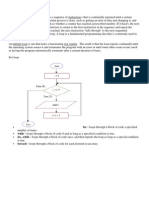
NCP For Acvute Pain
Diunggah oleh
Glenn ValerioDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NCP For Acvute Pain
Diunggah oleh
Glenn ValerioHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
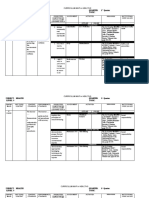
ASSESSMENT Nursing Diagnosis: Acute pain rlt swallowing S> Masakit kapag lumulunok ako.
Pain rated as 10/10 O Grimacing noted when swallowing Prefers soft foods and liquids Guarding behavior noted NGT insertion ordered Decrease interaction with people around Irritable
EXPLANATION OF THE PROBLEM The pain is due to anaplastic cancer of the thyroid.
GOALS & OBJECTIVES
INTERVENTIONS Dx: Monitor level of consciousness.
RATIONALE
EVALUATION
A decreased level of consciousness is a prime risk factor for aspiration. A depressed cough or gag reflex increases the risk of aspiration. Pockets of food can be easily aspirated at a later time. Choking indicates aspiration.
Assess cough and gag reflexes.
Monitor swallowing ability: o Assess for coughing or clearing of the throat after a swallow. o Assess for residual food in mouth after eating. o Assess for regurgitation of food or fluid through nares. o Monitor for choking during eating or drinking. Auscultate bowel sounds to evaluate bowel motility.
Decreased gastrointestinal motility increases the risk of aspiration because food or fluids accumulate in the stomach. Elderly patients have a decrease in esophageal motility, which delays esophageal emptying. When combined with
the weaker gag reflex of elderly patients, aspiration is a higher risk.
Auscultate breath sounds for development of crackles and/or rhonchi
Aspiration of small amounts can occur without coughing or sudden onset of respiratory distress, especially in patients with decreased levels of consciousness.
In patients with endotracheal or tracheostomy tubes, monitor the effectiveness of the cuff. Collaborate with the respiratory therapist, as needed, to determine cuff pressure. Tx: Keep suction setup available (in both hospital and home settings) and use as needed.
An ineffective cuff can increase the risk of aspiration.
This is necessary to maintain a patent airway.
Notify the physician or other health care provider immediately of noted decrease in
Early intervention protects the patients airway and prevents aspiration.
cough and/or gag reflexes or difficulty in swallowing.
Position patients who have a decreased level of consciousness on their sides
This protects the airway. Proper positioning can decrease the risk of aspiration. Comatose patients need frequent turning to facilitate drainage of secretions. This will help detect abnormalities early.
Supervise or assist patient with oral intake. Never give oral fluids to a comatose patient.
Offer foods with consistency that patient can swallow. Use thickening agents as appropriate. Cut foods into small pieces.
Semisolid foods like pudding and hot cereal are most easily swallowed. Liquids and thin foods like creamed soups are most difficult for patients with dysphagia.
Position patient at 90degree angle, whether in bed or in a chair or wheelchair. Use
Proper positioning of patients with swallowing difficulties is of primary
cushions or pillows to maintain position.
importance during feeding or eating.
Maintain upright position for 30 to 45 minutes after feeding.
The upright position facilitates the gravitational flow of food or fluid through the alimentary tract. If the head of the bed cannot be elevated because of the patients condition, use a right side-lying position after feedings to facilitate passage of stomach contents into the duodenum.
Provide oral care after meals.
This removes residuals and reduces pocketing of food that can be later aspirated. A displaced tube may erroneously deliver tube feeding into the airway.
In patients with nasogastric (NG) or gastrostomy tubes: o Check placement before feeding.
Use speech pathology consultation as appropriate.
A speech pathologist can be consulted to perform a dysphagia assessment that helps
determine the need for videofluoroscopy or modified barium swallow.
Edx: Explain to patient/caregiver the need for proper positioning.
This decreases the risk of aspiration.
Instruct on signs and symptoms of aspiration.
This aids in appropriately assessing high-risk situations and determining when to call for further evaluation.
