A Computer
Diunggah oleh
bprsflDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
A Computer
Diunggah oleh
bprsflHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
COMPUTER
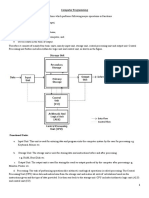
A computer receives incoming data, processes them and produces an output. Hence, in a typical computer, there is (a) An input device i.e., a key board (b) A Central Processing Unit (CPU) i.e., a box and (c) An output device i.e., a monitor or a Visual Display Unit (VDU) (a) Input Devices The most commonly used input device is a key board. It is just like a type-writer keyboard. Other types of input devices are Bar-Code Recognition, Hard-Held Terminal, and Hard Print Terminal or also called data tablet, Optical Mark Reading, Magnetic Ink Character Recognition (MICR), Optical Character Reader (OCR) etc. (b) Central Processing Unit (CPU) It has a box like appearance and is considered as the heart of the computer. It is consisted of; (i) Control Unit (CU) (ii) Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) and (iii) Primary Storage Unit, (i) Control Unit (CU) The control Unit organizes all the operations. It selects, interprets and executes the programme instructions, (ii) Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) It does all the arithmetic and logic operations i.e., adding, subtracting, multiplying, dividing and comparing, (iii) Primary Storage Unit
It is the memory section of CPU that stores data and programmes that are waiting to be processed or currently being processed. Generally two different types of memory are used in the computers; i.e. (1) Random Access Memory (RAM), and (2) Read Only Memory (ROM) RAM: It allows read/write but is volatile i.e., loses Memory when power is cut. ROM: It is non-volatile and is put in by the manufacturer. It is commonly used not storing of programme instructions that are not subject to change. There are various ROM chips to meet users specifications; like PROM Programme Read Only Memory EPROM Erasable Programme Read Only Memory EEROM Electrically Erasable Read Only Memory All the information's within the computer is stored in the form a BINARY SYSTEM i.e.. O's and 1's. (c) Output Devices: Output devices communicate the result to the users. They are (i) Visual Display Unit (VDU) (ii) Printers (iii) Plotters (i) VDU: It is like a T. V. screen or a monitor where all data can be displayed. (ii) Printers: The printers are devices that can be reproduced on papers, copies of programs, data or output from the computer's memory. Different kinds of printers are, Dot Matrix. Thermal, Ink Jet, Daisy wheel, Thimble, Spark, Drum, Chain and Laser printer. In Dot-matrix, characters are made up of patterns of dots. Dot-Matrix image with overlapping dots gives rise to Laser Printer. In Page Printer, one page is printed at a time, (iii) Plotters: A plotter is a device used to draw graphs, diagrams or any other drawings on the paper. Secondary Storage Devices All devices that are connected to the CPU for storing information's but are not part of the CPU, are called Secondary Storage Devices. The examples are; Magnetic Tap, magnetic disk. Optical disk, Winchester or Hard disk and Floppy disk.
Floppy disk Floppy disks or diskettes are most widely used in microcomputers and are very popular. These are thin, plastic disks on which computer data and programmes can be stored. The sizes may very from 3.5" to 5.25" to 8" and have large storage capacity. The information can be stored on the floppy either on one side, i.e., single-sided (ss) or in both sides i.e., double-sided (do) and in single density (sad) or double density (did) or high density (had). Winchester disk or Hard disk These are IBM innovation and can store much more data that can be stored in floppy disk and have more reliability. Hard disks usually come as sealed units. So they can not be removed or changed like floppy disk and cost is also 2-10 times more than floppies. But they have greater protection and do not need periodic maintenance. Hardware and Software Computer ware can be divided into two types e.g. hardware and software. Hardware All electronic, mechanical, magnetic, electrical and other devices used with the computer constitute the hardware. Software Software refers to various Programs or routines used