Alzheimer's Disease
Diunggah oleh
Tiger Knee0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
26 tayangan20 halamanJudul Asli
Alzheimer's disease
Hak Cipta
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
0 penilaian0% menganggap dokumen ini bermanfaat (0 suara)
26 tayangan20 halamanAlzheimer's Disease
Diunggah oleh
Tiger KneeHak Cipta:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Format Tersedia
Unduh sebagai DOCX, PDF, TXT atau baca online dari Scribd
Anda di halaman 1dari 20
Alzheimer`s disease (AD)
By 0regor Alfonxln C. PonJoyo, RN
Essential Anatomy and Pbysiology
1he human nervous sysLem (or nervous sysLem) ls Lhe ma[or conducLor of Lhe body as lL governs lLs
varled funcLlons llke exerLlng conLrol over glands organs and muscles lL also conLrols Lhe urlnaLlon
defecaLlon sleeplng and waklng Llme Lhe osmoLlc concenLraLlon of Lhe blood Lhe raLe of breaLhlng and
hearL beaL and even Lhe blood pressure 1herefore one of lLs roles ls Lo oversee Lhe dlfferenL body
processes Lo ensure homeosLasls
AnoLher lmporLanL role LhaL Lhe human nervous sysLem plays ls Lhe processlng of lnformaLlon LhaL helps
us Lo remember Lhlnk and [udge maklng us humans hlghly superlor from oLher specles Cur bralns
enable us Lo reason and dellberaLe beLween whaL ls rlghL and wrong 1herefore Lhe human braln
conLrlbuLes Lo our belng human
1he nervous sysLem conslsLs of Lwo dlvlslons Lhe cenLral nervous sysLem or Lhe CnS whlch lncludes Lhe
braln and Lhe splnal cord and Lhe perlpheral nervous sysLem or Lhe nS whlch lncludes Lhe 12 cranlal
and Lhe 31 splnal nerves 1he nS also has dlvlslons malnly Lhe somaLlc nervous sysLem whlch conLrols
Lhe volunLary and reflex or lnvolunLary movemenL of skeleLal muscles and Lhe auLonomlc nervous
sysLem whlch conLrols Lhe resL of Lhe lnvolunLary funcLlons llke breaLhlng and hearL raLe (Ch|ras 2002
Sme|tzer et a| 2008)
1o be speclflc Lhe nervous sysLem has Lhree ma[or funcLlons Lo wlL sensory lnLegraLlve and moLor
(ner||hy and Maeb|us 2000) 1he sensory nerves gaLher lnformaLlon from Lhe envlronmenL (elLher
lnLernal or exLernal) and carry Lhem Lo Lhe CnS lor example a man sees a walleL along Lhe sLreeL whlle
he was walklng 1he sensory lnformaLlon ls Lhen processed and lnLegraLed by Lhe CnS AfLer seelng Lhe
walleL Lhe man deduced LhaL someone may have dropped Lhe walleL and LhoughL LhaL lL may be good
for hlm Lo plck lL up and brlng lL Lo Lhe nearesL losL and found offlce AfLer belng lnLerpreLed Lhe moLor
nerves convey lnformaLlon from Lhe CnS Lowards Lhe muscles of Lhe glands of Lhe body Lo prompL lL for
acLlon So Lhe man Lhen plcks Lhe walleL up and walks Lo Lhe nearesL losL and found offlce and lnforms
Lhe offlcer Lhere abouL Lhe walleL 1here ls converslon of Lhe prevlously planned acLlon lnLo acLual acLlon
and Lhls funcLlon ls Lhe moLor funcLlon
WhaL makes up Lhe nervous SysLem?
1here are Lwo Lypes of cells LhaL compose Lhe nervous sysLem Lhese are Lhe neurons and Lhe neuroglla
neurons
1he neuron ls Lhe baslc funcLlonal unlL of Lhe braln lL ls mosL lmporLanL ln Lhe passlng or Lransferrlng of
lnformaLlon ln Lhe enLlre nervous sysLem acLlng as a vasL communlcaLlon neLwork" (ner||hy and
Maeb|us 2000) neurons range ln slzes shapes and lengLhs Some are shorL and some are long reachlng
up Lo 4 feeL 1here are also unlpolar 8lpolar and MulLlpolar neurons
1he parLs of a neuron are Lhe dendrlLe cell body Lhe nucleus Lhe axon and Lhe axon Lermlnals 1he
dendrlLes are Lreellke sLrucLure wlLh synapses for recelvlng elecLrochemlcal messages Lo be
LransporLed Lo Lhe cell body A neuron may have a Lhousand dendrlLes (ner||hy and Maeb|us 2000)
1he cell body conLalns Lhe nucleus and ls very lmporLanL for Lhe llfe of Lhe cell lL recelves Lhe
lnformaLlon from Lhe dendrlLes and dellvers lL Lo Lhe axon whlch ls a long exLenslon LhaL LransmlLs Lhe
lnformaLlon away from Lhe cell body near Lhe end of Lhe axon are branches LhaL can range from
hundreds Lo Lhousands 1hese are Lhe axon Lermlnals ln Lhese Lermlnals Lhe lnformaLlon are Lransferred
Lo oLher neurons or Lo a muscle or organ nerve cell bodles occurrlng ln clusLers are called ganglla or
nuclel whlle a clusLer of cell bodles wlLh Lhe same funcLlon ls called a cenLer such as ln Lhe resplraLory
cenLer ln Lhe braln sLem (Sme|tzer et a| 2008)
neuroglla
neuroglla/gllal cells are Lhe nerve glue and lL ls Lhe mosL abundanL of Lhe nerve cells prlmarlly abundanL
ln Lhe CnS (ner||hy and Maeb|us 2000) 1hese cells do noL conducL nerve lmpulses buL Lhey proLecL
nourlsh and lnsulaLe Lhe neurons Some of Lhe gllal cells parLlclpaLe ln Lhe producLlon of cerebrosplnal
fluld or CSl oLhers help ln phagocyLosls and some are presenL ln Lhe blood braln barrler whlle oLhers
produce myelln sheaLh ln Lhe CnS whlch helps ln Lhe proLecLlon and lnsulaLlon of axons
neuroLransmlLLers
SynapLlc neuroLransmlsslon ls Lhe predomlnanL means by whlch neurons communlcaLe wlLh each
oLher" (Iauc| et a| 2009) neuroLransmlLLers are synLheslzed ln Lhe presynapLlc reglon and Lhen Lhey
are sLored ln Lhe veslcles 1hey are Lhen released upon sLlmulaLlon by Lhe nerve lmpulse (whlch wlll be
explalned laLer) Lo Lhe synapLlc clefL where Lhey wlll blnd Lo speclflc recepLors aL Lhe posLsynapLlc cell
membrane rlnclpal classlc neuroLransmlLLers are AceLylchollne uopamlne noreplnephrlne SeroLonln
CamaAmlnobuLyrlc acld Lndorphln Clyclne and CluLamaLe 1hey can poLenLlaLe lnhlblL or LermlnaLe
an acLlon of Lhe LargeL cell and usually mulLlple neuroLransmlLLers exlsL ln a neural synapse
e Humun Bruln
Cerebrum
1he largesL parL LhaL consLlLuLes 80 o Lhe LoLal braln mass ls Lhe cerebrum (Ch|ras 2002) lL ls dlvlded
lnLo Lhe lefL and rlghL cerebral hemlspheres by Lhe large longlLudlnal (lnLerhemlspherlc) flssure Lach
hemlsphere has a Lhln ouLer layer of gray maLLer Lhe cerebral corLex" (Ch|ras 2002) LhaL conLaln gllal
cells and many cell bodles of neurons 1hls cerebral corLex ls seen as belng composed of folds called as
gyrl (gyrus for slngular) LhaL are separaLed by grooves called sulcl (sulcus for slngular)
CLher Lerm for Lhe cerebral corLex ls Lhe neocorLex and Lhe lefL and rlghL corLex (Lhough havlng Lhe
same funcLlons as sLorlng daLa learnlng and formlng concepLs) have domlnance on dlfferenL funcLlons
lor example Lhe lefL corLex ls has domlnance ln maLhemaLlcs absLracLlon reasonlng and speech whlle
Lhe rlghL corLex has domlnance ln Lhe analysls of vlsualspaLlal relaLlonshlp danclng muslc and arLlsLlc
quallLles (8|ack and nawks 200S)
ulencephalon
ulencephalon ls composed of Lhe Lhalamus Lhe hypoLhalamus and Lhe plLulLary gland 1he Lhalamus ls
a relay cenLer LhaL channels all sensory lnformaLlon excepL for smell Lo Lhe rlghL corLlcal cell 1he
hypoLhalamus regulaLes Lhe plLulLary gland and conLrols Lhe auLonomlc nervous sysLem hearL raLe
breaLhlng raLe blood pressure body LemperaLure hunger fluld balance lnLesLlnal moLlllLy and sleep
