L01 Earth
Diunggah oleh
Maica Domnului0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan2 halamanEarth Formation and Geological Time The age of the Universe can be constrained from the ages of the oldest stars and by estimating the rate of expansion (Hubble Constant) The Big Bang is currently thought to have occurred at 13. Ga (i.e. 13. Billion years ago) the formation of the solar system began with accretion of cm-sized particles from the cloud forming the galactic disc. The proto-Earth heated up through a combination of meteorite impacts, gravitational contraction and radioactive decay
Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
L01_earth
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniEarth Formation and Geological Time The age of the Universe can be constrained from the ages of the oldest stars and by estimating the rate of expansion (Hubble Constant) The Big Bang is currently thought to have occurred at 13. Ga (i.e. 13. Billion years ago) the formation of the solar system began with accretion of cm-sized particles from the cloud forming the galactic disc. The proto-Earth heated up through a combination of meteorite impacts, gravitational contraction and radioactive decay
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
16 tayangan2 halamanL01 Earth
Diunggah oleh
Maica DomnuluiEarth Formation and Geological Time The age of the Universe can be constrained from the ages of the oldest stars and by estimating the rate of expansion (Hubble Constant) The Big Bang is currently thought to have occurred at 13. Ga (i.e. 13. Billion years ago) the formation of the solar system began with accretion of cm-sized particles from the cloud forming the galactic disc. The proto-Earth heated up through a combination of meteorite impacts, gravitational contraction and radioactive decay
Hak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 2
CE3A8 SMJ Geology for Engineers
Earth Formation & Geological Time
The age of the Universe can be constrained from the ages of the oldest stars and by estimating the rate of expansion (Hubble Constant). The Big Bang is currently thought to have occurred at 13.7 Ga (i.e. 13.7 billion years ago). Formation of the Solar System Material rushing outward from the Big Bang did not form a uniform cloud. Gravitational instabilites in the interstellar cloud collapsed to form nebulae. The collapsing cloud span increasingly rapidly because of conservation of angular momentum. The cloud fragmented to form many galaxies. Galaxies were initially roughly spherical but attened into disks as they continued to spin. Formation of Planets Planet formation began with accretion of cm-sized particles from the cloud forming the galactic disc. Physical collision then produced planetesimals. Gravitational accretion became important, forming bodies on scales of 10100 km. Accretion continued to form proto-planet on scales of 1001000 km. Formation of the Earth The proto-Earth heated up through a combination of meteorite impacts, gravitational contraction and radioactive decay. Eventually, it melted and dierentiated to form a Fe-Ni metallic core surrounded by a mantle of Fe-Mg silicates. The new mantle began to expel incompatible gasses. Some of the expelled material was held near Earths surface to form the oceans and atmosphere. Our knowledge of these stages of planet formation and dierentiation comes from the study of meteorites. Measuring geological time Scientists have attempted to measure the age of the Earth and the passage of geological time using many methods. Methods which do not work include religous theory, ocean chemistry and planetary cooling 1 . Absolute age is measured by radiometric dating 2 . Relative age can be deduced by correlating layers of sediment and periods of uplift, erosion and deformation (stratigraphy). Evolution of organisms through geological time means that relative age can be deduced from the characteristic fossils contained in many rocks (biostratigraphy). High-resolution tuning of the geological timescale is now possible by studying climatic uctuations induced by changes in Earths orbit (down to 1000s Myr) 3 . Universe formed Earth formed Oldest mineral Oldest volcanic rocks Oldest sedimentary rocks Oldest life (algae) Oldest land creature Oldest Hominids Homo sapiens 13700 Ma 4540 Ma 4400 Ma 4030 Ma 3800 Ma 3400 Ma 428 Ma 45 Ma 0.13 Ma
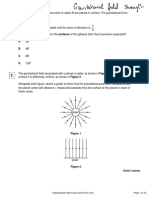
Age of the continents and oceans The mineral zircon forms by mantle melting in the presence of water and is a minor constituent of granite. Continents are formed predominantly of rocks of granitic composition. Identication of zircon crystals aged 4404 Ma therefore means that both liquid oceans and continental crust were present very early in Earths history 4 .
