Sample Questions For IIA Entrance Exam
Diunggah oleh
narayanan63Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sample Questions For IIA Entrance Exam
Diunggah oleh
narayanan63Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Sample Questions for IIA Entrance Exam
The syllabus for the IIA entrance exam is the standard BSc. & M.Sc Physics syllabus covering dierent areas of specialization. In particular, it presumes that the candidates have taken basic courses in Mathematical Physics, Classical Mechanics, Electromagnetic Theory, Quantum Mechanics, and Statistical Mechanics. There will be some questions in special subjects such as Condensed Matter Physics, Nuclear Physics etc in addition to coverage in applied areas such as Electronics, Instrumentation and Optics. The question paper will be multiple-choice. It will contain questions of two levels of diculty. The rst level will have 30 easier questions carrying 1 mark each. The second level will have 30 dicult questions carrying 3 marks each. Therefore, the test questions will have a total of 60 questions with 30 from each level, adding to a total maximum marks of 120. It is suggested that the candidate answer as many questions as possible in 3 hrs keeping in mind that negative marking for wrong answers is one third the value of the question (1 or 1/3) and concentrate on those questions within the candidates grasp or specialization. The current pattern could be subject to change in the future.
ONE MARK QUESTIONS 1. Black-body radiation, at temperature Ti lls a volume V . The system expands adiabatically and reversibly to a volume 8 V . The nal temperature Tf = xTi , where the factor x is equal to (a) 0.5 (b) 2.8 (c) 0.25 (d) 1
2. A particle of mass m, constrained to move along the x-axis. The potential energy is given by, V (x) = a + bx + cx2 , where a, b and c are positive constants. If the particle is disturbed slightly from its equilibrium position, then it follows that (a) it performs simple harmonic motion with period 2 (m/2c) (b) it performs simple harmonic motion with period 2 (ma/2b2 ) (c) it moves with constant velocity (d) it moves with constant acceleration 3. Consider a square ABCD, of side a, with charges +q, q, +q, q placed at the vertices, A, B, C, D respectively in a clockwise manner. The electrostatic potential at some point located at a distance r (where r a) is proportional to (a) a constant (b) 1/r (c) 1/r2 (d) 1/r3
4. The general solution of dy/dx y = 2ex is (where C is an arbitrary constant) (a) e2x + Cex (b) 2xex + Cex is (c) 2xex + C (d) ex + C
2
5. The value of lim
ln(1 + sin ) sin (c) 1
(a)
(b)
(d)
6. Two parallel innitely long wires separated by a distance D carry steady currents I1 and I2 (I1 > I2 ) owing in the same direction. A positive point charge moves between the wires parallel to the currents with a speed v at a distance D/2 from either wire. The magnitude of an electric eld that must be turned on to maintain the trajectory of the particle is proportional to (a) (c) (I1 I2 )v/D (I1 I2 )v 2 /D2 (b) (d) (I1 + I2 )v/D (I1 + I2 )v 2 /D2
7. An ideal gas of non-relativistic fermions in three dimensions is at a temperature of 0 K. When both the mass of the particles and the number density are doubled, the energy per particle is multiplied by a factor, (a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 21/3 (d) 1/21/3
THREE MARKS QUESTIONS 8. If p is the momentum operator, and are the three Pauli spin matrices, the eigenvalues of ( p) are (a) px and pz (b) px ipy (c) |p| (d) (px + py + pz )