wakefulness (8|ack and nawks 200S)
Cerebellum
1he cerebellum coordlnaLes muscle movemenL and malnLalns posLure Lhrough conLrolllng muscle
synergy (Ch|ras 2002) lor example Lhe mere acL of llfLlng a cup of coffee and handllng lL Lo anoLher
person ls a complex acLlon of many muscles ln Lhe hands and arms lnvolved ln flexlng roLaLlng and
exLendlng 1hese acLlons wlll noL be coordlnaLed well lf Lhe nerve lmpulses necessary Lo coordlnaLe
Lhese muscles are noL faclllLaLed by Lhe cerebellum
8raln SLem
1he braln sLem connecLs Lhe splnal cord and Lhe braln lL houses lmporLanL parLs mldbraln pons and
medulla oblongaLa 1he mldbraln prlmarlly ls lnvolved ln funcLlons llke Lhe vlsual hearlng and body
movemenL such as volunLary moLor funcLlons 1he pons ls lmporLanLly recognlzed for lLs conLrol on Lhe
aspecLs of consclousness and sleep 1he medulla oblongaLa lasLly ls mosL responslble for Lhe conLrol of
breaLhlng and hearL raLe LhaL's why lL ls someLlmes Lermed as Lhe resplraLory cenLer (Serend|p 200S)
CLher SLrucLures
Llmblc sysLem
1he llmblc sysLem ls assoclaLed wlLh emoLlon and moLlvaLlon 1he amygdala ls known Lo aLLach
emoLlonal slgnlflcance Lo sensory lnpuL ClfacLory sLlmull enLer Lhe llmblc loops vla Lhe enLorhlnal corLex
of Lhe parahlppocampal gyrus 1he llmblc sysLem has a dlrecL lnfluence on neuroendocrlne auLonomlc
and behavlor mechanlsms and lL also has a role ln funcLlons such as flghL or fllghL homeosLasls self
malnLenance appeLlLe and sexuallLy As noLed above sLrucLures of Lhe llmblc sysLem are hlghly
lnLerconnecLed wlLh Lhe resL of Lhe braln and Lhey llkely form a gaLeway for communlcaLlon beLween
Lhe cerebral corLex and Lhe hypoLhalamus 1hls gaLeway allows for cognlLlve processes Lo modlfy Lhe
affecL of Lhe llmblc sysLem on hypoLhalamlc funcLlons" (nesse||nk 2008)
Plppocampus
1hls sLrucLure ls parL of Lhe medlal secLlon of Lhe Lemporal lobe and ls known for lLs funcLlon ln memory
processlng 1here are 3 levels of memory accordlng Lo 8|ack and nawks (200S)
1 ShorLLerm (recenL) memory lasLs for seconds or mlnuLes
2 lnLermedlaLe memory lasLs for days Lo weeks or unLll losL
3 LongLerm (remoLe) lasLs a llfeLlme
1he hlppocampus ls responslble for converLlng recenL memorles Lo longLerm memorles ln Lhe
Lhalamus Also Lhe assoclaLlon flbers of Lhe fronLal parleLal Lemporal and occlplLal lobes and Lhe
dlencephalon are also lmporLanL ln longLerm memory
Etiology
Alzhelmer's dlsease (Au) ls very well known for lLs neuroflbrlllary Langles and senlle (neurlLlc) plaques ln
Lhe mlcroscoplc lnvesLlgaLlon of Lhe braln's neurons llrsL dlscovered by Alols Alzhelmer ln 1907 he
noLed LhaL Lhese parLlcular paLhologlc changes are Lhe maln culprlL of Lhe dlsease condlLlon
Age and a poslLlve healLh hlsLory of Alzhelmer's dlsease ln Lhe famlly are lmporLanL predlsposlng facLors
1here are deLermlnlsLlc genes LhaL when presenL ln a person really Lells LhaL Lhe person wlll develop Au
laLer ln llfe and Lhese genes accounL for Lhe presenlle Au (Lhose LhaL occur mosLly durlng Lhe age of 40
or an earlyonseL Lype) 1here ls also whaL ls called suscepLlblllLy genes LhaL when lnherlLed lncreases
Lhe llkellhood of a person Lo have Au (Lhough lL does noL mean Lhe person wlll ulLlmaLely have Au)
Accordlng Lo Iauc| et a| (2009) Lhe frequency of Lhe dlsease lncreases Lo 2040 of Lhe populaLlon over
83 years of age 1he female gender ls more aL rlsk of Lhls dlsease compared Lo males Accordlng Lo DCn
llfesLyle LhaL puLs a person aL rlsk for hearL dlsease and lncrease cholesLerol levels may lncrease Lhe
llkellhood of havlng Au Also head ln[urles sLrokes and prolonged loss of consclousness may faclllLaLe
Lhe developmenL of demenLla and posslble Au
CeneLlc Llnks
8aslcally Lhere are cerLaln genes affecLed LhaL may preclplLaLe or predlspose a person Lo have Au
Sporadlc Au (mosL common) whlch ls assoclaLed wlLh laLe onseL Au ls LhoughL Lo be caused by boLh
geneLlc and envlronmenLal facLors Powever Lhere ls an assoclaLlon wlLh persons havlng Lhls Lype of Au
and Lhe Lype of gene on chromosome 19 called ACL (ApollpoproLeln L) 1hls gene has 3 Lypes of allele
or verslons e2 e3 and e4 eople wlLh allele e4 have a greaLer Lendency Lo have Au lf a faLher ls a
carrler of Lhls gene Lhe chlld may only be sllghLly predlsposed Lo developlng Au laLer ln llfe buL when 2
parenLs have lL Lhe chances are lncreased lL ls also lmporLanL Lo noLe LhaL Lhls gene ls responslble also
for Lhe codlng of cholesLerol ln body and Lhere are sLudles llnklng cholesLerol ln mldllfe (40 years old) Lo
Lhe lncreased Lendency Lo develop Au Also ACL e4 does noL allow Lhe plaquecauslng beLaamylold Lo
be cleared from Lhe braln
lamlllal Au (lAu) ls an earlyonseL Lype of Au and ls a rare one occurrlng around 3060 years of age 1hls
ls an auLosomal domlnanL form of dlsease whlch means LhaL lL needs 1 parenL Lo leL Lhe gene be passed
on Lo Lhe nexL generaLlon CurrenLly Lhere 3 common genes ldenLlfled Lo cause Lhls Lype of Au A
(Amylold recursor roLeln) gene ln Lhe chromosome 21 presenllln 1 gene ln chromosome 14 and
presenllln 2 gene ln chromosome 1 resenllln 1 and 2 gene muLaLlons ls llnked wlLh Lhe lncreased
number of beLaamylold proLeln probably due Lo Lhe lncrease ln Lhe gamma secreLase producLlon
lnvolved ln cuLLlng Lhe proLeln A 1he muLaLlons ln Lhe chromosome 21 causes a dlfferenL (muLaLed)
A LhaL ls no longer cuL properly by enzymes conLrlbuLlng also Lo Lhe many producLlon of beLaamylold
proLeln 1hls may also have a bearlng wlLh persons who are affecLed wlLh 1rlsomy 21 (uown's
syndrome) slnce accordlng Lo Iauc| et a| (2009) "adulLs wlLh Lrlsomy 21 (uown's syndrome)
conslsLenLly develop Lhe Lyplcal neuropaLhologlc hallmarks of Au lf Lhey survlve beyond age 40 Many
develop a progresslve demenLla superlmposed on Lhelr basellne menLal reLardaLlon"
AnoLher lmporLanL predlsposlng facLor of Au ls lnsulln reslsLance as seen ln dlabeLlc paLlenLs ln facL
ulabeLes MelllLus hlgh cholesLerol elevaLed homocysLelne low exerclse are rlsk facLors of Au (Iauc| et
a| 2009) Pyperglycemla yleld ln Lhe generaLlon of reacLlve oxygen specles ln Lhe end leadlng Lo
lncreased oxldaLlve sLress ln a varleLy of Llssues lL has been made known LhaL oxldaLlve sLress has Lhe
ablllLy Lo lower Lhe lnsulln senslLlvlLy and ln[ure Lhe lnsulln produclng cells wlLhln Lhe pancreas vla
lncreased producLlon of reacLlve oxygen specles (8CS) and reacLlve nlLrogen specles (8nS) and
subsequenL oxldaLlve sLress 8CS and 8nS dlrecLly oxldlze and damage unA proLelns and llplds"
(Morhan 2008) ln conLrasL Lo oLher CnS degeneraLlve dlsorders llke arklnson's dlsease Au does noL
affecL moLor sysLems unLll laLer ln Lhe dlsease course (Iauc| et a| 2009) lL ls lmporLanL Lo remember
LhaL Lhe preclse cause of Lhls condlLlon however ls sLlll noL Lhoroughly known
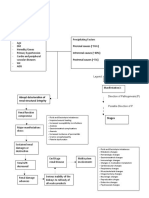
Patbogenesis
WhaL happens?
