NCP Head
Diunggah oleh
ann-lisel-manahan-7670Deskripsi Asli:
Judul Asli
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
NCP Head
Diunggah oleh
ann-lisel-manahan-7670Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
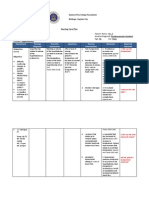
B. Nursing Management 1.
Nursing Care Plan Problem # 1: Hyperthermia
ASSESSMENT
PROBLEM
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Fever is the most common sign of systemic response to injury & it is most likely caused by indigenous pyrogens released from neutrophils & macrophages. These substance reset the hypothalamic thermoset, w/c controls body temp. & produce fecer. Leukocyosis, an increase in the synthesis & release of neutrophils from born marrow may occur to provide the body w/ greater ability to fight infection. During the process general non-specific symptoms develop, including malaise, loss of appetite, aching & weakness
OBJECTIVE
INTERVENTION
EVALUATION
S> O> Pt may manifest the following: >flushed skin >skin warm to touch >restlessness >weakness >Increased body temp of 38C >body malaise >seizures or convulsion >tachycardia >loss of appetite
Hyperthermi a
Short term: 1.Monitor & Short term: After 4 of NI, recorded VS The pt shall have the pt will for baseline maintained core maintain core temp will data temp will 2.Perform TSB decrease from decrease from heatloss by 39C to 37.5C. 39C to evaporation & 37.5C. conduction 3.Use blanket & wrap extremities w/ bath towel Long term: to minimize After 3 days of Long- term shivering NI, the pt will 4. monitor intake & be free of output complication to know if such as output is irreversible equal or close brain damage to intake & free from 5.provide adequate seizure rest periods activity. to regain energy through resting 6. instruct client to increase fluid intake to control possible fluid loss, to replace fluid loss & permit heat loss 7.Encourage client to eat balance diet and nutritious foods to meet increase metabolic demands 8. instruct pt to avoid tight fitting clothes
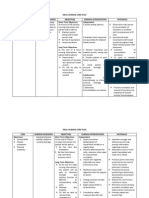
Problem # 2: Acute Pain
ASSESSMENT
PROBLEM
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Pain may arise from obstruction of the common blood on the brain. Inflammation and swelling depress the free nerve endings and cause the pain. Headaches following a head injury may be mild, moderate or severe and the extent of the injury itself is not always indicative of the severity of headaches. Mild headaches following a head injury are those that usually don't prevent a person from functioning daily.
OBJECTIVE
INTERVENTION
EVALUATION
S> O> The patient may manifest the following: >guarding behavior on RUQ portion of the skull >nausea vomiting >facial grimace >unable freely to move and
Acute Pain
Short Term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will be able to verbalize a decrease in pain. Long Term:
> self focusing >skull heaviness >narrowed focus >expressive favor >sleep disturbance
1.Monitor & recorded VS for baseline data 2.Assess patient quality onset, duration, location and intensity of pain. to be specific of the kind of pain experienced 3. Provide comfort measure such as quite environment using relaxation techniques, backrub, comfortable positioning to promote rest and enhance the effects of analgesics given 4. Provide individuals with opportunities to discuss fear and acknowledge the difficulty of situation. to assist patient and family to respond optimally to the individuals pain experience 5. Provide diversional activities to divert focus of the pt. to the pain. 6. Educate client regarding medications, dosage, side effects Understanding of all medications allows formore appropriate
Short term: The pt shall have maintained core temp will decrease from 39C to 37.5C.
