Inexp
Diunggah oleh
Ujwal SuriDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Inexp
Diunggah oleh
Ujwal SuriHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
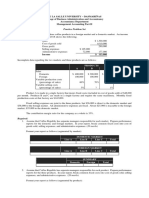
Analysis of Case Study: Inexperience
Para. Problem No. 1 Need for Cost Projection or Prediction: Revenue predictions are possible through accurate productivity measurement techniques and systems. But are there systems available for cost measurement and control? Need for maintenance of cost accounting records To understand the cost of each finished product there should be system to maintain cost records of all raw materials.
Info Required For Decision Making
Supplied Information
Source Of Supplied Information
Likely Source Of Missing Information
What are the available cost tracking and measurement systems available in MGPM manufacturers
Information is supplied only about system available for profit projection at MGPM.
This information is Internal cost accounting provided in the text. process and manuals at MGPM
What are the per-unit costs of raw materials used: cotton and wool? What are the volumes of raw materials used per unit finished product? What are the costs of ready-for-sale handicraft items?
Information is supplied only about the type of raw materials
This information is Various accounts and provided in the text. Ledgers. Cost accounting reports and records.
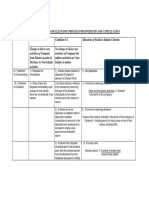
Para. Problem No. 3 Need for rational allocation of costs to measure productivity of individual functions At MGPM there is an urgent need to ascertain the causes of the financial losses. This requires analysis of costproductivity and profitability of all departments
Info Required For Decision Making
Supplied Information
Source Of Supplied Information
Likely Source Of Missing Information
Rational procedure to determine: - The proper breakup of costs. - Measure of cost per unit output. - Cost variation trends. - Methods for controlling costs.
The rational procedure for cost allocation involves: - Identification of cost objects, cost centers and cost units - Planning of cost allocation, apportionment and absorption in a scientific manner.
Jaswinder Singh, Friend of Mr. Joginder Marwah
Missing information about understanding of processes and techniques for scientific analysis and allocation of costs can be retrieved from cost accounting books and manuals as well as experienced cost accountants.
Comparison and Justification of costs allocated to individual functions In order to understand if an individual function is cost-productive, MGPM needs tools to analyze and justify the costs incurred Explanation and justification of the costs incurred at each function Function wise distribution of common costs incurred as a percentage of the total cost Joginders Study of costs at MGPM To analyze and compare the costs incurred at a function: comparison can be done with industry benchmark costs. Likely
by each function
source of such information can be competitor survey /intelligence and expert advice.
Accurate measurement of per unit cost of product In order to achieve rational pricing of a product and reduce the significant costs involved in making a product, measurement of unit cost is important For every product detailed costs involved are needed including raw material, labour, machine etc. For Handicrafts: 50% of cost is raw material cost, 30% is salary and labour cost, 5% is machine cost This information is Techniques and methods provided in the text. are needed to accurately distribute common costs: like utilities, storage, transportation costs etc. among all products per unit. This information can be retrieved from standard cost accounting manuals.
Comparison of costs of alternative production methods To evaluate two alternative production methods based on the per unit raw material costs for the two alternatives To compare costs of two alternative production methods: accurate data about the amount of raw materials involved in the 2 alternatives and per unit cost of these Cost of Pasting Material:Alternative 1: 225*Wt + 5000-200 Alternative 2: 425*Wt Therefore, if Weight of paste used at MGPM is more than 24 Kg, then alternative 1 is cheaper. Else alternative 2 is cheaper. This information is The actual amount of provided in the text. pasting material used at MGPM is not known: this figure can be retrieved if appropriate raw material usage records are maintained in all functions.
raw materials is needed. 7 Comparing in-house production cost versus outsourcing cost To evaluate proposals of outsourcing production for some of the products as compared to in-house production To evaluate proposal of getting production of a product outsourced, accurate estimate of costs incurred with inhouse production should be available Using electronic components from ME reduces warranty repair costs by 99.5%. New components from ME are costlier by Rs. 17.43. Additional fixed cost for machines required = Rs. 5000 Saving on selling existing machine to Mahavir Handicrafts = Rs. 575. This information is The percentage of provided in the text. warranty repairs carried out on dancing puppets, average amount of the rework costs and amount charged per unit by Mahavir Handicrafts for assembling need to be determined to evaluate the proposal. This information would be part of records of customer care department that handles repairs.
