R5210106 Fluid Mechanics
Diunggah oleh
sivabharathamurthyDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
R5210106 Fluid Mechanics
Diunggah oleh
sivabharathamurthyHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
CodeNo: R5210106
R5
II B.Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, Nov/Dec 2011 FLUID MECHANICS (Civil Engineering) Time: 3 hours Max Marks: 80 Answer any FIVE Questions All Questions carry equal marks
1. (a) Distinguish between i. ii. iii. iv. Ideal and Read Fluids Newtonian and Non- Newtonian Fluids Gases and Vapours. Adhesion and cohesion
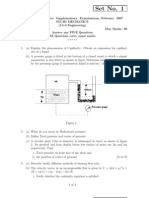
(b) The velocity distribution in a uid is give by u = 40000 y (1-2y) where u is the velocity in m/sec at a distance of y meters normal to the boundary. If the dynamic viscosity of uid is 1.8 104 poise, determine the shear stress at y = 0.2m. [8+8] 2. (a) What do you mean by Hydrostatic pressure. (b) Dene Total pressure and centre of pressure (c) A circular plate 2.5m in diameter is submerged in water as shown in gure 2c. Its greatest and least depths below free surface of water are 3m and 2m respectively. Find i. Total pressure on front face of the plate and ii. the position of centre of pressure [3+4+9]
Figure 2c 3. (a) Dierentiate between the Eulerian and Lagrangian methods of representing uid ow. (b) If stream function exists in a ow problem does it imply that velocity potential also exists. Explain. (c) The ow eld of a uid is given by V = xyi + 2yzj (yz + z 2 )K i. Show that it represents a possible three dimensional steady incompressible continuous ow. 1 of 2
CodeNo: R5210106
R5
ii. Is this ow rotational or irrotational ?. If rotational, determine at point A (2,4,6). [3+4+9] 4. (a) State and derive impulse momentum equation. What are the applications of impulse momentum equation. (b) A pipe line 0.6 cm diameter conveying oil (specic granity 0.85) at the ow rate of 1800 lit/sec has a 900 bend in the horizontal plane. The pressure at the entrance to the bend is 147.15KN/m2 and loss of head in the bend is 2m of oil. Find the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the oil on the bend. [8+8] 5. (a) What is meant by Magnus eect. Explain. (b) Describe with the help of a sketch, the variation of drag coecient for a cylinder over a wide range of Reynolds number. (c) A kite 0.8m0.8m weighing 3.924N assumes an angle of 120 to the horizontal. The string attached to the kite makes an angle of 45 0 to the horizontal. The pull on the string is 24.525N when the wind is owing at a speed of 30 Km/hr. Find the corresponding coecient of drag and lift. Take mass density of air as 1.25Kg/m3 . [3+4+9] 6. (a) Draw a neat sketch of Reynolds apparatus and explain how the laminar ow can be demonstrated with the help of the apparatus. (b) Two parallel plates kept 100 mm apart have laminar ow of oil between them with a maximum velocity of 1.5 m/sec. Calculate discharge per metre width, shear stress at the plates and the dierence in pressure between two points 20m apart. Assume viscosity of oil to be 24.5 poise. [8+8] 7. (a) Derive and expression for head lost due to sudden contraction of a pipe. (b) A pipe increases in diameter suddenly from 10 cm to 20 cm. If the discharge of water through the pipe is 100 lit/sec., determine the loss of head due to sudden enlargement of cross sectional area. Also determine the dierence of pressure between two sections of the pipe line. [8+8] 8. (a) Derive an equation for discharge of a venturimeter. (b) Explain why Cd of a venturimeter is more than that of orice meter. (c) A horizontal venturimeter with inlet and throat diameters 300 mm and 150mm respectively is used to measure the ow of water. The pressure intensity at inlet is 130 KN/m2 while the vacuum pressure head at the throat is 350 mm of mercury. Assuming that 3% of head is lost in between inlet and throat, nd Cd of venturimeter and rate of ow. [6+2+8]
2 of 2
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Dari EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Penilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Non-Metallic Inclusions in Steel PropertiesDokumen68 halamanNon-Metallic Inclusions in Steel PropertiesDeepak PatelBelum ada peringkat
- 2nd Preboard Design Nov 2018 EditedDokumen12 halaman2nd Preboard Design Nov 2018 EditedXprts Review100% (1)
- Anchor Chair Design CheckDokumen5 halamanAnchor Chair Design CheckManish542Belum ada peringkat
- Flow Assurance Training ManualDokumen108 halamanFlow Assurance Training ManualAbid Hussain100% (5)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Dari EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Penilaian: 3 dari 5 bintang3/5 (1)