1 See The Chronologers Quest: The search for the age of the Earth by Patrick Wyse Jackson of TCD Geology Department (Lecky 551.7 P6) 2 The Solid Earth 6 3 See handout on Climate 4 www.nature.com/nature/journal/v409/n6817/409175A0.html
CE3A8 SMJ Geology for Engineers
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Information For Your Astrocartography ConsultationDokumen2 halamanInformation For Your Astrocartography ConsultationChandrajith NairBelum ada peringkat
- Branches of Science, Theories On The Origin of Universe/solar SystemDokumen89 halamanBranches of Science, Theories On The Origin of Universe/solar SystemImee TiloBelum ada peringkat
- 8 Concepts Infographics by SlidesgoDokumen34 halaman8 Concepts Infographics by SlidesgoKate Hernández.Belum ada peringkat
- Sa GK 1Dokumen3 halamanSa GK 1Shafiullah RahiBelum ada peringkat
- Science9-Q3-Week 7-LeaPDokumen4 halamanScience9-Q3-Week 7-LeaPMark Jayson GonzagaBelum ada peringkat
- Fazaia Inter College Minhas Kamra Science - Iv 2 Bi Monthly Exams, 2018 Time Allowed: 80 Mins Total Marks: 25Dokumen3 halamanFazaia Inter College Minhas Kamra Science - Iv 2 Bi Monthly Exams, 2018 Time Allowed: 80 Mins Total Marks: 25Kinza ZahidBelum ada peringkat
- L1.1 Universe and Solar SystemDokumen50 halamanL1.1 Universe and Solar Systemrollyn_ponceBelum ada peringkat
- Traditional Indonesian Folklore Dances by SlidesgoDokumen55 halamanTraditional Indonesian Folklore Dances by Slidesgozaidan.a080516Belum ada peringkat
- Earth Science 11 - Q1 - M1Dokumen14 halamanEarth Science 11 - Q1 - M1Carlos Samson100% (1)
- Chaotic Academia Aesthetics School Center by SlidesgoDokumen38 halamanChaotic Academia Aesthetics School Center by SlidesgoChelsy Galuh OktarinBelum ada peringkat
- Orbital Motion - Kepler's Laws: Answer KeyDokumen8 halamanOrbital Motion - Kepler's Laws: Answer KeyBilal Salaam50% (4)
- Aboriginal Star KnowledgeDokumen9 halamanAboriginal Star KnowledgeEeko A FBluBelum ada peringkat
- Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9Dokumen2 halamanComet Shoemaker-Levy 9marvinBelum ada peringkat
- Gravitational Field StrengthDokumen78 halamanGravitational Field Strengthjingcong liuBelum ada peringkat
- Essential Cosmic Perspective The 8th Edition Ebook PDFDokumen61 halamanEssential Cosmic Perspective The 8th Edition Ebook PDFalla.adams464100% (44)
- Celestial Coordinate SystemsDokumen1 halamanCelestial Coordinate SystemsAnnisa NoviaBelum ada peringkat
- Assignment Sanketh 2010110310Dokumen1 halamanAssignment Sanketh 2010110310Chiru SankethBelum ada peringkat
- Rock LegendsDokumen212 halamanRock LegendsBEATRIZ MARTINBelum ada peringkat
- Candidate's Name:: Exam Cycle: Subject: Celestial Navigation Date: Rank: Second Officer Time Allowed: 2.5 HoursDokumen4 halamanCandidate's Name:: Exam Cycle: Subject: Celestial Navigation Date: Rank: Second Officer Time Allowed: 2.5 HoursJim JimiBelum ada peringkat
- Layers of The AtmosphereDokumen9 halamanLayers of The AtmosphereKathy MartinezBelum ada peringkat
- Practice Test 42Dokumen6 halamanPractice Test 42CachiBelum ada peringkat
- What To Do For World Nature Conservation Day Infographics by SlidesgoDokumen35 halamanWhat To Do For World Nature Conservation Day Infographics by Slidesgo23353014Belum ada peringkat
- Futuristic Engineering Center by SlidesgoDokumen44 halamanFuturistic Engineering Center by Slidesgoluiz fernando alarcon rojas100% (1)
- Soal Bhs Inggris Kel 8, MuchlishinDokumen5 halamanSoal Bhs Inggris Kel 8, MuchlishinMuchlishin Muchlishin0% (1)
- Tex Italia Versus Az Textiles: The Deadlock in NegotiationsDokumen61 halamanTex Italia Versus Az Textiles: The Deadlock in NegotiationsHari ChandanaBelum ada peringkat
- Analysis of Planetary EquationsDokumen31 halamanAnalysis of Planetary EquationsIan BeardsleyBelum ada peringkat
- Salinan Dari Social Inclusion Project Proposal by SlidesgoDokumen48 halamanSalinan Dari Social Inclusion Project Proposal by SlidesgoMuthya Putri KartikaBelum ada peringkat
- Planetary Geology: StratigraphyDokumen2 halamanPlanetary Geology: StratigraphyJohn Kenneth BentirBelum ada peringkat
- Astronomy Literature ReviewDokumen8 halamanAstronomy Literature Reviewafdtvdcwf100% (1)
- DLL Grade-11-1st-Quarter-Earth-ScienceDokumen26 halamanDLL Grade-11-1st-Quarter-Earth-ScienceRhea Ann Caparas100% (5)