Identifying variation in fixed and variable product costs as scale of production and inventory varies To identify whether increase in costs are in proportion to increased To identify whether increasing the production scale Due to increased production: Electircity bill has increased, New unskilled workers and supervisor This information is The information required provided in the text. for this can be found in inventory accounts, salary
production and to accurately identify inventory costs.
results in decrease in average costs: data is needed showing QoQ increase in production, increase in variable cost (utility, labour, raw material) and change in inventory level.
are hired, and raw material cost has increased. WIP and finished goods inventory has also increased.
accounts, raw materials accounts, inventory accounts and sales accounts
Projection of cash flow and liquidity and estimation of user cost of capital To accurately estimate that enough cash will be available for operations throughout the year even though sales may vary considerably. How much working capital will be made available by sales over the operation cycle and how much debt needs to be raised In the first and second quarters sales are projected to fall by 8%. In the third and fourth quarters sales are projected to grow at a compounded rate of 38%. 86% of the yearly export sales happen in December. Capital is needed for operations as well as for buying new warehouse. There will be a quarterly loss of interest money @ Rs. 7,50,000 if MGPMs own funds are used. This information is To accurately know the provided in the text. working capital required for operations: a system is needed to accurately accumulate all costs data and predict the expected quarterly operations costs. This system can be any SAP system applied in the company. This system should also be able to estimate quarterly capital requirements and costs of alternate sources of capital.
10
Selection of appropriate product mix to maximize profit margin and optimizing cost of raw materials used To determine whether to continue production of low margin products. To identify and minimize all controllable costs used in these products What is the amount of cost savings and effect on sales of other products if production of jewellery boxes is discontinued? What needs to be done regarding inputs used exclusively by discontinued products? The margins on jewellery boxes are lower than those on other products. Sales of other products may be adversely affected if jewellery box production is stopped. Margins on jewellery boxes can be improved by reducing the quantity of raw materials used getting sourcing them at lower prices This information is Improvement in margins provided in the text. on jewellery boxes by varying costs and amounts of raw materials can be evaluated through SAP system. If jewellery box production is stopped, alternative uses of the fixed and sunk costs associated with them must be planned using Master Production system.
11
Selection of appropriate raw material processing methods so as to yield more of higher value items. To determine optimal raw material processing methods that yield more of higher valued items. Segregation of skills possessed by labour so as The detailed cost analysis of each step involved in processing raw jute is needed. The market value of three types 20% cost saving is possible with new jute processing method. The 3 types of jutes will be produced in the ratio 30:40:30. If labour specializes in few standard activities it is easier to allocate This information is provided by craftsman Gopal. Detailed cost data of various sub operations of jute processing can again be obtained from appropriate SAP/cost management system. Data
to easily allocate labour costs to different products.
of processed jutes is needed to apportion the jute processing costs. Data is needed for time spend by all labour according to the task performed and the product on which it is perfomed.
labour costs to different products.
of labour time spent on an activity per product must be available through the time-sheet system in the company.
12
