DM Type 2 Pathophysiology
Diunggah oleh
uzumakirule0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
2K tayangan3 halamanEating too much sweets 2. Diet insulin resistance predisposing factors: 1. Family history of DM 2. Male Exhaustion of beta cells impaired insulin secretion Absorption of glucose by the cell Breakdown of fat.
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
dm type 2 pathophysiology
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniEating too much sweets 2. Diet insulin resistance predisposing factors: 1. Family history of DM 2. Male Exhaustion of beta cells impaired insulin secretion Absorption of glucose by the cell Breakdown of fat.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
2K tayangan3 halamanDM Type 2 Pathophysiology
Diunggah oleh
uzumakiruleEating too much sweets 2. Diet insulin resistance predisposing factors: 1. Family history of DM 2. Male Exhaustion of beta cells impaired insulin secretion Absorption of glucose by the cell Breakdown of fat.
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOC, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 3
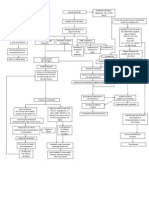
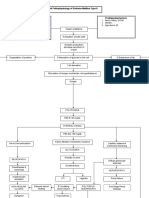
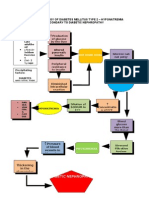
Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type II References: Black, J. and Jacobs, 2004. Medical-Surgical Nursing, .
Brunner and Suddarths Medical and Surgical Nursing
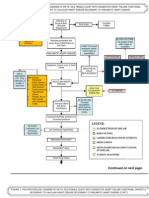
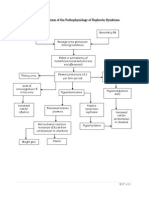
Precipitating factors: 1. eating too much sweets 2. diet Insulin resistance
Predisposing factors: 1. family history of DM 2. Male
Exhaustion of beta cells
Impaired insulin secretion
Absorption of glucose by the cell
Breakdown of fat
UNCONTROLLED HYPERGLYCEMIA
Fatty acids & glycerol ketone bodies in the general circulation Metabolic acidosis
Increase viscosity of blood
Microvascular vasoconstriction Thickening of blood vessel walls Occlusion of plaque Blood flow blocked Capillary basement membrane thickening
Glomerular hemodynamic changes Glomerular hyperfiltration and hyperperfusion
Nausea and vomiting
Circulating blood volume
Endothelial hyperplasia Bp HPN Neural hypoperfusion and ischemia
Dysfunction of autoregulatory response Increased extracellular matrix deposition
Poor appetite
Possible delayed wound healing
Weight loss
Glomerulosclerosis
Risk for impaired skin integrity
Nerve dysfunction PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY Tubulointerstitial fibrosis
Decreased glomerular filtration
Imbalance nutrition less than body requirement
Kidney excrete glucose
Numbness Impaired sensation on lower extremities
BUN and creatinine
GLYCOSURIA
Nephropathy
POLYURIA and albuminuria
Acidity of urine
Capillary basement membrane thickening Abnormal retinal vascular permeability Scarring
Urethral flora UTI
F & E imbalance
Number of solute relative to water
Blurring of vision
Sodium ions lost
Tissue dehydration POLYURIA
Fluid volume deficit
POLYDIPSIA
Musculoskeletal effects
Inhibit both protein synthesis and protein degradation in skeletal muscles
Risk for injury
Body weakness
Fatigue
hunger
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Pathophysiology of DiabetesDokumen88 halamanPathophysiology of DiabetesCahya SetiyaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular DiseaseDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Hypertensive Cardiovascular Diseasekhrizaleeh100% (9)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Dokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1CajRofuli100% (2)
- EndocrinologyDokumen50 halamanEndocrinologyDonanguyen100% (2)
- Pathophysiology HypertensionDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology HypertensionAlinor Abubacar100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Hypertension PathophysiologyDokumen2 halamanHypertension PathophysiologyJems60% (5)
- Diabetes Mellitus 2Dokumen42 halamanDiabetes Mellitus 2ien84% (19)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureTrixia Almendral100% (2)
- Prefix SuffixDokumen3 halamanPrefix SuffixuzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of DMDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaBelum ada peringkat
- The Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureDokumen4 halamanThe Pathology of Congestive Heart FailureMar Ble50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaBelum ada peringkat
- Liver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanLiver Cirrhosis PathophysiologyCaren ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Burn PathoDokumen1 halamanBurn PathoArlan AbraganBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokumen7 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jnrue_aerith96% (28)
- Complications of Diabetes An Overview of The PathophysiologyDokumen58 halamanComplications of Diabetes An Overview of The Pathophysiologyrachel0301Belum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology CVA (Final2)Dokumen10 halamanPathophysiology CVA (Final2)Jayselle Costes FelipeBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Cerebrovascular Disease: Predisposing Factors Etiology Precipitating FactorsLilot Antonio Rodriguez Vinarao100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormPen MontanteBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDokumen6 halamanPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresBelum ada peringkat
