Joints Summary
Diunggah oleh
Marta Noguero PueyoDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Joints Summary
Diunggah oleh
Marta Noguero PueyoHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
joints - general
2011. 11. 13.
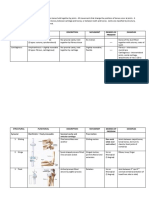
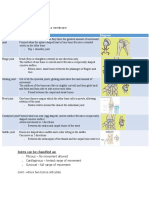
continuous joints (synarthrosis) syndesmosis (fibrous joint) interosseus membrane skull sutures (serrated, sqaumous, plane) gomphosis (teeth in the jaw) some special, very strong ligaments tibiofibular syndesmosis synchondrosis (cartilaginous joint) intervertabral disk epiphysial disk hip bone development in the skull (especially connections of temporal bone) symphysis (pubic symphysis) synostosis after epiphysisal disk ossification, hip bone ossification skull: between occipital and sphenoid bones sacrum ___________________________________________________________________________ discontinuous joints - diarthrosis, synovial joint, articulation ("real joint") obligatory parts of the synovial joints: articular surfaces - et least 2 surfaces, (convex: head, concave: socket) articular cartilage (hyaline cartilage (frequent) or fibrous cartilage (rare: temporomandibular, sacroiliac, sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular joints) articular capsule (fibrous membrane, synovial membrane) articular cavity articular ligaments additional features of the synovial joints: articular disks (temporo-mandibular, sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, radiocarpal joints) meniscus articularis (knee joint) articular lips (labrum articulare - shoulder joint, hip joint bursae articular muscles description of the joints: articular surfaces - exact names of the bony parts of the joint surfaces articular cartilage - is it hyaline cartilage or fibrous cartilage articular capsule - attachment line, is it taut or lax articular ligaments - names, origin, insertion, function are there any additional features? - if yes, the description of them functional description: movements in the joints: name of the movement (flexion-extension, anteflexion, retroflexion, abductionadduction, ulnar abduction - radial abduction, supination-pronation, opposition-reposition, rotation, circumduction) axis (around which the movement is carried out) - sometimes exact definitions are required! (e.g. the construction axis of the upper limb) angle of excursion (angle between its initial and final positions) limitations in the movements - ligamentous, bony, soft tissue limitations (muscles carriing out the movement) anatomical (normal) position versus midposition of the joint
joints - general
2011. 11. 13.
type of the joint: according to the shape of the surfaces or the degrees of freedom (number of the axes around which the bones are moved) plane surface two (or more) flat surfaces amphiarthrosis - very little, gliding movements (e.g. midcarpal joints, 2nd5th carpometacarpal joints, sacroiliac joint) restricted ball and socket - moveable in the three axes of the space - in a restricted manner (e.g. joints of the clavicle) 1 axis, 1 degree of freedom: cylindrical surfaces hinge joint (gynglymus) - the axis of the cylinder is perpendicular to the axes of the bones (e.g. interphalangeal joints, humeroulnar joint, talocrural joint) pivot joint (trochoid) (peg or rotary) - the axis of the cylinder is parallel with the axes of the bones (e.g. proximal and distal radioulnar joints, atlantoaxial joint, costovertabral joints, subtalar joint) 2 axes, 2 degree of freedom ellipsoid joint- a concave and a convex surface (e.g. radiocarpal joint, atlantooccipital joint) (2 main axes, but multiaxial - in the radiocarpal joint circumduction is possible) saddle joint (sellar) - 2 surfaces with concave and convex curvature in each (only in