Science Plan Thurs 03 11 2011
Diunggah oleh
dkat83Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Science Plan Thurs 03 11 2011
Diunggah oleh
dkat83Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Topic Planning 2011 : Key subject area Science - What is a circuit?
Beg:Date Objectives for week (Cross Curricular Objectives/ links identified need to be stated): To make a simple series circuit and recognise when/why a circuit will
not work. To know that a circuit needs a source of power and a devise that uses that power to make it work. To know that symbols can be used to represent the components of an electrical circuit in drawings. Sc4 1a Construct a circuit, incorporating a battery or power supply. 1c Know how to represent series circuits by drawings and conventional symbols, and how to construct series circuits on the basis of drawings and diagrams using conventional symbols. Breadth of study: 1d Carry out a range of scientific investigations. Sc1 2f Make systematic observations and measurements. 2e Use simple equipment and materials appropriately and take action to control risks.
Next steps (objectives):
To know that batteries and the mains are the most widely used sources of electricity. To know that electricity can be dangerous and that care needs to be taken using electrical appliances. Breadth of study: 2b Recognise that there are hazards in physical processes, and assess risks and take action to reduce risks to themselves and others. Sc1 1a Establish links between causes and effects.
Reason why (how does this fit with wider learning / real life) Differentiated SC LI: I can understand that a circuit needs a power source and needs to be complete I must recognise and make a complete circuit. I should identify why a circuit does not work. I could recognise circuit diagram symbols.
Key vocab See sheet
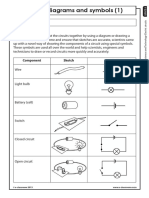
Introduction Recap on the learning that has been undertaken by the chn in KS1, by asking the chn to work in mixed ability pairs to complete a Thought Shower of all that they think of when given the words: electricity and circuits. Use this as a starter activity, to gather-up what the chn already know about the topic. At the end of this activity give each chd post it on which they write down a question that they would most like to find the answer to by the end of the topic. Keep the class concept map and the chns questions Ask children to look at drawings of circuits and decide and explain which will work and which will not. Show chn some circuit components and check they can name them (vocabulary for the Strand available in resources). Ch to complete concept cartoons stick in books)
Main activity Investigation: Ask children to make a circuit that will work, record it by drawing, and to annotate their drawings to indicate the purpose of each part e.g. the battery provides the power/electricity Use Bulging batteries chapter from Shocking Electricity Review vocabulary associated with circuits and conductors. Match drawings to electrical symbols Circuit, wires, battery, bulb, buzzer, electricity, switch. Incomplete circuits: Display a circuit for the chn to see, using batteries in a holder, connected to a bulb using wires and crocodile clips. This circuit should work i.e. the bulb will light up! Show the chn 3 circuits that dont work e.g. the batteries arent in the holder, the bulb is not in its holder, one of the crocodile clips isnt connected to the bulb or the batteries, none of the components are linked together. The chn draw each circuit and list the reasons why it does not work properly. This would benefit from TA support (see session resources). Independent activities: Working circuits: The chn have a range of components e.g. bulbs, bulb holders, batteries, battery holders, wires and crocodile clips, buzzers, motors. The chn build a working circuit i.e. the bulb lights up, the motor turns or the buzzer sounds! The chn then draw their circuit and label the parts. The chn give the purpose of each component in the circuit (see session resources).
Resou rces On cupbo ard at back!
Differentiation Mixed ability topic groups Working circuits: The chn have a range of components e.g. bulbs, bulb holders, batteries, battery holders, wires and crocodile clips, buzzers, motors. The chn build a working circuit i.e. the bulb lights up or the buzzer sounds! The chn then draw their circuit and label the parts. The chn give the purpose of each component in the circuit (see session resources).