9. The rotational part of the Hamiltonian of a diatomic molecule is (1/21 )(L2 + L2 ) + (1/22 )L2 where z y x 1 and 2 are moments of inertia. If 1 = 22 , the three lowest energy levels (in units of h2 /42 ) are given by (a) 0,2,3 (b) 0,1,2 (c) 1,2,3 (d) 0,2,4
10. A particle of mass 1 gm starts from rest and moves under the action of a force of 30 Newtons dened in the rest frame. It will reach 99% the velocity of light in a time of (a) 9.9 103 sec (b) 7 104 sec (c) 0.999 sec (d) 0.7 sec
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Continuum Mechanics: Concise Theory and ProblemsDari EverandContinuum Mechanics: Concise Theory and ProblemsPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (3)
- JEST Physics 2008 Sample PaperDokumen2 halamanJEST Physics 2008 Sample Paperiswaleha100% (1)
- Solutions Code 0 JEEAdvanced2013 VMC SolvedDokumen28 halamanSolutions Code 0 JEEAdvanced2013 VMC SolvedShashank ShekharBelum ada peringkat
- Jest QuestionDokumen16 halamanJest QuestionThirumugam SBelum ada peringkat
- Aakash Solutions For JEE ADVANCED PAPER 1Dokumen30 halamanAakash Solutions For JEE ADVANCED PAPER 1Tushar KumarBelum ada peringkat
- JEE Main Solved Paper 2010Dokumen24 halamanJEE Main Solved Paper 2010chithrasajeevBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Question PaperDokumen5 halamanPhysics Question Papervasudevan m.vBelum ada peringkat
- JEST-2023 - FLT-1 (Question File)Dokumen12 halamanJEST-2023 - FLT-1 (Question File)Mahitha GirishBelum ada peringkat
- Jest Physics Sample Question PaperDokumen3 halamanJest Physics Sample Question PaperSreejith Nhaloor0% (1)
- Sample Exam 1.0.0Dokumen24 halamanSample Exam 1.0.0Cameron LeungBelum ada peringkat
- Phys Sample GDokumen11 halamanPhys Sample GAbhijit SanjeevBelum ada peringkat
- Vidya Mandir Classes Study MaterialDokumen37 halamanVidya Mandir Classes Study Materialg_group43% (7)
- Assignment2 PDFDokumen9 halamanAssignment2 PDFSuresh ThallapelliBelum ada peringkat
- JEE Main 2022 (June 25 Morning Shift) Question Paper With Solutions (PDF)Dokumen24 halamanJEE Main 2022 (June 25 Morning Shift) Question Paper With Solutions (PDF)avaneesh khadyeBelum ada peringkat
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper Solutions 24 February MorningDokumen39 halamanJEE Main 2021 Question Paper Solutions 24 February MorningTanishq KaushikBelum ada peringkat
- Jest 2013 QN PaperDokumen12 halamanJest 2013 QN PaperAbhijit SanjeevBelum ada peringkat
- Tifr Dec2011 Question PaperDokumen15 halamanTifr Dec2011 Question Papertvsagar830% (1)
- KVPY Stream SB SX Solved Sample Paper 2015 Paper 1Dokumen37 halamanKVPY Stream SB SX Solved Sample Paper 2015 Paper 1keerthyBelum ada peringkat
- Keam (Engineering) Answer Key 2018: Questions & AnswersDokumen20 halamanKeam (Engineering) Answer Key 2018: Questions & AnswersswethaBelum ada peringkat
- Keam (Engineering) Answer Key 2018: Questions & AnswersDokumen20 halamanKeam (Engineering) Answer Key 2018: Questions & AnswersswethaBelum ada peringkat
- TIFR 2014 Physics Question Paper Set XDokumen24 halamanTIFR 2014 Physics Question Paper Set XiswalehaBelum ada peringkat
- Entrance PhysicsDokumen399 halamanEntrance PhysicsBikram Shah77% (22)
- BITSAT 2013 Paper - Solved by ArihantDokumen25 halamanBITSAT 2013 Paper - Solved by ArihantPranivoidBelum ada peringkat
- Neet Question Paper 2021 Code O1Dokumen71 halamanNeet Question Paper 2021 Code O1Deev SoniBelum ada peringkat
- S. No Questions Solutions Sol:1 (D) : L L T S L LDokumen8 halamanS. No Questions Solutions Sol:1 (D) : L L T S L LVaibhav SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Paper 1 PDFDokumen16 halamanPaper 1 PDFAbhishek AvhadBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Mains 2009 Question PaperDokumen28 halamanJee Mains 2009 Question PaperYASHBelum ada peringkat