the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb (carpometacarpea pollicis) - 2 main axes, but circumduction is possible) !!! trochogynglymus - compound joint, the elbow and the knew are here: elbow: 3 joints in 1 capsule, knee: hinge shape with 2 axes of movements 3 main axes, so infinite number of axes and infinite number of degrees ball and socket - sphere-like convex surface, and an appropriate socket (shoulder joint, radiohumeral joint, 2nd-5th metacarpophalangeal joints, hip joint, talocalcaneonavicular joint) (...restricted ball and socket may be mentioned here...) joints combined of necessity: at different points of the same bones (proximal and distal radioulnar joints; subtalar joint and talocalcaneonavicular joint)
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Improving Ankle and Knee Joint Stability: Proprioceptive Balancefit Discs DrillsDari EverandImproving Ankle and Knee Joint Stability: Proprioceptive Balancefit Discs DrillsBelum ada peringkat
- Human Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 9: ArticulationsDokumen5 halamanHuman Anatomy Study Guide: Chapter 9: ArticulationsSuperjunior8Belum ada peringkat
- Klouby EngDokumen34 halamanKlouby EngMatea RupčićBelum ada peringkat
- MLS 102 JointsDokumen2 halamanMLS 102 JointsBSMT1A ALMONIA, ERICKA ROSEBelum ada peringkat
- The Bigger JointsDokumen42 halamanThe Bigger JointsLonely RangerBelum ada peringkat
- JointsDokumen34 halamanJointsNandhana Kattuparambil SunojBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal System: Axial Bones - 80 Bones Divided Into The Skull, Vertebral Column, and Thoracic Cage RegionsDokumen4 halamanSkeletal System: Axial Bones - 80 Bones Divided Into The Skull, Vertebral Column, and Thoracic Cage RegionsMaria Lourdes MagtaasBelum ada peringkat
- Inroduction of Arthrology - Ruan-2015Dokumen45 halamanInroduction of Arthrology - Ruan-2015Kw ChanBelum ada peringkat
- ArticulatioDokumen37 halamanArticulatioIshry Ahsani aulia askarBelum ada peringkat
- Joints: Dr. Shahab Hanif Anatomy DepartmentDokumen27 halamanJoints: Dr. Shahab Hanif Anatomy DepartmentUSAMA AHMEDBelum ada peringkat
- Bones, Joints, MusclesDokumen37 halamanBones, Joints, MusclesQuEycaBelum ada peringkat
- JointsDokumen29 halamanJointsRica T. DagosBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Joints in The Human BodyDokumen2 halamanTypes of Joints in The Human BodyDolly AquinoBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Joints in The Human BodyDokumen2 halamanTypes of Joints in The Human BodyLois Kristi CervantesBelum ada peringkat
- ANAT20006 2020: MSK Practice Quiz Short Answer Question Model AnswersDokumen3 halamanANAT20006 2020: MSK Practice Quiz Short Answer Question Model AnswersJenniferChenBelum ada peringkat
- General Arthrology, Joints of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDDokumen33 halamanGeneral Arthrology, Joints of The Upper Limb: Petr Hájek, MD., PHDTodesengelBelum ada peringkat
- Back & Joints - AnatomyDokumen9 halamanBack & Joints - AnatomyNatalia ArdilaBelum ada peringkat
- Articular System NewDokumen28 halamanArticular System NewMohammed RamzyBelum ada peringkat
- O.L.Zharikova, PH.D., Associate Professor Department of Normal Anatomy BSMU, MinskDokumen37 halamanO.L.Zharikova, PH.D., Associate Professor Department of Normal Anatomy BSMU, MinsknishaninishaBelum ada peringkat
- 4 JointsDokumen47 halaman4 JointsFareez HamidBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture2-Skeleton of Upper LimbDokumen44 halamanLecture2-Skeleton of Upper LimbJeronim H'gharBelum ada peringkat
- GA&E 4 - Intro To Arthrology & Osteology IIDokumen55 halamanGA&E 4 - Intro To Arthrology & Osteology IISu ZikaiBelum ada peringkat
