him to sit down on a chair, then you cheat him and you remove the chair O.o and he falls down on his ischeial tuberosity! So if it breaks, he will not be able to flex his thigh because of the pain!
- A question by one of the students: what if the fracture was in the insertion? It will be the same; painful movements. - Another question: how can we tell if the fracture is in the origin or in the insertion of the muscle? By doing an x ray picture. 2. Semimembranosus: when you hold it and you go up, youll see that the tendon of its origin is a membrane; it is a very thin flat aponeurosis, therefore it is called semimembranosus. 3. Semitendinosus: and is so called because when you go to the lab and see the cadaver, youll see that half of it is a tendon and half of it is a muscle; therefore it is called semitendinosis.
Muscles of the leg:
In the leg we have the same problem of the fascia, as we have fascia lata of the thigh (the deep fascia of the thigh), we have in the leg what we call the crural fascia (the deep fascia of the leg) and it is a continuation of the fascia. When there is a fractured bone, then there is an injured blood vessel or there is bleeding. So here you dont see the swelling of the leg, here you see a tense leg! because the fascia will prevent expansion of the leg. So if the leg can't expand to the outside, then it's going to press anything inside the fascia; like the veins and the blood vessels, and you will stop having a peripheral pulse! And you have to immediately put a longitudinal incision to relieve the pressure.
Posterior muscles of the leg:
Now we will talk about the posterior muscles of the leg.We need these muscles during walking, when I walk I land, I unlock the knee then I prepare myself to push myself forward. Once I push myself forward, and I will contract the gluteus maximus. Then when I contract the gluteus maximus, I feel my heel is elevated and I want to continue,
so I need to do planter flexion of the foot so that I will fly; therefore I need a great power. Bur how do I get it? I get it from these muscles: 1. Gastrocnemius: This muscle has two heads crossing the knee and coming from above the condyles of the femur, therefore it has a weak action on the knee joint. Then they join together and form a strong tendon that is inserted into calcaneus bone. 2. Soleus: This muscle is deep to gastrocnemius muscle, arising from fibula, interosseous membrane, and tibia And then coming down and joining the tendon of the gastrocnemius. Then soleus muscle inserts on the upper part of the calcaneus. Now iliopsoas are two muscles that have one tendon, quadriceps muscles are four muscles that form one tendon, and here is another example two muscles that form one tendon. These two muscles -I mean soleus and gastrocnemius - they act together for propulsion; forceful planter flexion. Soleus muscle is full of blood vessels and it is called the second heart. When I contract my soleus, the blood will be pushed upward. When soleus muscle gets stabbed, it will bleed a lot because it is full of veins. Now in the army < fel jaish> the soldiers are supposed to stand for several hours where they are not allowed to do any movement !! even if a fly settles down on your nose :P and that is just to teach them patience they are allowed to do just one movement which is planter flexion to avoid fainting! So once they feel that they are going to faint, they elevate themselves one or two times and stand on their toes, then they come back to their standing position. When they do that they contract their soleus and gastocnemius muscles, and then they feel fresh again
Achilles tendon is the tendon of soleus and gastrocnemius muscles. Achilles is a Greek leader that received an arrow that cut his Achilles tendon, and was not able to walk! So it was named after him. This tendon you can feel it, it's very tough!! In real life you can't cut this tendon even with scissors, the scissors will break!
Now, we need more propulsion, so what do we do? We have more muscles to propel forward. As I said we need gluteus maximus to contract first, then we need planter flexors such as gastrocnemius and soleus, and then the last part that leaves the ground during walking is the big toe; the hallux, therefore we need a strong and a powerful planter flexor of the big toe which is the flexor hallucis longus. 3. flexor hallucis longus: This muscle is oblique to have a little bit extra length. Also this muscle is bipennate; this means that the muscle has central tendon, and the muscle fibers are on both sides of the tendon. And the flesh part is as low as it turns around the medial malleolus of tibia. So this is a very powerful muscle where the flesh or the contractile part on both sides of the central tendon go as down as the medial malleolus. Therefore this is an indication that this is a very powerful muscle because it is oblique, bipennate, and the flesh part is as low. I can't flex the big toe only; I need to flex the other toes as well! If you cut the hallux you can walk but not that efficient! Because the toes can't replace the big toe Now there is a big problem with the big toe if the nail of the big toe grows to the deep, so it becomes painful when pressing on it, therefore you will see that the person is not walking properly So if the right side is painful, you will walk properly on the left side, but on the affected side -which is the right- you extend the big toe so you walk in a way that you can't press on the big toe because that is painful. Youre lucky that we dont give you the walking process as a process! But start to look how people walk, and if you are a very good observer, you can identify where the disease is if someone's way of walking is not that good There are people who have a weak gluteus medius and minimus so they walk this way ((the Dr. start walking in a funny manner )) they cannot stabilize their hips !