- JEE - MAIN 2014 - Paper With Solution PDFDokumen23 halamanJEE - MAIN 2014 - Paper With Solution PDFpoornachandranBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Advance 2014 Phy I Questions SolutionsDokumen9 halamanJee Advance 2014 Phy I Questions SolutionsMohammed Aftab AhmedBelum ada peringkat
- Ala'a Nabil-Solved Re-TestDokumen2 halamanAla'a Nabil-Solved Re-TestMoh'd AlsalhiBelum ada peringkat
- 40468879-Paper-3-Class-XII 2009Dokumen16 halaman40468879-Paper-3-Class-XII 2009jiban15Belum ada peringkat
- JEE Main Physics Previous Year Questions With Solutions On Work Power EnergyDokumen10 halamanJEE Main Physics Previous Year Questions With Solutions On Work Power Energybagadatharva94Belum ada peringkat
- Field (A) Electromagnetic Sheet 10th of RamadanDokumen6 halamanField (A) Electromagnetic Sheet 10th of RamadanaboashoorBelum ada peringkat
- Physics Category C: Exam Date: 25th January 2020 Exam Timing: 4pm - 7pmDokumen9 halamanPhysics Category C: Exam Date: 25th January 2020 Exam Timing: 4pm - 7pmSurender SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Jee Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper With Solutions by VedantuDokumen23 halamanJee Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper With Solutions by VedantuAkshay guptha athmakuriBelum ada peringkat
- Wbjee 2009 PaperDokumen53 halamanWbjee 2009 PaperLokesh KumarBelum ada peringkat
- JEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2 PCM CombinedDokumen25 halamanJEE Main 24th Jan Shift 2 PCM CombinedVeda Vikas DBelum ada peringkat
- KVPY Stream SA Sample Paper 2016 Paper 1Dokumen15 halamanKVPY Stream SA Sample Paper 2016 Paper 1Anonymous V4SK3LkJBelum ada peringkat
- JEE MAINS Solved Paper 2007Dokumen25 halamanJEE MAINS Solved Paper 2007chithrasajeevBelum ada peringkat
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsDari EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsBelum ada peringkat
- A Course of Mathematics for Engineers and ScientistsDari EverandA Course of Mathematics for Engineers and ScientistsBelum ada peringkat
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenDari EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillBelum ada peringkat
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Dari EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)Belum ada peringkat
- The Advanced Geometry of Plane Curves and Their ApplicationsDari EverandThe Advanced Geometry of Plane Curves and Their ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyDari EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyBelum ada peringkat
- Method of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsDari EverandMethod of Moments for 2D Scattering Problems: Basic Concepts and ApplicationsBelum ada peringkat
- Tables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiDari EverandTables of Coefficients for the Analysis of Triple Angular Correlations of Gamma-Rays from Aligned NucleiBelum ada peringkat
- Mathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsDari EverandMathematics 1St First Order Linear Differential Equations 2Nd Second Order Linear Differential Equations Laplace Fourier Bessel MathematicsBelum ada peringkat
- Barron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewDari EverandBarron's Physics Practice Plus: 400+ Online Questions and Quick Study ReviewBelum ada peringkat
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)Dari EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)Belum ada peringkat