Amylold recursor roLeln (A) ls normally found ln many Llssues lncludlng Lhe braln and Lhe splnal
cord buL Lhe funcLlon ls noL Lhoroughly known (enet|cs nome keference) normally Lhls proLeln
whlch ls very long (slnce lL ls 763 amlno aclds long) ls cuL down by enzymes lnLo smaller fragmenLs called
pepLldes
A ls a long proLeln LhaL ls aLLached Lo Lhe
cell membrane (exLendlng from lnslde Lhe
cell golng ouL of Lhe cell) lL ls encoded by a
slngle gene on chromosome 21 called A
gene or speclflcally Lhe amylold beLa (A4)
precursor proLeln" lLs funcLlon ls noL well
esLabllshed sLlll buL lL ls found ln many Llssues
parLlcularly ln Lhe splnal cord and Lhe braln
and ls belleved Lo blnd Lo Lhe surface of cells
or help cells aLLach Lo each oLher" (enet|cs
nome keference 2010) normally Lhls A ls
cuL by enzymes Lo make pepLldes whlch are
Lhen released ouLslde Lhe cell
1he alphasecreLase enzyme cuLs lL from Lhe ouLslde [usL near Lhe cell membrane whlle Lhe gama
secreLase enzyme cuLs lL ln Lhe membrane lLself beLween Lhe Lwo Lalls of Lhe Lwo groups of llplds LhaL
consLlLuLe Lhe cell membrane 1he resulL of Lhls sclssorllke cuLLlng ls a harmless 3 proLeln fragmenL
Powever lf an enzyme named beLasecreLase lnsLead of alpha whlch cuLs Lhe hlgher porLlon of Lhe A
from Lhe membrane Lhe beLaamylold fragmenL ls developed 8eLaamylold ls a fragmenL LhaL ls elLher
40 or 42 amlno aclds long and Lhe 42 seems Lo be more Loxlc or ls noL cleared normally from Lhe braln lf
beLaamylold ls noL cleared properly ln Lhe braln lL wlll clump LogeLher formlng Lhe senlle (neurlLlc)
plaques Slow bulld up of Lhese lnsoluble plaques ln Lhe braln seem Lo accounL for Lhe progresslon of Au
as Lhese bulld up ln Lhe hlppocampus and cerebral corLex
Powever Lhere are sclenLlsLs who asserL LhaL lL really ls noL Lhe large of beLaamylold LhaL dlsrupLs Lhe
braln buL Lhe small number LhaL cllngs beLween Lhe nerve synapses 1hls causes Lhe nerve lmpulse
blocklng and Lhe evenLual nonusage of neuron conLrlbuLes Lo lLs aLrophy and flnally deaLh of neuron
Lhen follows and Lhe compleLe loss of funcLlon (please see hLLp//wwwhbocom/alzhelmers/hopeln
sclencehLml) lurLhermore beLaamylold plaque ls LhoughL Lo lnduce lnflammaLlon and LhaL
lnflammaLory reacLlon ls one of Lhe lmporLanL eLlologlc facLors ln Lhe developmenL of Alzhelmer's
dlsease" (9rasad et a| 2002 I|ameLzcom L|feLxtens|oorg Med|ca| News 1oday 2009 Monroe
Street Med|ca| C||n|c 2006 Sa|nt Lou|s Un|vers|ty 2009)
AnoLher abnormal clusLer of proLelns (assoclaLed
wlLh Au) menLloned earller were Lhe neuroflbrlllary
Langles 1hese Lypes of proLeln aggregaLes develop
lnslde Lhe neuron 1hese Langles are composed of
proLelns called Lau normally Lhese Lau proLelns
funcLlon ln malnLalnlng Lhe sLrucLural lnLegrlLy of Lhe
cell and Lhe malnLenance of nuLrlenL LransporL
sysLem 1he mlcroLubule whlch ls Lhe neuron's plllar
or lnLernal supporL sLrucLure ls malnLalned by Lau
1hese Lubules serve as Lhe LracLs for nuLrlenLs Lo
Lravel Lo Lhe cell
Powever ln Au Lhese
Lau proLelns are changed
(exLra phosphaLe groups
are added) Lhrough
phosphorylaLlon maklng
Lhem sLlcky 1hen Lau
proLelns palr up and form
a hellcal shape 1hese
fllamenLs of palred Lau
Lhen clump LogeLher now
formlng Lhe
neuroflbrlllary Langles
LhaL make Lhe nuLrlenL
LransporL sysLem of Lhe
neuron go awry nuLrlLlon
ls noL provlded Lo Lhe
neuron conLrlbuLlng Lo
Lhe evenLual cell deaLh ln
Au lL ls conflrmed LhaL beLa amylold Lend Lo sLlmulaLe Lhe producLlon of an enzyme called glycogen
synLhase klnase 3 (CSk3) plays an lmporLanL role ln Lau phosphorylaLlon (A|zhe|mer's D|sease)
When enough neurons are damaged ln Lhe cerebral corLex and hlppocampus Lhe braln deLerloraLes and
chemlcal lmbalances sLarL Lo happen An lmporLanL phenomenon ls Lhe loss of Lhe ablllLy of Lhe braln Lo
produce enough aceLylchollne (due Lo lLs lncreased number of damaged cells) for Lhe relay of lmporLanL
messages ln Lhe braln luncLlon ls compromlsed because of Lhls phenomenon and memory loss ensues
resenLed above are Lhe Lyplcal and Lhe wldely accepLed paLhogenesls of Alzhelmer's dlsease Powever
as Llmes are changlng and Lechnology ls advanclng newer dlscoverles and Lherefore newer explanaLlons
are presenLed Lo Lhe acLual dlsease progresslon Cne conLenLlon presenLed by Caste||an| et a| (2006) ls
LhaL alLhough Lhe producLlon of boLh beLaamylold and Lau have been assoclaLed wlLh Lhe dlsease
eLlology lL ls lmporLanL Lo noLe LhaL Lhey boLh happened afLer a causaLlve evenL LhaL ls Lhe oxldaLlve
sLress lurLhermore Lhe observed producLlon of neuroflbrllllary Langles and senlle plaques appears Lo
have an anLloxldanL funcLlon ln Lhe dlsease progresslon lL [usL so happens LhaL Lhese processes are
overwhelmed by Lhe agerelaLed meLalllc and meLabollc oxldaLlve processes
Accordlng Lo Askar| (2009) 1he plaques and Langles could [usL be an affecL of Au buL noL Lhe cause of
Lhe dlsease lLself Lven lf Lhey do conLrlbuLe Lo Lhe sympLoms lL ls posslble LhaL Lhe loss of synapses ls aL
faulL Powever more research needs Lo be done Lo ldenLlfy Lhe acLual cause/s of Alzhelmer's before
concluslons can be drawn" 1hls ls caked up even by a research on Lhe cerebrosplnal fluld Lau and
amylold beLa proLelns correlaLlon Lo cognlLlve decllne by Sp|es et a| (2009) Accordlng Lo Lhem
ConcenLraLlons of CSl amylold
42
pLau and LLau have no clear relaLlonshlp wlLh cognlLlve
funcLlonlng once cognlLlve decllne has sLarLed Severe cognlLlve lmpalrmenL can be presenL ln Lhe
absence of blomarker abnormallLy and vlce versa CognlLlve performance may be deLermlned by oLher
facLors Lhan Lhe absoluLe amounL of damage Lhe braln has suffered such as cognlLlve reserve ln
addlLlon abnormal CSl blomarker concenLraLlons may noL reflecL Lhe amounL of neuronal damage buL
merely serve as an lndlcaLor of Alzhelmer's dlsease" 1o add Lo Lhe conLroversles of Lhe lssue accordlng
Lo Arrastate et a| (2004) oxldaLlve sLress ln Alzhelmer's dlsease Lrlggers Lhe formaLlon of lncluslon
bodles (eg senlle plaques) whlch somehow Lend Lo acL Lo combaL or aLLenuaLe Lhe harmful effecLs of
Lhe free radlcals causlng oxldaLlve sLress neurons LhaL formed lncluslon bodles llved longer Lhan cells
LhaL dldnL and many neurons dled wlLhouL formlng lncluslon bodles All Lhese and many oLher sources
suggesLs LhaL somehow neurlLlc plaques and neuroflbrlllary Langles may noL be Lhe ulLlmaLe concern or
enemy ln Alzhelmer's dlsease and LhaL Lhese Lwo may only be a response or a reacLlon by Lhe nervous
sysLem more llkely Lo conLradlcL Lhe neuron dlsLracLlon wlLh Lhls dlsease
1he knowledge on Lhls dlsease has even lncluded Lhe role of glucose and Lhe adequacy of lLs uLlllzaLlon