Anterior muscles of the leg:
They can be of two types: - If they go anterior and stay anterior, then they are dorsiflexors. - If they go anterior and hook around, then they are planter flexers .
1. Tibialis anterior : This muscle is a good example on a muscle being anterior and a dorsiflexor of the foot at the ankle joint. It's just lateral to tibia, and then it comes down then it becomes a tendon in front of tarsal bones. Because it is in front of tarsal bones, then it's a dorsiflexor muscle, and it also inverts foot at the intertarsal joints. 2. Extensor digitorum longus: It's deeper and lateral to tibialis anterior. As it comes down, it splits into four tendons. Note: it is always better to stick to dorsiflexion and plantar flexion, but some people call the dorsiflexion as extension. 3. Extensor hallucis longus: This muscle is between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It emerges a tendon. We dont see this muscle because its deep to the two above muscles, it extends the hallux.
Lateral muscles of the leg:
Lateral group of muscles are called peroneus. We have two muscles: Peroneus longus Peroneus brevis The third peroneus muscle which is peroneus tertius belongs to the anterior group of muscles.
They -the lateral muscles- hook around the lateral malleolus, therefore they are planter flexors and evertors.
The Nerve supply
I was asked during the interval about the nerve supply. At this moment the plan of the nerve supply is very simple: - The anterior group of the thigh muscles are supplied by the femoral nerve. - The medial group of muscles -the adductors- are supplied by the obturator nerve. - The posterior group of the thigh muscles are supplied by the sciatic nerve. And the muscles below the knee are supplied by branches of sciatic branches of sciatic such as peroneal nerve and tibial nerve.
Some notes:
- If the lateral rotators of the hip are weak, then the medial rotators are stronger. And those people will walk with an internal rotation of the hip. - Some people walk in a way that their heal doesnt touch the ground, so if the nerve of the dorsiflexors is weak, then the planter flexors are stronger, and arch of the foot will be higher.
- And the same applies to the evertors and to the invertors muscles. - The popliteus muscle in the leg is used to unlock the knee during walking by laterally rotating the femur on the tibia (or medially rotating the tibia). This muscle arises mostly from the tibia above the soleal line. The capsule of the knee -well study it later- it has a hole in it, and this muscle passes through this hole.
- Plantaris muscle is a very small muscle like the Palmaris longus; it has a very short belly and a long tendon.
The Dr said that our knowledge about muscles doesn't end here! We have to study them from the book because the lecture gives headlines only At the end of the lecture the Dr. showed us how to use www.getbodysmart.com to study muscles
THE END
It was a pleasure for me to write this easy lec hope you like it & get benefit sorry for any mistake and sorry if it was done lately but be sure that it was out of my hands !!! 2keed ma ra7 2nsa 27keelek shokran ,, my sis and my best frn 3hed <3 <3 thanks for everything 3hed mn elboshar lal 6eba3a :PPPP may 2lla bless u hny <3 And special thanks for u nadia hawash 3la el flash memory :PP ya 27la jarah
See u in the next system..
