Anatomy
Diunggah oleh
Isaac FrankDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Anatomy
Diunggah oleh
Isaac FrankHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
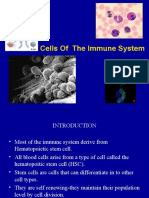
9) Differentiate between the functions of lymphocyte T cells and lymphocytes B cells. Lymphocyte T cells play a central immunity.
role in cell-mediated
Lymphocyte B cells play a large role in the humoral immune response (as opposed to the cell-mediated immune response, which is governed by T cells). Plasma B cells (also known as plasma cells) are large B cells that have been exposed to antigen and produce and secrete large amounts of antibodies, which assist in the destruction of microbes by binding to them and making them easier targets for phagocytes and activation of the complement system. make antibodies against antigens, perform the role of antigen-presenting cells(APCs) and eventually develop into memory B cells after activation by antigen interaction.
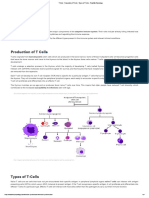
the presence of a special receptor on their cell surface called T cell receptors (TCR).
T helper cell (TH cells) assist other white blood cells in immunologic processes, including maturation of B cells into plasma cells and activation of cytotoxic T cells and macrophages Cytotoxic T cells (TC cells, or CTLs) destroy virally infected cells and tumor cells, and are also implicated in transplant rejection. Memory T cells are a subset of antigenspecific T cells that persist long-term after an infection has resolved. Regulatory T cells (Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells has the major role is to shut down T cell-mediated immunity toward the end of an immune reaction and to suppress auto-reactive T cells that escaped the process of negative selection in the thymus. Natural killer T cells (NKT cells) are a special kind of lymphocyte that bridges the adaptive immune system with the innate immune system.
Memory B cells are formed from activated B cells that are specific to the antigen encountered during the primary immune response.
an essential component of the adaptive immune system.
10) What are plasma cells and mega karyocytes?
Plasma cells, also called plasma B cells, plasmocytes, and effector B cells, are white blood cells that produce large volumes of antibodies. They are transported by the blood plasma and the lymphatic system. As such, they are an important part of the immune system. Plasma cells are formed from B cells. Like all blood cells, plasma cells ultimately originate in the bone marrow; however, these cells leave the bone marrow as B cells, before terminal differentiation into plasma cells, which usually happens in lymph nodes. Once produced, B cells mainly stay within the bone marrow and wait until an antigen appears in the body. The antigens bind to the B cell and stimulate it to form plasma cells. The plasma cell then produces antibodies to destroy the pathogen.
The megakaryocyte is the giant cell of bone marrow containing a greatly lobulated nucleus, from which mature blood platelets originate. It is responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. Megakaryocytes normally account for 1 out of 10,000 bone marrow cells but can increase in number nearly 10-fold in certain diseases. In general, megakaryocytes are 10 to 15 times larger than a typical red blood cell, averaging 50-100 m in diameter. During its maturation, the megakaryocyte grows in size and replicates its DNA without cytokinesis. As a result, the nucleus of the megakaryocyte can become very large and lobulated, which, under a light microscope, can give the false impression that there are several nuclei. Megakaryocytes are derived from hematopoietic stem cell precursor cells in the bone marrow.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- A Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisDari EverandA Simple Guide to the Blood Cells, Related Diseases And Use in Disease DiagnosisBelum ada peringkat