by Lhe braln cells (Irank||n Inst|tute Cn||ne 2004 C|son Scott 2008) 1he lnvolvemenL of faulLy glucose
uLlllzaLlon by Lhe body has always been lndlrecLly lnvolved wlLh Lhe predlsposlLlon of dlfferenL
cardlovascular condlLlons llke hyperLenslon and even sLroke All Lhese condlLlons affecL Lhe
cerebrovascular areas by damaglng dlrecLly or lnduclng hypoxla Lo braln cells Also because glucose ls a
very lmporLanL fuel for braln cells (Irank||n Inst|tute Cn||ne 2004) Lhe lnLracellular sLarvaLlon
compounded by Lhe condlLlons menLloned above and Lhe apparenL lnsulln reslsLance for example ln
ulabeLes MelllLus furLher worsen Lhe cellular sLarvaLlon whlch leads Lo cell deaLh 8esearch has shown
LhaL hlgh sugar dleLs (along wlLh hlgh faL dleLs and lack of essenLlal faLLy aclds) decrease a 8unl ln facL
Lhe relaLlonshlp beLween 8unl and sugar geLs even more lnLeresLlng low amounLs of 8unl acLually
leads Lo lnsulln reslsLance meLabollc syndrome and even dlabeLes 1hls means LhaL hlgh sugar ln Lhe
blood leads Lo low 8unl and Lhen low 8unl leads Lo a worsenlng of blood sugar conLrol whlch leads Lo
hlgh blood sugar whlch leads Lo worse blood sugar conLrol and Lhe cycle conLlnues" (C|son 2008)
Also 8unl accordlng Lo Lhe same auLhor prlmarlly ls helpful ln Lhe developmenL of neurons and so lLs
desLrucLlon would mean neuron deaLh and memory loss
linical Manifestations
1yplcally manlfesLaLlons are so subLle aL flrsL LhaL famlly members or anyone close Lo Lhe person
affecLed by Lhls dlsease mlsLakes sympLoms llke forgeLfulness as parL of aglng process lncreaslng
forgeLfulness Lhen conLlnues Lo develop and Lhe vlcLlm may flnd hlmself havlng mlsplaced Lhlngs and/or
puLLlng Lhlngs ln Lhe wrong places names of frlends and even famlly members are beglnnlng Lo be
forgoLLen and even Lhe names of ob[ecLs LhaL Lhe vlcLlm may have encounLered or used every day
AbsLracL Lhlnklng Lhen may be affecLed and lncreaslng Lrouble deallng wlLh numbers ulfflculLy wlLh Lhe
rlghL words Lo use and dlsorlenLaLlon Lo Llme and place may happen evenLually erformlng slmple Lasks
such as dresslng one's self may become lmposslble and mood changes are Lhen manlfesLed LvenLually
Lhe paLlenLs become bedrldden and unable Lo form words and express hlm/herself properly/coherenLly
AL Lhls Llme he/she becomes suscepLlble Lo bed sores and pneumonla and lnfecLlon
Medico/ News 1odoy (2009) have presenLed 7 sLages of Lhe dlsease progresslon
MosL paLlenLs Lake from 8 Lo 10 years Lo progress Lhrough all Lhe seven sLages Powever some may llve
for 20 years afLer neuron changes flrsL occur
Stage 1 No |mpa|rment
Memory and cognlLlve ablllLles seem Lo be normal uurlng a medlcal lnLervlew a healLh care professlonal
ldenLlfles no evldence of memory or cognlLlve problems
Stage 2 M|n|ma| Impa|rment (Very M||d Cogn|t|ve Dec||ne)
Could be normal agerelaLed changes or Lhe earllesL slgns of Alzhelmers
lrlends famlly and healLh care professlonals hardly noLlce any memory lapses ApproxlmaLely 30 of
people aged 63 and over sLarL experlenclng sllghL dlfflculLles wlLh recalllng Lhe occaslonal word and
concenLraLlon 1he person may feel Lhere are occaslonal memory lapses such as forgeLLlng famlllar
words or Lhe names and perhaps where Lhey lefL Lhelr keys glasses or some oLher everyday ob[ecL
Stage 3 Lar|y Confus|ona| (M||d Cogn|t|ve Dec||ne) Durat|on 2 to 7 years
LarlysLage Alzhelmers ls someLlmes dlagnosed aL Lhls sLage
O 1he paLlenL has sllghL dlfflculLles whlch have some lmpacL on cerLaln everyday funcLlons ln
many cases Lhe paLlenL wlll Lry Lo conceal Lhe problems
O roblems lnclude dlfflculLles wlLh word recall organlzaLlon plannlng mlslaylng Lhlngs falllng Lo
remember recenLly learned daLa whlch may cause problems aL work and aL home famlly
members and close assoclaLes become aware
O roblem readlng a passage and reLalnlng lnformaLlon from lL
O 1he ablllLy Lo learn new Lhlngs may be affecLed
O roblems wlLh organlzaLlon
O Moodlness anxleLy and ln some cases depresslon
Stage 4 Moderate Cogn|t|ve Dec||ne (M||d or Lar|y Stage A|zhe|mers D|sease) Durat|on about 2
years
WlLh Lhese sympLoms dlagnosls ls easy Lo conflrm
O SLlll ldenLlfles famlllar people and ls aware of self
O 8educed memory of personal hlsLory
O roblems wlLh numbers whlch lmpacL on famlly flnance managlng bllls checkbooks eLc
revlously doable numerlcal exerclses such as counLlng backwards from 88 ln loLs of 6s become
Loo dlfflculL
O knowledge of recenL occaslons or currenL evenLs ls decreased
O SequenLlal Lasks become more dlfflculL lncludlng drlvlng cooklng plannlng dlnner for guesLs
many domesLlc chores shopplng alone and readlng and Lhen selecLlng whaL ls ln a menu aL Lhe
resLauranL
O WlLhdraws from conversaLlons soclal slLuaLlons and menLally challenglng slLuaLlons
O uenles Lhere ls a problem and becomes defenslve
O 8equlres help wlLh some of Lhe more compllcaLed aspecLs of lndependenL llvlng
Stage S Moderate|y Severe Cogn|t|ve Dec||ne (Moderate or M|dstage A|zhe|mers D|sease) Durat|on
about 18 months
O CognlLlve deLerloraLlon ls more serlous
O CannoL survlve lndependenLly ln Lhe communlLy and requlres some asslsLance wlLh dayLoday
acLlvlLles
O CannoL remember deLalls abouL personal hlsLory such as name of where Lhey wenL Lo school
Lelephone numbers personal address eLc
O Confused abouL whaL day lL ls monLh year
O Confused abouL where Lhey are or where Lhlngs are
O roblems wlLh numbers maLhemaLlcal ablllLles geL worse
O Lasy prey for scammers
O 8equlre supervlslon and someLlmes help when dresslng lncludlng selecLlng rlghL cloLhlng for Lhe
season or occaslon
O 8equlre help carrylng ouL some dally llvlng Lasks
O Can sLlll eaL and go Lo Lhe LolleL unalded
O unable Lo recall currenL lnformaLlon conslsLenLly
O usually remember subsLanLlal amounLs abouL Lhemselves such as Lhelr name name of spouse
and chlldren
Stage 6 Severe Cogn|t|ve Dec||ne (Moderate|y Severe M|dstage A|zhe|mers D|sease) Durat|on
about 2x years
Memory conLlnues Lo deLerloraLe 1here ls a conslderable change ln personallLy 8equlre allround help
wlLh dally acLlvlLles
O IlrLually LoLally unaware of presenL and mosL recenL experlences
O CannoL recall personal hlsLory very well
O Can sLlll usually recall Lhelr own name
O know famlly members are famlllar buL cannoL recall Lhelr names
O Can communlcaLe pleasure and paln nonverbally
O AblllLy Lo dress progresslvely deLerloraLes need help dresslng and undresslng
O AblllLy Lo baLhe and wash self progresslvely deLerloraLes
O lecal and/or urlnary lnconLlnence more llkely
O need help when golng Lo Lhe LolleL flushlng wlplng dlsposlng of Llssues
O ulsrupLlon of sleep paLLerns
O Wander off and become losL
O Susplclous paranold aggresslve May belleve careglver ls an lmposLor devlous schemlng