To determine the batch size and sales price of orders to be fulfilled so that the order is profitable To find minimum quantity and price of premium items to be supplied to emporiums under a special order so that the order is profitable. It is needed to find the appropriate cost of a unit product when fulfilling a special batch/order. Also based on the cost, appropriate price to be quoted is to be found. For the special order a minimum margin of 55% is expected. The costs to be added in the product cost include material cost, labour cost, overhead expenses, interest charges @12% for internally generated funds used in manufacturing products, notional warehouse rent and notional salary of the owner. This information is Through the SAP system, provided in the text. profit analysis calculation for fulfilling an order must be possible. For example: min value of n can be found by Selling Price >= 1.55 x (average variable cost + total overhead cost/n)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Global Currency Reset - Revaluation of Currencies - Historical OverviewDokumen20 halamanGlobal Currency Reset - Revaluation of Currencies - Historical Overviewenerchi111196% (28)
- Introduction To Process CostingDokumen29 halamanIntroduction To Process Costingshersudsher67% (3)
- Process Costing ExplainedDokumen28 halamanProcess Costing Explainedbhavinpoldiya0% (1)
- Five Forces Industry AnalysisDokumen23 halamanFive Forces Industry AnalysisJohn Aldridge ChewBelum ada peringkat
- ACCA F5 - Part A - Specialist Cost and Management Accounting TechniquesDokumen5 halamanACCA F5 - Part A - Specialist Cost and Management Accounting TechniquesMuneera Al Hassan100% (2)
- MIGRATION TO PERIOD COSTDokumen9 halamanMIGRATION TO PERIOD COSTChandrababu Naidu BoyapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Proses Costing and Job Order CostingDokumen9 halamanProses Costing and Job Order CostingNefvi Desqi AndrianiBelum ada peringkat
- Philippine Review Institute for Accountancy (PRIA) Advanced Financial Accounting and Reporting (AFAR) Cost Accounting SystemsDokumen7 halamanPhilippine Review Institute for Accountancy (PRIA) Advanced Financial Accounting and Reporting (AFAR) Cost Accounting SystemsPau SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Set Mod 1Dokumen4 halamanProblem Set Mod 1Lindsay MadeloBelum ada peringkat
- Material Cost Estimates For OrderDokumen9 halamanMaterial Cost Estimates For OrderfharooksBelum ada peringkat
- Positional TradingDokumen69 halamanPositional TradingManoj Kumar0% (2)
- SAP CO MTO Scenario Product Cost by Sales Order Scenario 1611987778Dokumen30 halamanSAP CO MTO Scenario Product Cost by Sales Order Scenario 1611987778Khan Rock on100% (3)
- SAP - Material LedgerDokumen20 halamanSAP - Material LedgermelnatureBelum ada peringkat
- 7.-ICED OJK Risk - Management.due .DiligenceDokumen59 halaman7.-ICED OJK Risk - Management.due .DiligenceAryoAdiatmo100% (1)
- Basic TPS HandbookDokumen33 halamanBasic TPS HandbookSumith KobewattaBelum ada peringkat
- User Manual AcDokumen20 halamanUser Manual Acpower1001Belum ada peringkat
- SEM II Cost-Accounting Unit 1Dokumen23 halamanSEM II Cost-Accounting Unit 1mahendrabpatelBelum ada peringkat
- SAP CostingDokumen297 halamanSAP CostingNetaji Dasari100% (13)
- CITIC TOWER II: REAL OPTION VALUATIONDokumen5 halamanCITIC TOWER II: REAL OPTION VALUATIONUjwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- G S T - GundimaisammaDokumen3 halamanG S T - Gundimaisammasrinivasamurthy ballani100% (1)
- ADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING TECHNIQUESDokumen326 halamanADVANCED MANAGEMENT ACCOUNTING TECHNIQUESZahid UsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Ad 5933Dokumen2 halamanAd 5933Kaustuv MishraBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Management: A Case for Business Process Re-engineeringDari EverandCost Management: A Case for Business Process Re-engineeringBelum ada peringkat
- Sap & Finance - Sap Fico Interview Questions - Product CostingDokumen8 halamanSap & Finance - Sap Fico Interview Questions - Product CostingA KBelum ada peringkat
- Budgeting, Costing & EstimatingDokumen32 halamanBudgeting, Costing & Estimatingmastermind_asia9389Belum ada peringkat
- Joint & by ProductDokumen22 halamanJoint & by ProductanggandakonohBelum ada peringkat
- Amended Guidelines Abot-Kamay Pabahay Program'Dokumen30 halamanAmended Guidelines Abot-Kamay Pabahay Program'Ge-An Moiseah Salud AlmueteBelum ada peringkat
- Project Finance Guide: Risks, Structures and ValuationDokumen96 halamanProject Finance Guide: Risks, Structures and Valuationabhishekbehal5012Belum ada peringkat
- 7.1 Paculdo Vs Regalado DigestDokumen2 halaman7.1 Paculdo Vs Regalado Digesthectorjr100% (2)
- Management Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantageDari EverandManagement Accounting: Decision-Making by Numbers: Business Strategy & Competitive AdvantagePenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Milat TractorsDokumen10 halamanMilat TractorsUzair ShahBelum ada peringkat