Plenary / Key Questions explain why devices in some circuits shown in drawings will work but devices in other circuits will not eg the switch is open so there is a break in the circuit and the bulb wont light identify the purpose of components in a circuit Revise the basic understanding of a circuit: it needs to have a source of power, in the case of today this was provided using batteries, it needs to have a selectionof components, and these include wires and at least one# main component that uses the electrical energy to make something happen e.g. bulb light up, motor move, buzzer sound. Ask the chn: When I have a working, complete circuit, why is it a good idea to draw it? Why do you think symbols are used instead of drawing what the components really looks like? If the chn find this difficult, guide them i nto thinking that it makes the drawing simple to look at, easy to remake the circuit and that it is easily understood by everyone who also uses the same symbols. Next steps for children
:
Date:
1 table buzzer circui 1table light bulb circuit 1 table plug and play electronice 1 table electronics lab
/opt/scribd/conversion/tmp/scratch2756/80069119.doc
ICT
Any Health and Safety issues to address
Notes/ feedback about session/ next steps:
/opt/scribd/conversion/tmp/scratch2756/80069119.doc
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- Minh 1Dokumen7 halamanMinh 1api-551486913Belum ada peringkat
- SCIENCE SCRATCHLesson PlanDokumen4 halamanSCIENCE SCRATCHLesson PlanMarecar RabusaBelum ada peringkat
- Creating Complete CircuitsDokumen4 halamanCreating Complete CircuitsChristelle Mendoza PanopioBelum ada peringkat
- AngelDokumen11 halamanAngelMinerva AtanacioBelum ada peringkat
- Foss Lesson PlansDokumen5 halamanFoss Lesson PlansVanessa CaballeroBelum ada peringkat
- Sci Pptq3 w5 Day 1 5Dokumen72 halamanSci Pptq3 w5 Day 1 5Shielanie EsclandaBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan 4 - Electricity InquiryDokumen4 halamanLesson Plan 4 - Electricity Inquiryapi-457194169Belum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Class 6 CH Electricity and CircuitDokumen8 halamanLesson Plan Class 6 CH Electricity and CircuitUjjwal Kr. Sinha88% (8)
- Unitplanner ScienceDokumen9 halamanUnitplanner Scienceapi-361106677Belum ada peringkat
- MC Dermott - Tutoriales DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS-INTRODUCTIONDokumen4 halamanMC Dermott - Tutoriales DIRECT CURRENT CIRCUITS-INTRODUCTIONEvangelina LauraBelum ada peringkat
- Bulbs & Batteries in A Row - Activity - TeachEngineeringDokumen7 halamanBulbs & Batteries in A Row - Activity - TeachEngineeringDaeng HawangBelum ada peringkat
- Science Lesson Plan 2Dokumen4 halamanScience Lesson Plan 2Sarah SellBelum ada peringkat
- Pre-Planning: / Anchors PA/Common Core/StandardsDokumen10 halamanPre-Planning: / Anchors PA/Common Core/Standardsapi-278838777Belum ada peringkat
- Electricity LPDokumen3 halamanElectricity LPapi-201626802Belum ada peringkat
- Light Your Way - Design-Build A Series Circuit Flashlight - Activity - TeachEngineeringDokumen8 halamanLight Your Way - Design-Build A Series Circuit Flashlight - Activity - TeachEngineeringDaeng HawangBelum ada peringkat
- ELTR115 Sec2 InstructorDokumen143 halamanELTR115 Sec2 InstructorOmpad FelixBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan Battery BulbDokumen5 halamanLesson Plan Battery Bulbapi-267681158Belum ada peringkat
- Technology and Livelihood Education: Exploratory Course in Electrical Installation and MaintenanceDokumen13 halamanTechnology and Livelihood Education: Exploratory Course in Electrical Installation and MaintenanceSteven Escarmosa100% (1)
- InquiryDokumen2 halamanInquiryMike Mike VasayaBelum ada peringkat
- Science: Quarter 3 - Module 4: Electric CircuitDokumen26 halamanScience: Quarter 3 - Module 4: Electric Circuitmarkjhuncarl caccam0% (1)
- Grade 5 Q3 Week 5Dokumen9 halamanGrade 5 Q3 Week 5joan marie PeliasBelum ada peringkat
- Science Lesson - CircuitsDokumen9 halamanScience Lesson - Circuitsapi-280467536Belum ada peringkat