cunnlng dlshonesL
O 8epeaL words phrases or repeLlLlvely uLLers sounds
O 8epeLlLlve/compulslve behavlor such as Learlng up Llssues or wrlnglng hands
O ulsLurbed aglLaLed especlally laLer on ln Lhe day
O PalluclnaLlons also more common laLer on ln Lhe day May hear smell or see Lhlngs LhaL are noL
Lhere
O LvenLually need care and supervlslon buL can respond Lo nonverbal sLlmull
Stage 7 Very Severe Cogn|t|ve Dec||ne (Severe or Latestage A|zhe|mers D|sease) Durat|on 1 to 2x
years
uurlng Lhe lasL sLage of Alzhelmers dlsease paLlenLs lose Lhe ablllLy Lo respond Lo Lhelr envlronmenL
Lhey cannoL speak and evenLually cannoL conLrol movemenL 1he duraLlon of Lhls sLage may depend on
Lhe quallLy of care Lhe paLlenL recelves
O Severely llmlLed cognlLlve ablllLy
O aLlenLs lose Lhelr ablllLy Lo recognlze speech buL may uLLer shorL words or moans Lo
communlcaLe
O usually Lhe ablllLy Lo walk unalded ls losL flrsL Lhen Lhe ablllLy Lo slL unalded plus Lhe ablllLy Lo
smlle and evenLually Lhe ablllLy Lo hold Lhe head up
O 8ody sysLems sLarL Lo fall and healLh deLerloraLes
O Swallowlng becomes lncreaslngly more dlfflculL Chocklng when eaLlng/drlnklng becomes more
common
O 8eflexes become abnormal
O Selzures are posslble
O Muscles grow rlgld
O Cenerally bedrldden
O Spends more Llme asleep
O 8equlre roundLheclock care
Laboratory
A docLor can dlagnose mosL cases of Alzhelmers Powever nobody can be 100 sure unLll afLer deaLh
when a mlcroscoplc examlnaLlon of Lhe braln deLecLs plaques and Langles 1here ls no baslc LesLlng such
as a blood LesL urlne LesL blopsy or lmage scan for dlagnoslng Alzhelmers dlsease A braln scan may
help ldenLlfy changes ln Lhe braln
ku||ng out other cond|t|ons
uocLors wlll usually carry ouL some LesLs Lo rule ouL oLher condlLlons whlch Lyplcally have sympLoms
LhaL are also presenL ln Alzhelmers 8elow are some examples of dlseases and condlLlons LhaL need Lo
be ruled ouL
O AnxleLy
O 8raln Lumor
O uepresslon
O lnfecLlon
O 1hyrold problems
O IlLamln deflclency
1he fo||ow|ng tests may be ordered
O 8|ood tests Lo see lf Lhe paLlenL has a Lhyrold dlsorder or vlLamln deflclency
O Neuropsycho|og|ca| test|ng Lhls lnvolves an exLenslve assessmenL of cognlLlve (Lhlnklng) and
memory skllls lL can Lake several hours 1hese Lypes of LesLs are exLremely useful ln deLecLlng
Alzhelmers as well as oLher demenLlas early on
O MkI (magnet|c resonance |mag|ng) scan A powerful magneLlc fleld ls creaLed by passlng an
elecLrlc currenL Lhrough Lhe wlre loops Meanwhlle oLher colls ln Lhe magneL send and recelve
radlo waves 1hls Lrlggers proLons ln Lhe body Lo allgn Lhemselves Cnce allgned radlo waves
are absorbed by Lhe proLons whlch sLlmulaLe splnnlng Lnergy ls released afLer exclLlng Lhe
molecules whlch ln Lurn emlLs energy slgnals LhaL are plcked up by Lhe coll 1hls lnformaLlon ls
Lhen senL Lo a compuLer whlch processes all Lhe slgnals and generaLes lL lnLo an lmage 1he flnal
producL ls a 3u lmage represenLaLlon of Lhe area belng examlned whlch ln Lhls case would be
Lhe braln
O 9L1 (pos|tron em|ss|on tomography) scan uses radlaLlon or nuclear medlclne lmaglng Lo
produce 3dlmenslonal color lmages of Lhe funcLlonal processes wlLhln Lhe human body lL ls
very useful ln helplng Lhe docLor dlagnose Alzhelmers dlsease A L1 scan LhaL measures upLake
of sugar ln Lhe braln slgnlflcanLly lmproves Lhe accuracy of dlagnoslng a Lype of demenLla ofLen
mlsLaken for Alzhelmers dlsease a sLudy revealed
O C1 (computer|zed tomography) scan Lhls devlce uses dlglLal geomeLry processlng Lo generaLe a
3dlmenslonal (3u) lmage of Lhe lnslde of an ob[ecL 1he 3u lmage ls made afLer many 2
dlmenslonal xray lmages are Laken around a slngle axls of roLaLlon ln oLher words many
plcLures of Lhe same area are Laken from many angles and Lhen placed LogeLher Lo produce a 3
u lmage
Jhat |s the d|fference between a 9L1 C1 or MkI scan? A C1 or M8l scan can assess Lhe slze and shape
of body organs and Llssue Powever Lhey cannoL assess funcLlon A L1 scan looks aL funcLlon ln oLher
words M8l or C1 scans Lell you whaL lL looks llke whlle a L1 scan can Lell you how lL ls worklng
CLher LesLs glven Lo paLlenLs Lo dlagnose Alzhelmers lnclude (8ruton L|nda I 2007)
1) A c|ock draw|ng test 1he paLlenL ls asked Lo draw a clock and Lo puL Lhe numbers ln Lhelr
approprlaLe locaLlons 1he paLlenL ls Lhen lnsLrucLed Lo draw speclflc hours on Lhe clock le 300 or
1113
2) M|n|Menta| State Lxam|nat|on 1he MMSL ls a brlef LesL LhaL measures Lhe cognlLlve sLaLus ln
adulLs arL of Lhe LesLs asks Lhe paLlenL a serles of quesLlons LhaL are consldered baslc lnformaLlon
concernlng Lhelr surroundlngs lor example Lhe paLlenL may be asked Lo name Lhree household lLems
LhaL are ln Lhe room AfLer Lhe paLlenL responds Lhe quesLlons are conLlnued
1hen Lhe revlewer may asks Lhe paLlenL agaln Lo name Lhe orlglnal 3 household lLem SomeLlmes Lhe
paLlenL ls asked Lo counL backwards 1he person ls asked Lo name Lhe Lhree ob[ecLs agaln 1he LesL ls
lnLended Lo screen for cognlLlve lmpalrmenL and esLlmaLe Lhe severlLy of Lhelr menLal lmpalrmenL
3) Iunct|ona| Assessment Stag|ng 1est (IAS1) lnvolves a checkllsL of funcLlons requlred for dally llvlng
1he LesL evaluaLes Lhe changes ln funcLlonal performance
Epidemiology
Accordlng Lo 1avee and Sweeney (2010) LhaL ln 1996 4 mllllon people were dlagnosed wlLh Lhe dlsease
ln Lhe uS and LhaL Lhe flgure ls expecLed Lo Lrlple ln 30 years lL also appeared LhaL more women are
affecLed Lhan men ln a raLlo of 21 1hls ls because Lhe populaLlon of women Lo men ln ages older Lhan
70 years old ls hlgher buL even afLer sLaLlsLlcal correcLlon for longeLlvlLy Lhe raLlo ls sLlll up Age ls a very
lmporLanL rlsk facLor AL Lhe age of 60 years Lhe rlsk of developlng Au ls esLlmaLed Lo be 1 doubllng
every 3 years Lo reach 30 Lo 30 by Lhe age of 83
3
CLher reporLed rlsk facLors lnclude lower levels of
lnLelllgence and educaLlon (deflned as prlmary educaLlon only) small head slze and a famlly hlsLory of
Lhe dlsease
6
A meLaanalysls of head ln[ury as a rlsk facLor for Alzhelmers dlsease also demonsLraLed a
deflnlLe assoclaLlon ln men" (1avee and Sweeney 2010)
As of 2006 Alzhelmer's dlsease ln Lhe uS ls consldered Lhe 7
Lh
leadlng cause of deaLh and Lhe prlmary
cause of lL are lnLercurrenL lllnesses such as pneumonla for Lhose who have suffered advanced
Alzhelmer's dlsease hence lmmoblllLy and dlfflculLy swallowlng (Anderson 2010)
ln a worldwlde prevalence DCn esLlmaLed LhaL 11 mllllon people suffer and abouL 3 of people
reachlng 63 are affecLed whlle 1323 of people reachlng 83 are affecLed
1oday more Lhan 33 mllllon Amerlcans have Alzhelmer's and 10 mllllon careglvers wlll aLLend Lo Lhem