- 1: Traditional/Advanced Costing Methods: Why Need To Know Cost/unit?Dokumen52 halaman1: Traditional/Advanced Costing Methods: Why Need To Know Cost/unit?dwalcotBelum ada peringkat
- Acctg201 JobOrderCostingLectureNotesDokumen20 halamanAcctg201 JobOrderCostingLectureNotesaaron manacapBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Accounting Standards and Cost MGMT For Specific SectorsDokumen10 halamanCost Accounting Standards and Cost MGMT For Specific SectorsAjinkya ChincholeBelum ada peringkat
- Job Order vs Process Costing: Understanding the Key DifferencesDokumen3 halamanJob Order vs Process Costing: Understanding the Key DifferencesUmair Siyab100% (1)
- Afar 1 - TheoriesDokumen1 halamanAfar 1 - TheoriesAngela Miles DizonBelum ada peringkat
- SM ch04Dokumen30 halamanSM ch04Ngurah Panji Putra100% (1)
- In Experience Case AnalysisDokumen5 halamanIn Experience Case AnalysisChandramouli MouliBelum ada peringkat
- Activity Based Costing Real Time Cost Monitoring: All Rights ReservedDokumen10 halamanActivity Based Costing Real Time Cost Monitoring: All Rights Reservedjunlab0807Belum ada peringkat
- Tomas Claudio CollegesDokumen16 halamanTomas Claudio CollegesGemmillyn DigmaBelum ada peringkat
- ACCG200 SolutionCh 04 PDFDokumen32 halamanACCG200 SolutionCh 04 PDFlethiphuongdanBelum ada peringkat
- Managerial Accounting SummaryDokumen5 halamanManagerial Accounting Summarynabila IkaBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Cost DefinitionDokumen45 halamanStandard Cost DefinitionSandeep ShahBelum ada peringkat
- Shah Abdul Latif University Khairpur Mir's: SindhDokumen6 halamanShah Abdul Latif University Khairpur Mir's: SindhAfaque Ahmed BalouchBelum ada peringkat
- Process Costing ControlDokumen7 halamanProcess Costing Controlvijayadarshini vBelum ada peringkat
- Cost For p2Dokumen10 halamanCost For p2Elizabeth Zausa AseoBelum ada peringkat
- ABC CostingDokumen28 halamanABC CostingKiraYamatoBelum ada peringkat
- Bba 2003zxcvaeDokumen28 halamanBba 2003zxcvaeKLFelixChewBelum ada peringkat
- Job Costing and Activity-Based Costing ExplainedDokumen6 halamanJob Costing and Activity-Based Costing ExplainedmujeroenBelum ada peringkat
- Standard Costing and Variance Analysis ExplainedDokumen15 halamanStandard Costing and Variance Analysis ExplainedRashi Desai100% (1)
- Costing and Budgeting Report for Management Accounting AssignmentDokumen28 halamanCosting and Budgeting Report for Management Accounting AssignmentUdara H PereraBelum ada peringkat
- Cost AccountingDokumen23 halamanCost AccountingSEEMABelum ada peringkat
- Wa0000.Dokumen13 halamanWa0000.Divya DhandeBelum ada peringkat
- Allocation Forcosts of JointProducts ByproductsDokumen4 halamanAllocation Forcosts of JointProducts ByproductsMd. Ridoy HossainBelum ada peringkat
- Economic Analysis of New Business PDFDokumen8 halamanEconomic Analysis of New Business PDFshule1Belum ada peringkat
- Applied Overhead: Costing SheetDokumen8 halamanApplied Overhead: Costing SheetGK SKBelum ada peringkat
- Destin Brass Products Co.Dokumen5 halamanDestin Brass Products Co.qun100% (1)
- CHAPTER 4 Product and Service Costing: Overhead Application and Job-Order SystemDokumen28 halamanCHAPTER 4 Product and Service Costing: Overhead Application and Job-Order SystemMudassar Hassan100% (1)
- Process Costing..Dokumen26 halamanProcess Costing..Priyal Shah40% (5)
- Methods Costing Explained Job Batch Contract ProcessDokumen21 halamanMethods Costing Explained Job Batch Contract ProcessRupesh Shinde100% (1)
- Cost and Management Accounting 6Pca7RQV4i8tDokumen12 halamanCost and Management Accounting 6Pca7RQV4i8takhlaqur rahmanBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Driver Selection AND Analysis in The Manufacturing IndustryDokumen12 halamanCost Driver Selection AND Analysis in The Manufacturing IndustryShirish GanesanBelum ada peringkat
- 25 Cost AccountingDokumen148 halaman25 Cost AccountingAbhirup RudraBelum ada peringkat
- Ethics Predetermined Overhead Rate and CapacityDokumen2 halamanEthics Predetermined Overhead Rate and CapacityMuhammad UsmanBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced M ADokumen276 halamanAdvanced M ADark PrincessBelum ada peringkat
- AB-B - Rizky Fadillah Salam - Assignment Week 4 5Dokumen13 halamanAB-B - Rizky Fadillah Salam - Assignment Week 4 5Reta AzkaBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Accounting Book of 3rd Sem Mba at Bec DomsDokumen174 halamanCost Accounting Book of 3rd Sem Mba at Bec DomsBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)100% (1)