Long- term
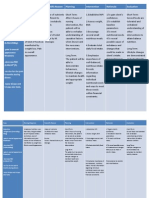
Problem # 3: Altered cerebral tissue perfusion related to hematoma
ASSESSMENT
PROBLEM
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE
OBJECTIVE
INTERVENTION
EVALUATION
S>
Altered Altered tissue cerebral perfusion is the O> The patient may tissue decrease in oxygen manifest the perfusion resulting in the following: related to failure to nourish hematoma the tissues at the >aletered mental capillary level. status Traumatic brain injury is a >speech devastating abnormalities problem with both high subsequent >behavioral morbidity and high changes mortality. Injury to the brain occurs >restlessness both at the time of the initial trauma >change in motor (the primary injury) response and subsequently due to ongoing >extremity cerebral ischemia weakness (secondary injury). Cerebral edema, >paralysis hypotension, and hypoxic conditions >changes in are well recognized papillary reactions causes of this secondary injury. In >difficulty in the intensive care swallowing unit, raised intracranial pressure (intracranial hypertension) is seen frequently after a severe diffuse brain injury (one that occurs over a widespread area) and leads to cerebral ischemia by compromising cerebral perfusion.
Short Term: After 4 hours of NI, the patient will demonstrate behavior changes to improve circulation like relaxation techniques and dietary program Long Term: After 3 days of NI, the patient will verbalize understanding of condition, therapy regimen, side effects of medications, and when to contact health care provider
1.Monitor & recorded VS Rationale: for baseline data 2. Determine factors related to individual situation, cause for coma, decreased cerebral perfusion, and potential for ICP. Rationale: Influences choice of interventions. Deterioration in neurological signs and symptoms or failure to improve after initial insult may reflect decreased intracranial adaptive capacity, which requires that client be admitted to critical care area for monitoring of ICP and for specific therapies geared to maintaining ICP within a specified range. 3. Monitor and document neurological status frequently and compare with baseline. Rationale: Assesses trends in LOC and potential for increased ICP and is useful in
Short term: The pt shall have demonstrate behavior changes to improve circulation like relaxation techniques and dietary program
Long- term The patient shall have verbalized understanding of condition, therapy regimen, side effects of medications, and when to contact health care provider
Problem # 4: Altered Thought Processes related physiological changes
ASSESSMENT
PROBLEM
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Disturbed thought processes is the disruption in cognitive operation and activities. Due to presence of predisposing and pecipitating factors, there is decreased blood supply in the frontal lobe. There is damaged in this are which causes psychotic manifestations.
OBJECTIVE
INTERVENTION
EVALUATION
S>
Altered Thought O> Pt may manifest Processes the following: related to altered level of - Memory deficits or consciousnes problems s and confusion - Inaccurate interpretation of environment - Inappropriate non reality based thinking
Short term:
1.Monitor & recorded VS After 4 of NI, Rationale: for the pt will baseline data recognize 2.Establish rapport changes in Rationale to gain thinking trust and to establish cooperation of the patient 3.Assess pt. condition Long term: Rationale to identify underlying After 3 days of health problems and NI, the pt will to identify demonstrate appropriate behaviors/ interventions to lifestyle correct the changes to problems seen prevent minimize 4. Utilize safety changes in measures to protect mentation client Rationale During acute phase, clients delusional thinking might dictate to them that they might have to hurt others for their safety 5. Be aware that clients delusions represent the way that he experiences reality Identifying the clients experiences allows the nurse to understand the clients feelings
Short term: The pt shall have maintained recognize changes in thinking
Long- term the pt shall have demonstrated behaviors/ lifestyle changes to prevent minimize changes in mentation
-Cognitive dissonance
Problem # 5: Impaired physical mobility related to motor, sensory, proprioceptive deficits, depressed consciousness level
ASSESSMENT
PROBLEM
BACKGROUND KNOWLEDGE Impaired physical mobility is the limitation of in independent, purposeful physical movement of the body or of one or more extremities. In head injury the head experienced a trauma in different lobes of the brain and by these the patient can experience restlessness and should be at bed rest at the moment.
