Drugs For GI Disorders
Diunggah oleh
Aalap ShahDeskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Drugs For GI Disorders
Diunggah oleh
Aalap ShahHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
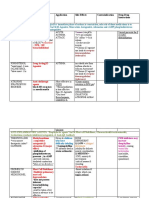
Anti-Secretory Agents Group Drugs H2 Blockers Cimetidine Ranitidine Famotidine Nizatidine
Mode of Action Competitive antagonist of H2 receptors.
Proton Pump Inhibitors
Oral: Omeprazole Lansoprazole Rabeprazole IV Pantoprazole
Irreversibly binds to the sulfhydryl groups (cysteine residues of proton pumps).
Side Effects Most associated w/ cimetidine Inhibits cytochrome P-450 (Prolongs t warfarin/ phenytoin) Anti-androgenic (High Doses) [Libido loss, gynecomastia & impotence in men, galactorrhea b/c prolactin in women] CNS disturbances Hematologic effects (All 4) Nausea, diarrhea, myalgia, rashes, & itching. Nausea, diarrhea, cramps 3% Headache, dizziness, rashes, somnolence Hypergastrinema Nocturnal Acid Breakthrough Bacterial Overgrowth in GI Inhibits cytochrome P-450 (in vitro) (rare)
Random Potency: Famotidine (40mg) > Ranitidine & Nizatidine (300mg) > Cimetidine (800mg) Tablets (One @ bedtime) & IV. Single bedtime dose as effective as multiple day doses. dose used for maintenance. Efficacy: 80-90% in 4-6 weeks
Substituted Benzimidazoles (weak bases) Prodrugs, only active at acidic pH (<5). Prodrug absorbed in intestine, transported back to stomach epithelium & conc. in parietal cell canaliculi. Omeprazole 20mg/d for dose Maintenance or full dose Acid secretion restarts only when new pumps are synthesized. MOST POTENT INHIBITORS. Higher efficacy & rates than H2 blocks: 90-95% in 4 weeks. Also used in anti-H-pylori therapy. Approved short-term treatment = 4-8 weeks. Effective long term in reducing secretion in gastric hypersecretory states (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome)
Antacids Drug Mode of Action Antacids Neutralize/Buffer Acids May Prostaglandins & mucus
Side Effects Mg-based: Diarrhea (laxative) Al-based: Constipation (adsorbent) Ca-based: Hypercalcemia & milk-alkali syndrome (w/ high doses) Risk of rebound secretion of acid, due to gastrin triggered by acidity (High in Mg/Al, Low in Ca)
Random Generally consist of MgOH, AlOH, CaCO3 & NaHCO3. Cost the same as H2 blockers & sucralfate Dosage: 4 doses of 140 meq of an antacid with high neutralizing capacity (3 post-meal & 1 bedtime); post-meal doses taken 1-3 hours after each meal. *Requires proper doing & compliance* Ca2+ stimulates gastrin & HCl release.
Cytoprotective Agents Drug Mode of Action Prostaglandins Cytoprotective: release of gastroduodenal mucus & bicarb. Antisecretory: Reduces cAMP levels, inhibiting histamine-stimulated acid release by parietal cells. Sucralfate - Acid turns it into sticky slurry that binds to hemoglobin & pepsin & acts as a barrier against further acid-pepsin damage. - tissue levels of prostaglandins & mucus. Bismuth Compounds - Binds to ulcer crater & protects it from damage - May stimulate mucus production & prostaglandin synthesis - Anti-H. pylori activity.
Side Effects Abortifacient Ab. Cramping Diarrhea (dose-dependent/self limited) Constipation Dry Mouth Reduces bioavailability of tetracycline, phenytoin, digoxin, cimetidine Black stool, dark tongue. Risk of bismuth & subsalicylate toxicity. ie. encephalopathy
Random Ex.: Misoprostol Synthetic PGE1 analog - Prevents NSAID-induced gastric ulcers - Protective, BUT at doses that acid release Non-absorbable Al salt of octasucrose. No acid neutralizing capacity. Dose: 4g a day (Usually 1g 4x a day) Same healing rate as H2-blockers & antacids. Limited use due to efficacy of other agents. Used in ICU to prevent stress-induced GI bleeds. Pepto-Bismol Bismuth subsalicylate & bismuth subcitrate.