Instruct on upperairway suctioning technique
To prevent accumulation of secretions in the oral cavity.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Atun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableDokumen2 halamanAtun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableCharissa Magistrado De LeonBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Care Plan (CASE STUDY DENGUE)Dokumen10 halamanNursing Care Plan (CASE STUDY DENGUE)NiooleBelum ada peringkat
- NCP AgnDokumen2 halamanNCP AgnMichael Vincent DuroBelum ada peringkat
- Or RRLDokumen4 halamanOr RRLAlponce Edal AdagBelum ada peringkat
- Imbalance Nutrition Less Than Body WieghtDokumen2 halamanImbalance Nutrition Less Than Body WieghtAustin Lorenz AlvarezBelum ada peringkat
- Case 052: Biliary ColicDokumen4 halamanCase 052: Biliary ColicZauzaBelum ada peringkat
- Research Evidence and Policy MakingDokumen20 halamanResearch Evidence and Policy Makingcmwangi2174Belum ada peringkat
- Hypokalemia PDFDokumen1 halamanHypokalemia PDFJanedear PasalBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology FinalDokumen2 halamanPathophysiology FinallarissedeleonBelum ada peringkat
- Deep Vein ThrombosisDokumen3 halamanDeep Vein ThrombosisAnonymous cwRgUKv2MQ100% (1)
- Chest InjuryDokumen4 halamanChest InjuryFRANCINE EVE ESTRELLANBelum ada peringkat
- DiverticulitisDokumen15 halamanDiverticulitisElisabeth MelisaBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Hypertensive EmergencyDokumen17 halamanManagement of Hypertensive EmergencyGiovanna AlguBelum ada peringkat
- THROMBOPHLEBITISDokumen50 halamanTHROMBOPHLEBITISmers puno100% (3)
- Prof Ad Day 1Dokumen136 halamanProf Ad Day 1Kareen ArnaizBelum ada peringkat
- SJMC.x-prioritized Nursing ProblemsDokumen8 halamanSJMC.x-prioritized Nursing ProblemsKatherine_Chyr_9112Belum ada peringkat
- IVT Procedure IDokumen47 halamanIVT Procedure Izhallene813Belum ada peringkat
- NCP DHFDokumen3 halamanNCP DHFjsdc_14Belum ada peringkat
- Cardiac TamponadeDokumen6 halamanCardiac TamponadeJara Maris Moreno BudionganBelum ada peringkat
- Definition and FocusDokumen20 halamanDefinition and FocusAbdul Azis G. CamidBelum ada peringkat
- Advanced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDokumen39 halamanAdvanced Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases1882Belum ada peringkat
- Case Study of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Group 2Dokumen19 halamanCase Study of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Group 2nicoleBelum ada peringkat
- Cholecystitis Litiasis EctomyDokumen23 halamanCholecystitis Litiasis EctomyTimothy WilliamsBelum ada peringkat
- ACute Pylonephris Case PresentationDokumen6 halamanACute Pylonephris Case PresentationbantilanBelum ada peringkat
- A Narrative Report On: Physical AssesmentDokumen11 halamanA Narrative Report On: Physical AssesmentchelseyBelum ada peringkat
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDokumen17 halamanAcute TonsillopharyngitisRachel Haide NaravalBelum ada peringkat
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDokumen5 halamanSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoBelum ada peringkat
- QuizDokumen16 halamanQuizDawn MarcoBelum ada peringkat
- Physical AssessmentDokumen64 halamanPhysical AssessmentWalaa ElleithyBelum ada peringkat
- EthicsDokumen1 halamanEthicsNadineBelum ada peringkat
- Gordon's Typology of 11 Functional Health PatternDokumen12 halamanGordon's Typology of 11 Functional Health PatternJ. ishtelleBelum ada peringkat
- NCP PainDokumen2 halamanNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Belum ada peringkat
- CASE STUDY (Role - in Infectious Diarrhea and Oral Thrush)Dokumen29 halamanCASE STUDY (Role - in Infectious Diarrhea and Oral Thrush)maeya18613550% (2)
- AMIDokumen44 halamanAMIsjamilmdfauzieBelum ada peringkat