- Desen ProdutoDokumen326 halamanDesen ProdutoKauê VelhoBelum ada peringkat
- Code No: 43035/43036Dokumen8 halamanCode No: 43035/43036SRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- Rr220301 Mechanics of FluidsDokumen8 halamanRr220301 Mechanics of Fluidslibrarian_abitBelum ada peringkat
- rr220301 Mechanics of FluidsDokumen8 halamanrr220301 Mechanics of FluidsSRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- r050210104 Fluid MechanicsDokumen10 halamanr050210104 Fluid MechanicsSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Rr212101 Mechanics of FluidDokumen8 halamanRr212101 Mechanics of FluidSrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of Fluids Rr220301Dokumen8 halamanMechanics of Fluids Rr220301Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of Fluids r05220302Dokumen8 halamanMechanics of Fluids r05220302Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryBelum ada peringkat
- Rr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDokumen8 halamanRr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerySrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- r050212102 Mechanics of FluidsDokumen8 halamanr050212102 Mechanics of FluidsSrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- FLUID MECHANICS AND HYDRAULIC MACHINERY PapersDokumen8 halamanFLUID MECHANICS AND HYDRAULIC MACHINERY PapersAshok KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Rr210106 Fluid MechanicsDokumen8 halamanRr210106 Fluid MechanicsSrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- r05220302 Mechanics of FluidsDokumen8 halamanr05220302 Mechanics of FluidsSRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- Rr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDokumen8 halamanRr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerySrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- MFHM Code No: 07A3EC02Dokumen2 halamanMFHM Code No: 07A3EC02rafikhanpathanBelum ada peringkat
- FMHM 8Dokumen8 halamanFMHM 829viswa12Belum ada peringkat
- Fluid mechanics and hydraulics machines exam questionsDokumen8 halamanFluid mechanics and hydraulics machines exam questionsNitin GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics Exam Questions and AnswersDokumen54 halamanFluid Mechanics Exam Questions and AnswersSony RamaBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid MechanicsDokumen2 halamanFluid MechanicsLokendra Singh JhalaBelum ada peringkat
- FMHM Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008Dokumen8 halamanFMHM Regular Jntu Question Papers 2008anjaneyulud100% (1)
- Set No. 1Dokumen8 halamanSet No. 129viswa12Belum ada peringkat
- 07a40105-Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDokumen8 halaman07a40105-Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- R13 Mechanics of Fluids ExamDokumen2 halamanR13 Mechanics of Fluids ExamarunBelum ada peringkat
- JNTU Fluid Mechanics Exam QuestionsDokumen9 halamanJNTU Fluid Mechanics Exam QuestionsnvemanBelum ada peringkat
- A-PDF Merger DEMO: Purchase FromDokumen66 halamanA-PDF Merger DEMO: Purchase Frommanju0806Belum ada peringkat
- Nr220301-Mechanics of FluidsDokumen8 halamanNr220301-Mechanics of FluidsSRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- r050212102 Mechanics of FluidsDokumen8 halamanr050212102 Mechanics of FluidsSrinivasa Rao GBelum ada peringkat
- Ece 2212 Fluid Mechanics IiDokumen4 halamanEce 2212 Fluid Mechanics IiJoe NjoreBelum ada peringkat
- Rr210106 Fluid MechanicsDokumen8 halamanRr210106 Fluid MechanicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- r7210202 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDokumen4 halamanr7210202 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Ce8394 FMMDokumen2 halamanCe8394 FMMsyed1188Belum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDokumen4 halamanFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery29viswa12Belum ada peringkat
- Answer Any FIVE Questions From Section-BDokumen2 halamanAnswer Any FIVE Questions From Section-BSri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorBelum ada peringkat
- Rr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDokumen8 halamanRr210201 Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- r7210202 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachineryDokumen1 halamanr7210202 Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic MachinerysivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Question Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Dokumen3 halamanQuestion Paper Code:: (10×2 20 Marks)Keesanth Geetha ChandrasekaranBelum ada peringkat
- Mee3221 Mee4205Dokumen18 halamanMee3221 Mee4205Lim WcBelum ada peringkat
