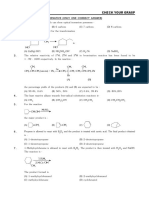
Chem. Imp. Questions
Diunggah oleh
Himanshu NikhurpaDeskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chem. Imp. Questions
Diunggah oleh
Himanshu NikhurpaHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Chemistry : Important Questions For CBSE Class XII ( Haloalkanes and Haloarenes) : Q.
1) Choose the incorrect statement about the benzyl chloride: ( 1 mark ) (a) It is less reactive than alkyl halides. (b) It can be oxidized to benzaldehyde by boiling with copper nitrate solution. (c) It is a lachrymatory liquid and answers beilstein s test. (d) It gives a white precipitate with alcoholic silver nitrate (Q.2) Dry ether The reaction RX + 2Na + RX _______________? R-R + 2NaXis called. ( 1 mark ) (a) Sandmeyer reaction (b) Fittig reaction (c) Wurtz reaction (d) Williamson s synthesis (Q.3) Substitution of chlorine takes place readily at higher temperature in : ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3CH=CH2 (b) H2C=CH2 (c) HC C (d) None of the above (Q.4) (CH3)3CMgBr on reaction with D2O gives: ( 1 mark ) (a) (CH3)3CD (b) (CH3)3COD (c) (CD3)3CD (d) (CD3)3OD (Q.5) The silver salt of fatty acid on refluxing with an alkyl halide gives an: ( 1 mark ) (a) Acid (b) Ester (c) Ether (d) Amine (Q.6) Which of the following is the most reactive towards nucleophilic substitut ion reaction? ( 1 mark ) (a) C6H5Cl (b) CH2=CHCl (c) ClCH2CH=CH2 (d) CH3CH=CHCl (Q.7) The molecule with the highest dipole moment is: ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3Cl (b) CH2Cl2 (c) CHCl3 (d) CCl4 (Q.9) What is added to chloroform to prevent to form phosgene gas: ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3COCH3 (b) C2H5OH (c) CH3COOH (d) CH3OH (Q.10) The most reactive nucleophile among the following is: ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3O(b) C6H5O(c) (CH3)2CHO(d) (CH3)3CO(Q.11) The correct order of decreasing dipole moment is: ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3Cl, CH3Br, CH3F (b) CH3Cl, CH3F, CH3Br (c) CH3Br, CH3Cl, CH3F (d) CH3Br, CH3F, CH3Cl (Q.12) HCl and HI do not give anti- markovnikov s addition to alkenes in the prese nce of peroxides because: ( 1 mark ) (a) Both are highly ionic (b) One is oxidizing and other is reducing
(c) One of the step is endothermic in both the cases (d) All the steps are exothermic in both the reactions. (Q.13) Which of the following is the correct: ( 1 mark ) (a) RF>RCl>RBr>RI (b) RF>RBr>RCl>RI (c) RCl>RBr>RF>RI (d) RI>RBr>RCl>RF (Q.14) HBr can be added easily to: ( 1 mark ) (a) CH2=CHCl (b) CH3-CH=CH2 (c) ClCH=CHCl (d) (CH3)2C=CH2 (Q.15) Which of the following is the most reactive towards the SN2 reaction: ( 1 mark ) (a) MeX (b) RCH2X (c) R2CHX (d) R3CX (Q.16) The correct order of Nucleophlicity is: ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3- < NH2- < HO- < F(b) NH2- > CH3- > HO- > F(c) CH3- > NH2- > HO- > F(d) NH2- > F- > HO- > CH3(Q.17) What are ambident nucleophiles? ( 1 mark ) (Q.18) 2-Phenyl-2-chloropropane on treatment with alc.KOH gives mainly: ( 1 mark ) (a) 2-Phenylpropene (b) 3-Phenylpropene (c) 1-Phenylpropan-2-ol (d) 1-Phenylpropan-3-ol (Q.19) When chlorine passed through propene at 400 degree Celsius, the product i s: ( 1 mark ) (a) Vinyl chloride (b) Allyl chloride (c) PVC (d) 1,2-dichloroethane (Q.20) The IUPAC name of CH3-CH=CHCH2Br is: ( 1 mark ) (a) 1-Bromo-2-butene (b) 1-Bromo-3-butene (c) 2-Butene-1-bromide (d) 4-Bromo-2-butene (Q.21) Why is sulphuric acid not used during the reactions of alcohols with KI? ( 1 mark ) (Q.22) Write the IUPAC name of the following compound. ClCH2CHClCH3 ( 1 mark ) (Q.23) Which is a better nucleophile, a bromide ion or iodide ion? ( 1 mark ) (Q.24) How will youget 1-bromopropane from propene? ( 1 mark ) (Q.25) Write the structure of 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane. ( 1 mark ) (Q.26) What is the nature of C-X bond of haloalkanes? ( 1 mark ) (Q.27) Arrange the compounds of each set in order of reactivity towards SN2 disp lacement: 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane, 2-Bromopentane. ( 1 mark ) (Q.28) What is an asymmetric carbon? ( 1 mark ) (Q.29) Which haloalkane has the maximum density and why? ( 1 mark ) (Q.30) What is Freon? ( 1 mark ) (Q.31) Write the full form of DDT. ( 1 mark ) (Q.32) Write a chemical reaction to illustrate Saytzeff s rule. ( 1 mark ) (Q.33) Write the IUPAC name of the following structure. CH2BrCH=CHCH2CHCl2 ( 1 m ark ) (Q.34) Arrange the following in increasing order of boiling point.