- Patho of MIDokumen2 halamanPatho of MIInchan Montesines0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever - Doc (Phil)Dokumen8 halamanPathophysiology of Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever - Doc (Phil)Firenze Fil0% (1)
- Nstemi PathoDokumen2 halamanNstemi PathoSheana TmplBelum ada peringkat
- CKD PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanCKD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokumen6 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Renz Ivan FuntilonBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of DMDokumen5 halamanPathophysiology of DMRgn Mckl100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jo_annamae4413100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney Disease: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsReina Samson0% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Rheumatoid ArthritisGerardeanne ReposarBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Liver CirrhosisDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Liver Cirrhosisgaelty100% (4)
- Blood Glucose MonitoringDokumen10 halamanBlood Glucose MonitoringSarah Jane MaganteBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokumen5 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2LesValenzuelaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Dokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokumen7 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2arbyjamesBelum ada peringkat
- 1 Diabetes Screening PO4047576719 696Dokumen4 halaman1 Diabetes Screening PO4047576719 696rishiranjan04Belum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Acute Kidney InjuryJane Arian Berzabal0% (1)
- Case 4Dokumen5 halamanCase 4Bikash ShresthaBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology DMDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology DMMJ AmarilloBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDokumen6 halamanPathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of AGEDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of AGEtinatin9890% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureAnonymous XvwKtnSrMR100% (10)
- Pathophysiology CHFDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology CHFKim Franzel M. Rabe100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CVADokumen1 halamanPathophysiology CVANenette Aquino100% (2)
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionDokumen2 halamanHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionMiguel Carlos Tacderan100% (1)
- Pathophysiology - Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Dokumen3 halamanPathophysiology - Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Francis Kevin Sagudo100% (10)
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDokumen1 halamanDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Dengue PoathoDokumen6 halamanDengue PoathoCleobebs Agustin100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDokumen3 halamanPathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDanielle Marie SamblacenoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusJerene67% (3)
- Pathophysiology CVDDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology CVDPamela Shiermaine FilomenoBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes Insipidus Pathophys DiagramDokumen1 halamanDiabetes Insipidus Pathophys Diagrampaupaulala100% (4)
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDokumen1 halamanPathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Nephrotic SyndromeRan MaBelum ada peringkat
- D5IMBDokumen1 halamanD5IMBPrincess Garrote50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type II and NephrolithiasisDokumen6 halamanPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type II and Nephrolithiasisdiane_mananganBelum ada peringkat
- Endocrine Disorders: Patho Phys Iolog yDokumen20 halamanEndocrine Disorders: Patho Phys Iolog yCres Padua QuinzonBelum ada peringkat
- Complications of DMDokumen9 halamanComplications of DMJennicaBelum ada peringkat
- Pa ThoDokumen2 halamanPa ThoHarvin FrancoBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology Schematic Diagram and NarrativeDokumen15 halamanPathophysiology Schematic Diagram and NarrativeKathrina CraveBelum ada peringkat
- Annotated-Reynolds nsg4612021 4Dokumen11 halamanAnnotated-Reynolds nsg4612021 4api-643186750Belum ada peringkat
- Diabetes and PeriodontitisDokumen25 halamanDiabetes and PeriodontitisAmrutha KasinaBelum ada peringkat
- Uremia and Uremic ToxinsDokumen48 halamanUremia and Uremic Toxinssaieefzaman71Belum ada peringkat
- Thesis Defense GuidelinesDokumen10 halamanThesis Defense GuidelinesJessica Laine TumbagaBelum ada peringkat
