CH 3 Water and Life
Diunggah oleh
wil7verDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CH 3 Water and Life
Diunggah oleh
wil7verHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Molecule that supports life
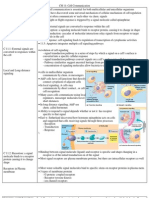
CH3 Water and Life Biological medium All living thins need water more than anything else Most cell are surrounded by water and most cells are 70-95% water Main reason earth is habitable, is the abundance of water 3.1 polar covalent bonds in water molecule result in hydrogen bonding 3.2 4 emergent properties of water contribute to earths suitability for life 3.3 acidic and basic conditions affect living organisms Water is a polar molecule: opposite ends have opposite charge Polarity allows hydrogen bonds to form with one another Bond form and separate very quickly, 1. cohesive behavior 2. ability to moderate temperature 3. expansion upon freezing 4. versatility as a solvent Cohesion- collective action of hydrogen bonds between water molecules Adhesion- attraction b/w water and other polar molecules Surface tension- property of a liquid that holds the surface together and allows it to resist and external force, related to cohesion Ex: think about water in a graduated cylinder, water makes a meniscus because of adhesion and water is brought up because of cohesion Water absorbs heat when around hot air, and releases heat when in cold air. Water can absorb and release large amounts of heat with a slight change in its temperature (high specific heat) Contributes to evaporative cooling Kinetic energy- the energy of motion Heat- measure measure of total amount of kinetic energy due to molecular motion Temperature- measures intensity heat due to average kinetic energy of molecules calorie (cal)- amount of heat required to raise temperature of 1g of water by 1C joule (J)- unit of energy that measures energy 1J=.0239 cal , 1 cal= 4.184 J Specific heat of a substance is the amount of heat that it absorbs or loses, for 1g of it to change by 1C. Waters high specific heat can be trace to hydrogen bonding, heat goes to bonds -heat is absorbed when hydrogen bonding break -heat is released when hydrogen bonds form High specific heat of water reduces fluctuation temp within that permits life Evaporation is the transformation of a substance from liquid to a gas Heat of evaporation- heat of liquid a substance absorbs so 1g can be a gas As liquid evaporates, water absorbs heat from surface and hottest molecules evaporate leaving cool ones, the rest of surface remains cool, process called evaporative cooling Evaporative cooling stabilized temp in organisms and bodies of water Ice floats on water because hydrogen bonds in ice are more ordered, making ice dense
Key Concepts
Polarity of water molecule result in hydrogen bonding 4 emergent properties of water
1) Cohesion
2) Moderation of Temperature by Water
Heat & Temperature
Waters high specific heat
Evaporative Cooling
3) Insulation of bodies of
water by floating ice
Molecules moves too slow to break hydrogen bond, so more bonds form to lock the water molecules to a crystalline lattice structure Water reaches greatest density at 4C, if ice sank water would freeze and make water lif impossible Solution- homogeneous mixture Solvent- does dissolving Solute- substance that dissolves Aqueous solution- solution in which water is the solvent Water is a versatile solvent due to is polarity When ionic compound is dissolved in water, each ion is surrounded by water molecules called hydration shell Water also dissolves nonionic polar molecules Even large polar molecules such as proteins can dissolve in water if they have ionic & polar regions like dissolves like A hydrophilic substance is one that has affinity (attraction) for water A Hydrophobic substance is one that doesnt have an affinity (attraction) for water oil molecules are hydrophobic because of their non-polar bonds Colloid is