CH3CH2CH2CH2Br, (CH3)3CBr, (CH3)2CHCH2Br. ( 1 mark ) (Q.35) Explain why thionyl chloride reaction is preferred forpreparing alkyl chl orides from alcohols? ( 1 mark ) (Q.36) Arrange the following in order of their decreasing reactivity in nucleoph ile substitution reactions: CH3F, CH3I, CH3Br, CH3Cl. ( 1 mark ) (Q.37) Define optical activity? ( 1 mark ) (Q.38) What are enantiomers? ( 1 mark ) (Q.39) What is racemic mixture or racemic modification? ( 1 mark ) (Q.40) Define retention? ( 1 mark ) (Q.41) The conversion of 2,3-dibromobutane to 2-butene with Zn and alcohol is a: ( 1 mark ) (a) Redox reaction (b) Alpha-elimination (c) Beta- elimination (d) Both redox and Beta-elimination (Q.42) Vicinal and gem dihalides can be distinguished by: ( 1 mark ) (a) aq. KOH (b) Zn dust (c) alc. KOH (d) Br2 (Q.43) Which of the following have the highest boiling point: ( 1 mark ) (a) Chlorobenzene (b) o-Dichlorobenzene (c) m-Dichlorobenzene (d) p-Dichlorobenzene (Q.44) The most suitable reaction for the preparation of n-propylbenzene is: ( 1 mark ) (a) Friedel-crafts reaction (b) Wurtz reaction (c) Wurtz-fitting reaction (d) Grignard reaction (Q.45) Chlorobenzene can be obtained from benzene diazonium chloride by: ( 1 mar k ) (a) Gattermann s reaction (b) friedel craft reaction (c) Wurtz reaction (d) Fittig reaction (Q.46) Most reactive halide towards SN1 reaction is ( 1 mark ) (a) n-Butyl chloride (b) sec-Butyl chloride (c) tert-Butyl chloride (d) Allyl chloride (Q.47) When HBr is added to propene in the absence of peroxides, in the first st ep there is the addition of: ( 1 mark ) (a) H+ (b) Br (c) H (d) Br (Q.48) In the presence of benzoylperoxide propene reacts with HCl gas. The produ ct is: ( 1 mark ) (a) 2-chloropropane (b) Allyl chloride (c) No reaction (d) n-Propyl chloride (Q.49) Cl2reacts with CS2in presence of I2to form ( 1 mark ) (a) CHCl3 (b) CCl4 (c) C2H5Cl (d) Cl3C NO2
(Q.50) If chloroform is left open in air in the presence of sunlight, it gives ( 1 mark ) (a) Carbon tetrachloride (b) Carbonyl chloride (c) Mustard gas (d) Lewisite (Q.51) 1,2-dichloroethane is known to exhibit. ( 1 mark ) (a) Optical isomerism (b) Geometrical isomerism (c) Metamerism (d) Tautomerism (Q.52) 2-Bromopentane is heated with potassium ethoxide in ethanol. The major pr oduct obtained is ( 1 mark ) (a) 2-Ethoxypentane (b) Pentene-1 (c) cis-Pentene-2 (d) trans-Pentene-2 (Q.53) The reactivity order of halides for dehydrohalogenation is ( 1 mark ) (a) R F > R Cl > R Br > R I (b) R I > R Br > R Cl > R F (c) R I > R Cl > R Br > R F (d) R F > R I > R Br > R Cl (Q.54) Which of the following is correct ? ( 1 mark ) (a) A and B are same and C is different (b) A and C are same and B is different (c) A, B and C are same (d) B and C are same and A is different (Q.55) In reaction, recemization takes place. It is due to ( 1 mark ) (a) inversion of configuration (b) retention of configuration (c) conversion of configuration (d) both (a) & (b) (Q.56) Identify Z in ( 1 mark ) (a) Mixture of CH3CHClCH2Cl and CH3CHOHCH2Cl (b) CH3CHOHCH2Cl (c) CH3CHClCH2OH (d) CH3CHClCH2Cl (Q.57) The reaction of with CuCl gives ( 1 mark ) (a) (b) (c) (d) (Q.58) Which of the following will give ethanal with aqueous KOH: ( 1 mark ) (a) Chloroacetic acid (b) 1,2-Dichloroethane (c) 1,1-dichloroethane (d) ethyl chloride (Q.59) Chlorobenzene on heating with NH3under pressure in the presence of cuprou s chloride gives ( 1 mark ) (a) Benzamide (b) Nitrobenzene (c) Aniline (d) o- and p-Chloroaminobenzene (Q.60) A new carbon-carbon bond formation is possible in: ( 1 mark ) (a) Cannizzaro reaction (b) Friedel Craft reaction (c) Clemmensen reduction (d) Wurtz reaction (Q.61) Benzenehexachloride is used as: ( 1 mark )
(a) dye (b) antimalarial drug (c) antibiotic (d) insecticide (Q.62) In the reaction of p-chlorotoluene with KNH2 in liquid NH3, the major pro duct is: ( 1 mark ) (a) o- toluidine (b) m-toluidine (c) p-toluidine (d) p-chloroaniline (Q.63) Chloroform is slowly oxidized by air in presence of light to form: ( 1 ma rk ) (a) Formyl chloride (b) Phosgene (c) Trichloroacetic acid (d) Formic acid (Q.64) Butane nitrile may be prepared by heating: ( 1 mark ) (a) Propyl alcohol with KCN (b) Butyl alcohol with KCN (c) Butyl chloride with KCN (d) Propyl chloride with KCN (Q.65) Benzylchloiride can be prepared from toluene by chlorination with: ( 1 ma rk ) (a) SO2Cl2 (b) SOCl2 (c) Cl2 (d) NaOCl (Q.66) The reaction of toluene with Cl2 in the presence of FeCl3 gives predomina ntly. ( 1 mark ) (a) Benzoyl chloride (b) m-chlorotoluene (c) Benzyl chloride (d) o- and p-chlorotoluene (Q.67) When 1-chloropropane is treated with alc. KOH, it forms an alkene. The re action is: ( 1 mark ) (a) Substitution reaction (b) Elimination reaction (c) Addition reaction (d) Dehydration reaction (Q.68) The possible number of enantiomeric pairs that can be produced during mon ochlorination of 2- methyl butane is: ( 1 mark ) (a) 2 (b) 3 (c) 4 (d) 1 (Q.69) Freon-12 is commonly used as: ( 1 mark ) (a) Insecticide (b) Refrigerant (c) Solvent (d) Fire extinguisher (Q.70) The trade name of trichloroethylene is: ( 1 mark ) (a) Westrosol (b) Freon (c) Westron (d) D.D.T. (Q.71) The C-H bond distance is longest in: ( 1 mark ) (a) C2H2 (b) C2H4 (c) C2H6 (d) C2H2Br2