- General Arthrology: Lab. Anatomi-Histology Fak. Kedokteran UnibrawDokumen32 halamanGeneral Arthrology: Lab. Anatomi-Histology Fak. Kedokteran UnibrawAnacleto Dos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Year 11 PDHPE Body in MotionDokumen27 halamanYear 11 PDHPE Body in MotiontkBelum ada peringkat
- MSK S1Dokumen38 halamanMSK S1mohammedalfadhil333Belum ada peringkat
- Classificationofjoints 140413054157 Phpapp01 161023170805Dokumen49 halamanClassificationofjoints 140413054157 Phpapp01 161023170805Adu-danquah StephenBelum ada peringkat
- Joints of The Upper LimbsDokumen16 halamanJoints of The Upper LimbsNandhana Kattuparambil SunojBelum ada peringkat
- Joints - Lower Limb: Prof. DR Slobodan MalobabićDokumen46 halamanJoints - Lower Limb: Prof. DR Slobodan MalobabićНемосјановић ЋудмилаBelum ada peringkat
- 511-525chapter 6-8 (2) An Introduction To ArticulationsDokumen3 halaman511-525chapter 6-8 (2) An Introduction To Articulationstomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayBelum ada peringkat
- JointsDokumen69 halamanJointsShekeyva SmalleyBelum ada peringkat
- Skeletal System 2: Dr. Garry NiedermayerDokumen44 halamanSkeletal System 2: Dr. Garry NiedermayerWeng Sze TingBelum ada peringkat
- Joint Classification SummaryDokumen3 halamanJoint Classification SummaryLewis RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Body JointsDokumen28 halamanBody JointsAlban Presley R. SangmaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy: Synovial JointsDokumen20 halamanAnatomy: Synovial JointsJayricDepalobosBelum ada peringkat
- Postions Movement Bones JointsDokumen8 halamanPostions Movement Bones JointsNini BakradzeBelum ada peringkat
- Resume AnafismaDokumen9 halamanResume AnafismaHumaira AR SagafBelum ada peringkat
- Exercise 13 - Articulations: Richland College Biol. 2401 Marieb A&P Lab Manual - 9 EditionDokumen2 halamanExercise 13 - Articulations: Richland College Biol. 2401 Marieb A&P Lab Manual - 9 EditionTHÂN TÂM VUI KHOẺBelum ada peringkat
- Joints: Dr. Vidhya Department of AnatomyDokumen27 halamanJoints: Dr. Vidhya Department of Anatomyelan suriyanBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture 9 - JointsDokumen50 halamanLecture 9 - JointsberhanuBelum ada peringkat
- Tut BManklefutcisDokumen71 halamanTut BManklefutcisosteoferdianBelum ada peringkat
- JointsDokumen27 halamanJointsVarsha Mol MohananBelum ada peringkat
- Magsombol, Hazel Anne A. OT2-1 Ankle and Feet BiomechanicsDokumen4 halamanMagsombol, Hazel Anne A. OT2-1 Ankle and Feet Biomechanicshazell_aseronBelum ada peringkat
- Education Notes 6Dokumen4 halamanEducation Notes 6Rwynn MemoryBelum ada peringkat
- Intro To Ortho Anatomy PDFDokumen55 halamanIntro To Ortho Anatomy PDFlanghalilafaBelum ada peringkat
- Pna Midterm Prep: Joints Classification of Joints:: Synovial Cavity Connective Tissue Fibrous JointsDokumen4 halamanPna Midterm Prep: Joints Classification of Joints:: Synovial Cavity Connective Tissue Fibrous JointsaamenaBelum ada peringkat
- Gen Ana Assignment 1 2Dokumen2 halamanGen Ana Assignment 1 2Jei SanBelum ada peringkat
- An Introduction To ArticulationsDokumen11 halamanAn Introduction To Articulationsyuni widodoBelum ada peringkat
- Synovial Joints and FunctionsDokumen4 halamanSynovial Joints and FunctionsNinaBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy of The Ankle and FootDokumen13 halamanAnatomy of The Ankle and FootRichard MillerBelum ada peringkat
- Joints HamedDokumen3 halamanJoints HamedMina EssamBelum ada peringkat
- Articulation and Body MovementsDokumen52 halamanArticulation and Body Movementsapi-295870217100% (1)
- CFF II: Exam 1 GuideDokumen25 halamanCFF II: Exam 1 GuideHilary MelloBelum ada peringkat
- Arthrology: DR N. ChikumbaDokumen50 halamanArthrology: DR N. ChikumbaNatty ChikumbaBelum ada peringkat
- Refleks & Arcus Refleks PDFDokumen23 halamanRefleks & Arcus Refleks PDFLisa HelledyBelum ada peringkat
