Chemical Principles
Diunggah oleh
Meri SunderDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chemical Principles
Diunggah oleh
Meri SunderHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
BIO205 - Ch 2 - Chemical Principles - RioSalado - AZ
Question Isotopes Chemical properties of atoms are largly a function of __. Valence
Answer Atoms w/different number of neutrons Ex: 16/8O, 17/8O, 18/8O Number of electrons in outermost electron shell. Valence Combining capacity of atom number of missing electrons in outermost electron shell - "bonding capacity". A molecule containing at least 2 different kinds of atoms. Number of protons in nucleus Total number of protons & neutrons Atoms sharing electrons Hold 2 electrons (1 orbital) Holds 8 electrons (4 orbitals) Holds 18 electrons (9 orbitals) The valence electrons of the combining atoms form attractive forces (chemical bonds) between atomic nuclei. Antigen-antibody reaction in which antibodies combine with antigens to combat infection. An atom where outer electron shell is less than 1/2 filled & will lose electrons to form positive ions - K+, Ca2+, Na+ Atom with more than 1/2 filled outer electron shell will gain electrons & form negative ions - I-, Cl-, S2Atom that has gained or lost an electron
Compound Atomic number Mass number Chemical bonds First shell Second shell Third shell Molecules held together because?
Example of weaker ionic bond in immune system.
Cations
Anions Ion
& carries + or _ charge. H+ = Hydrogen ion When atoms share one or more pairs of electrons - single stronger than ionic more common than ionic in organisms (H-H). 2 ions held together by opposite charges when atoms have gained or lost outer electrons - Ex: NaCl Two atoms sharing 2 electron pairs Sharing 3 electron pairs When 2 atoms don't share electrons equally - electronegative - water molecules is example. Weak attraction formed between covalently bound hydrogen atom & an electronegative atom - DNA is example holds 2 nucleotide strands together. Ions & polar molecules easily dissolve in it. Clustering of water molecules around a solute - multiple ions dispersed in a fluid. Adenosine Triphosphate Deoxyribonucleic acid - made 4 kinds of deoxyribonucleotides - adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine. Base-pairing - the sequence of bases encodes heritable information. Ribonucleic acids - made of 4 ribonucleotide monomers - uracil, adenine, guanine, & cytosine - How cell retrieves & uses genetic info in DNA to build proteins. Covalent - their outer electron shells are half-filled
Covalent bond
Ionic bond Double Covalent Bond Triple Covalent Bond Polar covalent bond
Hydrogen bond
Solvent Sphere of hydration ATP
DNA
RNA
Hydrogen & carbon form __ bond quite easy because __.
Covalent bonds are formed by __ electrons, while ionic are formed by __ between atoms that have lost or gained electrons. __ are weak but do serve as bridges between different molecules or between various portions of same molecule. In a molecule of water, all the electrons tend to be closer to the __ nucleus. Elements most frequently involved in hydrogen bond. molecular weight One __ of a substance is its molecular weight in grams. Chemical energy Chemical reaction that absorbs more energy than released. Chemical reaction that releases more energy than absorbed. Synthesis reaction Combining substances in reaction.
sharing-attraction (become + or charged).