(Q.72) The above structural formula refers to ( 1 mark ) (b) DNA (c) DDT (d) RNA (Q.73) Which of the following alkyl halides is used as a methylating agent? ( 1 mark ) (a) C2H5Br (b) C6H5Cl (c) CH3I (d) C2H5Cl (Q.74) obtained by chlorination of n-butane, will be ( 1 mark ) (a) meso-form (b) racemic mixture (c) d-form (d) I-form (Q.75) Hydrocarbon A reacts with bromine by substitution to form an alkyl bromid e which by Wurtz reaction is converted to gaseous hydrocarbon containing less th an four carbon atoms. A is: ( 1 mark ) (a) CH2=CH2 (b) HC C (c) CH4 (d) CH3-CH3 (Q.76) Which of the following will have the maximum dipole moment? ( 1 mark ) (a) (b) (c) (d) (Q.77) alc.KOH In the reaction CH3HC2I ______________? X ________? Y ________? Z , Z is: ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3CH2CN (b) CNCH2CH2CN (c) BrCH2CH2CN (d) BrCH=CHCN (Q.78) The order of reactivity of alkyl halides towards elimination reaction is ( 1 mark ) (a) 3 > 2 > 1 (b) 2 > 1 > 3 (c) 3 > 1 > 2 (d) 1 > 2 > 3 (Q.79) When primary amine reacts with chloroform in ethanolic KOH, then the prod uct is ( 1 mark ) (a) an isocyanide (b) an aldehyde (c) a cyanide (d) an alcohol (Q.81) Freon-12 is commonly used as ( 1 mark ) (a) Insecticide (b) Refrigerant (c) A solvent (d) A fire extinguisher (Q.82) mechanism proceeds through intervention of ( 1 mark ) (a) Carbonium ion (b) Transition state (c) Free radical (d) Carbanion (Q.83) Match list I (compound) with list II (use) and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists : ( 1 mark ) List I I. Acetylsalicylic acid
II. DDT III. Naphthalene IV. Carbon tetra-chloride List II A. Insecticide B. Drug C. Moth repellent D. Fire extinguisher E. Refrigerant (a) I-B, II-A, III-C, IV-D (b) I-E, II-C, III-D, IV-A (c) I-B, II-C, III-D, IV-A (d) I-E, II-A, III-C, IV-D (Q.84) Which of the following will give vinyl chloride ? ( 1 mark ) (a) (b) (c) (d) All (Q.85) Identify the set of reagent/reaction conditions 'X' and 'Y' in the follow ing set of transformations:( 1 mark ) (a) X = dilute aqueous NaOH, 20C; Y = HBr / acetic acid, 20C (b) X = concentrated alcoholic NaOH, 80C; Y = HBr / acetic acid, 20C (c) X = dilute aqueous NaOH, 20C; Y = Br2/ CHCl3, 0C (d) X = concentrated alcoholic NaOH, 80C; Y = Br2/ CHCl3, 0C (Q.86) The reaction of benzyl chloride with sodium cyanide followed by reduction with hydrogen in the presence of nickel gives ( 1 mark ) (a) -Phenylethylamine (b) N-Isobutylaniline (c) Benzylamine (d) Aniline (Q.87) When chlorine is passed through propene at 400C, which of the following is formed? ( 1 mark ) (a) PVC (b) Allyl chloride (c) Vinyl chloride (d) 1,2-Dichloroethane (Q.88) SN2 mechanism proceeds through the intervention of: ( 1 mark ) (a) Carbonium ion (b) Transition state (c) Free radical (d) Carbanion (Q.89) Chloroform on treatment with alc.KOH and aniline gives: ( 1 mark ) (a) Phenyl isocyanide (b) Phenol (c) Cyanobenzene (d) None of these (Q.90) The product of reaction of alcoholic silver nitrate with ethyl bromide is : ( 1 mark ) (a) Ethylene (b) Ethyl nitrite (c) Nitro ethane (d) Ethyl alcohol (Q.91) In the reaction CH3CHCl2 intermediate X, X is ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3CHO (b) (CH3)2CO (c) CH3CH2OH (d) HO-CH2CH2OH (Q.92) Which of the following will have zero dipole moment? ( 1 mark ) (a) 1,1-Dichloroethylene (b) cis-1,2-Dichloroethylene
(c) trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene (d) none of these (Q.93) Only two isomeric monochloro derivatives are possible for: ( 1 mark ) (a) n-hexane (b) 2,4-Dimethylpentane (c) benzene (d) 2-methylpropane (Q.94) Alkyl halide on treatment with alc. KOH gives: ( 1 mark ) (a) Alcohols (b) Alkenes (c) Alkanes (d) Aldehydes (Q.95) Chlorination of toluene in the presence of light and heat followed by tre atment with aqueous NaOH gives: ( 1 mark ) (a) o-cresol (b) p-cresol (c) 2,4-Dihydroxytoluene (d) Benzoic acid (Q.96) Which of the following can not be used in friedel-crafts reaction: ( 1 ma rk ) (a) FeCl3 (b) FeBr3 (c) AlCl3 (d) NaCl (Q.97) The fire extinguisher with brand name Pyrene is chemically ( 1 mark ) (a) Dichloromethane. (b) Trichloromethane. (c) Tetrachloromethane. (d) Geminal dichloride. (Q.98) Reimer-Tiemann reaction involving chloroform produces ( 1 mark ) (a) Salicylic acid. (b) Benzoic acid. (c) Salicyladehyde. (d) Benzaldehyde. (Q.99) Primary and secondary chloroalkanes are prepared by passing HCl gas throu gh a suitable alcohol in the presence of anhydrous zinc chloride. This reaction is known as ( 1 mark ) (a) Swarts reaction. (b) Finkelstein reaction. (c) Borodine reaction. (d) Grove reaction. (Q.100) Breathing about 900 ppm of chloroform for a short time can cause dizzine ss, fatigue and headache. The part of body that metabolizes chloroform to phosge ne is ( 1 mark ) (a) Kidneys. (b) Gall bladder. (c) Pancreas. (d) Liver. (Q.101) In the Grove s process, chloroalkanes are prepared by passing HCl gas thro ugh a suitable alcohol in the presence of anhydrous zinc chloride. The purpose o f using zinc chloride is ( 1 mark ) (a) to help in the cleavage of C-C bond. (b) to help in the cleavage of C-H bond. (c) to help in the cleavage of C-O bond. (d) to provide the reaction with moisture free conditions. (Q.102) The chlorobenzene is commercially prepared by Raschig s process in which a mixture of benzene vapours, air and hydrogen chloride is passed over heated ( 1 mark ) (a) Copper powder.