durlng Lhe comlng year lf we do noL flnd a way of prevenLlng Lhls dlsease Lhere wlll be abouL 8 mllllon
cases by 2030 and as many as 16 mllllon ln 2030 Alzhelmer's ls economlcally as well as emoLlonally
burdensome dlrecL and lndlrecL cosLs of Lhe dlsease amounL Lo over $100 bllllon annually accordlng Lo
Lhe naLlonal lnsLlLuLe on Aglng" (8arg|ow 2010)
onclusion
knowledge and undersLandlng of Alzhelmer's dlsease ls advanclng 8ecause of Lhe fasLpaced change lL
ls lmporLanL for nurses as fronL llners ln healLhcare workforce Lo be always updaLed ln Lhe medlcal and
nurslng knowledge ln order Lo provlde Lhe mosL upLodaLe and mosL effecLlve evldenced based
lnLervenLlons Lo Lhelr cllenLs/paLlenLs Along wlLh Lhe emerglng undersLandlng and slowly foreseen
paradlgm shlfL ln Lhe dlsease undersLandlng ls Lhe solldlfylng knowledge LhaL Lhe braln ls affecLed noL
only by vlruses or forelgn bodles buL also by llfesLyle changes 1haL oLher parLs of Lhe body can also
conLrlbuLe Lo Lhe developmenL of Lhls dlsease lf Lhey are abused such as wlLh llfesLyle changes LhaL are
harmful for Lhe hearL and glucose meLabollsm
1he cure Lo Lhls deblllLaLlng dlsease may be aL hand buL when lL comes Lo Lhe old prescrlpLlon of eaLlng
well and exerclse regularly noLhlng has changed WhaLs good for your hearL ls good for your head!
Chooslng Lo eaL well and exerclse can help reduce your rlsk for developlng Alzhelmers (A|zhe|mer
Soc|ety Co|umb|a 2010)
S
?ou mlghL have Lhls quesLlon as you read Lhe paper WhaL ls CxldaLlve SLress?
l have an answer
oxldaLlve sLress
1 any of varlous paLhologlc changes seen ln llvlng organlsms ln response Lo excesslve levels of cyLoLoxlc
oxldanLs and free radlcals ln Lhe envlronmenL
2 use of anLloxldanL lnLake ln Lhe dleL Lo provlde boLh prevenLlve and LherapeuLlc advanLage and reduce
Lhe damaglng effecLs of free radlcals on cellular consLlLuenLs
Mosbys Medlcal ulcLlonary 8Lh edlLlon 2009 Llsevler
oxldaLlve sLress
o an lmbalance of Lhe prooxldanL anLloxldanL raLlo ln whlch Loo few anLloxldanLs are produced or
lngesLed or Loo many oxldlzlng agenLs are produced
!onas Mosbys ulcLlonary of ComplemenLary and AlLernaLlve Medlclne (c) 2003 Llsevler
oxldaLlve sLress
A Lerm used Lo descrlbe Lhe effecL of oxldaLlon ln whlch an abnormal level of react|ve oxygen spec|es
(kCS) such as Lhe free radlcals (eg hydroxyl nlLrlc acld superoxlde) or Lhe nonradlcals (eg hydrogen
peroxlde llpld peroxlde) lead Lo damage (called ox|dat|ve damage) Lo speclflc molecules wlLh
consequenLlal ln[ury Lo cells or Llssue lncreased producLlon of 8CS occurs as a resulL of fungal or vlral
lnfecLlon lnflammaLlon agelng uI radlaLlon polluLlon excesslve alcohol consumpLlon clgareLLe
smoklng eLc 8emoval or neuLrallzaLlon of 8CS ls achleved wlLh ant|ox|dants endogenous (eg caLalase
gluLaLhlone superoxlde dlsmuLase) or exogenous (eg vlLamlns A C L bloflavonolds caroLenolds)
CxldaLlve damage Lo Lhe eye parLlcularly Lhe reLlna and Lhe lens ls a conLrlbuLlng facLor Lo agerelaLed
macular degeneraLlon and caLaracL
MlllodoL ulcLlonary of CpLomeLry and Ilsual Sclence 7Lh edlLlon 2009 8uLLerworLhPelnemann
oxldaLlve sLress
1he presence of oxygen free radlcals whlch are generaLed by varlous sLressanLseg Lobacco alcohol
Lhe prlmary anLloxldanL ls gluLaLhlone oLher anLloxldanLs lnclude vlLamlns A C and L oxldaLlve
sLress may be one of Lhe key facLors ln Lhe early paLhogenesls of AluS ln whlch Lhe producLlon of 1nl
Lhe producLlon of free radlcals ln 1 cells See lree radlcals
McCrawPlll Conclse ulcLlonary of Modern Medlclne 2002 by 1he McCrawPlll Companles lnc
(1hefreed|ct|onarycom)
ources:
Alzhelmers ulsease aLhophyslology (2010) Medlclne Lncyclopedla 8eLrleved on november 26 2010
from hLLp//medlclne[rankorg/pages/80/AlzhelmersulseaseaLhophyslologyhLml
Alzhelmer's ulsease Cvervlew of ulagnosLlc 1esLs (2003) cleovelooJ cllolcotq 8eLrleved on uecember
4 2010 from hLLp//wwwcchsneL/healLh/healLhlnfo/docs/2300/2346asp?lndex9176
Alzhelmer's ulsease (2006 uecember 17) Cteot coottovetsles lo Neotobloloqy 8eLrleved on uecember
3 2010 from hLLps//wlklbrownedu/confluence/dlsplay/8n0193S04/ro[ecL+Croup+3
Alzhelmer's ulsease (2006) 8epubllc of Lhe hlllpplnes ueparLmenL of PealLh 8eLrleved on november
20 2010 from hLLp//wwwdohgovph/faq/show/489hLml
Alzhelmer's ulsease (nd) Medlclne webbookscom 8eLrleved on uecember 8 2010 from
hLLp//wwwwebbookscom/eLlbrary/Medlclne/neurologlcal/AlzhelmerhLm#1op
Anderson PeaLher S (2010 !uly 22) Alzhelmer's ulsease MeJscope 8eLrleved on uecember 8 2010
from hLLp//emedlclnemedscapecom/arLlcle/1134817overvlew
A (2010 november 7) Ceoetlcs nome kefeteoce 8eLrleved on uecember 3 2010 from
hLLp//ghrnlmnlhgov/gene/A
ArrasaLe MonLserraL MlLra SlddharLha SchwelLzer Lrlk S Segal Mark 8 and llnkbelner SLeven
(2004 CcLober 14) lncluslon body formaLlon reduces levels of muLanL hunLlngLln and Lhe rlsk of
neuronal deaLh Notote lobllsbloq Ctoop 8eLrleved on uecember 7 2010 from
hLLps//wlklbrownedu/confluence/download/aLLachmenLs/11719/naLure
PunLlngLlnspdf?verslon1modlflcaLlonuaLe1163777192000
Askarl lamla (2009) Alzhelmer's research on prevenLlon managemenL and care 8eLrleved on
uecember 7 2010 from hLLp//wwwmedllnkukorg/SlLe/documenLs/Alzhelmers2010/Askarllpdf
8arglow 8aymond (2010 lebruary 23) Alzhelmer's ulsease Pow Long 8efore We llnd a Cure? 1he
8erkley ually laneL 8eLrleved on uecember 3 2010 from
hLLp//wwwberkeleydallyplaneLcom/lssue/20100223/arLlcle/34707?headllneAlzhelmersulsease
PowLong8eforeWellndaCure
8lack !oyce M and Pawks !ane P (2004) MedlcalSurglcal nurslng Cllnlcal ManagemenL for oslLlve
CuLcomes volume 2 7
Lh
edlLlon Llsevler hlllpplnes page 21622170
8raln SLrucLures and 1helr luncLlons (2003 !une 3) 5eteoJlp 8eLrleved on november 12 2010 from
hLLp//serendlpbrynmawredu/bb/klnser/SLrucLure1hLml
8ruLon Llnda ! (2007 lebruary 20) Alzhelmers ulsease ulagnosLlc 1esLs and 1ools 8eLrleved on
uecember 2 2010 from hLLp//ezlnearLlclescom/?AlzhelmersulseaseulagnosLlc1esLsand
1oolsld434483
Calml C Carollo C and Lo resLl 8 (2003) OxlJotlve 5ttess ooJ ulobetes Mellltos 8eLrleved on
uecember 6 2010 from hLLp//wwwmedscapecom/vlewarLlcle/463121_4
CasLellanl 8udy ! Lee Pyounggon erry Ceorge and SmlLh Mark A (2006) AnLloxldanL proLecLlon
and neurodegeneraLlve dlsease 1he role of amyloldf3 and Lau Amerlcan !ournal of Alzhelmers ulsease
and CLher uemenLlas Iolume 21 number 2 March/Aprll 2006 8eLrleved from
hLLps//wlklbrownedu/confluence/download/aLLachmenLs/11719/neuropdf?verslon1modlflcaLlonu
aLe1162739321000
Chronlc lnflammaLlon (nd) lomezcom 8eLrleved on uecember 2 2010 from
hLLp//wwwflameezcom/lnflammaLlon
laucl AnLhony S 8raunwald Lugene kasper uennls L Pauser SLephen L Longo uan L !ameson !