- Usuals CHIEF COMPLAINT: (Reason Why The Patient Is inDokumen3 halamanUsuals CHIEF COMPLAINT: (Reason Why The Patient Is inuzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- Virus Shortcut RemovalDokumen1 halamanVirus Shortcut RemovalSakthivel VelusamyBelum ada peringkat
- TesdaDokumen2 halamanTesdaMayj RiveraBelum ada peringkat
- The Negative Effects of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia: Crassipes) IN COTABATO CITYDokumen5 halamanThe Negative Effects of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia: Crassipes) IN COTABATO CITYuzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- The Negative Effects of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia: Crassipes) IN COTABATO CITYDokumen5 halamanThe Negative Effects of Water Hyacinth (Eichhornia: Crassipes) IN COTABATO CITYuzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- Grade 6 English ReadingDokumen5 halamanGrade 6 English ReadinguzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- Pongayan, Kapangan 3rd WKDokumen111 halamanPongayan, Kapangan 3rd WKuzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- Subic Bay Information TravelDokumen76 halamanSubic Bay Information TraveluzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- Conclusion and RecommendationDokumen1 halamanConclusion and RecommendationuzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- Problem: DOB ASSESSMENT S: "Hindi Siya MakahingaDokumen13 halamanProblem: DOB ASSESSMENT S: "Hindi Siya MakahingauzumakiruleBelum ada peringkat
- DIABETES BookDokumen2 halamanDIABETES BookMaria Kimberly NazarenoBelum ada peringkat
- 63 - Original ArticleDokumen5 halaman63 - Original ArticlechairulBelum ada peringkat
- Cda Revalida Caregiving NC 2020Dokumen7 halamanCda Revalida Caregiving NC 2020Rowena Lalongisip De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Presentation 1Dokumen6 halamanPresentation 1Maya RentinaBelum ada peringkat
- American Heart Association Guide For Improving Cardiovascular HealthDokumen24 halamanAmerican Heart Association Guide For Improving Cardiovascular HealthLorena Galindo GuerreroBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes Cheat SheetDokumen2 halamanDiabetes Cheat Sheetmanuel iglesiasBelum ada peringkat
- Running Head: SWEETER CHOICE 1Dokumen5 halamanRunning Head: SWEETER CHOICE 1api-302415380Belum ada peringkat
- Name: Insong, Osannah Irish B.: No, There IsDokumen1 halamanName: Insong, Osannah Irish B.: No, There IsOsannah Irish InsongBelum ada peringkat
- NENC Regional SGLT2 Top Tips v1.2 NTAG Approved March 2023Dokumen5 halamanNENC Regional SGLT2 Top Tips v1.2 NTAG Approved March 2023Nehal ElnagarBelum ada peringkat
- Solution Manual For Dosage Calculations A Multi Method Approach 0132158620Dokumen13 halamanSolution Manual For Dosage Calculations A Multi Method Approach 0132158620RandallValdezypfqw100% (86)
- Jurnal Internasional Dan Nasional IntanDokumen12 halamanJurnal Internasional Dan Nasional Intanherli padli wijayaBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan Nephrotic SyndromeDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan Nephrotic SyndromeJhusmin BambicoBelum ada peringkat
- Advisory Board PPT (Dr-2. Ida Ayu Kshanti SPPD, KEMD)Dokumen29 halamanAdvisory Board PPT (Dr-2. Ida Ayu Kshanti SPPD, KEMD)scribdBelum ada peringkat
- Semaglutifes Sustaine ComparadoresDokumen10 halamanSemaglutifes Sustaine ComparadoresIvan Dario Hernandez ErazoBelum ada peringkat
- Demensia DMDokumen5 halamanDemensia DMNadia Rezki ErlizaBelum ada peringkat
- Blood Sugar Level Chart: MG/DL General Target RangesDokumen11 halamanBlood Sugar Level Chart: MG/DL General Target RangesbobbymeenaBelum ada peringkat
- Diabetes Mellitus of The Human Digestive SystemDokumen7 halamanDiabetes Mellitus of The Human Digestive SystemCHRISTINE KARENDIBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment of Factors Influencing Adherence To AntDokumen7 halamanAssessment of Factors Influencing Adherence To AntJob MarenBelum ada peringkat
- PH.D Syllabus: (Part-I:Paper III)Dokumen10 halamanPH.D Syllabus: (Part-I:Paper III)praveena thanavelBelum ada peringkat
- Retinopatía Diabética en ChileDokumen9 halamanRetinopatía Diabética en ChileUlises GilBelum ada peringkat
- NHS FPX 6004 Assessment 2 Policy ProposalDokumen6 halamanNHS FPX 6004 Assessment 2 Policy Proposaljoohnsmith070Belum ada peringkat
- Himalayas 2022: Medical FormDokumen4 halamanHimalayas 2022: Medical FormDeepak WaradBelum ada peringkat
- Listening, Use of English and Reading: 1 A B C 2 A B CDokumen4 halamanListening, Use of English and Reading: 1 A B C 2 A B Cleandro lozanoBelum ada peringkat
- BMEN4110 Lab1 PartA Artificial Pancreas 2021Dokumen15 halamanBMEN4110 Lab1 PartA Artificial Pancreas 2021William GoldbergBelum ada peringkat
- Basal Bolus Insulin Titration AhsDokumen2 halamanBasal Bolus Insulin Titration AhsAnn A.100% (1)
- SN Erra Fazira Jururawat Terlatih U29 Jabatan Kecemasan, HAT Wilayah Kota KinabaluDokumen14 halamanSN Erra Fazira Jururawat Terlatih U29 Jabatan Kecemasan, HAT Wilayah Kota Kinabaluyein yenBelum ada peringkat
- Sodium and Water Need To KnowDokumen48 halamanSodium and Water Need To KnowkartikaparamitaBelum ada peringkat