(b) Cuprous chloride. (c) Cupric chloride. (d) Alumina. (Q.103) Bromoalkanes are obtained by refluxing a suitable alcohol with constant boiling hydrobromic acid in the presence of conc. H2SO4 as catalyst. The constan t boiling HBr has aqueous composition of ( 1 mark ) (a) 48%. (b) 58%. (c) 68%. (d) 78%. (Q.104) Iodoform was earlier used as an antiseptic for dressing wounds, its anti septic properties are due to liberation of a substance when iodoform comes in co ntact with skin, the substance is ( 1 mark ) (a) Phosgene. (b) Iodine. (c) Chlorine. (d) Hydrogen iodide. (Q.105) The addition of hydrogen halides to an unsymmetrical alkenes takes place according to ( 1 mark ) (a) SN1 mechanism. (b) SN2 mechanism. (c) Markownikoff s Rule. (d) Saytzeff s Rule. (Q.106) The alkyl halide that depletes the ozone layer significantly is ( 1 mark ) (a) Monochloromethane. (b) Dichloromethane. (c) Trichloromethane. (d) Tetrachloromethane. (Q.107) For the same alkyl group, the boiling points of haloalkanes decreases in the order ( 1 mark ) (a) RF>RCl>RBr>RI. (b) RCl>RBr>RI>RF. (c) RBr>RI>RF>RCl. (d) RI>RBr>RCl>RF. (Q.108) Most widely used refrigerant freon (freon-12) is prepared by ( 1 mark ) (a) Etard s reaction. (b) Swarts reaction. (c) Finkelstein reaction. (d) Birnbaum-Simonini reaction. (Q.109) Cinnamyl chloride is ( 1 mark ) (a) 3-Chloro-1-phenylprop-1-ene. (b) 2-Chloro-1-phenylprop-2-ene. (c) 1-Chloro-3-phenylprop-1-ene. (d) 2-Chloro-3-phenylprop-2-ene. (Q.110) DDT was first prepared in 1873 but it was not until 1939 that Paul Mulle r at Geigy pharmaceuticals in Switzerland, discovered the effectiveness of DDT a s an insecticide, he was awarded Noble Prize for this discovery in 1948 in subje ct ( 1 mark ) (a) Chemistry. (b) Medicines and Physiology. (c) Biochemistry. (d) Pharmaceuticals. (Q.111) The DDT is prepared by heating chlorobenzene with chloral in the presenc e of conc. H2SO4, the chloral is ( 1 mark ) (a) Trichloroacetaldehyde. (b) Dichloroacetaldehyde. (c) Trichloroacetone. (d) Dichloroacetone. (Q.112) The markownikoff s rule reverses in the presence of peroxide, but this is
possible only in case of ( 1 mark ) (a) HI. (b) HBr. (c) HCl. (d) HF. (Q.113) Dehydrohalogenation or elimination reactions of alkyl halides having str ongly acidic ?-hydrogen takes place through ( 1 mark ) (a) E1 mechanism. (b) E2 mechanism. (c) E1cB mechanism. (d) Benzyne mechanism. (Q.114) The nucleophilicity order of different halide ions is as ( 1 mark ) (a) I->Br->Cl->F-. (b) Br->Cl->F->I-. (c) Cl->F->I->Br-. (d) F->I->Br->Cl-. (Q.115) When chlorobenzene is treated with NaNH2 in liquid ammonia at 196K, anil ine is formed. This reaction takes place by ( 1 mark ) (a) E1 mechanism. (b) E2 mechanism. (c) E1cB mechanism. (d) Benzyne mechanism. (Q.116) During the preparation of iodoalkanes a suitable alcohol is refluxed wit h constant boiling hydriodic acid (57%). HI may also be prepared in situ by the action of ( 1 mark ) (a) Phosphoric acid on KI. (b) Sulphuric acid on KI. (c) Phosphoric acid on KIO3. (d) Sulphuric acid on KIO3. (Q.117) A copper strip is heated strongly in Bunsen flame till it ceases to impa rt any greenish or bluish flame, then a pinch of organic halide is placed on thi s hot strip and reintroduced into the flame, if a green or bluish green flame re appears it indicates the presence of halogen but does not confirm the nature of halogen. This test is ( 1 mark ) (a) Lassaigne s test. (b) Mollisch s test. (c) Victor Mayer test. (d) Beilstein test. (Q.118) Williamson s synthesis is a nucleophilic substitution reaction of alkyl ha lides which results in the formation of ( 1 mark ) (a) Esters. (b) Ethers. (c) Amides. (d) Acid anhydrides. (Q.119) The incorrect statement about DDT is ( 1 mark ) (a) The problems related to extensive use of DDT began to appear in early 1970s. (b) Many species of insects developed resistance to DDT and it was also discover ed to have high toxicity towards fish. (c) The chemical stability of DDT and its fat solubility further increased the p roblems. (d) DDT is not completely biodegradable and gets deposited in fatty tissues, its use has been banned in USA since 1973. (Q.120) The allylic bromination can be carried out with the help of ( 1 mark ) (a) N-bromosuccinic acid. (b) N-bromosalicylic acid. (c) N-bromosalicylamide. (d) N-bromosuccinimide. (Q.121) If in lassaigne s test, AgNO3 reacts with lassaigne s extract to give white ppt that are soluble in NH4OH, it indicates the presence of ( 1 mark ) (a) Fluorine.