on the hardware to facilitate the user's efficient operation of the computer. The software can be divided into two kinds; System software used to manage the operations of the machine i.e., the Operating Systems (OS) and Application softwares are used for the user applications i.e., a programme that is employed for data bases for railway enquiry or reservation system or airlines booking etc.. The Operating System (OS) The Operating System (OS) of a computer is a set of specialized programmes that manages all the operations of the computer; such as CPU, Memory, key board, Floppy Disks, VDU etc. The Operating System is responsible for the communications between the computer and its peripheral. From small personal computer (Micro Computer) to super computers, the OS operates in all the computer systems. Very commonly used operating systems for microcomputers are PC-DOS (Personal Computer Disk Operating System), MS-DOS, Window and XENIX. IBM's PC-DOS is a very popular OS. UNIX another very powerful OS is much more versatile and also offered many more capabilities than any other OS.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- TLE-ICT-CHS - Operating System (July 27,2018)Dokumen2 halamanTLE-ICT-CHS - Operating System (July 27,2018)Marvin GoBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Computers in 40 CharactersDokumen8 halamanIntroduction to Computers in 40 CharactersJontex 254Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Hardware Units of A ComputerDokumen12 halamanBasic Hardware Units of A ComputerRobinson JoshuaBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Computer Hardware Notes in PDFDokumen7 halamanBasic Computer Hardware Notes in PDFSa FarBelum ada peringkat
- Information Technology (It) : ComputerDokumen53 halamanInformation Technology (It) : ComputerRicky Ryan AndasBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Basics: Basic Parts of A Desktop ComputerDokumen10 halamanComputer Basics: Basic Parts of A Desktop ComputerManuel PachekoBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Computer Course, For Beginners and Technology StudentsDari EverandBasic Computer Course, For Beginners and Technology StudentsBelum ada peringkat
- COMPUTER FUNDAMENTALAND WORD 96428ad9 7fbe 47c2 9e15 46003c090a67 1e8c0f4b 34e0 4ade 8d7c Ae43fc3757fdDokumen24 halamanCOMPUTER FUNDAMENTALAND WORD 96428ad9 7fbe 47c2 9e15 46003c090a67 1e8c0f4b 34e0 4ade 8d7c Ae43fc3757fdHimanshiBelum ada peringkat
- Section1 Notes (Grd-9)Dokumen6 halamanSection1 Notes (Grd-9)Moody GauchoBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction to Computers Notes OUTPUT DevicesDokumen20 halamanIntroduction to Computers Notes OUTPUT Devicesmunaxemimosa8Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Computer Hardware Notes in PDFDokumen8 halamanBasic Computer Hardware Notes in PDFNandyal Water SupplyBelum ada peringkat
- How computer software helps run hardware componentsDokumen6 halamanHow computer software helps run hardware componentsRavi Mohan BhattBelum ada peringkat
- Computr Appltion 1 and 2Dokumen46 halamanComputr Appltion 1 and 2george manBelum ada peringkat
- Unit1-The Computer SystemDokumen14 halamanUnit1-The Computer SystemLen CumminsBelum ada peringkat
- 01 Notes Hardware ConceptsDokumen11 halaman01 Notes Hardware ConceptsAbhinav AnandBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To HardwareDokumen14 halamanIntroduction To HardwarePriya AgrawalBelum ada peringkat
- ENGLAISDokumen15 halamanENGLAISDan BurgBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Hardware SoftwareDokumen41 halamanComputer Hardware SoftwareKatheryn Rose QuilapioBelum ada peringkat
- Computer System & Organization1111Dokumen27 halamanComputer System & Organization1111spiagent2007Belum ada peringkat
- 2nd Quarter - Review - INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING COMPUTER SYSTEMSDokumen21 halaman2nd Quarter - Review - INSTALLING AND CONFIGURING COMPUTER SYSTEMSAlyzzaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Computer Hardware (IT FUNDAMNETALS)Dokumen6 halamanWhat Is Computer Hardware (IT FUNDAMNETALS)JSON AMARGABelum ada peringkat
- Chapter OneDokumen65 halamanChapter Oneaddim6748Belum ada peringkat
- Computer Basics: An Introduction to Concepts and ComponentsDokumen32 halamanComputer Basics: An Introduction to Concepts and ComponentsCristin Porcadilla AranteBelum ada peringkat
