Capsule Proposal
Diunggah oleh
tho2793Deskripsi Asli:
Hak Cipta
Format Tersedia
Bagikan dokumen Ini
Apakah menurut Anda dokumen ini bermanfaat?
Apakah konten ini tidak pantas?
Laporkan Dokumen IniHak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Capsule Proposal
Diunggah oleh
tho2793Hak Cipta:
Format Tersedia
Title: Author:
Cost-effective analysis of the combination therapies, Losartan + Hydrochlorothiazide and Bisoprolol + Hydrochlorothiazide for Hypertension Inolino, Emilyn Aira A. Mahinay, Desteen Abegail F. Maosa, Jose Marlo B.
Co-Author: Aya-ay, Adorico, Ph.D. Salva, Edna Pasicolan, Vivien Leigh Introduction: Medicines can be expensive and often make up a large portion of any family's health care budget. And the burden can be even greater for people in poor countries, where the cost of vital medicines can push them into poverty (Hoban, 2010). This problem is further escalated by the fact that more people worldwide are being diagnosed with diseases such as diabetes and hypertension that could entail treatment that could last a lifetime. As the costs of our treatment continue to rise, many of our patients find themselves in a dilemma, forcing them to budget tightly their medication expenses. Hypertension is an especially difficult condition because it is common for physicians to test several different medications before finding the one optimal for our patient (Weber, M.D. 2008). This could lead our patient being unable to reach our treatment goal leading to increased treatment cost and eventually poor and inadequate blood pressure control. Fixed-dose combination treatments offer several potential benefits, including simplification of the treatment regimen, convenience, and more importantly decreased cost (Jennifer Frank MD, Journal of the American Academy of Family Physicians, 2008). Overall, 20% of the worlds adult population has hypertension. In the United States, approximately 50 million are afflicted with this disease. Although breakthroughs in our field has managed to enable effective management of hypertension among at risk and afflicted individuals, 30% of adults are unaware that they have hypertension. Even among individuals that have been diagnosed with hypertension, 40% are not r\eceiving treatment and a further 67% do not attain the treatment goal of reducing the patients blood pressure to less than
140/80 mm Hg (Kamran Riaz, MD, Medscape, 2011). Hypertension is one of the most common diseases worldwide. It is a very important public health challenge due to its associated morbidity and mortality. Its cost to society is great. According to the government, nearly eight million adult Filipinos suffer from hypertension and its cardiovascular complications. Of these, tens and thousands are unnecessarily disabled and/or die prematurely from it. Hypertension and the complications it cause is the Top 2 cause of mortality here in the Philippines, second only to heart diseases (Department of Health, 2009). Of all age groups, the elderly are the ones most at risk of hypertension. The prevalence of hypertension dramatically increases in patients older than 60 years. In most countries, 50% of people older than 60 years have hypertension (Kamran Riaz, MD, Medscape, 2011). As mentioned earlier, 67% of patients do not attain the treatment goal of less than 140/80 mm Hg. We currently have about 125 antihypertensive drugs available. Most of them are very effective drugs. Yet, we struggle to control our patients blood pressure. The problem lays in the stepped care approach in the treating hypertension. This concepts states that in the treatment of chronic illnesses, we give patients as few drugs as possible at the lowest doses possible, increasing the dose in response to its efficacy to the patient. However, as we increase the dose, the risks of dose-dependent side effects increase. This creates a limit where we are forced to sacrifice the attainment of our therapeutic goal for the safety of our patient. The solution to this problem is the use of combination therapy. The use of two complementary antihypertensive agents in combination will always result in greater efficacy than high-dose monotherapy. For example, small doses of hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) (6.25 mg) added to small doses of bisoprolol (10 mg) are more effective than high-dose HCTZ monotherapy (25 mg) and more effective than high-dose bisoprolol (40 mg). Drug combinations using agents that act by different mechanisms have an additive effect. The use of combination therapy will provide greater efficacy, fewer side effects and greater convenience than can be achieved with
monotherapy, and most importantly, will increase significantly blood pressure control (Joel M. Neutel, Oxford College Journals, 2005). The object of this study is to determine the cost-effectiveness of the available combination therapy in the management of hypertension. Determining the cost-effectiveness ratio of each of these combination therapies would provide health care professionals a guide in providing medicine that will best fit the patients needs to manage both their disease and their finances.
Statement of the Problem This study will analyze the cost-effectiveness of combination therapy for the management of hypertension in patients ages 30 - 80 available in the market today. This study will answer the following questions: 1. Is there a significant difference in the cost factors stated below between Losartan + HCTZ and Bisoprolol + HCTZ in the management of hypertension? 1.1. Cost of Acquisition 1.2. Cost of Administration 1.3. Cost of Monitoring 1.4. Cost of Adverse Effects 2. Is there a significant difference between the total costs of Losartan + HCTZ and Bisoprolol + HCTZ in the management of hypertension? 3. Is there a significant difference in the cost factors when analyzed by the gender of the patients? 4. Is there a significant difference in the cost factors when analyzed by the age of the patients? 5. What is the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio of Losartan + HCTZ and Bisoprolol + HCTZ in the management of Hypertension?