Antimicrobials (Anti-H. pylori therapy) Therapy Triple Therapy Random PPI PPI agents may have some antimicrobial actions. 90% cure rate 2 week regimen First-line therapy Lower ulcer reoccurrence rate than H2 or PPI (10%vs90%) Quadruple Triple Therapy +Tinizadole 90% duodenal ulcers (But requires good patient Therapy Tetracycline + Metronidazole + Bismuth + H2-antagonist (or PPI) compliance) 2 week regimen & cheap Other Combos Ranitidine bismuth citrate Amoxicillin (Tritec) Metronidazole Clarithromycin Tetracycline (2 of these) Omeprazole + Amoxicillin + Levofloxacin There are metronidazole & clarithromycin-resistant H. pylori. Antibiotic Amoxicillin Metronidazole Clarithromycin Tetracycline (2 of these)
Treats Constipation Group Mode of Action Bulk-forming -Absorbs water agents (Dietary - growth of intestinal bacteria Fiber) -fermentation by bacterial action produces metabolites that alter colonic handling of fluid and electrolytes. -Digestion by bacterial action to metabolites that increase stool osmolality Pulls water & ions into GI Saline (Osmotic) -Poorly absorbed, osmotically active Laxatives salts which increase water in colon Stimulant Laxatives Lubricants (Stool Softeners) Group - secretion of H2O & electrolytes into GI - colonic motility - Acts as lubricants - Emulsified in stool & softens it.
Side Effects Minimal - Intestinal Gas
Random Safest/Least expensive Plant Cell walls Patient should drink lots of water to prevent impaction. Expect increased initially. - Bran, Rice & psyllium (Metamucil)
Very NON-toxic Fluid Loss Abuse can lead to cathartic colon
Onset: 3-4 hours Often used in prep for surgeries Mg Salts, Lactulose, Sorbitol, Osmotic lavage fluids Rectal Onset 1-2 hr. Oral Onset 6-12 hr. Ex. Castor Oil, Bisacodyl, Senna Ex. Docusate sodium (Detergent), Mineral Oil ( fat soluble vitamin absorption) & Glycerin (suppository). Side Effects Random Less effective than other diarrheals Bismuth subsalicylate (Pepto-bismol) Relieves mild diarrhea Mainstay drug
Treat Diarrhea Drugs Bulk Forming Agents Kaopectate: kaolin (Al) & pectin (fruit) Donnagel: attapulgite (= kaolin) Bismuth Compounds
Adsorbents/ Demulcents
Mode of Action - Water absorption ( bowel fluidity & bulk) Bind intestinal bacteria & toxins
Adsorbent to bacteria, toxins, Abuse & viruses Anti Microbial Act via and opiate receptors Slow GI motility ( ACh release). Ab. pain, emesis, constipation, fatigue, drowsiness.
Opiates
Loperimide: Poor CNS penetration Diphenoxylate w/ atropine Difenoxin w/ atropine: active metabolite of diphenoxylate
Antiemetic Group Drug Mode of Action Dopamine Prochlorperazine -Blocks dopamine receptors in Antagonist CTZ & GI Metoclopramide -Blocks dopamine receptors in CTZ and GI -GI motility and emptying: prokinetic (via cholinomimetic action) act centrally (CTZ) & peripherally (vestibular apparatus) Blocks H1 receptors
Side Effects Dystonias Dystonias, Parkinsonism, somnolence, nervousness, galactorrhea ( prolactin); diarrhea. Sedation and dry mouth (therapeutic doses) 4 Confusion and memory loss
Random Phenothiazine Not effective against motion sickness, or patients achieving chemo Benzamide
Anticholinergic Scopolamine Antihistamines (H1 Blockers) Cyclizine Meclizine Dimenhydrinate Promethazine
Serotonin Antagonists
Ondansetron Dolasetron Granisetron
Blocks 5-HT3 receptors in CTZ & Vagal terminals
Constipation Diarrhea Headache
Prevents motion sickness. Given orally, by injection, or transdermal patch Promethazine Most effective, but sedating Prevents motion sickness (Also is anticholinergic) Control Post-Op Emesis Little Potency against chemo-induced emesis Available by injection or tablet General Anti-emetic NOT effective against motion sickness Originally used against cisplatin effects. Approved in 2003 Used as adjunct to standard antiemetics to control emesis from highly emetogenic chemo.