- Cells in Immune SystemDokumen15 halamanCells in Immune SystemSrestha SealBelum ada peringkat
- Cells of ImmunityDokumen3 halamanCells of ImmunityLenc AbaloBelum ada peringkat
- L 4 Cellular Component of The Immune SystemDokumen11 halamanL 4 Cellular Component of The Immune SystemaugustongoviBelum ada peringkat
- T and B CellsDokumen13 halamanT and B CellsFaisal Jamshed100% (1)
- T CellDokumen36 halamanT CellSurja DasBelum ada peringkat
- Blood CellsDokumen36 halamanBlood Cellsprahashitha.s.2525Belum ada peringkat
- IMMUNOLOGY - MillsDokumen3 halamanIMMUNOLOGY - MillsEmmanuel KwakunakaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction Biology Humoral and Cell Mediated ResponseDokumen3 halamanIntroduction Biology Humoral and Cell Mediated ResponseReshana SimonBelum ada peringkat
- محاضرةة الانسجةDokumen17 halamanمحاضرةة الانسجةAymen MouradBelum ada peringkat
- Cells and Organs of The Immune SystemDokumen26 halamanCells and Organs of The Immune SystemMithila BanikBelum ada peringkat
- Lecturer 2 Innate Immune System and Adaptve Immune SystemDokumen6 halamanLecturer 2 Innate Immune System and Adaptve Immune SystemKevin KipropBelum ada peringkat
- Cell and Organs of The Immune SystemDokumen43 halamanCell and Organs of The Immune Systemcyrhenmie100% (1)
- Part 2 Basics of ImmunologyDokumen6 halamanPart 2 Basics of Immunologyabc abcBelum ada peringkat
- Lymphocytes and MonocytesDokumen7 halamanLymphocytes and MonocytesSarfraz Hussain MalikBelum ada peringkat
- Irwansyah Nur Oktafian - 180342618025 - Immunology TasksDokumen5 halamanIrwansyah Nur Oktafian - 180342618025 - Immunology TasksIRWANSYAH NURBelum ada peringkat
- იმუნოს ზეპირი 1 1Dokumen65 halamanიმუნოს ზეპირი 1 1Levani KartvelishviliBelum ada peringkat
- Cells of Immune SystemDokumen13 halamanCells of Immune Systemkiranshanes50% (2)
- Organs of Immune SystemDokumen1 halamanOrgans of Immune SystemvicmomBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology Presentation 2.0Dokumen10 halamanImmunology Presentation 2.0Emmanuel KwakunakaBelum ada peringkat
- Cells of The Immune SystemDokumen38 halamanCells of The Immune SystemprabuBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology: Group MembersDokumen19 halamanImmunology: Group Membersalisha khanBelum ada peringkat
- Immune System by Asif PresentationDokumen35 halamanImmune System by Asif PresentationHassan AsifBelum ada peringkat
- White Blood CellDokumen21 halamanWhite Blood CellAnonymous 0C4OZmRBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFDokumen61 halamanChapter 2 Cells and Organs of The Immune System PDFanaraudhatulBelum ada peringkat
- T Cells - Production of T Cells - Types of T Cells - TeachMePhysiologyDokumen3 halamanT Cells - Production of T Cells - Types of T Cells - TeachMePhysiologyNobodyBelum ada peringkat
- Immuno 1 Unit I SemDokumen5 halamanImmuno 1 Unit I Sempriyanshu guptaBelum ada peringkat
- Histology BloodDokumen6 halamanHistology BloodNeneng Cutin GanzonBelum ada peringkat
- Lecture - Cells Tissues and Organs - ImmunologyDokumen29 halamanLecture - Cells Tissues and Organs - Immunologyrockyrawat01012003Belum ada peringkat
- Hematopoiesis and Cells of The Immune SystemDokumen19 halamanHematopoiesis and Cells of The Immune SystemCGM BF OFFICEBelum ada peringkat