a stable suspension of fine particles in a liquid Most biochemical reactions occur in water Chemical reactions depend on collision of molecules; therefore concentration of solutes in aqueous solution Molecular mass- sum of all masses of all atoms in a molecule usually measured in mole, where 1 mole (mol) = 6.02 x 10^23 molecules Avogadros number and the unit Dalton were defined such that 6.02 x 10^23 daltons = 1g Molarity (M)- number of moles of solute per liter of solution Hydrogen atom in a hydrogen bond between 2 water molecules can go to one another - hydrogen atom leaves electron behind and transferred as a proton, or hydrogen ion (H+) -molecule with extra proton is now hydronium ion (H3O+), also H+ -molecule that lost proton: hydroxide ion (OH-) Water is in equilibrium when molecules dissociate as same rate as being formed Dissociation of water is very rare, but has great effect on organisms Changes in H+ and OH- can drastically change affect a cells chemistry drastically H+ and OH- are equal in pure water Adding certain solutes.. -acid- any substance that increases the H+ concentration of solution -base- any substance that reduces H+ concentration of solution Acid any substance that increases the H+ concentration of solution
4) Water solvent of life
Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Substances
Solute Concentration in Aqueous solution
C: 3.3 Acidic and basic conditions affect living organisms
Acid and Bases
pH scale
Base any substance that reduces the H+ concentration of solution
Ph of solution is defined as pH=-log[H+] Acidic solutions have pH less than 7 Basic solution have pH higher than 7 Most biological fluids are around 6-8 Buffers Internal pH of cells must stay close to 7 Buffers are substances that minimizes changes in hydronium and hydroxides in a solution Buffers consists of acid-base pair that reversely combines with H+
Acidification: a threat to water quality
Human release CO2 from fossil fuels Human activities release pollutants that form acid in atmosphere - acid precipitation Acid precipitation means rain, snow, or fog with pH less that 5.6 Caused mainly by water mixing with pollutants in air; can fall distant from source Effect: - damage to lake and rivers - effects on soil chemistry causing some forest decline
You should now be able to: List and explain 4 properties of water that are possible because of hydrogen bonds Distinguish between : - hydrophobic and hydrophilic substances - solute, solvent, solution Define acid, base, and pH Explain how buffers work
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- CH 14 Mendel and The Gene IdeaDokumen6 halamanCH 14 Mendel and The Gene Ideawil7ver100% (2)
- CH 11 Cell CommunicationDokumen4 halamanCH 11 Cell Communicationwil7ver100% (2)
- CH 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life CyclesDokumen4 halamanCH 13 Meiosis and Sexual Life Cycleswil7verBelum ada peringkat
- CH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation WordDokumen5 halamanCH 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Wordwil7ver100% (1)
- CH 6 A Tour of The CellDokumen7 halamanCH 6 A Tour of The Cellwil7verBelum ada peringkat
- CH 4 Carbon and Molecular Diversity of LifeDokumen3 halamanCH 4 Carbon and Molecular Diversity of Lifewil7ver100% (1)
- CH 1 Themes in The Study of LifeDokumen4 halamanCH 1 Themes in The Study of Lifewil7verBelum ada peringkat
- Gnossienne 2Dokumen2 halamanGnossienne 2wil7ver100% (9)
- Gnossienne 3Dokumen2 halamanGnossienne 3wil7ver100% (16)
- Gnossienne 2Dokumen2 halamanGnossienne 2wil7ver100% (9)
- Gnossienne 3Dokumen2 halamanGnossienne 3wil7ver100% (16)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Phosphorus Removal On DewateringDokumen39 halamanPhosphorus Removal On DewateringAlberto SemillánBelum ada peringkat
- Basics of RadiobiologyDokumen61 halamanBasics of RadiobiologyLikhon Amin AponBelum ada peringkat