hydrogen bonds
oxygen oxygen & nitrogen Sum of the atomic weights of all its atoms. mole - ex: 1 mole of H2O = 18g [(2x1)+16] Change of energy whenever bonds are formed/broken during chemical reaction. Endergonic reaction Exergonic reaction When 2 or more atoms/ions/molecules combine into larger molecules - "new bonds formed" A+B=AB reactants
Pathways of synthesis reaction in living organisms are anabolic (anabolism) __. 2 examples of anabolism (1) combining of sugar molecules to form starch & (2) amino acids to form proteins bonds are broken - larger molecules split into smaller - AB=A + B = catabolism in living organisms. (1) breakdown of sucrose (table sugar) intoglucose & fructose during digestion, (2) bacterial
Decomposition Reaction 2 examples of catabolism
decomposition/bioremediation. Inorganic compounds lack __. What 2 elements are always fround in organic compounds? Most common bonds in organic compounds. __ is the medium for most chemical reactions. The total charge of H2O molecule is __ but oxygen retion __ and hydrogen. Every H2O molecule can form __ hydrogen bonds with nearby molecules. solvent dissociation solute Polarity of H2O facilitates splitting & rejoining of __ & __ ions. What protects cell from temperature fluctuations? ionization An __ dissociates into 1 or more H+ (cations) ions & 1 or more negative ions (anions). carbon - structurally simple - water, oxygen, CO2, salts, acids, bases, etc. Carbon & hydrogen - structurally complete. Covalent bonds - atoms sharing one or more pairs of electrons. water neutral, negative, positive 4 Dissolving medium - ex: water due to polarity Separation into individual molecules in water. A substance dissolved in another substance hydrogen (H+) & hydroxide (OH-) Hydrogen bonds of water Breaking apart (dissociation) into ions acids & bases acid - proton (H+) donor
A __ dissociates into 1 or more H+ (cations) ions plus negative charged hydroxide (OH-) that can accept base - proton (H+) acceptor protons. pH measures? Fungi tolerate __ conditions & prokaryotes __. Amount of H+ in solution - "potential of hydrogen" acidic - alkaline
isomer
2 molecules with same chemical formula, but different structures & properties - ex: glucose & fructose Contain an aldehyde or a ketone group, and one or more hydroxyl groups mainly hydrocarbon Are one or more polypeptide chains with as many as several thousand covalently linked amino acids. Chains of units that each consists of a 5carbon sugar, phosphate, & a nitrogencontaining base Have long-chain fatty acids tightly packed & bonded to long-chain alchols or carbon rings lipids w/no fatty acids - Cholesterol Small organic compounds with amino group, carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, & its R group. Used in constructing proteins. Bonds formed in polypeptide chains 3 or more amino acids In nucleotides (ATP), DNA, RNA - many proteins - phospholipids. Water soluble acidic. -SH - In amino acid cystine - helps stabolize protein structure - disulfide bridges. Subunits of larger molecules Large organic molecule containing subunits. -OH, In alcohols (amino acids, sugars) water soluble - easy place to split or join
carbohydrates lipids proteins
nucleic acids (nucleotides)
waxes sterols
Amino acid
Peptide bond Polypeptide chain Phosphate
Sulfhydrl Monomers Polymers Hydroxyl
molecules. Methyl Carbonyl Fatty acid chains - insoluable in water In sugars, amino acids, nucleotides water soluable (aldehyde & ketone) prone to electron transfers. In amino acids, fatty acids, water soluable - highly polar - acts as acids releases H+ In amino acids & nucleotides - base accepts H+ - water soluble Simple carb/short chain sugar/"complex carbohydrates" Nonpolar hydrocarbons - don't dissolve in water - mix with other nonpolar substances Lipids w/1, 2, or 3 fatty acid tails from glycerolmolecule. Starts as carboxyl group attached to carbon atoms Contain one or more double covalent bonds Single bonds only Triglycerides - 3 fatty acid tails & 1 glycerol head - butter, lard, vegetable oils. Molecules that contain carbon and at least 1 hydrogen Consist only of hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to carbon - gasoline, fossil fuels Organic compounds which are particular atoms or clusters of atoms covalently bonded to carbon.