(b) Chlorine. (c) Bromine. (d) Iodine. (Q.122) The nucleophilic substitution of halide group with isocyanide group can be affected by reacting alky halide with ( 1 mark ) (a) NaCN. (b) KCN. (c) AgCN. (d) LiCN. (Q.123) Quantitative estimation of active hydrogens in an organic compound can b e done by ( 1 mark ) (a) Lassaigne s method. (b) Mollisch s method. (c) Victor Mayer method. (d) Zerewitnoff s method. (Q.124) Benzal chloride is ( 1 mark ) (a) 1,2-Dichloro-1-phenylethane. (b) 1,1-Dichloro-1-phenylmethane. (c) 1,1-Dichloro-2-phenylethane. (d) 1,1,1-Trichloro-1-phenylmethane. (Q.125) Aryl chlorides can also prepare Grignard reagents but solvent used inste ad of ether (used for alkyl chlorides) is ( 1 mark ) (a) Pyridine. (b) Methanol. (c) Ethanol. (d) Tetrahydrofuran. (Q.126) Walden inversion takes place in ( 1 mark ) (a) Free radical mechanisms. (b) Electrophilic mechanisms. (c) SN1 mechanisms. (d) SN2 mechanisms. (Q.127) Preparation of alkyl fluorides by heating suitable chloro or bromoalkane s with inorganic fluorides such as AsF3, SbF3, CoF3, AgF, Hg2F2 etc. is known as ( 1 mark ) (a) Etard s reaction. (b) Swarts reaction. (c) Mendius reaction. (d) Birnbaum-Simonini reaction. (Q.128) Halogenation of alkanes that is reversible is ( 1 mark ) (a) Fluorination. (b) Chlorination. (c) Bromination. (d) Iodination. (Q.129) The dehydrohelogenation of haloalkanes results in the formation of ( 1 m ark ) (a) an alkane. (b) an alkene. (c) an alkyne. (d) an aromatic hydrocarbon. (Q.130) The optimum temperature for allylic halogenation of alkenes is ( 1 mark ) (a) 473K. (b) 573K. (c) 673K. (d) 773K. (Q.131) The most convenient method for the preparation of haloalkanes involves t he substitution of OH group of an alcohol by the halogen atom. For a given alcoho l, the reactivity of halogen acids decreases in the order ( 1 mark ) (a) HCl>HBr>HI. (b) HBr>HI>HCl.
(c) HI>HCl>HBr. (d) HI>HBr>HCl. (Q.132) PBr3 and PI3 used for the preparation of alkyl halides from alcohols, ar e not very stable compounds, these are generally prepared in situ by the action of a substance on bromine and iodine respectively, the substance is ( 1 mark ) (a) Red phosphorous. (b) White phosphorous. (c) Potassium iodide. (d) Silver iodide. (Q.133) If the structure of alkyl halide during dehydrohalogenation reaction is such that it can undergo H-elimination from two different sites, then the more h ighly substituted alkene is the major product. This generalization is known as ( 1 mark ) (a) Markownikoff s Rule. (b) Saytzeff s Rule. (c) Kharasch s effect. (d) Racemization. (Q.134) Side chain-halogenation of haloarenes is a reaction having ( 1 mark ) (a) SN1 mechanism. (b) SN2 mechanism. (c) Free radical mechanism. (d) Benzyne mechanism. (Q.135) The iodoalkanes can be prepared from corresponding chloro or bromoalkane s by heating with NaI in acetone or methanol, this reaction is called as ( 1 mar k ) (a) Etard s reaction. (b) Swarts reaction. (c) Finkelstein reaction. (d) Birnbaum-Simonini reaction. (Q.136) The sandmeyar reaction is modified to gattermann reaction by using a mix ture of freshly prepared copper powder in the presence of halogen acid instead o f cuprous halide dissolved in corresponding halogen acid (sandmeyer reaction), t he yield of gattermann reaction is around ( 1 mark ) (a) 40%. (b) 60%. (c) 80%. (d) 90%. (Q.137) Victor Grignard discovered Grignard reagents (RMgX) in1900, for this dis covery, he was awarded Noble Prize in chemistry in ( 1 mark ) (a) 1902. (b) 1912. (c) 1922. (d) 1932. (Q.138) Alkyl halides are converted into ethers by Williamson s synthesis, another way to convert alkyl halides into ethers is by using ( 1 mark ) (a) Silver hydroxide. (b) Sodium hydroxide. (c) Dry silver oxide. (d) Sodium peroxide. (Q.139) For the nucleophilic substitution of OH group by halide ion during the pr eparation of haloalkanes from alcohols, the reactivity order of different alcoho ls is ( 1 mark ) (a) tertiary>secondary>primary. (b) secondary>primary>tertiary. (c) primary>tertiary>secondary. (d) tertiary>primary>secondary. (Q.140) When the aqueous ethanolic solution of a haloalkane (particularly iodoal kanes) is heated with silver cyanide, the chief product formed is ( 1 mark ) (a) Alkyl cyanides. (b) Alkyl isocyanides.
(c) Alkyl cyanates. (d) Alkyl isocyanates. (Q.141) Due to prevailing basic conditions of the reaction, the Wurtz reaction i s not responded by ( 1 mark ) (a) Tertiary alkyl halides. (b) Secondary alkyl halides. (c) Primary alkyl halides. (d) Sodium metal. (Q.142) In Borodine-Hunsdiecker reaction, bromoalkanes are prepared by refluxing the silver salt of a fatty acid with bromine in ( 1 mark ) (a) Ethanol. (b) Acetone. (c) Diethyl ether. (d) Carbon tetrachloride. (Q.143) Tetraethyl lead (TEL) is an important antiknocking agent in gasoline use d for running vehicles, it is prepared by reacting alkyl halide with an alloy of lead in the presence of dry ether, the alloy of lead is ( 1 mark ) (a) Li-Pb. (b) Na-Pb. (c) Hg-Pb. (d) Zn-Pb. (Q.144) The incorrect explanation to the low reactivity of aryl halides in compa rison to that of alkyl halides is ( 1 mark ) (a) Resonance effect. (b) Difference in hybridization of carbon atoms in C-X bond. (c) Polarity of C-X bond. (d) +I effect of benzene ring. (Q.145) The silver salts of carboxylic acids on refluxing with I2 dissolved in C Cl4 gives esters of carboxylic acid instead of iodoalkanes. This reaction is kno wn as ( 1 mark ) (a) Etard s reaction. (b) Swarts reaction. (c) Finkelstein reaction. (d) Birnbaum-Simonini reaction. (Q.146) The Dow s process is used for the preparation of ( 1 mark ) (a) Chlorobenzene. (b) Fluorobenzene. (c) Bromobenzene. (d) Phenol. (Q.147) Organohalogen compound amongst the following that is used as an anaesthe tic agent is ( 1 mark ) (a) Chloramphenicol. (b) Chloroquine. (c) Chloromycetin. (d) Halothane. (Q.148) Picric acid is ( 1 mark ) (a) 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (b) 2,4,6-Trinitroaniline. (c) 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol. (d) 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene. (Q.149) The benzene diazonium chloride needed for the sandmeyer reaction to prod uce aromatic halides is produced by diazotisation reaction that takes place at ( 1 mark ) (a) 0-50C. (b) 5-100C. (c) 10-150C. (d) 15-200C. (Q.150) The metallic powder that is used in Ullmann synthesis of diphenyl is ( 1 mark ) (a) Manganese powder.