- HydraulicsDokumen5 halamanHydraulicsAmit GhadeBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Dokumen7 halamanFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)29viswa12Belum ada peringkat
- Answer Any Two QuestionsDokumen11 halamanAnswer Any Two QuestionsKirtismita TalukdarBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer April May 2008 Question PaperDokumen8 halamanFluid Mechanics and Heat Transfer April May 2008 Question PaperelimelekBelum ada peringkat
- FMHM 7Dokumen8 halamanFMHM 729viswa12Belum ada peringkat
- Jntuworld: R09 Set No. 2Dokumen9 halamanJntuworld: R09 Set No. 2saiteja1234Belum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics Exam QuestionsDokumen3 halamanFluid Mechanics Exam QuestionsAkshay RajanBelum ada peringkat
- CE203-C Image Marked Image Marked PDFDokumen2 halamanCE203-C Image Marked Image Marked PDFtawam100% (1)
- 07a40302 Fluid Mechanics & Heat TransferDokumen8 halaman07a40302 Fluid Mechanics & Heat TransferSRINIVASA RAO GANTABelum ada peringkat
- Question BankDokumen21 halamanQuestion Bankjai_selvaBelum ada peringkat
- Gojan School of Business and Technology: Department of Aeronautical EngineeringDokumen7 halamanGojan School of Business and Technology: Department of Aeronautical EngineeringRameez FaroukBelum ada peringkat
- Mechanics of Fluids May2004 RR 220301Dokumen8 halamanMechanics of Fluids May2004 RR 220301Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryBelum ada peringkat
- II B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May - 2012 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachinesDokumen44 halamanII B. Tech I Semester, Supplementary Examinations, May - 2012 Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulic MachineshvrkBelum ada peringkat
- CE-6451 Fluid Mechanics Part-BDokumen6 halamanCE-6451 Fluid Mechanics Part-BMinu.j.jBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Mechanics-I - Code No CE15223Dokumen2 halamanFluid Mechanics-I - Code No CE15223Sri E.Maheswar Reddy Assistant ProfessorBelum ada peringkat
- Enhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsDari EverandEnhanced Oil Recovery: Resonance Macro- and Micro-Mechanics of Petroleum ReservoirsPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Analytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportDari EverandAnalytical Modeling of Solute Transport in Groundwater: Using Models to Understand the Effect of Natural Processes on Contaminant Fate and TransportBelum ada peringkat
- The Mediterranean Sea: Temporal Variability and Spatial PatternsDari EverandThe Mediterranean Sea: Temporal Variability and Spatial PatternsBelum ada peringkat
- SSC Social Textbook (AP)Dokumen100 halamanSSC Social Textbook (AP)sivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- SSC Telugu (FL) (AP)Dokumen232 halamanSSC Telugu (FL) (AP)sivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 07A4EC01 Environmental StudiesDokumen1 halaman07A4EC01 Environmental StudiessivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Control Systems (CS) Notes As Per JntuaDokumen203 halamanControl Systems (CS) Notes As Per Jntuasivabharathamurthy100% (3)
- R7410407 Operating SystemsDokumen1 halamanR7410407 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7311506 Operating SystemsDokumen1 halamanR7311506 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A13701 Robotics and AutomationDokumen4 halaman9A13701 Robotics and AutomationsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R5410201 Neural Networks & Fuzzy LogicDokumen1 halamanR5410201 Neural Networks & Fuzzy LogicsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- Code: R7311306: (Electronics & Control Engineering)Dokumen1 halamanCode: R7311306: (Electronics & Control Engineering)sivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7410506 Mobile ComputingDokumen1 halamanR7410506 Mobile ComputingsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7312301 Transport Phenomena in BioprocessesDokumen1 halamanR7312301 Transport Phenomena in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A05707 Software Project ManagementDokumen4 halaman9A05707 Software Project ManagementsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7311205 Distributed DatabasesDokumen1 halamanR7311205 Distributed DatabasessivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7310306 Heat TransferDokumen1 halamanR7310306 Heat Transfersivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- R7310506 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmsDokumen1 halamanR7310506 Design & Analysis of AlgorithmssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7310406 Digital CommunicationsDokumen1 halamanR7310406 Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A10505 