- Zglobovi Donjeg Uda IXDokumen55 halamanZglobovi Donjeg Uda IXmontenegro brend100% (1)
- Gen Ana Assignment 1 2Dokumen2 halamanGen Ana Assignment 1 2Jei SanBelum ada peringkat
- 2 - Joints and Muscles GraysDokumen21 halaman2 - Joints and Muscles GraysDunkin DonutBelum ada peringkat
- Shoulder JointDokumen35 halamanShoulder JointscribdarnabBelum ada peringkat
- The Skeletal SystemDokumen5 halamanThe Skeletal SystemCharles VollmersBelum ada peringkat
- Refleks & Arcus RefleksDokumen23 halamanRefleks & Arcus Reflekswandry octaBelum ada peringkat
- CRANIOFACIAL Anomalies in ChildrenDokumen55 halamanCRANIOFACIAL Anomalies in ChildrenDr. Shirley Mausi N.Belum ada peringkat
- 10 Day Nervous System Challenge: Posture Reset For RegulationDokumen18 halaman10 Day Nervous System Challenge: Posture Reset For RegulationFaten SalahBelum ada peringkat
- The Abo Blood Group SystemDokumen3 halamanThe Abo Blood Group Systemchippai123Belum ada peringkat
- COMPLEMENT SYSTEM NoteDokumen6 halamanCOMPLEMENT SYSTEM NoteKaren AgbaegbuBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology Exam 01 Subtitle NotesDokumen8 halamanImmunology Exam 01 Subtitle NotesMiriame Jean-FelixBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Codominance and Multiple Alleles1Dokumen16 halaman3 Codominance and Multiple Alleles1John Carlo VillenaBelum ada peringkat
- Meanings of Houses in Vedic AstrologyDokumen4 halamanMeanings of Houses in Vedic Astrologyshivashakti19746Belum ada peringkat
- Cytologic Findings of Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor (PTT) of ScalpDokumen4 halamanCytologic Findings of Proliferating Trichilemmal Tumor (PTT) of Scalpma hBelum ada peringkat
- Material Mini NetterDokumen13 halamanMaterial Mini NetterVALENTINA ALBORNOZ BASTÍASBelum ada peringkat
- ABO Blood Group System. LegitDokumen11 halamanABO Blood Group System. LegitShestrelmay Launico UmingaBelum ada peringkat
- Hip Knee Ankle Foot OrthosisDokumen44 halamanHip Knee Ankle Foot OrthosisGulzar Ahmad100% (1)
- Exercise Chapter 4 F1Dokumen5 halamanExercise Chapter 4 F1Nadwah HasBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Alcoholic Liver DiseaseDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Alcoholic Liver Diseaseshailendra tripathiBelum ada peringkat
- Cell ModificationDokumen2 halamanCell ModificationArwen GarciaBelum ada peringkat
- General Expressions in Medical DiagnosisDokumen6 halamanGeneral Expressions in Medical DiagnosisSergej ElekBelum ada peringkat
- 10th 100 Marks MCQs Test The HopeDokumen63 halaman10th 100 Marks MCQs Test The Hopegmian9012100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology MeaslesDokumen3 halamanAnatomy and Physiology MeaslesCamila DaludadoBelum ada peringkat
- Central Nervous System Grade 5Dokumen21 halamanCentral Nervous System Grade 5shamshadBelum ada peringkat
- Feoutal AddDokumen9 halamanFeoutal AddDHUPGURI DIAGNOSTICBelum ada peringkat
- Polycythemia VeraDokumen18 halamanPolycythemia VeraHSC UNITEDBelum ada peringkat
- Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) Pathophysiology September 2016Dokumen46 halamanVenous Thromboembolism (VTE) Pathophysiology September 2016Nick GouvatsosBelum ada peringkat
- Salt and Water BalanceDokumen17 halamanSalt and Water BalancevonyBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolism and ShockDokumen162 halaman5 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolism and Shocksinte beyuBelum ada peringkat
- Assessing Neurologic System: Mabini CollegesDokumen25 halamanAssessing Neurologic System: Mabini CollegesNicole NipasBelum ada peringkat
- 5 HemophiliaDokumen57 halaman5 HemophiliaRabia AzharBelum ada peringkat
- Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Martini Solutions ManualDokumen12 halamanEssentials of Anatomy and Physiology 6th Edition Martini Solutions Manualscarletba4cc100% (34)