(Only work which is the product of inner compulsion can have spiritual meaning). Walter Gropius
NOOR SAMA
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- HandsOn Muscle TherapyDokumen38 halamanHandsOn Muscle TherapyPhoenixRising61100% (2)
- Table of Lower Limb MusclesDokumen7 halamanTable of Lower Limb MuscleskavindukarunarathnaBelum ada peringkat
- Shreddin8 Muscle AnatomyDokumen16 halamanShreddin8 Muscle Anatomysambelov100% (2)
- Anatomy Physiology of Hip JointDokumen6 halamanAnatomy Physiology of Hip JointSundaraBharathiBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in SportDokumen64 halamanUnit 1 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology in Sportdomhughes1093Belum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Dokumen70 halamanHuman Anatomy. The Human Muscles.Stefania Ungureanu100% (1)
- Analysis of MovementDokumen18 halamanAnalysis of MovementEfren Jonicel Daguio Domingo50% (2)
- Drawing Anatomy: An Artist's Guide to the Human FigureDari EverandDrawing Anatomy: An Artist's Guide to the Human FigurePenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- BRS Gross Anatomy 7th 2012Dokumen506 halamanBRS Gross Anatomy 7th 20126003101008ชวิศ อาภรณ์วิรัตน์Belum ada peringkat
- Lumbar Spine AnatomyDokumen8 halamanLumbar Spine AnatomyFizioterapiaBelum ada peringkat
- Lab 9 - Gross Anatomy of The Muscular SystemDokumen13 halamanLab 9 - Gross Anatomy of The Muscular Systemsidro12380% (5)
- Muscles NamingDokumen17 halamanMuscles NamingAbraham MendezBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyDari EverandAnatomy for Artists: A Complete Guide to Drawing the Human BodyPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (3)
- Smooth Muscle Physiology by Bushra Akhtar Dhillon (07.04.2020)Dokumen24 halamanSmooth Muscle Physiology by Bushra Akhtar Dhillon (07.04.2020)Laraib SohailBelum ada peringkat
- Rosenberg AcupointsDokumen4 halamanRosenberg AcupointsxnrvBelum ada peringkat
- Any PDFDokumen252 halamanAny PDFRaja VeerappanBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy: Subject: Done By: Doctor: DateDokumen16 halamanAnatomy: Subject: Done By: Doctor: Datenida3mk7446Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy 18Dokumen11 halamanAnatomy 18Nur Hamizah ShaharinBelum ada peringkat
- 21 - MSK8 Carpal TunnelDokumen51 halaman21 - MSK8 Carpal TunnelNTRisforthinkersBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy For Beginners 1 - MovementDokumen20 halamanAnatomy For Beginners 1 - MovementDea Philia SwastikaBelum ada peringkat
- Morphosphysiology of The KneeDokumen18 halamanMorphosphysiology of The KneeAlejo RoseroBelum ada peringkat
- Prof. Dr. Fouad Heikel.: Subject: Hip JointDokumen6 halamanProf. Dr. Fouad Heikel.: Subject: Hip JointHashim OmarBelum ada peringkat
- Post Abd Wall Complete)Dokumen17 halamanPost Abd Wall Complete)Joseph EstradaBelum ada peringkat
- The Muscles in The Anterior Compartment: Knee JointDokumen9 halamanThe Muscles in The Anterior Compartment: Knee JointZA IDBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of A Human BeingDokumen6 halamanAnatomy of A Human BeingIshimaru ThorBelum ada peringkat
- Matt and MariaDokumen4 halamanMatt and MariaJanelle05110% (1)
- Vol 2 Anatomie Oase Anul 1Dokumen39 halamanVol 2 Anatomie Oase Anul 1ANNNA ELLEBelum ada peringkat
- 1muscles ObjectivesDokumen20 halaman1muscles ObjectivesZahra AdanBelum ada peringkat
- GROUP 8 - Chapter 10 - Muscular System Gross AnatomyDokumen145 halamanGROUP 8 - Chapter 10 - Muscular System Gross Anatomygooglegirl18Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 7: Anatomy: Excerpt From A LectureDokumen4 halamanUnit 7: Anatomy: Excerpt From A LectureAnonymous Wfl201YbYoBelum ada peringkat