- FergDokumen16 halamanFergSwetha SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- Aircraft Materials BrochureDokumen6 halamanAircraft Materials BrochureAdnan ColoBelum ada peringkat
- Factors Influencing ToxicityDokumen7 halamanFactors Influencing ToxicityderrickBelum ada peringkat
- Flex-Rez 1084AS A TDSDokumen1 halamanFlex-Rez 1084AS A TDSBorja AzkargortaBelum ada peringkat
- D 2295 - 96 R02 - RdiyotuDokumen3 halamanD 2295 - 96 R02 - RdiyotuJorgeBelum ada peringkat
- A Brief Review On Optical Properties of Polymer Composites - Insights Into Light-Matter Interaction From Classical To Quantum Transport Point of ViewDokumen28 halamanA Brief Review On Optical Properties of Polymer Composites - Insights Into Light-Matter Interaction From Classical To Quantum Transport Point of Viewomkar BembalgeBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 6 Practice Test (Periodic Table)Dokumen5 halamanUnit 6 Practice Test (Periodic Table)Xazerco LaxBelum ada peringkat
- Design 2 MLDDokumen9 halamanDesign 2 MLDANIL KUMAR H CBelum ada peringkat
- Distillation Column Autocad Drawing Design: July 2017Dokumen3 halamanDistillation Column Autocad Drawing Design: July 2017Tera EducativoBelum ada peringkat
- PFI PPMG Polypropylene Meltblown New DatasheetDokumen1 halamanPFI PPMG Polypropylene Meltblown New Datasheetbennypartono407Belum ada peringkat
- Advanced Inorganic Chemistry (CHM4301) : Alkenes and AlkynesDokumen19 halamanAdvanced Inorganic Chemistry (CHM4301) : Alkenes and AlkynesAnonymous lClX1bBelum ada peringkat
- Vacancy-Induced Fano Resonances in Zigzag Phosphorene NanoribbonsDokumen9 halamanVacancy-Induced Fano Resonances in Zigzag Phosphorene NanoribbonsAntonio GaleoteBelum ada peringkat
- Operation ProceduresDokumen53 halamanOperation ProceduresmabrarahmedBelum ada peringkat
- HY10 1630US 5 2012-Diaphragm AccumulatorsDokumen6 halamanHY10 1630US 5 2012-Diaphragm AccumulatorsAlejandro GilBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis of 2 - (2,4-Diaminothiazol-5-Oyl) BenzothiazolesDokumen4 halamanSynthesis of 2 - (2,4-Diaminothiazol-5-Oyl) BenzothiazolesABBS FEN REJI T. F.Belum ada peringkat
- Design For Temperature-Controlled Solar Heated Chick BrooderDokumen7 halamanDesign For Temperature-Controlled Solar Heated Chick Brooderchristian emeka okaforBelum ada peringkat
- Sika Igasol - 17: High Build, Bituminous Emulsion CoatingDokumen3 halamanSika Igasol - 17: High Build, Bituminous Emulsion CoatingAhmed AbdallahBelum ada peringkat
- Four Steps To Effective Pigment Dispersions Jadel Baptista DCC LanscoDokumen5 halamanFour Steps To Effective Pigment Dispersions Jadel Baptista DCC LanscoEyad AlsheiikhBelum ada peringkat
- Palm Oil RefiningDokumen10 halamanPalm Oil Refiningharrison_sBelum ada peringkat
- CoordinationDokumen3 halamanCoordinationNiteshNarukaBelum ada peringkat
- Biology O Level Notes PDFDokumen36 halamanBiology O Level Notes PDFGB Hacker100% (1)
- Essential Variables API 1104Dokumen4 halamanEssential Variables API 1104Madidj_2014Belum ada peringkat
- Using The Logarithmic Concentration Diagram, Log C, To Teach Acid Base EquilibriumDokumen5 halamanUsing The Logarithmic Concentration Diagram, Log C, To Teach Acid Base EquilibriumMario FloresBelum ada peringkat
- The Frenkel-Kontorova Model - IntroductionDokumen5 halamanThe Frenkel-Kontorova Model - Introductionreal thinkerBelum ada peringkat
- Agfa Cassettes Manual PDFDokumen32 halamanAgfa Cassettes Manual PDFcarlosBelum ada peringkat
- Ultramet 2507: Stainless Steel Electrodes Product Data SheetDokumen1 halamanUltramet 2507: Stainless Steel Electrodes Product Data Sheetshaan1001gbBelum ada peringkat
- Lignocellulosic Biomass A Sustainable Platform For Production of Bio-Based - Isikgor2015 PDFDokumen62 halamanLignocellulosic Biomass A Sustainable Platform For Production of Bio-Based - Isikgor2015 PDFNatasha Mgt JoharBelum ada peringkat
- AssociationDokumen2 halamanAssociationRichmond EresmasBelum ada peringkat