Carboxyl
Amino monosaccharides/oligosaccharide/polysaccharides
Lipids
fats Fatty acid Unsaturated fatty acid Saturated fatty acid Neutral fats
Organic compounds
Hydrocarbons
Functional groups
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- List of People Regarded As Father of A Scientific FieldDokumen3 halamanList of People Regarded As Father of A Scientific FieldMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Verbal Reasoning Shortcuts DTDokumen14 halamanVerbal Reasoning Shortcuts DTMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Sprouts Curry - Simple Indian RecipesDokumen3 halamanSprouts Curry - Simple Indian RecipesMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Appam - Aapam - Simple Indian RecipesDokumen6 halamanAppam - Aapam - Simple Indian RecipesMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Differences Between Mitosis and MeiosisDokumen4 halamanDifferences Between Mitosis and MeiosisMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- PTN FoldingDokumen6 halamanPTN FoldingMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Tamil Computer Book - Adobe Photo ShopDokumen41 halamanTamil Computer Book - Adobe Photo ShopSakthivel100% (19)
- Algal Cell Walls - CSIR NET Life SciencesDokumen2 halamanAlgal Cell Walls - CSIR NET Life SciencesMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Guidelines For Heritage Education ActivitiesDokumen3 halamanGuidelines For Heritage Education ActivitiesMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Ranking TestDokumen13 halamanRanking TestMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Pulse FieldDokumen2 halamanPulse FieldMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- List of People Regarded As Father of A Scientific FieldDokumen3 halamanList of People Regarded As Father of A Scientific FieldMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- How To Compost at HomeDokumen4 halamanHow To Compost at HomeMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- List of People Regarded As Father of A Scientific FieldDokumen3 halamanList of People Regarded As Father of A Scientific FieldMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Relations - ReasoningDokumen10 halamanBlood Relations - ReasoningMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Verbal Analogy Shortcuts - IntroductionDokumen8 halamanVerbal Analogy Shortcuts - IntroductionMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter AaDokumen38 halamanChapter AaMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
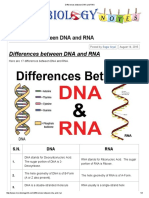
- Differences Between DNA and RNADokumen3 halamanDifferences Between DNA and RNAMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Algal Cell Walls - CSIR NET Life SciencesDokumen2 halamanAlgal Cell Walls - CSIR NET Life SciencesMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Library+Classification+Theory+Unit 13Dokumen15 halamanLibrary+Classification+Theory+Unit 13Uday PaliBelum ada peringkat
- Alpha-Numeric-Symbol Test (Part - II)Dokumen9 halamanAlpha-Numeric-Symbol Test (Part - II)Meri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Seating Arrangement Practice ProblemsDokumen19 halamanSeating Arrangement Practice ProblemsMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter AaDokumen38 halamanChapter AaMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- PG Diploma in Food Safety and Quality ManagementDokumen5 halamanPG Diploma in Food Safety and Quality ManagementMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- How To Read A PedigreeDokumen40 halamanHow To Read A PedigreeMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- B CDokumen34 halamanB CvicksaumBelum ada peringkat
- GospelDokumen280 halamanGospelMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Structure of MoleculesDokumen5 halamanStructure of MoleculesMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- QuotesDokumen2 halamanQuotesMeri SunderBelum ada peringkat