- Crestor (Rosuvastatin Calcium) : Abbreviations Abbrev Definitions Dictionary ICD9 Codes Equipment Hospitals Drugs More.Dokumen2 halamanCrestor (Rosuvastatin Calcium) : Abbreviations Abbrev Definitions Dictionary ICD9 Codes Equipment Hospitals Drugs More.Aidi RahmanBelum ada peringkat
- CABRAL Essential Hypertension Case Presentation and DiscussionDokumen9 halamanCABRAL Essential Hypertension Case Presentation and DiscussionCalingalan Hussin CaluangBelum ada peringkat
- Out Patient DepartmentDokumen9 halamanOut Patient DepartmentBiway RegalaBelum ada peringkat
- Dialysis ReviewerDokumen16 halamanDialysis ReviewerlarraBelum ada peringkat
- Case Pre - Rhd+capDokumen61 halamanCase Pre - Rhd+capAlexies Cassandra SasoyBelum ada peringkat
- Diarrhea, Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDokumen6 halamanDiarrhea, Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitEfzell Dean BangilanBelum ada peringkat
- Fitrawati Arifuddin - Nursing Care Plan Deficiency of Fluid VolumeDokumen12 halamanFitrawati Arifuddin - Nursing Care Plan Deficiency of Fluid VolumefitrawatiarifuddinBelum ada peringkat
- Acute Tonsillopharyngitis - NonexudativeDokumen12 halamanAcute Tonsillopharyngitis - NonexudativeLemuel GuevarraBelum ada peringkat
- Young InfantDokumen69 halamanYoung InfantAurora Doris BatagaBelum ada peringkat
- Problems With The PassagewayDokumen2 halamanProblems With The PassagewayPrilay Pring AlcopraBelum ada peringkat
- Volume ImpairmentDokumen32 halamanVolume ImpairmentAcohCChaoBelum ada peringkat
- HemorrhoidsDokumen15 halamanHemorrhoidspologroBelum ada peringkat
- CNN Practice QuestionsDokumen5 halamanCNN Practice QuestionsUri Perez MontedeRamosBelum ada peringkat
- Crizotinib Improves ProgressionDokumen3 halamanCrizotinib Improves ProgressionIsabella RoselliniBelum ada peringkat
- Principles of Sterile Technique: Them That Varies. These Principles Are Applied in TheDokumen22 halamanPrinciples of Sterile Technique: Them That Varies. These Principles Are Applied in Thecoosa liquorsBelum ada peringkat
- Legal Issues NotesDokumen79 halamanLegal Issues NotesIconMaicoBelum ada peringkat
- Assisting Lumbar Puncture: By: Bonifacio P. Marilao Jr. Kirstine Anne Camille F. NuezDokumen25 halamanAssisting Lumbar Puncture: By: Bonifacio P. Marilao Jr. Kirstine Anne Camille F. NuezTheSweetpea501Belum ada peringkat
- Pulmonary HypertensionDokumen10 halamanPulmonary HypertensionCkaye GansubinBelum ada peringkat
- CHNDokumen12 halamanCHNJhara100% (1)
- Geria NursingDokumen23 halamanGeria NursingMaia Saivi OmegaBelum ada peringkat
- Pediatric Cardiac DisordersDokumen5 halamanPediatric Cardiac DisordersJerome DazBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Self-Concept RT Body Image (Pott's Dse)Dokumen3 halamanNCP - Self-Concept RT Body Image (Pott's Dse)yanny03Belum ada peringkat
- CholecystectomyDokumen6 halamanCholecystectomyjhodaneBelum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDari EverandA Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Care of The Patient With DysphagiaDokumen15 halamanCare of The Patient With DysphagiaNeesha MBelum ada peringkat
- NCP StrokeDokumen2 halamanNCP StrokeMichael John F. NatividadBelum ada peringkat
- PneumoniaDokumen55 halamanPneumoniaGlenn ValerioBelum ada peringkat
- LoopingDokumen2 halamanLoopingGlenn ValerioBelum ada peringkat
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDokumen593 halamanHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- SocanthroDokumen1 halamanSocanthroGlenn ValerioBelum ada peringkat
- C JDokumen3 halamanC JGlenn ValerioBelum ada peringkat
- Pathophysiology MyomaDokumen4 halamanPathophysiology MyomaGlenn ValerioBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Different Immediate Dentin Sealing Techniques On The Microtensile Bond Strength PDFDokumen6 halamanEffect of Different Immediate Dentin Sealing Techniques On The Microtensile Bond Strength PDFclaudiaBelum ada peringkat