- Technology-Enhanced Science Unit: Target Population: 8 Grade Middle School Physical ScienceDokumen38 halamanTechnology-Enhanced Science Unit: Target Population: 8 Grade Middle School Physical ScienceNguyễn Huy ĐạtBelum ada peringkat
- Edt 441 IuDokumen8 halamanEdt 441 Iuapi-339178048Belum ada peringkat
- Klimova CircuitslfinalDokumen4 halamanKlimova Circuitslfinalapi-298993945Belum ada peringkat
- Educ630 Lesson Plan 4 Electricity and Energy Circuits Ayer ShannaDokumen4 halamanEduc630 Lesson Plan 4 Electricity and Energy Circuits Ayer Shannaapi-288261699Belum ada peringkat
- Inquiry Activities On: ElectricityDokumen21 halamanInquiry Activities On: ElectricityVan Phuong NguyenBelum ada peringkat
- Q3 - Science5 - Week 5Dokumen17 halamanQ3 - Science5 - Week 5Maria Ronavie Davalos Mantes100% (1)
- Circuit Building Lesson Plan Hanna SalakDokumen3 halamanCircuit Building Lesson Plan Hanna Salakapi-697430197Belum ada peringkat
- Edms 545-4th-FlippingtheswitchDokumen16 halamanEdms 545-4th-Flippingtheswitchapi-253399358Belum ada peringkat
- Electricity Unit Prac and WRKSHTDokumen52 halamanElectricity Unit Prac and WRKSHTDiana GanapathyBelum ada peringkat
- Simple InstructorDokumen46 halamanSimple InstructorLOURDES BEATA CABANACANBelum ada peringkat
- Flashlights and Batteries: Lesson FocusDokumen8 halamanFlashlights and Batteries: Lesson FocusmiaBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Circuits An Introduction Grade 4 Jessica DutcherDokumen42 halamanElectrical Circuits An Introduction Grade 4 Jessica Dutcherapi-302628627Belum ada peringkat
- Grade 5 Q3 Week 5Dokumen8 halamanGrade 5 Q3 Week 5Mary Mae Llorente100% (3)
- Mini UnitDokumen37 halamanMini Unitapi-299710151100% (1)
- 005 001 000 014 Electric SwitchesDokumen8 halaman005 001 000 014 Electric SwitchesBalian1908Belum ada peringkat
- Build simple circuitsDokumen4 halamanBuild simple circuitsHanan ArsadBelum ada peringkat
- Part 1: Answer The Following Questions (20 Points) : Manuel CusicanquiDokumen3 halamanPart 1: Answer The Following Questions (20 Points) : Manuel CusicanquiAlexander RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- ELTR 100 Course OverviewDokumen124 halamanELTR 100 Course OverviewifeniyiBelum ada peringkat
- Series and Parallel Circuits: Lesson FocusDokumen8 halamanSeries and Parallel Circuits: Lesson FocusJOe Y VEnBelum ada peringkat
- Circuit Symbols PDFDokumen6 halamanCircuit Symbols PDFRonald Huynh100% (1)
- IGCSE - Physics - Lesson Plan 7 - Current and Voltage in CircuitsDokumen4 halamanIGCSE - Physics - Lesson Plan 7 - Current and Voltage in CircuitsHoracio FerrándizBelum ada peringkat
- CO3-SCIENCE (4a's) - Series and Parallel CircuitsDokumen7 halamanCO3-SCIENCE (4a's) - Series and Parallel CircuitsmagnojoanmaeBelum ada peringkat
- Electrical Symbols 11to14 Lesson-Plan PDFDokumen3 halamanElectrical Symbols 11to14 Lesson-Plan PDFApril Ann OliverosBelum ada peringkat
- I. Objective: A. Topic: Electricity Circuits B. Sub-Topic: Series Circuit C. Materials/Tools/GadgetsDokumen7 halamanI. Objective: A. Topic: Electricity Circuits B. Sub-Topic: Series Circuit C. Materials/Tools/GadgetsJhoana Marie RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Connect materials to make a series circuitDokumen4 halamanConnect materials to make a series circuitMichelle Milano100% (1)
- SSC Gr10 Electronics Q4 Module 2 WK 2 - v.01-CC-released-15June2021Dokumen17 halamanSSC Gr10 Electronics Q4 Module 2 WK 2 - v.01-CC-released-15June2021Vj AleserBelum ada peringkat
- Science - 5 E Model - Simple CircuitsDokumen3 halamanScience - 5 E Model - Simple CircuitsJessie SanchezBelum ada peringkat
- Lesson Plan - More Wires 3Dokumen4 halamanLesson Plan - More Wires 3api-300214415Belum ada peringkat
- AwDokumen4 halamanAwNeilzs FloresBelum ada peringkat
- ODokumen3 halamanOtodejis283Belum ada peringkat
- DLP in Science 5Dokumen6 halamanDLP in Science 5Al Mark MirafuentesBelum ada peringkat
- E-Lesson Plan ElectricityDokumen2 halamanE-Lesson Plan ElectricityChhabi BhatnagarBelum ada peringkat
- Teaching Electrostatics: A Teacher's Resource for Increasing Student EngagementDari EverandTeaching Electrostatics: A Teacher's Resource for Increasing Student EngagementBelum ada peringkat
- Build Your Own Circuit WorksheetDokumen3 halamanBuild Your Own Circuit WorksheetChantelle BelcherBelum ada peringkat