- Managerial Accounting 5th Edition Jiambalvo Solutions ManualDokumen35 halamanManagerial Accounting 5th Edition Jiambalvo Solutions Manualwannesswoodsarehv0t06100% (25)
- A to Z Cost Accounting Dictionary: A Practical Approach - Theory to CalculationDari EverandA to Z Cost Accounting Dictionary: A Practical Approach - Theory to CalculationBelum ada peringkat
- Sandeep VermaDokumen5 halamanSandeep VermaUjwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Balram Analysis RR270920123Dokumen11 halamanBalram Analysis RR270920123Ujwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Geometry FormulasDokumen4 halamanGeometry FormulasInderjit SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Application Form PGDM PTDokumen2 halamanApplication Form PGDM PTUjwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Application Form PGDM PTDokumen2 halamanApplication Form PGDM PTUjwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 7: Accounting Based ValuationDokumen11 halamanChapter 7: Accounting Based ValuationUjwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Maria HernandezDokumen2 halamanMaria HernandezUjwal Suri100% (1)
- Application Form PGDM PTDokumen2 halamanApplication Form PGDM PTUjwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Maria HernandezDokumen2 halamanMaria HernandezUjwal Suri100% (1)
- Literature of Working Capital ManagementDokumen62 halamanLiterature of Working Capital ManagementNaveen KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Maria HernandezDokumen2 halamanMaria HernandezUjwal Suri100% (1)
- Maria HernandezDokumen2 halamanMaria HernandezUjwal Suri100% (1)
- Maria HernandezDokumen1 halamanMaria HernandezUjwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Exam Schedule T3Dokumen1 halamanExam Schedule T3Ujwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- 12 StiglitzDokumen8 halaman12 StiglitzguskurniawanBelum ada peringkat
- Pricing Muscle Paper WiproDokumen14 halamanPricing Muscle Paper WiproUjwal SuriBelum ada peringkat
- Proclamation of Sale: Motor VehiclesDokumen12 halamanProclamation of Sale: Motor VehiclesJCMARRIE YUSOFBelum ada peringkat
- CLEANSING PROCESS FOR DIVIDENDS AND GAINSDokumen2 halamanCLEANSING PROCESS FOR DIVIDENDS AND GAINSAbdul Aziz MuhammadBelum ada peringkat
- Tutorial 2 Eco411 2013Dokumen4 halamanTutorial 2 Eco411 2013Mohamad Izzuddin ZakariaBelum ada peringkat
- Trend Analysis Balance SheetDokumen4 halamanTrend Analysis Balance Sheetrohit_indiaBelum ada peringkat
- Working Capital Management and Banks' Performance: Evidence From IndiaDokumen13 halamanWorking Capital Management and Banks' Performance: Evidence From Indiaboby.prashantkumar.boby066Belum ada peringkat
- 2Dokumen3 halaman2Ruth TenajerosBelum ada peringkat
- V LO Wroclaw Sprawdzian Kompetencji Jezykowych 2020 PDokumen11 halamanV LO Wroclaw Sprawdzian Kompetencji Jezykowych 2020 PARKIBelum ada peringkat
- DEPOSITSLIP#192792#1Dokumen1 halamanDEPOSITSLIP#192792#1AsadBelum ada peringkat
- Revision Question Topic 3,4Dokumen4 halamanRevision Question Topic 3,4Nur Wahida100% (1)
- Business Environment-Monetary & Fiscal PolicyDokumen10 halamanBusiness Environment-Monetary & Fiscal Policymanavazhagan0% (1)
- Monthly Digest from Byju's Exam Prep provides important news and events of February 2022Dokumen31 halamanMonthly Digest from Byju's Exam Prep provides important news and events of February 2022PRADIP WANIBelum ada peringkat
- Mergers, Acquisitions and RestructuringDokumen34 halamanMergers, Acquisitions and RestructuringMunna JiBelum ada peringkat
- Cash Flow and Ratio AnalysisDokumen7 halamanCash Flow and Ratio AnalysisShalal Bin YousufBelum ada peringkat
- CKSBDokumen23 halamanCKSBayushiBelum ada peringkat
- Taxation Short Questions AnswersDokumen4 halamanTaxation Short Questions AnswersSheetal IyerBelum ada peringkat
- Customization of Sub-Ledger AccountingDokumen15 halamanCustomization of Sub-Ledger Accountingbarber bobBelum ada peringkat
- Bitong v. CADokumen36 halamanBitong v. CAReemBelum ada peringkat
- BISMACDokumen2 halamanBISMACCharles Mclin TejeroBelum ada peringkat
- Straegic Management AuditDokumen5 halamanStraegic Management AuditDavyieBelum ada peringkat
- Summer Internship 2013-14: Amity Business School, Amity University, Lucknow Campus 1Dokumen10 halamanSummer Internship 2013-14: Amity Business School, Amity University, Lucknow Campus 1Deepak Singh NegiBelum ada peringkat
- Bangko Sentral NG Pilipinas Coins and Notes - Commemorative CurrencDokumen4 halamanBangko Sentral NG Pilipinas Coins and Notes - Commemorative Currencrafael oviedoBelum ada peringkat