Principles of CommunicationsDokumen4 halaman9A10505 Principles of CommunicationssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7311006 Process Control InstrumentationDokumen1 halamanR7311006 Process Control InstrumentationsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R5310204 Power ElectronicsDokumen1 halamanR5310204 Power ElectronicssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7310106 Engineering GeologyDokumen1 halamanR7310106 Engineering GeologysivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R7310206 Linear Systems AnalysisDokumen1 halamanR7310206 Linear Systems AnalysissivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignDokumen8 halaman9A14503 Principles of Machine DesignsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A05505 Operating SystemsDokumen4 halaman9A05505 Operating SystemssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- R5310406 Digital CommunicationsDokumen1 halamanR5310406 Digital CommunicationssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessesDokumen4 halaman9A23501 Heat Transfer in BioprocessessivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A15502 Digital System DesignDokumen4 halaman9A15502 Digital System Designsivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDokumen8 halaman9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A04504 Digital IC ApplicationsDokumen4 halaman9A04504 Digital IC ApplicationssivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIDokumen4 halaman9A02505 Electrical Machines-IIIsivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- 9A03505 Heat TransferDokumen4 halaman9A03505 Heat TransfersivabharathamurthyBelum ada peringkat
- MEMS TechnologyDokumen22 halamanMEMS Technologyavishekghosh1985Belum ada peringkat
- Strength Analyses of Sandwich Pipes For Ultra Deep PDFDokumen172 halamanStrength Analyses of Sandwich Pipes For Ultra Deep PDFClaudio PazBelum ada peringkat
- Acoustic Market Survey (Vins) FinalDokumen33 halamanAcoustic Market Survey (Vins) FinalVISHAL SHARMA55% (11)
- ThermodynamicsDokumen79 halamanThermodynamicsDannemanBelum ada peringkat
- Bending and Creep Buckling Response of Viscoelastic Functionally Graded Beam-Columns PDFDokumen9 halamanBending and Creep Buckling Response of Viscoelastic Functionally Graded Beam-Columns PDFMehmedBelum ada peringkat
- Gas-Vapor Mixtures and Air-Conditioning Study Guide in PowerpointDokumen38 halamanGas-Vapor Mixtures and Air-Conditioning Study Guide in PowerpointRenzmore GalvanBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmaceutical SuspensionsDokumen17 halamanPharmaceutical SuspensionscsdharBelum ada peringkat
- Fluid Flow ProjectsDokumen271 halamanFluid Flow ProjectsNathalia Delgado100% (1)
- Stress Analysis ReportDokumen21 halamanStress Analysis ReportGuillermo HerreraBelum ada peringkat
- ANS 002 Determination of Cristallinity of PET by DSCDokumen2 halamanANS 002 Determination of Cristallinity of PET by DSCTiwiBelum ada peringkat
- Heat Transfer Nov2002 NR 310803Dokumen6 halamanHeat Transfer Nov2002 NR 310803Nizam Institute of Engineering and Technology LibraryBelum ada peringkat
- Bullseye Annealing Thick Slabs PDFDokumen1 halamanBullseye Annealing Thick Slabs PDFAnonymous X0SrEQR0mXBelum ada peringkat
- Softening Point of Bitumen PDFDokumen8 halamanSoftening Point of Bitumen PDFbishry ahamedBelum ada peringkat
- 84 Practical IC Projects WarringDokumen139 halaman84 Practical IC Projects WarringHacia la LuzBelum ada peringkat
- Concrete Pavement Design Methods for Rural RoadsDokumen47 halamanConcrete Pavement Design Methods for Rural RoadsTarak A Positive100% (2)
- Nano Material Volumes Applications Holman Lux ResearchDokumen29 halamanNano Material Volumes Applications Holman Lux Researchlili_puma100% (2)
- E 0211Dokumen23 halamanE 0211Thinh ViproBelum ada peringkat
- Calculation of Load Capacity of Shafts and Axles: German Standard October 2000Dokumen6 halamanCalculation of Load Capacity of Shafts and Axles: German Standard October 2000Karthik VaidhyanathanBelum ada peringkat
- Pec Chapter 3 1Dokumen37 halamanPec Chapter 3 1relkunkoBelum ada peringkat
- Field Validation of A Coiled Tubing Fatigue Model: April 2003Dokumen7 halamanField Validation of A Coiled Tubing Fatigue Model: April 2003moorpvrBelum ada peringkat
- 재료과학 20장 본문 광자재료Dokumen47 halaman재료과학 20장 본문 광자재료박동진Belum ada peringkat
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDokumen2 halamanMicroscope Parts and FunctionsMhais Angelika DyBelum ada peringkat
- NAQPDokumen9 halamanNAQProhitBelum ada peringkat
- Nanosecond Electromagnetic Pulse Effect On Phase CompositionDokumen8 halamanNanosecond Electromagnetic Pulse Effect On Phase CompositionAKBelum ada peringkat