(b) Chromium powder. (c) Magnesium powder. (d) Copper powder. (Q.151) When phosphorous trihalide is reacted with a suitable alcohol to form ha loalkane, the side product of reaction is ( 1 mark ) (a) Hypophosphorous acid. (b) Phosphorous acid. (c) Phosphoric acid. (d) Pyrophosphoric acid. (Q.152) The reaction amongst the following that does not involve the use of aryl halides is ( 1 mark ) (a) Wurtz reaction. (b) Wurtz-Fittig reaction. (c) Fittig reaction. (d) Ullmann reaction. (Q.153) The allylic chlorination is generally done with chlorine at 773K, but it can also be carried out at lower temperature with the help of ( 1 mark ) (a) CuCl/HCl. (b) Cu/HCl. (c) HCl. (d) SO2Cl2. (Q.154) The chlorobenzene can be converted into benzene by reduction with nascen t hydrogen produced by an alloy(metallic) in the presence of alkali, the metalli c alloy used is ( 1 mark ) (a) Cd-Al. (b) Ni-Cd. (c) Hg-Cd. (d) Ni-Al. (Q.155) The thionyl chloride method is preferred over hydrogen chloride or phosp horous chloride method for the preparation of haloalkanes because both the by-pr oducts (SO2 and HCl) in this case are gases and escape leaving behind pure chlor oalkane. This reaction takes place in the presence of ( 1 mark ) (a) Conc. sulphuric acid. (b) Phosphoric acid. (c) Anhydrous zinc chloride. (d) Pyridine. (Q.156) The poisonous gas phosgene is chemically ( 1 mark ) (a) Thionyl chloride. (b) Carbonyl chloride. (c) Sulphonyl chloride. (d) Sulphuryl chloride. (Q.157) The fluoroarenes are prepared by heating the corresponding diazonium tet rafluoroborates that are in turn obtained by diazotisation of suitable primary a mine with aqueous NaNO2 in the presence of fluoroboric acid (HBF4) at 273-278K. This reaction is known as ( 1 mark ) (a) Balz-Schiemann reaction. (b) Swarts reaction. (c) Finkelstein reaction. (d) Birnbaum-Simonini reaction. (Q.158) The optimum temperature required for the Riemer-Tiemann reaction is ( 1 mark ) (a) 240K. (b) 340K (c) 440K (d) 540K (Q.159) The substance that is added to destroy traces of phosgene formed by aeri al oxidation of chloroform on prolonged storage is ( 1 mark ) (a) Ether. (b) Ester. (c) Alcohol.
(d) Carboxylic acid. (Q.160) The reaction of haloalkanes with aqueous sodium or potassium hydroxide o r moist silver oxide to produce alcohols is an example ( 1 mark ) (a) Elimination reaction. (b) Dehalogenation reaction. (c) Reduction reaction. (d) Hydrolysis reaction. (Q.161) The hydride ion transfer takes place at each step in the reduction done by using ( 1 mark ) (a) H2 in the presence of Nickel. (b) Sodium in the presence of ethanol. (c) LiAlH4. (d) Zn and NH4OH. (Q.162) Grignard reagents (RMgX) are potential sources of carbanions because of ( 1 mark ) (a) polar C-Mg bond. (b) +I effect of alkyl group. (c) solvent properties of ether with which it is stored. (d) their ability of react in any medium. (Q.163) The maximum dipole moment amongst the different halomethanes is that of ( 1 mark ) (a) CH3F. (b) CH3Cl. (c) CH3Br. (d) CH3I. (Q.164) Refluxing is ( 1 mark ) (a) Continuous heating of a liquid at isothermal conditions. (b) Adiabatic heating of liquid in an isolated system. (c) Adiabatic heating of liquid in an isolated system. (d) The process of heating a liquid in a flask with a condenser so that the vapo urs are condensed back into the same flask. (Q.165) Alkyl halide with Garlic like odour is ( 1 mark ) (a) vinyl chloride. (b) methyl iodide. (c) benzyl iodide. (d) allyl iodide. (Q.166) Westron is a highly toxic halogen derivative liquid used as fumigant and insecticide formed the reaction of acetylene with the halogen that is ( 1 mark ) (a) Fluorine. (b) Chlorine. (c) Bromine. (d) Iodine. (Q.167) Teflon is a white, dense, highly crystalline, extremely inert compound. Chemically it is ( 1 mark ) (a) poly monochlorotrifuoroethylene. (b) poly monofluorotrichloroethylene. (c) poly tetrafluoroethylene. (d) poly tetrachloroethylene. (Q.168) The fluorinating agent generally used for the preparation of Freon-12 is ( 1 mark ) (a) MgF2. (b) WF3. (c) TiF4. (d) SbF5. (Q.169) A hydrocarbon C5H10 does not react with chlorine but gives a single mono chloro compound, C5H9Cl in bright sunlight. Identify the hydrocarbon. ( 2 Marks ) (Q.170) Identify isomers are possible monochloro structural isomers that would b e expected to form on free radical chlorination of
(CH3)2CHCH2CH3. ( 2 Marks ) (Q.171) Write the Finkelstein reaction. ( 2 Marks ) (Q.172) Complete the following reactions: (a) C6H5ONa + C2H5Cl -------- (b) CH3CH2CH2OH + SOCl2 ------> (Q.173) p-dichlorobenzene has higher melting point and lower solubility than oand m-isomer. Explain? ( 2 Marks ) (Q.174) How will you bring about the following conversions? (a) Ethane to bromoethane (b) 1-Chlorobutane to n-octane ( 2 Marks ) (Q.175) Identify chiral and achiral molecules in each of the following pair of c ompounds. ( 2 Marks ) (Q.176) Haloalkanes react with aqueous KOH to form alcohols but react with alcoh olic KOH to form alkenes. Why? ( 2 Marks ) (Q.177) Write the Sandmeyer reaction. ( 2 Marks ) (Q.178) How will you prepare DDT? ( 2 Marks ) (Q.179) Identify the A and B in following reaction: ( 2 Marks ) (Q.180) Write the mechanism of the following reaction:( 2 Marks ) nBuBr + KCN nBuCN (Q.181) Explain why alkyl halides are generally not prepared in the laboratory b y free radical halogenation of alkanes. ( 2 Marks ) (Q.182) CHF3 is less acidic than CHCl3. Why? ( 2 Marks ) (Q.183) How the following conversions can be carried out? (a) 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane (b) Aniline to chlorobenzene (c) Benzene to diphenyl ( 3 Marks ) (Q.184) Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitutions whereas haloarenes underg o electrophilic substitutions. Why? ( 3 Marks ) (Q.185) Explain why? (a) Alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water. (b) Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions? ( 3 Mar ks ) (Q.186) Write the following name reactions. (a) Friedal-Crafts acylation. (b) Friedal-Crafts alkylation. (c) Wurtz-Fittig reaction. ( 3 Marks ) (Q.187) Write the following name reactions. (a) Gattermann reaction. (b) Balz-Schiemann reaction. (c) Hunsdiecker reaction..