OBJECTIVE
INTERVENTION
EVALUATION
S>
Impaired physical O> Pt may manifest mobility the following: related to motor, sensory, proprioceptiv > Edema (none deficits, pitting) depressed consciousnes Limited ROM s level Limited muscle strength or control Inability to move purposefully in the environment Impaired coordination
> After 4-6 of NI patient will verbalize understanding of situation and individual treatment regimen and safety measures
1.Monitor & recorded VS Rationale:for baseline data 2.Assess patients general condition
Short term: The pt shall have verbalized understanding of situation and individual treatment Rationale:To regimen and determine present safety measures health status 3. Determine comfortable position for patient
Rationale:To > Long- term: determine the need Long- term for repositioning After 2-3 days The patient shall 4. Provide safety by of NI, patient have will raising side rails demonstrated demonstrate behaviors that behaviors that enable enable resumption of resumption of Rationale:Prevent activities activities injury from falls 5. Provide adequate rest Rationale:Provide energy for exercise 6. Encourage intake of nutritious foods Rationale:To provide optimum nutrition for fast healing 7.Provide early ambulation and out
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Life Style Wellness Coaching PDFDokumen275 halamanLife Style Wellness Coaching PDFSundar Prabhu71% (7)
- Barangay Nutrition Scholar Ordinances DraftDokumen4 halamanBarangay Nutrition Scholar Ordinances Draftcorinabasubas91% (11)
- 5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansDokumen19 halaman5 Benign Febrile Convulsions Nursing Care PlansRoanna Alyssa Sy Jimenez75% (4)
- John Balik, Total Muscularity: SuperStar Nutrition (Santa Monica, 1979) - Physical Culture StudyDokumen11 halamanJohn Balik, Total Muscularity: SuperStar Nutrition (Santa Monica, 1979) - Physical Culture Studygomitadelimon100% (2)
- NCP Head InjuryDokumen3 halamanNCP Head InjuryAngel Mae Alsua100% (2)
- Case Study (Nasopharyngeal Cancer)Dokumen31 halamanCase Study (Nasopharyngeal Cancer)aj christian93% (15)
- Pathophysiology of Acute PancreatitisDokumen1 halamanPathophysiology of Acute PancreatitisHarvin FrancoBelum ada peringkat
- Cap NCPDokumen6 halamanCap NCPMarlo Parayno100% (2)
- Mindset 1 Unit 1-2-3 ReadingDokumen2 halamanMindset 1 Unit 1-2-3 ReadingMai ThaiBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiomyopathy Concept MapDokumen2 halamanCardiomyopathy Concept Mapfriendofnurse100% (1)
- Handbook of Nutrition and Food PDFDokumen1.613 halamanHandbook of Nutrition and Food PDFZahid Ali100% (1)
- Rufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Dokumen6 halamanRufino, Leslie Kriztel S. BSN 3-2 Group 1Deinielle Magdangal RomeroBelum ada peringkat
- NCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputDokumen3 halamanNCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputErienne Lae Manangan - CadalsoBelum ada peringkat
- NCP CvaDokumen4 halamanNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeBelum ada peringkat
- NCP AneurysmDokumen4 halamanNCP AneurysmJanielle Christine Monsalud100% (1)
- Diarrhea Care PlanDokumen2 halamanDiarrhea Care Planzepoli_zepoly6232100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDokumen5 halamanNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizBelum ada peringkat
- Patient Education PlanDokumen4 halamanPatient Education Planapi-248022066Belum ada peringkat
- Potts Disease NCP .. JustificationDokumen8 halamanPotts Disease NCP .. JustificationMicah SalesBelum ada peringkat
- NCP CKDDokumen3 halamanNCP CKDRiel TumandaBelum ada peringkat
- NCP CholeraDokumen2 halamanNCP CholeraMichael Angelo Garcia RafananBelum ada peringkat
- Surgical NCPDokumen6 halamanSurgical NCPAreeya SushmitaBelum ada peringkat