- EIM 12 Q1 Module 4Dokumen23 halamanEIM 12 Q1 Module 4Rodgene L Malunes (Lunduyan)Belum ada peringkat
- Battery Lab Activity PlanDokumen5 halamanBattery Lab Activity PlanPhillip CookBelum ada peringkat
- ELTR115 Sec1Dokumen96 halamanELTR115 Sec1Tshering WangdiBelum ada peringkat
- Chapters 20 and 21: Physical Science Unit 7 - Electricity and MagnetismDokumen21 halamanChapters 20 and 21: Physical Science Unit 7 - Electricity and MagnetismPatry sanchezBelum ada peringkat
- OutletsDokumen226 halamanOutletsPraveen Kumar Saini100% (1)
- Eun 9e International Financial Management PPT CH01 AccessibleDokumen29 halamanEun 9e International Financial Management PPT CH01 AccessibleDao Dang Khoa FUG CTBelum ada peringkat
- American Buffalo - DAVID MAMETDokumen100 halamanAmerican Buffalo - DAVID MAMETRodrigo Garcia Sanchez100% (10)
- Glass Fiber CompositesDokumen21 halamanGlass Fiber CompositesChoice NwikaBelum ada peringkat
- Concepts of Cavity Prep PDFDokumen92 halamanConcepts of Cavity Prep PDFChaithra Shree0% (1)
- Kasapreko PLC Prospectus November 2023Dokumen189 halamanKasapreko PLC Prospectus November 2023kofiatisu0000Belum ada peringkat
- Write The Missing Words of The Verb To Be (Affirmative Form)Dokumen1 halamanWrite The Missing Words of The Verb To Be (Affirmative Form)Daa NnaBelum ada peringkat
- Noise Blinking LED: Circuit Microphone Noise Warning SystemDokumen1 halamanNoise Blinking LED: Circuit Microphone Noise Warning Systemian jheferBelum ada peringkat
- Credit Card Statement: Payment Information Account SummaryDokumen4 halamanCredit Card Statement: Payment Information Account SummaryShawn McKennanBelum ada peringkat
- Challan Form OEC App Fee 500 PDFDokumen1 halamanChallan Form OEC App Fee 500 PDFsaleem_hazim100% (1)
- Jamaica's Unemployment Aims, Causes and SolutionsDokumen23 halamanJamaica's Unemployment Aims, Causes and Solutionsnetzii300067% (3)
- Module 1: Overview of Implementation of The NSTP (Activities)Dokumen3 halamanModule 1: Overview of Implementation of The NSTP (Activities)RonnelBelum ada peringkat
- 51 JointventureDokumen82 halaman51 JointventureCavinti LagunaBelum ada peringkat
- Chapter 2 Review of Related Lit - 1Dokumen83 halamanChapter 2 Review of Related Lit - 1CathyBelum ada peringkat
- Reviewer in Intermediate Accounting IDokumen9 halamanReviewer in Intermediate Accounting ICzarhiena SantiagoBelum ada peringkat
- Music Literature (Western Music)Dokumen80 halamanMusic Literature (Western Music)argus-eyed100% (6)
- Kerala Dinesh Beedi - WikipediaDokumen12 halamanKerala Dinesh Beedi - Wikipediaaymanamna2016Belum ada peringkat
- PSE Inc. V CA G.R. No. 125469, Oct 27, 1997Dokumen7 halamanPSE Inc. V CA G.R. No. 125469, Oct 27, 1997mae ann rodolfoBelum ada peringkat
- Subsurface Sewage DisposalDokumen174 halamanSubsurface Sewage DisposalSanthi KrishnaBelum ada peringkat
- Intertrigo and Secondary Skin InfectionsDokumen5 halamanIntertrigo and Secondary Skin Infectionskhalizamaulina100% (1)
- Research Paper 1 Eng Lang StudiesDokumen4 halamanResearch Paper 1 Eng Lang Studiessastra damarBelum ada peringkat
- English 2Dokumen53 halamanEnglish 2momonunu momonunuBelum ada peringkat
- TarotDokumen21 halamanTarotKrystal Jacquot100% (2)
- Recommendation Letter - One Young WorldDokumen2 halamanRecommendation Letter - One Young WorldNabeel K. AdeniBelum ada peringkat
- Oral READING BlankDokumen2 halamanOral READING Blanknilda aleraBelum ada peringkat
- Final Script Tokoh NilamDokumen1 halamanFinal Script Tokoh NilamrayyanBelum ada peringkat
- Pilar College of Zamboanga City, IncDokumen14 halamanPilar College of Zamboanga City, IncIvy VillalobosBelum ada peringkat
- 4 5895601813654079927 PDFDokumen249 halaman4 5895601813654079927 PDFqabsBelum ada peringkat
- Safe Handling of Solid Ammonium Nitrate: Recommendations For The Environmental Management of Commercial ExplosivesDokumen48 halamanSafe Handling of Solid Ammonium Nitrate: Recommendations For The Environmental Management of Commercial ExplosivesCuesta AndresBelum ada peringkat
- Bluetooth Modules - Martyn Currey PDFDokumen64 halamanBluetooth Modules - Martyn Currey PDFAng Tze Wern100% (1)