- Ancross MateriDokumen6 halamanAncross MateriAnnaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of LEG TrainingDokumen53 halamanAnatomy of LEG TrainingDiego Tzompa AcostaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter - 2 Anatomy and Physiology of Body SystemsDokumen46 halamanChapter - 2 Anatomy and Physiology of Body SystemsSharlaine CabanayanBelum ada peringkat
- Acland Human AnatomyDokumen51 halamanAcland Human Anatomyjust for download matterBelum ada peringkat
- ANAT:Lecture Note Forearm1Dokumen7 halamanANAT:Lecture Note Forearm1Nur Liyana MohamadBelum ada peringkat
- Ex7 Libres Frix PhBioSci18Lab 1BDokumen8 halamanEx7 Libres Frix PhBioSci18Lab 1BFrix LibresBelum ada peringkat
- Hip AnatomyDokumen8 halamanHip AnatomyRusu AdrianBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study For CastDokumen10 halamanCase Study For CastMaria JuvilisaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDokumen5 halamanAnatomy and PhysiologyGretchen BadayosBelum ada peringkat
- JSS2 Basic Science Lesson Note PDFDokumen40 halamanJSS2 Basic Science Lesson Note PDFJuddy ScienceBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy,: Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Appendicular MusclesDokumen70 halamanHuman Anatomy,: Chapter 12 Lecture Outline: Appendicular MusclesdewkmcBelum ada peringkat
- Document 5Dokumen22 halamanDocument 5dawidkubiak222Belum ada peringkat
- VB Muscle Premium Preview 033015Dokumen15 halamanVB Muscle Premium Preview 033015John DavidBelum ada peringkat
- External Anatomy of Frog 2Dokumen25 halamanExternal Anatomy of Frog 2STEM 15 - John Benedict SebucaoBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular SystemDokumen7 halamanMuscular Systemchristianoliver.aceroBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology of The HipDokumen6 halamanAnatomy and Physiology of The HipJayson OlileBelum ada peringkat
- Bones of The KneeDokumen5 halamanBones of The KneeJessica AdhykaBelum ada peringkat
- The Human Skeletal SystemDokumen6 halamanThe Human Skeletal System201090182Belum ada peringkat
- 4 MyologyDokumen57 halaman4 MyologyAbhijith S. PBelum ada peringkat
- The Term Muscle TissueDokumen3 halamanThe Term Muscle Tissueximipa5.almadisyafarelinBelum ada peringkat
- The Human Skeletal SystemDokumen6 halamanThe Human Skeletal Systemdplsss1Belum ada peringkat
- Unit 7 - VocabularyDokumen3 halamanUnit 7 - VocabularyAnonymous Wfl201YbYoBelum ada peringkat
- Different Parts of The Muscle: Extensor Carpi Radialis BrevisDokumen4 halamanDifferent Parts of The Muscle: Extensor Carpi Radialis Breviscryxtal_iceBelum ada peringkat
- What Is The Importance of The Skeletal System To Your BodyDokumen11 halamanWhat Is The Importance of The Skeletal System To Your BodyKenny James CuberoBelum ada peringkat
- The Human SkeletonDokumen10 halamanThe Human Skeletonanwar safwanBelum ada peringkat
- ANATOMYDokumen33 halamanANATOMYPhoebe LiasosBelum ada peringkat
- Pe 1 Midterm Exam Reviewer 2023 2024Dokumen2 halamanPe 1 Midterm Exam Reviewer 2023 2024xbautista124Belum ada peringkat
- The Musculoskeletal System Is Made Up of The Body's Bones (The Skeleton), MusclesDokumen17 halamanThe Musculoskeletal System Is Made Up of The Body's Bones (The Skeleton), MusclesrajBelum ada peringkat
- Living Anatomy of The Limbs and Back (With Answers)Dokumen15 halamanLiving Anatomy of The Limbs and Back (With Answers)Aaron Nameer Abrar RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy 5 PDFDokumen25 halamanAnatomy 5 PDFMohammad Jamal OwesatBelum ada peringkat
