T
Diunggah oleh
api-38440670 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
167 tayangan3 halaman3 mHmwd Questions 13 are related to the following information. A block traveling on a rough horizontal surface with an initial speed of 40 m / s stops completely after traveling 160 m. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
t
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen Ini3 mHmwd Questions 13 are related to the following information. A block traveling on a rough horizontal surface with an initial speed of 40 m / s stops completely after traveling 160 m. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
167 tayangan3 halamanT
Diunggah oleh
api-38440673 mHmwd Questions 13 are related to the following information. A block traveling on a rough horizontal surface with an initial speed of 40 m / s stops completely after traveling 160 m. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
4 اياد
(1) A ball is thrown vertically upwards from the ground, the ball
is caught 2 s later by a person 10 m above the ground. What is
the initial velocity of the ball?
(2) A ball thrown horizontally from the top of the building 100 m
high, the ball strikes the ground at 65 m horizontally from the
bottom of the building. What is the speed of the ball just before it
strikes the ground?
(3) A car going around a curve of radius R at speed v experiences
a centripetal acceleration ac if it goes around a curve of radius 3R
at speed of 2v, what is the new acceleration?
(4) A projectile was fired at 35o above the horizontal; at the
highest point its speed was 200 m/s, what is the initial vertical
component velocity?
(5) An object initially at the origin has a velocity v = 4i − 6 j 10
seconds later the object has a velocity of v `= 12i + 6 j find the
average acceleration?
(6) A particle moves at constant speed in a circular path with a
radius of 2 cm. if the particle makes 4 revolutions each second,
then what is the magnitude of acceleration?
(7) A particle that is moving a long straight line deceleration
uniformly from 40 m/s2 to 20 m/s2 in 0.5 s and then has a
constant acceleration of 20 m/s2 during the next 4 s, calculate the
average speed over the whole time interval?
3 محمود
Questions 1- 3 are related to the following information:
Given the two vectors:
A = 4i – 3k
B = i + 2j + 2k
Q1: The vector A – 3B is:
(a) i + 6j -9k (b) i - 6j +9k (c) i + 6j + 9k
(d) i - 6j -9k
Q2: The angle between B and the positive z-axis is:
(a) Cos-1 (-2/3) (b) Cos-1 (2/3) (c) Cos-1 (-3/2) (d)
Cos (3/2)
-1
Q3: The vector C such that A – 4B + C = 0 is:
(a) 8j - 11k (b) 8i + 5k (c) 8j + 11k (d) 8i
+ 8j + 5k
5 محمود
Example 5.22: A vertical rope is attached to an object that has a
mass of 40.0 kg and is at rest. The tension in the rope needed to
give the object an upward speed of 3.50 m/s in 0.700 s is:
(a) 592 N (b) 390 N (c) 200 N (d) 980 N (e) 720 N
(Exercise 5.1) A block traveling on a rough horizontal surface
with an initial speed of 40 m/s stops completely after traveling
160 m. find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block
and the surface?
(Exercise 5.2) If an object travels at a constant speed of 30 m/s
as it makes a horizontal circular turn of 200 m radius, what is the
magnitude of the resultant force on the 80 kg object?
(Exercise 5.4) A 10 kg crate is
placed on a rough horizontal surface
of µ k = 0.4 and connected with 12 kg
hanging mass via a string that passes
over a massless and frictionless pulley as shown in the figure.
What is the mass must be added to crate to make it move with
constant velocity?
7 محمود
Example 7.27: A block of mass m is pushed up against a spring,
compressing it a distance x, and is the released. The spring
projects the block along a frictionless horizontal surface, giving
the block a speed v. The same spring projects a second block of
mass 4m, giving it a second block of mass 4m, giving it a speed
3v. What distance was the spring compressed in the second case?
a) x (b) 2x (c) 3x (d) 4x (e) 6x)
Example 7.28: A block of wood with a mass M = 4.65 kg is
resting on a horizontal surface when a bullet with mass m = 18 g
and moving with a speed of v = 725 m/s strikes it. The
coefficient of friction between the block and the surface is μ =
0.35. The distance the block moves across the surface is:
a) 1.1 m (b) 3.3 m (c) 0.41 m (d) 11 m (e) 15.1 m)
Exercise 7.2
For A = 3 i + j - k، B = - i + 2 j + 5 k، and C = 2 j – 3 k،
find C· (A – B).