Substance P (Neurokinin 1) Antagonists
Aprepitant
Blocks NK-1 receptor in emesis center
Generally well tolerated, but: Fatigue (most common), anorexia, constipation, diarrhea. Aprepitant is metabolized by P-450; potential drug interactions
Benzamides
Metoclopramide Cisapride (No longer available) Cisapride (No longer available)
Mode of Action Cholinomimetics ACh release from enteric neurons & response to Ach
Side Effects Extrapyramidal effects
Cardiotoxic effects (Ik block) when coadministered with drugs/foods which metabolism: - QT interval - arrhythmias - cardiac arrest
Random Used to increase gastric motility and emptying Treats GERD dopamine-blocking effect may contribute to prokinetic effect NO dopamine blockage NO extrapyramidal effects Prolongs action potentials May contribute to use as heartburn drug by enhancing contractions of esophageal sphincter
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Antibiotic Summary - DraftDokumen10 halamanAntibiotic Summary - DraftStrept Pneumonia100% (1)
- Classification of AntibioticsDokumen4 halamanClassification of AntibioticsNico AvellanaBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Dokumen40 halamanAntibiotics.: Prepared by L.Mbise OCTOBER 2012Moses MberwaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology Section on Antibiotics, Antivirals and AntifungalsDokumen5 halamanPharmacology Section on Antibiotics, Antivirals and AntifungalsPathalee ThalpavilaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug InteractionsDokumen3 halamanDrug Name Mechanism Application Side Effects Contraindication Drug-Drug Interactionsazhar hussinBelum ada peringkat
- Quinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist and Urinary Tract Antitb and LeprosyDokumen124 halamanQuinolones, Folic Acid Antagonist and Urinary Tract Antitb and LeprosyrenBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Emetic DrugsDokumen3 halamanAnti Emetic DrugsFaria Islam JuhiBelum ada peringkat
- Antibiotic GuideDokumen6 halamanAntibiotic GuideAnnTran100% (1)
- Mu 002Dokumen10 halamanMu 002chandanBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherDokumen4 halamanDrug Outline: Autonomic Nervous System Drug Class Drug OtherCess Lagera YbanezBelum ada peringkat
- Manteux TestDokumen25 halamanManteux TestEvaNatashaBelum ada peringkat
- Augmenten (Amoxicillin Clavulan)Dokumen2 halamanAugmenten (Amoxicillin Clavulan)Adrianne BazoBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Retro Viral DrugsDokumen33 halamanAnti-Retro Viral Drugsapi-306036754Belum ada peringkat
- Antidiarrheal DrugsDokumen4 halamanAntidiarrheal DrugsNadhirah ZulkifliBelum ada peringkat
- Top 10 Drug InteractionsDokumen4 halamanTop 10 Drug InteractionsLeyla MajundaBelum ada peringkat
- Aminogycoside AntibioticsDokumen31 halamanAminogycoside AntibioticsNurul Febrina100% (2)
- Non-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS)Dokumen5 halamanNon-Steroidal Anti Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDS)Pardhasaradhi PantaBelum ada peringkat
- TizanidineDokumen2 halamanTizanidinebhawanisrBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of The GITDokumen31 halamanPharmacology of The GITmarviecute22Belum ada peringkat
- Protein-Calorie Malnutrition Legal RiskDokumen6 halamanProtein-Calorie Malnutrition Legal RiskfirdakusumaputriBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Infectives and AntibioticsDokumen38 halamanAnti-Infectives and AntibioticsKarel Lu0% (1)
- DrugsDokumen20 halamanDrugsLee Won100% (1)
- SAQ Short Form 2006Dokumen1 halamanSAQ Short Form 2006Hanan DaghashBelum ada peringkat
- Nursing Theory: Asthma (Presentation)Dokumen13 halamanNursing Theory: Asthma (Presentation)vinda astri permatasari100% (1)
- ClindamycinDokumen3 halamanClindamycinShaira TanBelum ada peringkat
- Anti-Infective Pharmacology ReviewerDokumen5 halamanAnti-Infective Pharmacology ReviewerArianne Pearl PrimeroBelum ada peringkat