- The Nervous System, Part 1 Crash Course AP 8.mp3Dokumen5 halamanThe Nervous System, Part 1 Crash Course AP 8.mp3Carmen Florentina VlaseBelum ada peringkat
- 025e6f8e7b4c4-HUMAN BRAIN CLASS NOTES PDFDokumen27 halaman025e6f8e7b4c4-HUMAN BRAIN CLASS NOTES PDFRyuu SSDBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine Physiology Case Study - BathshebaDokumen6 halamanEndocrine Physiology Case Study - BathshebaMc Lindssey PascualBelum ada peringkat
- Back Up Slide ALL SkingDokumen20 halamanBack Up Slide ALL SkingFebry BieluciousBelum ada peringkat
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignDari EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (137)
- Carpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresDari EverandCarpentry Made Easy - The Science and Art of Framing - With Specific Instructions for Building Balloon Frames, Barn Frames, Mill Frames, Warehouses, Church SpiresPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (2)
- Advanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignDari EverandAdvanced Modelling Techniques in Structural DesignPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (3)
- Marine Structural Design CalculationsDari EverandMarine Structural Design CalculationsPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (13)
- Pocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataDari EverandPocket Guide to Flanges, Fittings, and Piping DataPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (22)
- Structural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignDari EverandStructural Cross Sections: Analysis and DesignPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (19)
- Green Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsDari EverandGreen Roofs, Facades, and Vegetative Systems: Safety Aspects in the StandardsBelum ada peringkat
- Flow-Induced Vibrations: Classifications and Lessons from Practical ExperiencesDari EverandFlow-Induced Vibrations: Classifications and Lessons from Practical ExperiencesTomomichi NakamuraPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (4)
- Bridge Design: Concepts and AnalysisDari EverandBridge Design: Concepts and AnalysisPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Structural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsDari EverandStructural Steel Design to Eurocode 3 and AISC SpecificationsBelum ada peringkat
- Pile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbDari EverandPile Design and Construction Rules of ThumbPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (15)
- Climate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingDari EverandClimate Adaptation Engineering: Risks and Economics for Infrastructure Decision-MakingBelum ada peringkat
- Bridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsDari EverandBridge Engineering: Classifications, Design Loading, and Analysis MethodsPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (16)
- Transmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualDari EverandTransmission Pipeline Calculations and Simulations ManualPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (10)
- Engineering for Kids: Building and Construction Fun | Children's Engineering BooksDari EverandEngineering for Kids: Building and Construction Fun | Children's Engineering BooksPenilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (2)
- Advanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresDari EverandAdvanced Design Examples of Seismic Retrofit of StructuresPenilaian: 1 dari 5 bintang1/5 (1)
- Design and Construction of Soil Anchor PlatesDari EverandDesign and Construction of Soil Anchor PlatesPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)