- What Is Stroke?: BY: Luis Alberto Sanchez Hernandez Physical TherapistDokumen12 halamanWhat Is Stroke?: BY: Luis Alberto Sanchez Hernandez Physical TherapistLidiaAMonroyRBelum ada peringkat
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDokumen9 halamanFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- TIA Case StudyDokumen3 halamanTIA Case StudySanny Ramos100% (1)
- Tetralogy of FallotDokumen5 halamanTetralogy of FallotCharity OaniaBelum ada peringkat
- Doxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsDokumen33 halamanDoxofylline: D 400 MG TabletsBibek Singh Mahat100% (2)
- Head Injury .Dokumen26 halamanHead Injury .Lenjun100% (4)
- Myocardial InfarctionDokumen45 halamanMyocardial InfarctionGopal SinghBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertensive NephrosclerosisDokumen14 halamanHypertensive Nephrosclerosisreysanne100% (1)
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDokumen5 halamanANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDavid CalaloBelum ada peringkat
- Acs Nstemi Vs Ua - PathoDokumen2 halamanAcs Nstemi Vs Ua - PathoJerom YamatBelum ada peringkat
- Case Scenario: Hot Spells, Porous BonesDokumen10 halamanCase Scenario: Hot Spells, Porous Bonesjaira magbanua100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryDokumen4 halamanNursing Care Plan For Acute Head InjuryAngie Mandeoya67% (3)
- MorphineDokumen3 halamanMorphineAizat KamalBelum ada peringkat
- Stevens Johnson Syndrome CASEDokumen53 halamanStevens Johnson Syndrome CASEKathrina CraveBelum ada peringkat
- NCP OrthoDokumen1 halamanNCP Orthoroger0% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac Output FinalDokumen2 halamanDecreased Cardiac Output FinalSandraDeeBelum ada peringkat
- Penicillin GDokumen2 halamanPenicillin Gapi-295691235Belum ada peringkat
- Burns - Airway Clearance, Risk For IneffectiveDokumen2 halamanBurns - Airway Clearance, Risk For Ineffectivemakyofrancis20Belum ada peringkat
- Assessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGDokumen11 halamanAssessment Explanation Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Objective: STG: STGGrape JuiceBelum ada peringkat
- MGH 8 - Ihd - NCPDokumen12 halamanMGH 8 - Ihd - NCPSesinando Niez Quilao Jr.100% (1)
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDokumen2 halamanImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisBelum ada peringkat
- TherablocDokumen3 halamanTherablocianecunar100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDokumen11 halamanNursing Care Plan Renal Failurenosevad88850% (2)
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Dokumen4 halamanNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezBelum ada peringkat
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDokumen6 halamanDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarBelum ada peringkat
- Fistula NCPDokumen1 halamanFistula NCPHasna LisnaBelum ada peringkat
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusDokumen3 halamanWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNBelum ada peringkat
- CVADokumen116 halamanCVAkathy100% (1)
- Complications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETDokumen6 halamanComplications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETRadiyan MeidhiyantoBelum ada peringkat
- Impaired Physical MobilityDokumen2 halamanImpaired Physical MobilityAbdelhafiz SusmiranBelum ada peringkat
- Ineffective ProtectionDokumen7 halamanIneffective Protectionapi-283822730Belum ada peringkat
- Risk For Impaired Skin IntegrityDokumen3 halamanRisk For Impaired Skin IntegrityDharylle CariñoBelum ada peringkat
- Otitis Media AcuteDokumen30 halamanOtitis Media AcuteDede Gustina AyuBelum ada peringkat
- NCP - Hyperthermia - FEUNRMFDokumen5 halamanNCP - Hyperthermia - FEUNRMFJk SalvadorBelum ada peringkat
