What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
Diunggah oleh
Ymelda ComediamDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
What Is A Urinary Tract Infection
Diunggah oleh
Ymelda ComediamHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
What is a urinary tract infection (UTI)?
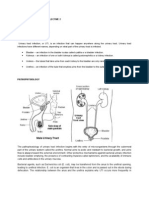
The urinary tract is comprised of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra (see Figure 1). A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection caused by pathogenic organisms (for example, bacteria, fungi, or parasites) in any of the structures that comprise the urinary tract. However, this is the broad definition of urinary tract infections; many authors prefer to use more specific terms that localize the urinary tract infection to the major structural segment involved such as urethritis(urethral infection), cystitis(bladder infection), ureter infection, and pyelonephritis (kidney infection). Other structures that eventually connect to or share close anatomic proximity to the urinary tract (for example, prostate, epididymis, and vagina) are sometimes included in the discussion of UTIs because they may either cause or be caused by UTIs. Technically, they are not UTIs and will be only briefly mentioned in this article. UTIs are common, more common in women than men, leading to approximately 8.3 million doctor visits per year. Although some infections go unnoticed, UTIs can cause problems that range from dysuria (pain and/or burning when urinating) to organ damage and even death. The kidneys are the active organs that, during their average production of about 1.5 quarts of urine per day, function to help keep electrolytesand fluids (for example, potassium, sodium, water) in balance, assist removal of waste products (urea), and produce a hormone that aids to form red blood cells. If kidneys are injured or destroyed by infection, these vital functions can be damaged or lost. While some investigators state that UTIs are not transmitted from person to person, other investigators dispute this and say UTIs may be contagious and recommend that sex partners avoid relations until the UTI has cleared. There is no dispute about UTIs caused by sexually transmitted disease(STD) organisms; these infections (gonorrhea, chlamydia) are easily transmitted between sex partners and are very contagious.
A urinary tract infection or UTI is a bacterial infection that occurs when bacteria invade the urinary tract system; the bacteria multiply throughout the urinary track system. While the majority of urinary tract infections or UTIs are not serious, they often cause severe symptoms such as pain and/or burning upon urination. The urinary tract system is the body's filtering system for removal of liquid waste. The urinary tract consists of the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. About half of all women will have at least one UTI in her lifetime, while many women suffer through several infections throughout their lifetime. Women are particularly susceptible to urinary tract infections or UTI. This is because women have a shorter urinary tract than men. The good news: Infections are easily treated with antibiotics. However, some women seem prone torecurrent UTIs than others and for them it can be a frustrating battle. What Causes Urinary Tract Infections? The most common cause of UTIs are bacteria from the bowel that live on the skin near the rectum or in the vagina, which can spread and enter the urinary tract through the urethra. Once these bacteria enter the urethra, they travel upward, causing infection in the bladder and sometimes other parts of the urinary tract. Sexual intercourse is a common cause of urinary tract infections because the female anatomy can make women more prone to urinary tract infections. During sexual activity, bacteria in the vaginal area are sometimes massaged into the urethra.
Women who change sexual partners or begin having sexual intercourse more frequently may experience bladder or urinary tract infections more often than women who are celibate or in monogamous relationships. Although it is rare, some women get a urinary tract infection every time they have sex. Another cause of bladder infections or UTI is waiting too long to urinate. The bladder is a muscle that stretches to hold urine and contracts when the urine is released. Waiting too long past the time you first feel the need to urinate can cause the bladder to stretch beyond its capacity. Over time, this can weaken the bladder muscle. When the bladder is weakened, it may not empty completely and some urine is left in the bladder. This may increase the risk of urinary tract infections or bladder infections. Other factors that also may increase a woman's risk of developing UTI include pregnancy, having urinary tract infections as a child, menopause, or diabetes. See: 10 Ways To Prevent UTI