- Chemotherapy NDokumen28 halamanChemotherapy NFaisal MehboobBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Card Solu-MEDROLDokumen2 halamanDrug Card Solu-MEDROLBenBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of ActionDokumen13 halamanGeneric Name Brand Names Common Uses Possible Side Effects Mechanism of Actionangel3424Belum ada peringkat
- Antibiotics 9Dokumen11 halamanAntibiotics 9Beth Morales100% (1)
- Animal Bites Approach GuideDokumen39 halamanAnimal Bites Approach GuideNetii FarhatiBelum ada peringkat
- Asthma Inhaler Device Techiques ChecklistDokumen2 halamanAsthma Inhaler Device Techiques Checklistdaniel ragonjanBelum ada peringkat
- Cholinergic Drugs - TablesDokumen7 halamanCholinergic Drugs - TablesThuan Tăng NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Practical Guide to Urinalysis Screening and InterpretationDokumen9 halamanPractical Guide to Urinalysis Screening and InterpretationyuppierajBelum ada peringkat
- Antiemetic Drugs PDFDokumen12 halamanAntiemetic Drugs PDFDanisha Laila100% (2)
- Drug StudyDokumen3 halamanDrug StudyGena Manimtim100% (1)
- Pharmacist's Letter: Prescriber's LetterDokumen6 halamanPharmacist's Letter: Prescriber's LetterJaved AkhtarBelum ada peringkat
- Pharm 4 Fun Suzanne Morris MetronidazoleDokumen2 halamanPharm 4 Fun Suzanne Morris MetronidazoleJasmyn RoseBelum ada peringkat
- Anti Tubercular DrugsDokumen63 halamanAnti Tubercular DrugsYasir KhanBelum ada peringkat
- Oxytocin and Methylergonovine Nursing StudyDokumen16 halamanOxytocin and Methylergonovine Nursing StudyDinarkram Rabreca EculBelum ada peringkat
- Generic Name: BudesonideDokumen8 halamanGeneric Name: BudesonidemeangelmeBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 13 PharmacologyDokumen35 halamanChapter 13 PharmacologyEdelrose LapitanBelum ada peringkat
- Drugs Affecting the Respiratory SystemDokumen137 halamanDrugs Affecting the Respiratory SystemUmar Bakshi100% (1)
- Complete Drugs StudyDokumen13 halamanComplete Drugs StudyPeace Andong PerochoBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDokumen33 halamanPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarfaizaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug Study Pyrantel & CefuroximeDokumen2 halamanDrug Study Pyrantel & CefuroximeMikhael Briones ApasBelum ada peringkat
- Anticoagulants DrugsDokumen6 halamanAnticoagulants DrugsHusam Al-OdatBelum ada peringkat
- Tiotropium uses and side effectsDokumen2 halamanTiotropium uses and side effectsjulieBelum ada peringkat
- Chemotherapeutic DrugsDokumen122 halamanChemotherapeutic Drugsdex7reme100% (1)
- Antibiotic Class by CoverageDokumen3 halamanAntibiotic Class by Coverageayy1Belum ada peringkat
- Predisposing Factors of ADRsDokumen7 halamanPredisposing Factors of ADRssuhas reddyBelum ada peringkat
- Antiviral AgentsDokumen14 halamanAntiviral AgentsKate MendozaBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacotherapy of - Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDokumen4 halamanPharmacotherapy of - Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaBaarid HamidiBelum ada peringkat
- Management of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Dari EverandManagement of Tuberculosis: A guide for clinicians (eBook edition)Belum ada peringkat
- A Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDari EverandA Simple Guide to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Inflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDari EverandInflamed Trachea, (Tracheitis) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacotherapy of Peptic Ulcer: DR ZareenDokumen50 halamanPharmacotherapy of Peptic Ulcer: DR ZareenGareth BaleBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacotherapy of Peptic Ulcer: Classification and Mechanisms of DrugsDokumen50 halamanPharmacotherapy of Peptic Ulcer: Classification and Mechanisms of DrugsGareth BaleBelum ada peringkat
- Pharmacology of The Gastrointestinal Drugs (I)Dokumen12 halamanPharmacology of The Gastrointestinal Drugs (I)anaBelum ada peringkat