- Application of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDari EverandApplication of Derivatives Tangents and Normals (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Chem. 266 Physical Chemistry III: Quantum MechanicsDokumen70 halamanChem. 266 Physical Chemistry III: Quantum MechanicsJohn Edward ZapaterBelum ada peringkat
- There Are No Particles, There Are Only Fields PDFDokumen52 halamanThere Are No Particles, There Are Only Fields PDFSatkas DimitriosBelum ada peringkat
- Particle Zoo: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDokumen7 halamanParticle Zoo: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediajubaeBelum ada peringkat
- Big Bang TimelineDokumen1 halamanBig Bang TimelinePrecious PanganibanBelum ada peringkat
- Modern Physics @kvpy - AspirantsDokumen5 halamanModern Physics @kvpy - AspirantssagarBelum ada peringkat
- Lagrangian FormulationDokumen7 halamanLagrangian FormulationAdrian ArasuBelum ada peringkat
- Atomic Energy and PeriodicityDokumen26 halamanAtomic Energy and PeriodicityHenu AryudaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Quantum Field TheoryDokumen261 halamanIntroduction To Quantum Field TheorykoutariBelum ada peringkat
- Chem 373 - Lecture 12: Harmonic Oscillator-IIDokumen29 halamanChem 373 - Lecture 12: Harmonic Oscillator-IINuansak3Belum ada peringkat
- 460 Harm OscDokumen7 halaman460 Harm OscdidikkrisBelum ada peringkat
- A2 TPM-7 QP (2020) PDFDokumen9 halamanA2 TPM-7 QP (2020) PDFABelum ada peringkat
- تجربة دافيسون وجيرمرDokumen5 halamanتجربة دافيسون وجيرمرSara Ali100% (1)
- Note Sad DangDokumen16 halamanNote Sad DangEverton LimaBelum ada peringkat
- Sound Through MetalDokumen3 halamanSound Through Metalm.edwards06Belum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 1Dokumen2 halamanTutorial 1Syrus SylarBelum ada peringkat
- Electron Irradiation Effect On Al2O3Dokumen63 halamanElectron Irradiation Effect On Al2O3younessinaBelum ada peringkat
- 8.9 Radioactivity:: The Nature of DecayDokumen6 halaman8.9 Radioactivity:: The Nature of Decay...Belum ada peringkat
- Peskin Chapter 4Dokumen34 halamanPeskin Chapter 4Gary OaksBelum ada peringkat
- Lu 22 CorrelatedDokumen23 halamanLu 22 CorrelatedwhateverBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Supersymmetry and Supersymmetry BreakingDokumen56 halamanIntroduction To Supersymmetry and Supersymmetry BreakingUmer ZubairBelum ada peringkat
- Quantum Chemistry Program in FortranDokumen41 halamanQuantum Chemistry Program in FortranSoumya GangulyBelum ada peringkat
- Q. Marks. 1. 2. 3. Total : Minor Examination PYL556Dokumen7 halamanQ. Marks. 1. 2. 3. Total : Minor Examination PYL556asdfghBelum ada peringkat
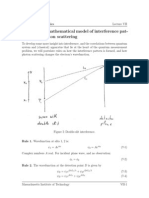
- Double Slit: Mathematical Model of Interference Pat Tern and Photon ScatteringDokumen12 halamanDouble Slit: Mathematical Model of Interference Pat Tern and Photon ScatteringOliver58Belum ada peringkat
- Forces PicsDokumen19 halamanForces PicsGarry Lloyd TuzonBelum ada peringkat
- Latihan Soal-Soal Bab 1-4 (Fismod)Dokumen35 halamanLatihan Soal-Soal Bab 1-4 (Fismod)Nisrina Kamilia SalsabilaBelum ada peringkat
- Schrodinger, Erwin PDFDokumen4 halamanSchrodinger, Erwin PDFcreeshaBelum ada peringkat
- Ahmed Rebai, PHD in Nuclear PhysicsDokumen34 halamanAhmed Rebai, PHD in Nuclear PhysicsAhmed RebiiBelum ada peringkat
- S Chaw Low and TownesDokumen5 halamanS Chaw Low and TownesAgnivesh SharmaBelum ada peringkat
- EFSchubert Physical Foundations of Solid State DevicesDokumen273 halamanEFSchubert Physical Foundations of Solid State Devicespantarai100% (1)