- BasicComputerSkills NotesDokumen31 halamanBasicComputerSkills NotesVanamala MahathiBelum ada peringkat
- It Workshop LAB MANUALDokumen45 halamanIt Workshop LAB MANUALNanny BoppanaBelum ada peringkat
- Components of ComputerDokumen4 halamanComponents of ComputerSheikh Hammad Bin KhalidBelum ada peringkat
- Complete CP NotesDokumen91 halamanComplete CP NotesAnonymous 1HlNy6nBelum ada peringkat
- Cs2 Chapter 3 and 4 FYJCDokumen12 halamanCs2 Chapter 3 and 4 FYJCshubhammukriBelum ada peringkat
- Portfolio in Robotics (1st Quarter)Dokumen29 halamanPortfolio in Robotics (1st Quarter)No NameBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment 1: 1.explain in Brief About Different Types of Input and Output Devices Used in Computer Systems?Dokumen10 halamanAssignment 1: 1.explain in Brief About Different Types of Input and Output Devices Used in Computer Systems?Nabin TamangBelum ada peringkat
- Computer System DeviceDokumen55 halamanComputer System DevicesanthiyaperemelBelum ada peringkat
- It Questions g7 - 022640Dokumen8 halamanIt Questions g7 - 022640Celestine Lumuli MadataBelum ada peringkat
- Understanding Computers: Hardware, Software, Input/Output DevicesDokumen7 halamanUnderstanding Computers: Hardware, Software, Input/Output DevicesRaj Kumar OadBelum ada peringkat
- ReviewerDokumen24 halamanReviewerXylind Del ValleBelum ada peringkat
- Resource 20230220140657 Grade 11 Computer HandoutsDokumen257 halamanResource 20230220140657 Grade 11 Computer HandoutsSasidaran SasiBelum ada peringkat
- Electronic Document Preparation and Management Notes For CXC ExamDokumen18 halamanElectronic Document Preparation and Management Notes For CXC ExamJabari Morgan88% (8)
- 2nd Finial Term 2023Dokumen3 halaman2nd Finial Term 2023mahmoodBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ComputerDokumen74 halamanIntroduction To ComputerJade TobiasBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Computer?: 1. With A Neat Schematic Block Diagram of A Digital Computer Describe Its Functional UnitsDokumen38 halamanWhat Is A Computer?: 1. With A Neat Schematic Block Diagram of A Digital Computer Describe Its Functional Unitsranga231980Belum ada peringkat
- PC Hardware Components and FunctionsDokumen20 halamanPC Hardware Components and Functionschris73% (45)
- Computer Appreciation: Designed by Legitimate ICTDokumen16 halamanComputer Appreciation: Designed by Legitimate ICTMiracle UchechukwuBelum ada peringkat
- COMPUTER HARDWARE bSOFTWARE PDFDokumen9 halamanCOMPUTER HARDWARE bSOFTWARE PDFsheokandytBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Hardware & SoftwareDokumen9 halamanComputer Hardware & SoftwareAkhilesh BhuraBelum ada peringkat
- NEW BASIC OF COM KulDokumen13 halamanNEW BASIC OF COM KulPawan KumarBelum ada peringkat
- COMPUTER Tutors Copy 2Dokumen23 halamanCOMPUTER Tutors Copy 2alfred asajileBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Computer?Dokumen25 halamanWhat Is A Computer?حسين ناهضBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson 3Dokumen5 halamanLesson 3stephaniejeancortez522Belum ada peringkat
- Introduction To ComputersDokumen35 halamanIntroduction To ComputersmallapishyamreddyBelum ada peringkat
- Computer ApplicationDokumen42 halamanComputer Applicationriya wadhwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Computer: Made by Surbhi JainDokumen25 halamanComputer: Made by Surbhi JainniveshjainBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter Two: Computer SystemDokumen18 halamanChapter Two: Computer SystemJOHN COBelum ada peringkat
- tiếng anh cn cntt 02Dokumen11 halamantiếng anh cn cntt 02Hoan NguyễnBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Computer HardwareDokumen3 halamanTypes of Computer HardwareManuel Delfin Jr.Belum ada peringkat
- 1basic Computer OrganizationDokumen13 halaman1basic Computer OrganizationAdrija SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Computer Peripherals GuideDokumen10 halamanComputer Peripherals Guideblue gamingidBelum ada peringkat
- ICT BookDokumen9 halamanICT Booksenzoc1Belum ada peringkat