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-3Dokumen6 halaman12 Chemistry Q.p.set-3HpBelum ada peringkat
- MCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenesDokumen27 halamanMCQ Halo Alkanes and ArenessarahBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1Dokumen6 halaman12 Chemistry Q.p.set-1HpBelum ada peringkat
- Multiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesDokumen27 halamanMultiple Choice Questions: Question Bank Class: Xii, Chemistry Unit 4: Haloalknaes & HaloarenesAkshita BoroBelum ada peringkat
- Set-B: Section ADokumen6 halamanSet-B: Section ADrk ZeusBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-3Dokumen8 halaman12 Chemistry Q.p.set-3Samarth ShrivastavaBelum ada peringkat
- Gate 2001 CyDokumen9 halamanGate 2001 CySumanta- 14Belum ada peringkat
- QP - Sol - NSEC 2012-13Dokumen10 halamanQP - Sol - NSEC 2012-13Vardaan Bhatnagar100% (1)
- Nsec 1999Dokumen12 halamanNsec 1999CorneliaBelum ada peringkat
- Hydrocar SHEET3Dokumen4 halamanHydrocar SHEET3Aayush SaxenaBelum ada peringkat
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankDokumen16 halamanHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Question BankBrown HustlerBelum ada peringkat
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokumen5 halamanHaloalkanes and Haloareneskavitha2511977Belum ada peringkat
- Aromatic CompoundsDokumen16 halamanAromatic CompoundsadityaBelum ada peringkat
- National Standard Examination in Chemistry 2014: QP Code C 203Dokumen15 halamanNational Standard Examination in Chemistry 2014: QP Code C 203Karan TejwaniBelum ada peringkat
- Test - D26 Dec 2022Dokumen15 halamanTest - D26 Dec 2022PrinceBelum ada peringkat
- HaloDokumen17 halamanHaloadityakatariya157Belum ada peringkat
- Prof Shekhar ChemistryDokumen9 halamanProf Shekhar Chemistryveer_sBelum ada peringkat
- MHT-CET 2016: Chemistry - Actual Test Paper: (Solution at The End)Dokumen10 halamanMHT-CET 2016: Chemistry - Actual Test Paper: (Solution at The End)SushantBelum ada peringkat
- There Is No Negative MarkingDokumen9 halamanThere Is No Negative MarkingDrk ZeusBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry ExamDokumen8 halamanChemistry ExamAnubrata SarkarBelum ada peringkat
- Aromatic Compounds (13th)Dokumen24 halamanAromatic Compounds (13th)Raju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Alkyl and Aryl Halide TestDokumen6 halamanAlkyl and Aryl Halide TestSoren Sharma50% (6)
- Practice Test Chemistry CL 12Dokumen10 halamanPractice Test Chemistry CL 12Coopin loopBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry MCQ XiiDokumen53 halamanChemistry MCQ XiiHassan RedaBelum ada peringkat
- Term 1 Model Examination 2021-22 Chemistry (043) : General InstructionsDokumen14 halamanTerm 1 Model Examination 2021-22 Chemistry (043) : General InstructionsAngelina SelinBelum ada peringkat
- Alkyl HalideDokumen8 halamanAlkyl HalideMegh Raj BhattBelum ada peringkat
- 12 Chemistry Q.p.set-4Dokumen6 halaman12 Chemistry Q.p.set-4Sai gokulBelum ada peringkat
- Organic Questions 1Dokumen3 halamanOrganic Questions 1SABARI SRINIVAS ABelum ada peringkat
- 6 - QP and MS - Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokumen9 halaman6 - QP and MS - Haloalkanes and Haloareneskrish dabhi0% (1)
- Halo Alkanes Sample PaperDokumen6 halamanHalo Alkanes Sample PapervasuBelum ada peringkat
- Sample Paper 3: ChemistryDokumen13 halamanSample Paper 3: ChemistryPr SathishBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry MCQsDokumen13 halamanChemistry MCQssopmaBelum ada peringkat
- 12th Board Test Exam Chemistry GSEB - (21-12-2023)Dokumen6 halaman12th Board Test Exam Chemistry GSEB - (21-12-2023)Jenis PatelBelum ada peringkat
- Ics - 8 Test Paper: Semester - 3Dokumen7 halamanIcs - 8 Test Paper: Semester - 3xanshahBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry 2 Year Ch-08 & 10 Marks.50 Timing: 1:30 HourDokumen2 halamanChemistry 2 Year Ch-08 & 10 Marks.50 Timing: 1:30 HourMusaddiq AzizBelum ada peringkat
- GujCET Chemistry 2010Dokumen5 halamanGujCET Chemistry 2010nayan159100% (1)
- JEE Main Chemistry Model Paper 3Dokumen6 halamanJEE Main Chemistry Model Paper 3PremKumarKalikiri100% (1)
- Chemistry: (Mock Test-1) 41Dokumen5 halamanChemistry: (Mock Test-1) 41hazeBelum ada peringkat
- Chemistry (Inter) Set 1 10Dokumen186 halamanChemistry (Inter) Set 1 10Valerie LaneBelum ada peringkat
- Halogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQDokumen11 halamanHalogen Derivetives of Alkane MCQParshantKumarBajaj92% (13)
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HODokumen29 halamanExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: O CH HO HOHet PrajapatiBelum ada peringkat
- Preboard-I Xii A Chemistry Set BDokumen8 halamanPreboard-I Xii A Chemistry Set BDiksha TBelum ada peringkat
- DPQ - 62. Questions PDFDokumen2 halamanDPQ - 62. Questions PDFAbhijeeth A.S.Belum ada peringkat