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Managing Economies of Scale in Supply ChainsDokumen25 halamanManaging Economies of Scale in Supply ChainsWei JunBelum ada peringkat
- Staad FoundationDokumen25 halamanStaad FoundationAnonymous nwByj9L100% (2)
- Stheory Balagtas Activity Lesson 15Dokumen6 halamanStheory Balagtas Activity Lesson 15xVlad LedesmaBelum ada peringkat
- Engineering Graphics (046) Marking Scheme: Sample Question Paper (2017-18)Dokumen8 halamanEngineering Graphics (046) Marking Scheme: Sample Question Paper (2017-18)RaghuSrinivasanBelum ada peringkat
- An Overview On Reliability, Availability, Maintainability and Supportability (RAMS) EngineeringDokumen15 halamanAn Overview On Reliability, Availability, Maintainability and Supportability (RAMS) EngineeringKrinta AlisaBelum ada peringkat
- VHDL ExperimentsDokumen55 halamanVHDL Experimentssandeepsingh93Belum ada peringkat
- M.SC - Physics 3rd Sem FinalDokumen12 halamanM.SC - Physics 3rd Sem FinalKhileswar ChandiBelum ada peringkat
- SERIES-90 180cc SERVICE BLN-2-41695 1997-05Dokumen52 halamanSERIES-90 180cc SERVICE BLN-2-41695 1997-05thailanBelum ada peringkat
- Triad Over Root Chords Companion PDF 2.1Dokumen18 halamanTriad Over Root Chords Companion PDF 2.1Vlado PetkovskiBelum ada peringkat
- SSC JE Mechanical Study Material Strength of Materials PDFDokumen13 halamanSSC JE Mechanical Study Material Strength of Materials PDFSameer ShahBelum ada peringkat
- EE6010-High Voltage Direct Current TransmissionDokumen12 halamanEE6010-High Voltage Direct Current Transmissionabish abish0% (1)
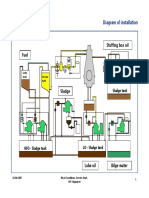
- Westfalia Separator Installation DiagramDokumen68 halamanWestfalia Separator Installation DiagramOno Jr Araza100% (3)
- Digital Techniques/Electronic Instrument SystemsDokumen29 halamanDigital Techniques/Electronic Instrument SystemsE DBelum ada peringkat
- Brahma 152 192sm CM MMDokumen6 halamanBrahma 152 192sm CM MMThiago FernandesBelum ada peringkat
- Experiment 1 - Friction Losses in PipesDokumen34 halamanExperiment 1 - Friction Losses in PipesKhairil Ikram33% (3)
- Chapter 4 Worksheets Algebra 1Dokumen110 halamanChapter 4 Worksheets Algebra 1Amanda GeorginoBelum ada peringkat
- The Experimental Model of The Pipe Made PDFDokumen4 halamanThe Experimental Model of The Pipe Made PDFGhassan ZeinBelum ada peringkat
- Altera - ENDokumen8 halamanAltera - ENDoanh NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- 14GMK 6250 TelescopeDokumen13 halaman14GMK 6250 TelescopeВиталий РогожинскийBelum ada peringkat
- Problem Solving 1 Arithmetic SequenceDokumen62 halamanProblem Solving 1 Arithmetic SequenceCitrus National High SchoolBelum ada peringkat
- D200801 Slope and Offset Adjustment For A Pressure SensorDokumen4 halamanD200801 Slope and Offset Adjustment For A Pressure SensorBrian McMorrisBelum ada peringkat
- Propulsion ResistanceDokumen14 halamanPropulsion ResistanceEduardo LopesBelum ada peringkat
- PDF Ecs h81h3 Ad DDDokumen37 halamanPDF Ecs h81h3 Ad DDsanak tiuhBelum ada peringkat
- Math 2nd Year CompleteDokumen369 halamanMath 2nd Year CompleteJabir Ali Siddique100% (1)
- SP 5500 V5.1 1.0Dokumen17 halamanSP 5500 V5.1 1.0Rama Tenis CopecBelum ada peringkat
- Peak Performance 4.3-Inch GPS ManualDokumen16 halamanPeak Performance 4.3-Inch GPS ManualmcneelydBelum ada peringkat
- CADAM - Model Parameters: General InformationDokumen4 halamanCADAM - Model Parameters: General InformationmyapmisBelum ada peringkat
- POWER Nav1 - MIDTERM - Topic 1 & 2Dokumen31 halamanPOWER Nav1 - MIDTERM - Topic 1 & 2CLIJOHN PABLO FORD100% (1)
- Proceeding Book SIBE 2017Dokumen625 halamanProceeding Book SIBE 2017Yochanan meisandroBelum ada peringkat
- Power System Stability-Chapter 3Dokumen84 halamanPower System Stability-Chapter 3Du TrầnBelum ada peringkat