- CP - NCPDokumen15 halamanCP - NCPjezreel terreBelum ada peringkat
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome CASEDokumen38 halamanStevens-Johnson Syndrome CASEChristy Rose AgrisBelum ada peringkat
- PathophysiologyDokumen1 halamanPathophysiologyHazel PalomaresBelum ada peringkat
- NCP FVDDokumen1 halamanNCP FVDsisjing88510Belum ada peringkat
- NCP (Or) ThyroidectomyDokumen3 halamanNCP (Or) ThyroidectomyChiz CorreBelum ada peringkat
- Ncps TetanyDokumen18 halamanNcps TetanyBob Joyce Dela PeñaBelum ada peringkat
- ScriptDokumen12 halamanScriptTrishia Nhicole HoBelum ada peringkat
- Anemia NCPDokumen20 halamanAnemia NCPNursidar Pascual Mukattil80% (5)
- NCPDokumen10 halamanNCPbabycheska08Belum ada peringkat
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDokumen6 halamanCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Reason Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationKatrina Ponce86% (7)
- Jurnal Makro Dan MikroDokumen11 halamanJurnal Makro Dan Mikrozull spotBelum ada peringkat
- This Awareness of Multivitamin Hair Growth Uses and Benefit of Shampoo and Hair Ampule in Saudi AdultsDokumen18 halamanThis Awareness of Multivitamin Hair Growth Uses and Benefit of Shampoo and Hair Ampule in Saudi AdultsIJAR JOURNALBelum ada peringkat
- Curing All Chronic Disease by Changing DietDokumen57 halamanCuring All Chronic Disease by Changing DietAnil SinghviBelum ada peringkat
- POSHAN Abhiyaan PDFDokumen2 halamanPOSHAN Abhiyaan PDFVishal Pal Vishal PalBelum ada peringkat
- Rough Draft Coffee ConsumptionDokumen5 halamanRough Draft Coffee ConsumptionMariana Cedeño RamosBelum ada peringkat
- CTU Insulin Sliding ScalesDokumen2 halamanCTU Insulin Sliding ScalesnindylistyBelum ada peringkat
- Mapeh 8Dokumen7 halamanMapeh 8Anonymous K0o40KJ0% (1)
- Oyster Meat F.S.Dokumen25 halamanOyster Meat F.S.mxviolet50% (2)
- Recreatinal SlidesDokumen28 halamanRecreatinal Slidesnerlyn100% (1)
- Shakes To Lose Weight: 10 Weight Loss Shake RecipesDokumen21 halamanShakes To Lose Weight: 10 Weight Loss Shake RecipesDuston McGroarty100% (1)
- Athul Samson 2015 TropicalfruitwastemanagementthroughwineproductionDokumen89 halamanAthul Samson 2015 TropicalfruitwastemanagementthroughwineproductionMinichil AshebirBelum ada peringkat
- Food Safety and Standards Eastasia 2013 CDokumen60 halamanFood Safety and Standards Eastasia 2013 CKo NgeBelum ada peringkat
- AssessmentDokumen3 halamanAssessmentLOUISE JOSEL TACLAYBelum ada peringkat
- Quiz Osteopathic Part 3 of 4Dokumen54 halamanQuiz Osteopathic Part 3 of 4MedShare100% (4)
- Manoj Jain - Jain FoodDokumen80 halamanManoj Jain - Jain FoodAnonymous 3YNFShCBelum ada peringkat
- 103 Lab 2 CarbohydratesDokumen7 halaman103 Lab 2 Carbohydratessweeneyc84497Belum ada peringkat
- Huda Baharoon and Sarah Hitham During The Program People's Anteraction During The ExplaintionDokumen3 halamanHuda Baharoon and Sarah Hitham During The Program People's Anteraction During The Explaintionالصراحة راحةBelum ada peringkat
- Consumer AttitudesDokumen6 halamanConsumer AttitudesGerlyn Lariosa Pag-ongBelum ada peringkat
- HyperthyroidismDokumen73 halamanHyperthyroidismZNEROL100% (1)
- Pathfit 2 Lesson 5Dokumen10 halamanPathfit 2 Lesson 5Steffany Anne PobladorBelum ada peringkat
- Test Bank For Nutrition For Sport and Exercise 4th Edition DunfordDokumen15 halamanTest Bank For Nutrition For Sport and Exercise 4th Edition DunfordharolddungmujBelum ada peringkat
- Weeks 1-3 - Windshield Assessment TemplateDokumen17 halamanWeeks 1-3 - Windshield Assessment TemplateQazim Raza50% (2)
- HOME SCIENCE (Code No. 064) : (Classes - Xi and Xii)Dokumen15 halamanHOME SCIENCE (Code No. 064) : (Classes - Xi and Xii)Rhea NegiBelum ada peringkat
- Alzheimer's Disease: CausesDokumen4 halamanAlzheimer's Disease: CausesDenise PoBelum ada peringkat