Larry and Loscalzo !oseph (2009) nottlsoos Mooool of MeJlcloe 17
tb
Jltloo new ?ork McCraw Plll
Medlcal pages 2478 2340 2341
Pessellnk !ohn 8 (2008) 1PL 1LMC8AL LC8L LlM8lC S?S1LM uCSu neuroradlology 8eLrleved on
uecember 8 2010 from hLLp//splnwarpucsdedu/neuroWeb/1exL/br800eplhLm
lnflammaLlon Chronlc (nd) llfe xteosloootq 8eLrleved on uecember 1 2010 from
hLLp//wwwleforg/proLocols/prLcl146shLml
Morhan Slmona u Chong ZhaoZhong and Malese kenneLh (2008) CxldaLlve SLress and ulabeLes
Parlem Chlldren SocleLy 8eLrleved on uecember 8 2010 from
hLLp//wwwharlemchlldrensocleLyorg/mlsc/SLudenLlnfo/MorhanSlmona/paper_morhanpdf
nordqvlsL ChrlsLlan (2009 !une 31) WhaL ls Alzhelmer's ulsease? WhaL Causes Alzhelmer's ulsease?
MeJlcol News 1oJoy 8eLrleved on uecember 8 2010 from
hLLp//wwwmedlcalnewsLodaycom/arLlcles/139442php
norman Wllllam (2009 november 27) neuron Clucose MeLabollsm Alzhelmers ulsease 8eLrleved
on november 29 2010 from hLLp//wwwehowcom/abouL_3693133_neuronglucosemeLabollsm
alzhelmer_sdlseasehLml
nourlsh CarbohydraLes luel ?our 8raln (2004) 1be tookllo lostltote Oolloe 8eLrleved on uecember 6
2010 from hLLp//wwwfledu/learn/braln/carbshLml
Clson ScoLL (2008 november 12) WhaL Sugar uoes Lo ?our 8raln 8eLrleved on uecember 6 2010 from
hLLp//olsonndcom/whaLsugardoesLoyourbraln/
CxldaLlve SLress (2010) 1be tee ulctloooty8eLrleved on uecember 3 2010 from hLLp//medlcal
dlcLlonaryLhefreedlcLlonarycom/oxldaLlve+sLress
rasad kedar n Cole Wllllam C and rasad k Che (2002) 8lsk lacLors for Alzhelmer's ulsease 8ole
of MulLlple AnLloxldanLs nonSLeroldal AnLllnflammaLory and Chollnerglc AgenLs Alone or ln
ComblnaLlon ln revenLlon and 1reaLmenL !ournal of Lhe Amerlcan College of nuLrlLlon Iol 21 no 6
306322 8eLrleved on uecember 3 2010 from hLLp//www[acnorg/cgl/conLenL/full/21/6/306
8and !ames 8 (2007) AceLylchollne wotm8ookotq 8eLrleved on uecember 6 2010 from
hLLp//wwwwormbookorg/chapLers/www_aceLylchollne/aceLylchollnehLml
8lensLra uouwe (november 2006) Medlclne lor eople! 8eLrleved on uecember 4 2010 from
hLLp//wwwrlensLracllnlccom/newsleLLer/2006/2006novhLml
SalnL Louls unlverslLy (2009 !uly 9) lnflammaLlon May 1rlgger Alzhelmers ulsease 5cleoceuolly
8eLrleved uecember 9 2010 from hLLp//wwwsclencedallycom /releases/2009/07/090708181204hLm
SmelLzer Suzanne C 8are 8renda C Plnkle !anlce L and Cheever kerry P (2008) 1exLbook of
MedlcalSurglcal nurslng volume 2 11
Lh
LdlLlon LlpplncoLL Wllllams and Wllklns hlllpplnes age 2320
2323
Sples eLra L Claassen !urgen SlaLs ulane 8lkkerL Marcel Ierbeek Marcel and kessels 8oy (2009
May 10) Cerebrosplnal lluld 1au and Amylold 8eLa roLelns uo noL CorrelaLe WlLh CognlLlve
luncLlonlng ln CognlLlvely lmpalred Memory Cllnlc aLlenLs cN5 5pecttoms 8eLrleved on uecember 6
2010 from hLLp//wwwcnsspecLrumscom/aspx/arLlcledeLallaspx?arLlcleld2836
1avee !lnny and Sweeney aLrlck (2010 AugusL 1) Alzhelmer's ulsease 8eLrleved on uecember 4
2010 from
hLLp//wwwclevelandcllnlcmededcom/medlcalpubs/dlseasemanagemenL/neurology/alzhelmers
dlsease/
Additional reading materials
Adams Amy (2000 SepLember 8) Cenes Can Cause Alzhelmer's ulsease CeneLlc PealLh 8eLrleved on
uecember 8 2010 from hLLp//wwwgeneLlchealLhcom/alz_geneLlcs_of_alzhelmers_dlseaseshLml
Alumlnlum and Alzhelmer's ulsease (SepLember 2008) Alhelmer's SocleLy 8eLrleved on uecember 8
2010 from hLLp//alzhelmersorguk/slLe/scrlpLs/documenLs_lnfophp?documenLlu99
Alzhelmer's ulsease (nd) unA Learnlng CenLer Pome 8eLrleved on november 23 2010 from
hLLp//wwwyourgenesyourhealLhorg/alz/whaLlslLhLm
Campbell uenls (2009 AugusL 4) Mlddleaged smokers aL hlgher rlsk of demenLla 1be CootJloo
8eLrleved on uecember 7 2010 from hLLp//wwwguardlancouk/llfeandsLyle/2009/aug/04/mlddle
agedsmokersrlskdemenLla
Champeau 8achel (2006 May 22) uCLA SLudy llnds LhaL Slmple LlfesLyle Changes May lmprove
CognlLlve luncLlon and 8raln Lfflclency uclA Newstoom 8eLrleved on uecember 7 2010 from
hLLp//wwwnewsroomuclaedu/porLal/ucla/uCLASLudyllndsLhaLSlmpleLlfesLyle
7062aspx?8elnum7062
Ceorge kelly (2010 CcLober 26) new sLudy Smoklng can lead Lo Alzhelmer's and uemenLla
Lxamlnercom 8eLrleved on uecember 8 2010 from hLLp//wwwexamlnercom/healLhyLrendsln
aLlanLa/newsLudysmoklngcanleadLoalzhelmersanddemenLla
PealLhy 8raln (2010) Alzbelmet 5oclety colomblo 8eLrleved on uecember 8 2010 from
hLLp//wwwalzhelmerbcorg/AlzhelmersulseaseanduemenLla/8ralnllLnesslanaspx
Lowe uerek (2010 March 16) 8eLaAmylold An AnLlbloLlc? lo 1be llpelloe 8eLrleved on uecember 7
2010 from hLLp//plpellnecoranLecom/archlves/2010/03/16/beLaamylold_an_anLlbloLlcphp
Mayo Cllnlc SLaff (2010 AugusL 3) Alzhelmer's ulsease Alzhelmer's genes Are you aL rlsk? Moyo
oooJotloo fot MeJlcol Jocotloo ooJ keseotcb 8eLrleved on uecember 7 2010 from
hLLp//wwwmayocllnlccom/healLh/alzhelmersgenes/AZ00047
Sample lan (2009 SepLember 6) Alzhelmer's research llnks Lhree genes Lo dlsease 1be CootJloo
8eLrleved on uecember 7 2010 from hLLp//wwwguardlancouk/sclence/2009/sep/06/alzhelmers
dlseasegenesresearch
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDari EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RacePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDari EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (838)
- Voting Number in The ConstitutionDokumen2 halamanVoting Number in The ConstitutionTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Mens MonthDokumen1 halamanMens MonthTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Breast Cancer AssignmentDokumen25 halamanBreast Cancer AssignmentTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Specpro DigestsDokumen9 halamanSpecpro DigestsTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Logic AnswersDokumen3 halamanLogic AnswersTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Marriage SettlementsDokumen4 halamanMarriage SettlementsTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Fundamental Distinctions Among Leasehold Tenancy, Tenant Emancipation Decree and CARPDokumen17 halamanFundamental Distinctions Among Leasehold Tenancy, Tenant Emancipation Decree and CARPTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Rule 105 Special ProceedingDokumen3 halamanRule 105 Special ProceedingTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- G.R. Nos. 197592 & 20262 November 27, 2013 The Province of Aklan, Petitioner, Jody King Construction and Development Corp., RespondentDokumen33 halamanG.R. Nos. 197592 & 20262 November 27, 2013 The Province of Aklan, Petitioner, Jody King Construction and Development Corp., RespondentTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Amendments To The Rules of Court On Declaration of Absolute Nullity of Marriage Etc...Dokumen10 halamanAmendments To The Rules of Court On Declaration of Absolute Nullity of Marriage Etc...Tiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Synthesis Paper On The Framework For Pathophysiology: EtiologyDokumen4 halamanSynthesis Paper On The Framework For Pathophysiology: EtiologyTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Dokumen7 halamanPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure (Overview)Tiger Knee100% (3)