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- One Dimensional Steady State Conduction: By: Taz 1Dokumen52 halamanOne Dimensional Steady State Conduction: By: Taz 1Adam AndualemBelum ada peringkat
- Rationale of Natural Gas Processing & ExtractionDokumen9 halamanRationale of Natural Gas Processing & ExtractionUJJWALBelum ada peringkat
- Dissociation of Hydrogen 1 LangmuirDokumen15 halamanDissociation of Hydrogen 1 LangmuirpomodoroBelum ada peringkat
- Use The Table Below To Answer The Questions That Follow.: A. Multiple-Choice and Bimodal QuestionsDokumen13 halamanUse The Table Below To Answer The Questions That Follow.: A. Multiple-Choice and Bimodal QuestionsHUY NGUYỄN PHƯƠNG PHÚCBelum ada peringkat
- Design of 750 MW Combined Cycle Power Plant: Water LoopDokumen19 halamanDesign of 750 MW Combined Cycle Power Plant: Water LoopAdrian BundalianBelum ada peringkat
- Term SymbolDokumen23 halamanTerm SymbolCyriac Mathew73% (11)
- Skew T Adiabatic Diagram: Temperature in Degrees CelsiusDokumen1 halamanSkew T Adiabatic Diagram: Temperature in Degrees CelsiusMihai Mirel RusuBelum ada peringkat
- G9 Matter in Our Surroundings Q.bank 1Dokumen21 halamanG9 Matter in Our Surroundings Q.bank 111Yeshwanth ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Matriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneDokumen30 halamanMatriculation Chemistry (Hydrocarbon) Part 2 AlkaneridwanBelum ada peringkat
- Xii Physics NotesDokumen170 halamanXii Physics Notesiamyasirali68Belum ada peringkat
- Structure of SolidsDokumen22 halamanStructure of SolidsNicole Anne Borromeo100% (1)
- 5-Black Oil SimulationDokumen84 halaman5-Black Oil SimulationAssholeBelum ada peringkat
- Catalase and Hydrogen Peroxide Experiment: Problem: What Happens When A Potato Is Combined With Hydrogen Peroxide?Dokumen1 halamanCatalase and Hydrogen Peroxide Experiment: Problem: What Happens When A Potato Is Combined With Hydrogen Peroxide?Big CinemaBelum ada peringkat
- Boltzmann's and Saha's EquationsDokumen22 halamanBoltzmann's and Saha's Equationssujayan2005Belum ada peringkat
- Syllabus PCB PDFDokumen5 halamanSyllabus PCB PDFSujay HvBelum ada peringkat
- The ALUREC ProcessDokumen7 halamanThe ALUREC ProcesscarlosiqmBelum ada peringkat
- Fator de Watson KW Ie50312a018Dokumen5 halamanFator de Watson KW Ie50312a018Luiz Roberto TerronBelum ada peringkat
- 14.1 Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 14 Chemical KineticsDokumen43 halaman14.1 Multiple-Choice Questions: Chapter 14 Chemical KineticsanonBelum ada peringkat
- Day 2 - Part 2: Equation of State ModelsDokumen42 halamanDay 2 - Part 2: Equation of State ModelsZico VersusBelum ada peringkat
- Laser Beam Machining Definition Working Process Principle Advantages Disadvantages Application NotesDokumen4 halamanLaser Beam Machining Definition Working Process Principle Advantages Disadvantages Application NotesMD Al-AminBelum ada peringkat
- Transport Phenomena: Contents of Heat TransferDokumen85 halamanTransport Phenomena: Contents of Heat TransferalbeiroBelum ada peringkat
- (SSC) Consumer Chemistry9 Q1 M6 W6Dokumen24 halaman(SSC) Consumer Chemistry9 Q1 M6 W6.Belum ada peringkat
- Synthetic RubbersDokumen3 halamanSynthetic RubbersKamal KishoreBelum ada peringkat
- Phosphorescence Excitation Spectrum of Benzophenone at Liq.N TemperatureDokumen5 halamanPhosphorescence Excitation Spectrum of Benzophenone at Liq.N TemperatureNisar Ali Mphil-Chem ABelum ada peringkat
- Tinogard Q TdsDokumen4 halamanTinogard Q TdsMarlon2370100% (1)
- R&ACDokumen2 halamanR&ACsubramanian jBelum ada peringkat
- Solid State: Objective Type Questions Multiple Choice QuestionsDokumen5 halamanSolid State: Objective Type Questions Multiple Choice QuestionsSnehashis BoseBelum ada peringkat
- 05.2 Activation Energy and Enthalpy ChangeDokumen17 halaman05.2 Activation Energy and Enthalpy ChangeanthorBelum ada peringkat
- Kmno4 TitrationDokumen3 halamanKmno4 Titrationcocomelon8454Belum ada peringkat
- Seminar PaperDokumen14 halamanSeminar Paperdarshan singh kambojBelum ada peringkat