- Drug CardsDokumen17 halamanDrug CardsJoane LacapBelum ada peringkat
- Prperman 2016 14 3 (Spec. 14Dokumen8 halamanPrperman 2016 14 3 (Spec. 14celia rifaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter-5 Contract ManagementDokumen43 halamanChapter-5 Contract Managementprem kumarBelum ada peringkat
- Project Cost ForecastDokumen11 halamanProject Cost ForecastJames MendesBelum ada peringkat
- Classification of MatterDokumen2 halamanClassification of Matterapi-280247238Belum ada peringkat
- Seismic Design Guide (2010)Dokumen102 halamanSeismic Design Guide (2010)ingcarlosgonzalezBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 - J - Chir - Nastase Managementul Neoplaziilor Pancreatice PapilareDokumen8 halaman2022 - J - Chir - Nastase Managementul Neoplaziilor Pancreatice PapilarecorinaBelum ada peringkat
- Description MicroscopeDokumen4 halamanDescription MicroscopeRanma SaotomeBelum ada peringkat
- The Ideal Structure of ZZ (Alwis)Dokumen8 halamanThe Ideal Structure of ZZ (Alwis)yacp16761Belum ada peringkat
- Utilization of Wood WasteDokumen14 halamanUtilization of Wood WasteSalman ShahzadBelum ada peringkat
- Mohammad R. Mestarihi: About Me ObjectiveDokumen1 halamanMohammad R. Mestarihi: About Me ObjectiveMhmd MsttBelum ada peringkat
- Hearing God Through Biblical Meditation - 1 PDFDokumen20 halamanHearing God Through Biblical Meditation - 1 PDFAlexander PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- "The Meeting of Meditative Disciplines and Western Psychology" Roger Walsh Shauna L. ShapiroDokumen13 halaman"The Meeting of Meditative Disciplines and Western Psychology" Roger Walsh Shauna L. ShapiroSayako87Belum ada peringkat
- Roxas Avenue, Isabela City, Basilan Province AY: 2018-2019: Claret College of IsabelaDokumen2 halamanRoxas Avenue, Isabela City, Basilan Province AY: 2018-2019: Claret College of IsabelaJennilyn omnosBelum ada peringkat
- Broom Manufacture Machine: StartDokumen62 halamanBroom Manufacture Machine: StartHaziq PazliBelum ada peringkat
- Vernacular Architecture: Bhunga Houses, GujaratDokumen12 halamanVernacular Architecture: Bhunga Houses, GujaratArjun GuptaBelum ada peringkat
- Educating The PosthumanDokumen50 halamanEducating The PosthumanCatherine BrugelBelum ada peringkat
- PoiconverterDokumen2 halamanPoiconvertertaco6541Belum ada peringkat
- Graphs & Charts SummariesDokumen20 halamanGraphs & Charts SummariesMaj Ma Salvador-Bandiola100% (1)
- CPS Layoffs BreakdownDokumen21 halamanCPS Layoffs BreakdownjroneillBelum ada peringkat
- Makerwys - Exe Version 4.891: by Pete Dowson © 2019 InstructionsDokumen11 halamanMakerwys - Exe Version 4.891: by Pete Dowson © 2019 InstructionsRafrol RamonBelum ada peringkat
- Biosynthesis of FlavoursDokumen9 halamanBiosynthesis of FlavoursDatta JoshiBelum ada peringkat
- Valentine Gifting - Accessories EditionDokumen25 halamanValentine Gifting - Accessories EditionPriyanath PaulBelum ada peringkat
- Case Analysis of CriminologyDokumen12 halamanCase Analysis of CriminologyinderpreetBelum ada peringkat
- Pub - Perspectives On Global Cultures Issues in Cultural PDFDokumen190 halamanPub - Perspectives On Global Cultures Issues in Cultural PDFCherlyn Jane Ventura TuliaoBelum ada peringkat
- Pahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryDokumen285 halamanPahang JUJ 2012 SPM ChemistryJeyShida100% (1)
- Liugong 938 Wheel Loader Parts ManualDokumen20 halamanLiugong 938 Wheel Loader Parts Manualjonathan100% (49)
- Analogue Lab Manual AL7212 V2.1-Panduan Praktek DSR Elektronika-DikonversiDokumen235 halamanAnalogue Lab Manual AL7212 V2.1-Panduan Praktek DSR Elektronika-DikonversiAl-FarabiBelum ada peringkat
- Resp Part 4Dokumen95 halamanResp Part 4Kristian CadaBelum ada peringkat
- Product Differentiation and Market Segmentation As Alternative Marketing StrategiesDokumen7 halamanProduct Differentiation and Market Segmentation As Alternative Marketing StrategiesCaertiMBelum ada peringkat
- Appraisal Sample PDFDokumen22 halamanAppraisal Sample PDFkiruthikaBelum ada peringkat