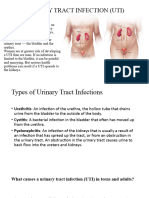
What Are the Symptoms of Urinary Tract Infections? Symptoms of UTI or bladder infection are not easy to miss and include a strong urge to urinate that cannot be delayed, which is followed by a sharp pain or burning sensation in the urethra when the urine is released. Most often very little urine is released and the urine that is released may be tinged with blood. The urge to urinate recurs quickly and soreness may occur in the lower abdomen, back, or sides. This cycle may repeat itself frequently during the day or night--most people urinate about six times a day, when the need to urinate occurs more often a bladder infection should be suspected. When bacteria enter the ureters and spread to the kidneys, symptoms such as back pain, chills, fever, nausea, and vomiting may occur, as well as the previous symptoms of lower urinary tract infection. Proper diagnosis is vital since these symptoms also can be caused by other problems such as vaginal infections or vulva . Only your physician can make the distinction and make a correct diagnosis. How Is a Diagnosis of UTI Made? The number of bacteria and white blood cells in a urine sample is the basis for diagnosing urinary tract infections. Urine is examined under a microscope and cultured in a substance that promotes the growth of bacteria. A pelvic exam also may be necessary.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen7 halamanUrinary Tract InfectionNader Smadi100% (7)
- Infection Urinary Tract Urine Bladder KidneyDokumen18 halamanInfection Urinary Tract Urine Bladder KidneygdquijanoBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen3 halamanWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionStepyn SalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDokumen17 halamanUrinary Tract Infectionss.khan9211rediffmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary TractDokumen4 halamanUrinary TractRoland APARECEBelum ada peringkat
- Types of Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen4 halamanTypes of Urinary Tract InfectionGencris Medrano Giray RNBelum ada peringkat
- Theoretical Background Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen7 halamanTheoretical Background Urinary Tract Infectiondenebrench23Belum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen5 halamanUrinary Tract InfectionDRABelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen2 halamanWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionLunaBelum ada peringkat
- UTIDokumen6 halamanUTIAyessa Marie BarbosaBelum ada peringkat
- Uti PathoDokumen15 halamanUti PathoEden Astred ObilloBelum ada peringkat
- RLE Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen13 halamanRLE Urinary Tract InfectionAliza AlyyBelum ada peringkat
- Cystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesDari EverandCystitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition Treatment And Urinary DiseasesBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheetDokumen10 halamanUrinary Tract Infection UTI and Dementia FactsheettoobaziBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen10 halamanUrinary Tract Infectionjaah diazBelum ada peringkat
- CASE STUDY #3 Urinary System (Urninary Tract Infection or UTI)Dokumen5 halamanCASE STUDY #3 Urinary System (Urninary Tract Infection or UTI)Lerma PagcaliwanganBelum ada peringkat
- What Is A Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen3 halamanWhat Is A Urinary Tract InfectionVanessa MendezBelum ada peringkat
- Coli Bacterial Strains That Usually Inhabit The ColonDokumen4 halamanColi Bacterial Strains That Usually Inhabit The Colonemman122392Belum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection Diet: A Beginner’s 4-Step Guide for Women on Managing UTI Through Diet, With Sample Curated RecipesDari EverandUrinary Tract Infection Diet: A Beginner’s 4-Step Guide for Women on Managing UTI Through Diet, With Sample Curated RecipesBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection Diet: A Beginner's 4-Step Guide for Women on Managing UTI Through Diet, With Sample Curated RecipesDari EverandUrinary Tract Infection Diet: A Beginner's 4-Step Guide for Women on Managing UTI Through Diet, With Sample Curated RecipesBelum ada peringkat
- Female Urinary System: Types of Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen6 halamanFemale Urinary System: Types of Urinary Tract InfectionCarmela BedanoBelum ada peringkat