- Pizza Hut and Dominos - A Comparative AnalysisDokumen19 halamanPizza Hut and Dominos - A Comparative AnalysisSarvesh Kumar GautamBelum ada peringkat
- PROD - Section 1 PDFDokumen1 halamanPROD - Section 1 PDFsupportLSMBelum ada peringkat
- Leon County Sheriff'S Office Daily Booking Report 18-Oct-2020 Page 1 of 3Dokumen3 halamanLeon County Sheriff'S Office Daily Booking Report 18-Oct-2020 Page 1 of 3WCTV Digital TeamBelum ada peringkat
- Techno LabDokumen3 halamanTechno LabA M FaisalBelum ada peringkat
- 1716 ch05Dokumen103 halaman1716 ch05parisliuhotmail.comBelum ada peringkat
- BFPPPDokumen15 halamanBFPPPFaith JacalanBelum ada peringkat
- MahuaDokumen12 halamanMahuaVinay ChhalotreBelum ada peringkat
- شيتات محطات كهربية PDFDokumen8 halamanشيتات محطات كهربية PDFhazem saeidBelum ada peringkat
- Wastewater Treatment Lab TestDokumen8 halamanWastewater Treatment Lab TesthuyBelum ada peringkat
- Issues Pertaining To Maintenance of WifeDokumen2 halamanIssues Pertaining To Maintenance of WifeVaishnavi YadavBelum ada peringkat
- Peter H. Rossi - Mark W. Lipsey - Howard E. Freeman - Evaluation - A Systematic ApproachDokumen417 halamanPeter H. Rossi - Mark W. Lipsey - Howard E. Freeman - Evaluation - A Systematic ApproachHector Urzua50% (2)
- FPC Manual PreviewDokumen5 halamanFPC Manual PreviewIbrahim Levent AkkoyunluBelum ada peringkat
- Silicon Epitaxial Planar Transistor 2SA1179: Galaxy ElectricalDokumen5 halamanSilicon Epitaxial Planar Transistor 2SA1179: Galaxy ElectricalsacralBelum ada peringkat
- C783 - Intake Manifold 1 Temperature-Abnormal Rate of ChangeDokumen4 halamanC783 - Intake Manifold 1 Temperature-Abnormal Rate of ChangeLucas CamposBelum ada peringkat
- Carti Libraria Victor Papilian Ian 2015Dokumen8 halamanCarti Libraria Victor Papilian Ian 2015Petru AcozmeiBelum ada peringkat
- Why Is ICS Important For Schools?Dokumen8 halamanWhy Is ICS Important For Schools?Spit FireBelum ada peringkat
- Icu2 Vol22 Sepsisincriticalcare 29marchDokumen52 halamanIcu2 Vol22 Sepsisincriticalcare 29marchricardoatejassBelum ada peringkat
- Transmission Line BOQ VIMPDokumen72 halamanTransmission Line BOQ VIMPkajale_shrikant2325Belum ada peringkat
- 4th Laboratory Activity Gallus DomesticusDokumen4 halaman4th Laboratory Activity Gallus DomesticusZia Ammarah SaripBelum ada peringkat
- 2.10 A Substrate Is Decomposed in The Presence of An Enzyme According To The Michaelis-MentenDokumen2 halaman2.10 A Substrate Is Decomposed in The Presence of An Enzyme According To The Michaelis-MentenEureca ParraBelum ada peringkat
- "Mode One" Author & Dating Coach Alan Roger Currie Releases Criticism of Alleged Harvey Weinstein BehaviorDokumen3 halaman"Mode One" Author & Dating Coach Alan Roger Currie Releases Criticism of Alleged Harvey Weinstein BehaviorPR.com100% (1)
- Manoshe Street Takeaway MenuDokumen9 halamanManoshe Street Takeaway MenuimaddakrBelum ada peringkat
- Employee Turnover ReportDokumen10 halamanEmployee Turnover ReportDon83% (6)
- The Consumption of WaterDokumen2 halamanThe Consumption of WaterasungapeBelum ada peringkat
- The Learner The Learner : 1 QuarterDokumen4 halamanThe Learner The Learner : 1 QuarterRode Jane SumambanBelum ada peringkat
- Work Immersion Rubric & Assessment ReportDokumen2 halamanWork Immersion Rubric & Assessment ReportJEE AR CANTEREBelum ada peringkat
- Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology and Determinative BacteriologyDokumen2 halamanBergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology and Determinative BacteriologyGeetha Anjali0% (1)
- Bcba CourseworkDokumen8 halamanBcba Courseworkafjwoamzdxwmct100% (2)
- 17.8 Inheritance IGCSE CIE Biology Ext Theory MS - LDokumen9 halaman17.8 Inheritance IGCSE CIE Biology Ext Theory MS - LBlessing TshumaBelum ada peringkat