- Lymphocytes T-Cells & B-Cells: Urmia University Supervisor: Dr. NajafiDokumen59 halamanLymphocytes T-Cells & B-Cells: Urmia University Supervisor: Dr. NajafiMh BzBelum ada peringkat
- Копия Diseases - of - Immunity.-2021. - копияDokumen77 halamanКопия Diseases - of - Immunity.-2021. - копияManav VyasBelum ada peringkat
- The Roles of B-Cell, T-Cells, and Antigens in The Immune SystemDokumen5 halamanThe Roles of B-Cell, T-Cells, and Antigens in The Immune SystemSam MansfieldBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 1,2,3 y 4Dokumen15 halamanTopic 1,2,3 y 4Olaya De Dios HuertaBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology 09122012Dokumen5 halamanImmunology 09122012Sonia KhoslaBelum ada peringkat
- 2.cells of Immune System Notes PowerpointDokumen34 halaman2.cells of Immune System Notes Powerpointt4ths999Belum ada peringkat
- Immunology NotesDokumen8 halamanImmunology NotesSumit Mukherjee100% (1)
- Cells of Immune SystemDokumen16 halamanCells of Immune SystemKrishnanand NagarajanBelum ada peringkat
- Lymphoid Cells & TissuesDokumen18 halamanLymphoid Cells & TissuesdrkalyanvikramBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction of ImmunologyDokumen33 halamanIntroduction of ImmunologyMenard Paisley MarchalBelum ada peringkat
- Difference Between T Cells and B Cells: September 2017Dokumen10 halamanDifference Between T Cells and B Cells: September 2017Bambang PriyambodoBelum ada peringkat
- Adaptive DefenseDokumen27 halamanAdaptive Defenseayesha sanaBelum ada peringkat
- About LymphomaDokumen17 halamanAbout LymphomaSelviBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirDokumen29 halamanImmunology: Dr. A.K.M. Akbar KabirRakib's exploration worldBelum ada peringkat
- Pathomorphology of Immune System. Reactions and Mech Anisms of HypersensitivityDokumen72 halamanPathomorphology of Immune System. Reactions and Mech Anisms of HypersensitivityEdi Kerina SembiringBelum ada peringkat
- Guia de Estudios PCFDokumen7 halamanGuia de Estudios PCFOmar AguilarBelum ada peringkat
- What Are The Main Cells of The Immune System?Dokumen5 halamanWhat Are The Main Cells of The Immune System?Idrissa John Sebeh ContehBelum ada peringkat
- The Immune Sytem Phagocytes: Origin & Mode of Action: BloodDokumen24 halamanThe Immune Sytem Phagocytes: Origin & Mode of Action: BloodTafadzwaBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan PlenoDokumen5 halamanBahan PlenoFitri Amelia RizkiBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology Overview: Armond S. Goldman Bellur S. PrabhakarDokumen45 halamanImmunology Overview: Armond S. Goldman Bellur S. PrabhakarIoana AsziaBelum ada peringkat
- Wiki T CellDokumen12 halamanWiki T Cellالولد الخطير تابعونيBelum ada peringkat
- CMI EnglishDokumen5 halamanCMI EnglishAndika PesakBelum ada peringkat
- Immuno PathologyDokumen28 halamanImmuno PathologyIdrissa John Sebeh ContehBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 1immunology OverviewDokumen37 halamanChapter 1immunology OverviewSania HairahBelum ada peringkat
- Cells and Immune SystemDokumen4 halamanCells and Immune SystemdaramolamekaiahBelum ada peringkat
- Bahan Kuliah Id-1-2020Dokumen63 halamanBahan Kuliah Id-1-2020Andi SaputraBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Concepts in ImmunologyDokumen56 halamanBasic Concepts in ImmunologyDedy SambahtraBelum ada peringkat
- Immune ResponseDokumen3 halamanImmune ResponseRachell ZighemBelum ada peringkat
- Organs of The Immune SystemDokumen19 halamanOrgans of The Immune SystemprabuBelum ada peringkat
- Biology - Cells and Anatomy of The Immune SystemDokumen9 halamanBiology - Cells and Anatomy of The Immune SystemFelix LupulescuBelum ada peringkat