- Elective 2 ReportDokumen7 halamanElective 2 ReportJem TellainBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and It's ManagementDokumen8 halamanUrinary Tract Infection: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and It's ManagementAyat RajpootBelum ada peringkat
- UTI in AdultsDokumen4 halamanUTI in Adultsjoan_padilla2000Belum ada peringkat
- Infeksi Saluran KemihDokumen65 halamanInfeksi Saluran KemihHaziq AnuarBelum ada peringkat
- UTI (Urinary Tract Infection)Dokumen9 halamanUTI (Urinary Tract Infection)Carson BirthBelum ada peringkat
- The Urinary System. The Urinary System Helps Maintain Proper Water and Salt Balance ThroughoutDokumen4 halamanThe Urinary System. The Urinary System Helps Maintain Proper Water and Salt Balance ThroughoutArjay EspañolBelum ada peringkat
- Written Assignment 7 Hs2211Dokumen7 halamanWritten Assignment 7 Hs2211Cali GureBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDokumen5 halamanUrinary Tract InfectionsEben Leonel Albano MaiopueBelum ada peringkat
- Prevalence of Uti in Benin PDFDokumen54 halamanPrevalence of Uti in Benin PDFcamiladovalle95Belum ada peringkat
- Uti ReadingsDokumen6 halamanUti ReadingskarenbelnasBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Dokumen9 halamanUrinary Tract Infection (UTI)ogwal andrewictynetBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A Guide For WomenDokumen2 halamanUrinary Tract Infection (UTI) : A Guide For WomenBily ManBelum ada peringkat
- Symptoms: For Bladder InfectionsDokumen5 halamanSymptoms: For Bladder InfectionsGene Ryuzaki SeseBelum ada peringkat
- Function of The Urinary SystemDokumen2 halamanFunction of The Urinary SystemniknokaBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)Dokumen6 halamanUrinary Tract Infection (UTI)Anonymous iG0DCOfBelum ada peringkat
- Anatomy and Physiology Uti Adawdiasdfkuhasdlukfhalkfjashdkljfahrguilahrluihadfkljnxj, CnalksefhauehDokumen4 halamanAnatomy and Physiology Uti Adawdiasdfkuhasdlukfhalkfjashdkljfahrguilahrluihadfkljnxj, CnalksefhauehVandie MagallanesBelum ada peringkat
- Prevalence of Uti in BeninDokumen49 halamanPrevalence of Uti in Benincamiladovalle95Belum ada peringkat
- Understanding Urinary Incontinency: A Simplified GuideDari EverandUnderstanding Urinary Incontinency: A Simplified GuideBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study (Uti)Dokumen6 halamanCase Study (Uti)Bible EvergardenBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection (Uti) Definition:: TypesDokumen2 halamanUrinary Tract Infection (Uti) Definition:: TypesAneela ManzoorBelum ada peringkat
- Ec2 UrinaryDokumen4 halamanEc2 UrinaryDiana Marie ReyesBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection: Point Wise Lecture Along With Consisted Table, Image and Schematic DiagramsDokumen15 halamanUrinary Tract Infection: Point Wise Lecture Along With Consisted Table, Image and Schematic DiagramsVipinBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen13 halamanUrinary Tract InfectionAlexis PiocosBelum ada peringkat
- A Case Study On UtiDokumen10 halamanA Case Study On UtiMark Tristan AsuncionBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract InfectionDokumen2 halamanUrinary Tract InfectionAnonymous KillerBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary SystemDokumen2 halamanUrinary SystemнастяBelum ada peringkat
- An Individual Case Study ON Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : Southern Isabela General HospitalDokumen20 halamanAn Individual Case Study ON Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) : Southern Isabela General HospitalhanapotakoBelum ada peringkat
- Article For Patient EducationDokumen4 halamanArticle For Patient EducationZaveri Hemant GirishkumarBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Track Infection Pathopysiology 1Dokumen3 halamanUrinary Track Infection Pathopysiology 1rraven16Belum ada peringkat
- Kidney InfectionDokumen3 halamanKidney InfectionMaxpein Zin Dell Valle-MoonBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infections in Teens and Adults: Topic OverviewDokumen1 halamanUrinary Tract Infections in Teens and Adults: Topic OverviewRaRa PRawitaBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection in AdultsDokumen8 halamanUrinary Tract Infection in AdultsFeenyxBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection 1Dokumen17 halamanUrinary Tract Infection 1Annie Lou AbrahamBelum ada peringkat
- Uti Case StudyDokumen7 halamanUti Case StudyStephBelum ada peringkat
- OverviewDokumen3 halamanOverviewAlhaisa BejemilBelum ada peringkat
- Readings: Acute PyelonephritisDokumen6 halamanReadings: Acute PyelonephritisMauriceBelum ada peringkat
- Urinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Dokumen16 halamanUrinary Tract Infection (Maramag Eunice Laman Jenny Pearl)Carlojay IniegoBelum ada peringkat
- Handout 2Dokumen1 halamanHandout 2api-320812761Belum ada peringkat