- Basic Operations of A Computer SystemDokumen11 halamanBasic Operations of A Computer SystemJanus Michael FaustoBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Computers: by Rave Harpaz Computer Science Dept. Brooklyn CollegeDokumen28 halamanIntroduction To Computers: by Rave Harpaz Computer Science Dept. Brooklyn CollegeKibrom HaftuBelum ada peringkat
- 3 Understanding The Computer SystemDokumen60 halaman3 Understanding The Computer SystemsanchaibenasBelum ada peringkat
- Get admission in computer courses and earn a degree after examsDokumen2 halamanGet admission in computer courses and earn a degree after examsShahbaz HassanBelum ada peringkat
- InnQuest Software Launches Stayfull Channel ManagerDokumen3 halamanInnQuest Software Launches Stayfull Channel ManagerPR.comBelum ada peringkat
- CG 15cs62 Model QP SolutionsDokumen60 halamanCG 15cs62 Model QP SolutionsYasha DhiguBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Software Project Management GuideDokumen12 halamanApplied Software Project Management GuidelogaritymBelum ada peringkat
- CV Software Tester Nguyen Thi Ngoc ThuyDokumen5 halamanCV Software Tester Nguyen Thi Ngoc ThuyNguyễn ThiệnBelum ada peringkat
- Implementation of An FPGA - Raspberry Pi SPI Connection: Haissam Hajjar Hussein MouradDokumen6 halamanImplementation of An FPGA - Raspberry Pi SPI Connection: Haissam Hajjar Hussein MouradscribbshitBelum ada peringkat
- 3D Animator User GuideDokumen85 halaman3D Animator User GuidecarlcoxBelum ada peringkat
- 4.2 Acitivity SoftwareModelingIntroduction - REVISED-2Dokumen5 halaman4.2 Acitivity SoftwareModelingIntroduction - REVISED-2Catherine RosenfeldBelum ada peringkat
- Wesern Digital RaptorDokumen2 halamanWesern Digital RaptorcedlanioBelum ada peringkat
- Magic 8 Ball Fortune Telling Game Project ReportDokumen23 halamanMagic 8 Ball Fortune Telling Game Project ReportHidden Gem50% (2)
- Input and Output Devices ExplainedDokumen96 halamanInput and Output Devices Explaineddhruv shahBelum ada peringkat
- METHOD OF PROCEDURE FOR LTE G2-OSS L17A UpgradeDokumen18 halamanMETHOD OF PROCEDURE FOR LTE G2-OSS L17A UpgradeEdu Mmoja Mutai100% (1)
- Major 7th Chords: Extracted From "The Complete Book of Improvisation" by Fred LipsiusDokumen182 halamanMajor 7th Chords: Extracted From "The Complete Book of Improvisation" by Fred LipsiusJuan Carlos Fiallos Rodas100% (1)
- Oracle APSDokumen13 halamanOracle APSAnindita Nath100% (1)
- TCPIP Protocol Suite (4th Edition)Dokumen24 halamanTCPIP Protocol Suite (4th Edition)Sumit ShakyaBelum ada peringkat
- Surecom Ep-4904sx ManualDokumen53 halamanSurecom Ep-4904sx ManualCarlos Eduardo Dos SantosBelum ada peringkat
- Allotment Order DetailsDokumen1 halamanAllotment Order DetailsPavan MandapakalaBelum ada peringkat
- 2007 TL Navigation Diagnostic MenuDokumen13 halaman2007 TL Navigation Diagnostic MenuZsolt GeraBelum ada peringkat
- Sorting algorithms explainedDokumen24 halamanSorting algorithms explainedabdulazizBelum ada peringkat
- Build cross-platform mobile apps with React NativeDokumen31 halamanBuild cross-platform mobile apps with React Nativedvirus2012Belum ada peringkat
- SECTION 4 - RF System DesignDokumen44 halamanSECTION 4 - RF System DesignBelachew AndualemBelum ada peringkat
- Example Curriculum VitaeDokumen4 halamanExample Curriculum VitaeGugun NugrahaBelum ada peringkat
- Distance Sensors Catalog-8014441Dokumen404 halamanDistance Sensors Catalog-8014441etorinBelum ada peringkat
- 11.2.3.11 Packet TR Logging From Multiple Sources InstructionsDokumen4 halaman11.2.3.11 Packet TR Logging From Multiple Sources InstructionsNBelum ada peringkat
- Test Suite Siprotec 5Dokumen27 halamanTest Suite Siprotec 5Guillermo BetancourtBelum ada peringkat
- MESDDokumen311 halamanMESDsarath rocksBelum ada peringkat
- LESSON 1 - History and Evolution of ComputersDokumen18 halamanLESSON 1 - History and Evolution of ComputersKeana Cerela GironBelum ada peringkat
- SSH Key Generation ReferenceDokumen6 halamanSSH Key Generation ReferenceBabjee ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Technical Application AND Programming GuideDokumen44 halamanTechnical Application AND Programming GuideHasib KhanBelum ada peringkat
- IP Security: Henric Johnson Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden Henric - Johnson@bth - SeDokumen31 halamanIP Security: Henric Johnson Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden Henric - Johnson@bth - Seahmadamminudin89Belum ada peringkat