- JEE Main 2015 Sample Paper 5Dokumen15 halamanJEE Main 2015 Sample Paper 5sap_jan1981Belum ada peringkat
- VITEEE Chemistry 2014Dokumen8 halamanVITEEE Chemistry 2014SachinBelum ada peringkat
- Chemical KineticsDokumen3 halamanChemical Kineticsvivek daveBelum ada peringkat
- Indian Association of Chemistry Teachers: National Standard Examination in Chemistry 2008-2009Dokumen7 halamanIndian Association of Chemistry Teachers: National Standard Examination in Chemistry 2008-2009Anmol AroraBelum ada peringkat
- BITSAT Practise TestsDokumen336 halamanBITSAT Practise Testssiddharth1996Belum ada peringkat
- MCQ, Case-Case Study and Assertion Reason Question Bank For Periodic Assessment 1Dokumen42 halamanMCQ, Case-Case Study and Assertion Reason Question Bank For Periodic Assessment 1Mohammed AmmaarBelum ada peringkat
- JMS-5 Paper - 2Dokumen7 halamanJMS-5 Paper - 2janmanchiBelum ada peringkat
- Haloalkanes & HaloarenesDokumen8 halamanHaloalkanes & HaloarenesAyushi RaiBelum ada peringkat
- GUJCET - D22 Mar 2024Dokumen13 halamanGUJCET - D22 Mar 20249bshrutiyadav16Belum ada peringkat
- Iit JeeDokumen4 halamanIit JeeAvinash BillaBelum ada peringkat
- Haloalkanes and HaloarenesDokumen18 halamanHaloalkanes and HaloarenesBhavesh KBelum ada peringkat
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersDokumen8 halamanHaloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 MCQs Questions With AnswersThrik esh100% (1)
- Carbonyl Compounds 12thDokumen24 halamanCarbonyl Compounds 12thRaju SinghBelum ada peringkat
- SET 2 Question PaperDokumen8 halamanSET 2 Question PaperKrityapriya BhaumikBelum ada peringkat
- Chirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesDari EverandChirality in Supramolecular Assemblies: Causes and ConsequencesF. Richard KeeneBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionDari EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Lesson 2 TleDokumen9 halamanLesson 2 TleMary Ann Valenzuela BusaniaBelum ada peringkat
- BÀI TẬP THÌ HIỆN TẠI ĐƠNDokumen16 halamanBÀI TẬP THÌ HIỆN TẠI ĐƠNphoto tailieuBelum ada peringkat
- Culture of Hot Drinks: Tea and CoffeeDokumen10 halamanCulture of Hot Drinks: Tea and CoffeeHalayitBelum ada peringkat
- Calories in Indian Food - Indian Food Calories - Calorie Chart of Indian FoodDokumen2 halamanCalories in Indian Food - Indian Food Calories - Calorie Chart of Indian Foodvenkateshbabu2004Belum ada peringkat
- JD FlavorWheel BookletDokumen4 halamanJD FlavorWheel BookletVidel PenyBelum ada peringkat
- Vitamin BeerDokumen12 halamanVitamin BeerMarvin Rhick BulanBelum ada peringkat
- By: Chhavi Bajaj Priya VermaDokumen33 halamanBy: Chhavi Bajaj Priya VermaAkashVermaBelum ada peringkat
- CatalogDokumen30 halamanCatalogAliArababadiBelum ada peringkat
- Insights 5 U4 Test StandardDokumen6 halamanInsights 5 U4 Test StandardCaba ArturoBelum ada peringkat
- Revision - Basic GrammarDokumen4 halamanRevision - Basic GrammarTuisyen Dewan Hj AliBelum ada peringkat
- Fareeha Zubair LHRDokumen5 halamanFareeha Zubair LHRfareeha zubairBelum ada peringkat
- Data Stok 25kDokumen4.367 halamanData Stok 25kRosiati NarniBelum ada peringkat
- Mkt201 Term PaperDokumen26 halamanMkt201 Term PaperQQunBelum ada peringkat
- Countableuncountable-Nouns 23794Dokumen3 halamanCountableuncountable-Nouns 23794Rungthip Kumkaew100% (1)
- TM 10-7360-226-13PDokumen368 halamanTM 10-7360-226-13PAdvocate100% (1)
- Technical Service Manual: EmissioneDokumen59 halamanTechnical Service Manual: EmissioneTskBelum ada peringkat
- Cider PDFDokumen8 halamanCider PDFKimche VíctorBelum ada peringkat
- CSR of AmulDokumen20 halamanCSR of AmulBrent Miller67% (3)
- Industrial Training at Lalit Ashok BangaloreDokumen89 halamanIndustrial Training at Lalit Ashok BangaloreSatyaki Roy80% (5)
- Active and Passive VoiceDokumen14 halamanActive and Passive Voicekitty killer100% (1)
- 4 Hour Body PointsDokumen7 halaman4 Hour Body PointsMatjaz Krc100% (2)
- 2024 New Wedding BrochureDokumen12 halaman2024 New Wedding BrochureIsadora SobredoBelum ada peringkat
- Sushi KnowledgeDokumen10 halamanSushi KnowledgeAngel100% (1)
- Past Simple Interactive Worksheet: Esl / Efl ResourcesDokumen2 halamanPast Simple Interactive Worksheet: Esl / Efl ResourcesJuliana Giacobelli100% (2)
- Shopping AroundDokumen3 halamanShopping AroundLasses HazarBelum ada peringkat
- The Secrets Men KeepDokumen190 halamanThe Secrets Men KeepVienna Marie Sambajon0% (1)
- Diet Plan For 1800 Calorie DietDokumen7 halamanDiet Plan For 1800 Calorie DietAchyut TodiBelum ada peringkat
- Heritage Trees of Tiruchi DistrictDokumen4 halamanHeritage Trees of Tiruchi DistrictV.SUNDARARAJUBelum ada peringkat
- 5 Kitchen EquipmentDokumen208 halaman5 Kitchen Equipmentmelgarcia829Belum ada peringkat
- 0 Half Marathon GuideDokumen45 halaman0 Half Marathon GuidedasBelum ada peringkat