- Substance Related DisordersDokumen56 halamanSubstance Related DisordersTiger Knee100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Sensation Seeking TheoryDokumen50 halamanSensation Seeking TheoryTiger Knee100% (1)
- The Filipino FamilyDokumen11 halamanThe Filipino FamilyTiger Knee97% (38)
- Schistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Dokumen10 halamanSchistosomiasis (From Anatomy To Pathophysiology)Tiger Knee100% (1)
- Nasogastric Tube Insertion: Nursing Guidelines and ConsiderationsDokumen39 halamanNasogastric Tube Insertion: Nursing Guidelines and ConsiderationsTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsDokumen10 halamanPathophysiology of Alzheimer's Disease With Nursing ConsiderationsTiger Knee100% (1)
- Myths and CultureDokumen4 halamanMyths and CultureTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Alzheimer's Disease (Mini Presentation)Dokumen51 halamanAlzheimer's Disease (Mini Presentation)Tiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- Heart in ProgressDokumen27 halamanHeart in ProgressTiger KneeBelum ada peringkat
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Dari EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Penilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDari EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDari EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDari EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDari EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (400)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDari EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FuturePenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDari EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDari EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseverancePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDari EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (271)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDari EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (45)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDari EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (74)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDari EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDari EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDari EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You ArePenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDari EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyPenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (2259)
- Rise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnoreDari EverandRise of ISIS: A Threat We Can't IgnorePenilaian: 3.5 dari 5 bintang3.5/5 (137)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Dari EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Penilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDari EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (821)
- Impact of Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program On EducationDokumen10 halamanImpact of Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program On EducationEllyssa Erika MabayagBelum ada peringkat
- Speech On Viewing SkillsDokumen1 halamanSpeech On Viewing SkillsMera Largosa ManlaweBelum ada peringkat
- MCI Approved Medical College in Uzbekistan PDFDokumen3 halamanMCI Approved Medical College in Uzbekistan PDFMBBS ABROADBelum ada peringkat
- 22 Khan S.Dokumen7 halaman22 Khan S.scholarlyreseachjBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Screenwriting UEADokumen12 halamanIntroduction To Screenwriting UEAMartín SalasBelum ada peringkat
- Review On AlgebraDokumen29 halamanReview On AlgebraGraziela GutierrezBelum ada peringkat
- Peer PressureDokumen13 halamanPeer PressuremightymarcBelum ada peringkat
- ECE Companies ListDokumen9 halamanECE Companies ListPolaiah Geriki100% (1)
- Technology Based Project: Special Track 1)Dokumen14 halamanTechnology Based Project: Special Track 1)Kim ChiquilloBelum ada peringkat
- Core ValuesDokumen1 halamanCore ValuesIan Abel AntiverosBelum ada peringkat
- Friction: Ultiple Hoice UestionsDokumen5 halamanFriction: Ultiple Hoice Uestionspk2varmaBelum ada peringkat
- Julia Dito ResumeDokumen3 halamanJulia Dito Resumeapi-253713289Belum ada peringkat
- Physics Education Thesis TopicsDokumen4 halamanPhysics Education Thesis TopicsPaperWriterServicesCanada100% (2)
- 01 托福基础课程Dokumen57 halaman01 托福基础课程ZhaoBelum ada peringkat
- Interlocking Block TechnologyDokumen15 halamanInterlocking Block TechnologyChaula Trivedi100% (5)
- Brand Strategy - in B2BDokumen6 halamanBrand Strategy - in B2BKrishan SahuBelum ada peringkat
- Wner'S Anual: Led TVDokumen32 halamanWner'S Anual: Led TVErmand WindBelum ada peringkat
- An Annotated Bibliography of Timothy LearyDokumen312 halamanAn Annotated Bibliography of Timothy LearyGeetika CnBelum ada peringkat
- Hướng Dẫn Chấm: Ngày thi: 27 tháng 7 năm 2019 Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề) HDC gồm có 4 trangDokumen4 halamanHướng Dẫn Chấm: Ngày thi: 27 tháng 7 năm 2019 Thời gian làm bài: 180 phút (không kể thời gian giao đề) HDC gồm có 4 trangHưng Quân VõBelum ada peringkat
- UT Dallas Syllabus For Govt4396.002.08s Taught by Gregory Thielemann (Gregt)Dokumen2 halamanUT Dallas Syllabus For Govt4396.002.08s Taught by Gregory Thielemann (Gregt)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupBelum ada peringkat
- SSP 237 d1Dokumen32 halamanSSP 237 d1leullBelum ada peringkat
- Sveba Dahlen - SRP240Dokumen16 halamanSveba Dahlen - SRP240Paola MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- CL57T V4.0Dokumen14 halamanCL57T V4.0dimitriBelum ada peringkat
- LSCM Course OutlineDokumen13 halamanLSCM Course OutlineDeep SachetiBelum ada peringkat
- Winter CrocFest 2017 at St. Augustine Alligator Farm - Final ReportDokumen6 halamanWinter CrocFest 2017 at St. Augustine Alligator Farm - Final ReportColette AdamsBelum ada peringkat
- Applied Economics 2Dokumen8 halamanApplied Economics 2Sayra HidalgoBelum ada peringkat
- Cummin C1100 Fuel System Flow DiagramDokumen8 halamanCummin C1100 Fuel System Flow DiagramDaniel KrismantoroBelum ada peringkat
- SachinDokumen3 halamanSachinMahendraBelum ada peringkat
- Prevention of Waterborne DiseasesDokumen2 halamanPrevention of Waterborne DiseasesRixin JamtshoBelum ada peringkat
- Eloy-Stock English Full PDFDokumen0 halamanEloy-Stock English Full PDFR.s. WartsBelum ada peringkat