- Dr. Witra Irfan, SP.B (K) V - DVTDokumen29 halamanDr. Witra Irfan, SP.B (K) V - DVTmuhammad azharanBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 005 QuestionsDokumen24 halamanChapter 005 QuestionsCaitlin EsguerraBelum ada peringkat
- Immunology Exam Q S With AnswersDokumen28 halamanImmunology Exam Q S With AnswersIceBearBelum ada peringkat
- Chapt 27 Ap2Dokumen5 halamanChapt 27 Ap2candybio83Belum ada peringkat
- Form 2 Inte-Science Paper 1Dokumen5 halamanForm 2 Inte-Science Paper 1saajid hafizBelum ada peringkat
- Leaf Structure and Function - Worksheet 2Dokumen1 halamanLeaf Structure and Function - Worksheet 2Hasmira Nor100% (3)
- Disseminated Intravascular CoagulationDokumen37 halamanDisseminated Intravascular CoagulationhipoclaudioBelum ada peringkat
- Syndrome Differentiation of The Zang-Fu Organs - 1Dokumen99 halamanSyndrome Differentiation of The Zang-Fu Organs - 1clerise3Belum ada peringkat
- General Biology 1 Tissues and Cell Types Quarter 3, Module 2bDokumen17 halamanGeneral Biology 1 Tissues and Cell Types Quarter 3, Module 2bSam KimBelum ada peringkat
- Prolong Storage of Blood in EDTADokumen5 halamanProlong Storage of Blood in EDTAGriffin MulofwaBelum ada peringkat
- Paradox of ChoiceDokumen2 halamanParadox of ChoiceCarelessBelum ada peringkat
- Case Scenario 3 - Musco-Skeletal SystemDokumen3 halamanCase Scenario 3 - Musco-Skeletal SystemWill KnightBelum ada peringkat
- Circulatory and Respiratory Test Study Guide Answer KeyDokumen3 halamanCirculatory and Respiratory Test Study Guide Answer KeyMae Ann Tomimbang MaglinteBelum ada peringkat
- Oral Mucosal Drug Delivery and TherapyDokumen289 halamanOral Mucosal Drug Delivery and TherapyАлександр ВолошанBelum ada peringkat
- Head and Neck McqsDokumen3 halamanHead and Neck McqsRajitha DilhanBelum ada peringkat
- Clinical Embriology and Anatomy of Gi Tract Part1Dokumen44 halamanClinical Embriology and Anatomy of Gi Tract Part1trianaamalia100% (1)
- Barbarian Neck TrainingDokumen14 halamanBarbarian Neck TrainingLuis Moro100% (1)
- RH Incompatibility: A Case Analysis OnDokumen62 halamanRH Incompatibility: A Case Analysis OnMonique LeonardoBelum ada peringkat
- PathologyDokumen31 halamanPathologyStudy Usmle100% (1)
- Liver & Gall Bladder: Presented by DR - Sujaya NairDokumen102 halamanLiver & Gall Bladder: Presented by DR - Sujaya Nairjoy rajBelum ada peringkat
- Unit 7: Genes and Inheritance Lesson 7.1: Chromosomes, Genes and DNADokumen44 halamanUnit 7: Genes and Inheritance Lesson 7.1: Chromosomes, Genes and DNAhypezakramBelum ada peringkat
- Cranial Nerve: Dr. Dian Prasetyo Wibisono, M.SCDokumen49 halamanCranial Nerve: Dr. Dian Prasetyo Wibisono, M.SCgeneBelum ada peringkat
- Topic 9 Cardiovascular SystemDokumen36 halamanTopic 9 Cardiovascular SystemAlejandra CastilloBelum ada peringkat
- Cell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesDokumen8 halamanCell Te Unit of Life Revision NotesHarismita AlagurajBelum ada peringkat
- AAST Renal Injury ScaleDokumen11 halamanAAST Renal Injury ScaleyuenkeithBelum ada peringkat
- Du and Ren Meridians 2Dokumen79 halamanDu and Ren Meridians 2Bryant Villarin Baldivicio100% (1)
- Atpug BroDokumen339 halamanAtpug BroKurniadi Yusuf100% (1)
- Excretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17Dokumen8 halamanExcretion: Unit - Human Physiology Chapter 17edeceBelum ada peringkat
- Screenshot 2023-09-03 at 1.27.00 AMDokumen8 halamanScreenshot 2023-09-03 at 1.27.00 AMhuzaifaawais27Belum ada peringkat
- Iii. Hasil Dan PembahasanDokumen10 halamanIii. Hasil Dan PembahasanHarditya FirdhausBelum ada peringkat