- Adaptable Polarity: Movement, Muscles & Meridians Lateral Line of Fascia & Gallbladder ChannelDokumen98 halamanAdaptable Polarity: Movement, Muscles & Meridians Lateral Line of Fascia & Gallbladder ChannelAngel RuelasBelum ada peringkat
- Maam Recio Reviewer PrelimDokumen14 halamanMaam Recio Reviewer PrelimJonnifer LagardeBelum ada peringkat
- Pathfit ReviewerDokumen7 halamanPathfit ReviewerbantayalagaBelum ada peringkat
- Core 2 ADokumen16 halamanCore 2 AJasmiine AlzateeBelum ada peringkat
- Notes For Case 3+4 - by Salah DwikatDokumen2 halamanNotes For Case 3+4 - by Salah Dwikatnida3mk7446Belum ada peringkat
- CaseDokumen2 halamanCasenida3mk7446Belum ada peringkat
- Microbiology of The Musculo-Skeletal SystemDokumen24 halamanMicrobiology of The Musculo-Skeletal Systemnida3mk7446Belum ada peringkat
- Anatomy - Lec.15Dokumen13 halamanAnatomy - Lec.15nida3mk7446Belum ada peringkat
- Ally Rose - Muscular SystemDokumen4 halamanAlly Rose - Muscular SystemGogo El-HawBelum ada peringkat
- Antero Lateral RegionDokumen13 halamanAntero Lateral RegionNoemi Nagy-CicealăBelum ada peringkat
- Muscles Lab Report - NoDokumen3 halamanMuscles Lab Report - Noapi-3801039Belum ada peringkat
- Muscular SystemDokumen4 halamanMuscular Systemquosha2Belum ada peringkat
- Kinesiology-I: Introduction To Manual Muscle TestingDokumen12 halamanKinesiology-I: Introduction To Manual Muscle TestingKanwal KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Hip Joint AnatomyDokumen14 halamanHip Joint AnatomyIlham Ristananda0% (1)
- Test On Superior Extremity Long QuestionsDokumen1 halamanTest On Superior Extremity Long Questionsapi-19916399Belum ada peringkat
- Locomotor ApparatusDokumen25 halamanLocomotor Apparatusbiokta 2Belum ada peringkat
- Physical Education in The Tertiary LevelDokumen35 halamanPhysical Education in The Tertiary Levelhatsune mikuBelum ada peringkat
- Report Summary and QuestionsDokumen7 halamanReport Summary and QuestionsSkyNayvieBelum ada peringkat
- Upper Limb DR AymanDokumen4 halamanUpper Limb DR Aymanqarafi4007Belum ada peringkat
- Rutinas Max OTDokumen18 halamanRutinas Max OTe717fa0dBelum ada peringkat
- Class 5 - Science Chapter 3Dokumen18 halamanClass 5 - Science Chapter 3deviBelum ada peringkat
- Muscle GroupsDokumen25 halamanMuscle GroupsRoxana LorenteBelum ada peringkat
- Muscle Ligaments & TendonsDokumen5 halamanMuscle Ligaments & TendonsMahnoor JawadBelum ada peringkat
- Screenshot 2024-01-12 at 7.10.04 AMDokumen1 halamanScreenshot 2024-01-12 at 7.10.04 AMlukeBelum ada peringkat
- TWSTRSDokumen3 halamanTWSTRSMuhammad Naqvi Al FarisiBelum ada peringkat
- Plantillas Cuerpo Humano Plastilina Esqueleto OrganosDokumen13 halamanPlantillas Cuerpo Humano Plastilina Esqueleto OrganosMari Trolli JijiBelum ada peringkat
- Muscular System Study Guide 2015 AnswersDokumen16 halamanMuscular System Study Guide 2015 AnswersLinet HuchuBelum ada peringkat
- ANAPHYSIODokumen2 halamanANAPHYSIOEli AyaseBelum ada peringkat
- Miopatías Inflamatorias IdiopáticasDokumen14 halamanMiopatías Inflamatorias IdiopáticasGerarBelum ada peringkat
- Bakasana: Crow Pose, Crane PoseDokumen1 halamanBakasana: Crow Pose, Crane PoseSaiteja Varma DatlaBelum ada peringkat
- ANATOMY: Muscular System Quiz Study Guide Part 1Dokumen4 halamanANATOMY: Muscular System Quiz Study Guide Part 1jbradeeBelum ada peringkat
- What Are Similarities Between Cardiac and Skeletal MuscleDokumen3 halamanWhat Are Similarities Between Cardiac and Skeletal MuscleWafa Nabilah KamalBelum ada peringkat