- Drug Name Dose & Frequency Classificati ON Action Adverse Effect Contraindic Ations Nursing Responsibil ItisDokumen3 halamanDrug Name Dose & Frequency Classificati ON Action Adverse Effect Contraindic Ations Nursing Responsibil ItisYmelda ComediamBelum ada peringkat
- 1st LAWDokumen2 halaman1st LAWYmelda ComediamBelum ada peringkat
- Perioperative CareDokumen59 halamanPerioperative CareYmelda ComediamBelum ada peringkat
- Amen Orr Hoe ADokumen13 halamanAmen Orr Hoe AYmelda ComediamBelum ada peringkat
- Basic Human NeedsDokumen58 halamanBasic Human NeedsYmelda ComediamBelum ada peringkat
- LC 67002000 B Hr-Jumbo enDokumen2 halamanLC 67002000 B Hr-Jumbo enJulio OrtegaBelum ada peringkat
- MVC Training Course Prerequisite: WWW - Focustech.InDokumen2 halamanMVC Training Course Prerequisite: WWW - Focustech.InLakshman Samanth ReddyBelum ada peringkat
- Amazon VS WalmartDokumen5 halamanAmazon VS WalmartBrandy M. Twilley100% (1)
- Hydraulic Excavator: Engine WeightsDokumen28 halamanHydraulic Excavator: Engine WeightsFelipe Pisklevits LaubeBelum ada peringkat
- ESG Conundrum PDFDokumen30 halamanESG Conundrum PDFVijay Kumar SwamiBelum ada peringkat
- Workshop Manual: 3LD 450 3LD 510 3LD 450/S 3LD 510/S 4LD 640 4LD 705 4LD 820Dokumen33 halamanWorkshop Manual: 3LD 450 3LD 510 3LD 450/S 3LD 510/S 4LD 640 4LD 705 4LD 820Ilie Viorel75% (4)
- Manual ML 1675 PDFDokumen70 halamanManual ML 1675 PDFSergio de BedoutBelum ada peringkat
- Synopsis SsDokumen14 halamanSynopsis SsJYOTI KATIYAR SVUBelum ada peringkat
- Applications PDFDokumen90 halamanApplications PDFahmedBelum ada peringkat
- Notes 3 Mineral Dressing Notes by Prof. SBS Tekam PDFDokumen3 halamanNotes 3 Mineral Dressing Notes by Prof. SBS Tekam PDFNikhil SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Mge - Ex11rt - Installation and User Manual PDFDokumen38 halamanMge - Ex11rt - Installation and User Manual PDFRafa TejedaBelum ada peringkat
- Case Study On "Unilever in Brazil-Marketing Strategies For Low Income Consumers "Dokumen15 halamanCase Study On "Unilever in Brazil-Marketing Strategies For Low Income Consumers "Deepak BajpaiBelum ada peringkat
- Module 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentDokumen19 halamanModule 8 - Emotional Intelligence Personal DevelopmentRoxan Binarao-Bayot60% (5)
- Trox Quick Selection GuideDokumen47 halamanTrox Quick Selection GuideErwin LouisBelum ada peringkat
- Attitude of Tribal and Non Tribal Students Towards ModernizationDokumen9 halamanAttitude of Tribal and Non Tribal Students Towards ModernizationAnonymous CwJeBCAXpBelum ada peringkat
- ELS 15 Maret 2022 REVDokumen14 halamanELS 15 Maret 2022 REVhelto perdanaBelum ada peringkat
- Competent Testing Requirements As Per Factory ActDokumen3 halamanCompetent Testing Requirements As Per Factory Actamit_lunia100% (1)
- OSX ExpoDokumen13 halamanOSX ExpoxolilevBelum ada peringkat
- Procedure Manual - IMS: Locomotive Workshop, Northern Railway, LucknowDokumen8 halamanProcedure Manual - IMS: Locomotive Workshop, Northern Railway, LucknowMarjorie Dulay Dumol80% (5)
- Contemporary Architecture Is The Architecture of The 21st Century. No Single Style Is DominantDokumen2 halamanContemporary Architecture Is The Architecture of The 21st Century. No Single Style Is DominantShubham DuaBelum ada peringkat
- MODULE 8. Ceiling WorksDokumen2 halamanMODULE 8. Ceiling WorksAj MacalinaoBelum ada peringkat
- Exploring Nurses' Knowledge of The Glasgow Coma Scale in Intensive Care and Emergency Departments at A Tertiary Hospital in Riyadh City, Saudi ArabiaDokumen9 halamanExploring Nurses' Knowledge of The Glasgow Coma Scale in Intensive Care and Emergency Departments at A Tertiary Hospital in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabianishu thapaBelum ada peringkat
- Job Stress InterventionsDokumen5 halamanJob Stress InterventionscocaralucamihaelaBelum ada peringkat
- Viking 062293Dokumen8 halamanViking 062293Lukman ZakariyahBelum ada peringkat
- Heart Attack Detection ReportDokumen67 halamanHeart Attack Detection ReportAkhil TejaBelum ada peringkat
- American University of Beirut PSPA 210: Intro. To Political ThoughtDokumen4 halamanAmerican University of Beirut PSPA 210: Intro. To Political Thoughtcharles murrBelum ada peringkat
- Emulsion LectureDokumen30 halamanEmulsion LectureRay YangBelum ada peringkat
- HP 6940 Manual CompleteDokumen150 halamanHP 6940 Manual CompletepaglafouBelum ada peringkat
- Carpentry NC Ii: Daniel David L. TalaveraDokumen5 halamanCarpentry NC Ii: Daniel David L. TalaveraKhael Angelo Zheus JaclaBelum ada peringkat
- Introduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Dokumen75 halamanIntroduction To Cobit Framework - Week 3Teddy HaryadiBelum ada peringkat