Significance of the Study The purpose of this study is to determine the cost-effectiveness of the available combination therapy utilized in the management of hypertension using the cost factors in the management of the said disease. The results of this study will be a great contribution to those people who suffer hypertension. This pharmacoeconomic study could also be of great help to health professionals especially those from the Mindanao Heart Center and its Pharmacy and Therapeutics Committee in making formulary decisions, designing disease management programs and measuring the cost-effectiveness of programs in managed care. This pharmacoeconomic study could also encourage more cost-effective analyses to be performed in the hospital practice. Studies modeled like this one could be a great tool in aiding health care professionals in their choice of therapeutic agents. This study could also encourage more cost-effective analysis in the University of the Immaculate Conception. This type of research could help the students of the university be better prepared in their future career, being mindful of the relative costs of different medications available in the market. Methodology The descriptive design aims to gather information from the patient records of one of the tertiary hospital in Davao City it also include how the samples will be determine, how the data will be gather, interpreted and what statistical tool will be used to answer the research question of the study. Research Design The study will utilize the survey approach of research precisely the descriptive method. The researcher will be using cost-effective analysis to identify the most cost-effective of the available combination therapy for the management of hypertension for the elderly.
Research Locale The researchers will conduct the study in one of the tertiary hospital in Davao City. This is because the said establishment is a public tertiary hospital that caters to a large number of patients that qualify to be the subject of the study.
Research Subject The respondents of the study will be hypertensive patients, both male and female those are 30 to 80 years old and no preexisting condition. They will be purposively selected by the researchers.
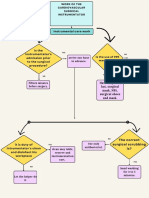
Research Instruments This research will utilize a pharmacoeconomics consult particularly a basic pharmacoeconomic calculation sheet. This form helped structure the calculations and considerations in determining the cost-effectiveness of a drug. It incorporated all the basic information regarding the patient, the cost factors and the calculated results.
Sampling Procedure The researchers will use purposive sampling procedure. In the purposive sampling it targets a particular group of people. When the desired population for the study is rare or very difficult to locate and recruit for the study, purposive sampling may be the only option (Wadsworth Cengage Learning 2005). The actual composition of the sample itself does not determine whether or not it was a random (Lane, 2006). Research Procedure Data collection Before starting the project the protocol was submitted to Mindanao Heart Center Administration for approval. Data collection occurred between June to December 2011.
Measuring Cost All relevant of the study will be identify by their measurement and estimation. The cost of an intervention includes cost of therapy, cost of acquisition, cost of administration, cost of monitoring, and cost of adverse effects.
Determining Cost Effectiveness Cost-Effectiveness Ratio (CER) The Cost- effectiveness ratio is an important summary statistics for comparing the costs and effectiveness of Combizar and Ziac. It is a useful aid in statistical aid in decision making process and in allocation of healthcare resources (Pisapia, 2000). In addition, the cost-effectiveness ratio is the cost at which the new or alternative intervention delivers one unit of health benefit, relative to the standard intervention to which the new intervention is being compared (Gardiner et al.,2003).
Statistical Treatment A Single-Classification ANOVA and T-test will be used in the study because they provide an appropriate analysis in comparing the significant differences between two or more groups when given various treatments. The Single-Classification ANOVA analysis juxtaposed the cost-effectiveness between Ziac and Combizar in the treatment of Hypertension by determining the significant difference of the age and gender to the different cost factors. On the other hand, the T-test will be used to determine the significant difference of the cost factors between the use of Combizar and Ziac.
Anda mungkin juga menyukai
- User's Guide to Natural Therapies for Cancer Prevention and ControlDari EverandUser's Guide to Natural Therapies for Cancer Prevention and ControlPenilaian: 5 dari 5 bintang5/5 (1)
- Drug Adherence in Hypertension and Cardiovascular ProtectionDari EverandDrug Adherence in Hypertension and Cardiovascular ProtectionMichel BurnierBelum ada peringkat
- ResearchDokumen75 halamanResearchArun AhirwarBelum ada peringkat
- Supportive Care in Pediatric Oncology: A Practical Evidence-Based ApproachDari EverandSupportive Care in Pediatric Oncology: A Practical Evidence-Based ApproachJames H. FeusnerBelum ada peringkat
- Evidence Synthesis in Healthcare: A Practical Handbook for CliniciansDari EverandEvidence Synthesis in Healthcare: A Practical Handbook for CliniciansBelum ada peringkat
- Vital Signs: Awareness and Treatment of Uncontrolled Hypertension Among Adults - United States, 2003-2010Dokumen8 halamanVital Signs: Awareness and Treatment of Uncontrolled Hypertension Among Adults - United States, 2003-2010Widya Setiabudi AseliBelum ada peringkat
- JJJGJHGJHGHDokumen6 halamanJJJGJHGJHGHTaufik NurohmanBelum ada peringkat
- Cost Effectiveness and Resource AllocationDokumen7 halamanCost Effectiveness and Resource AllocationSarah AmeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Role of Pharmacist in Reducing Healthcare CostsDokumen8 halamanRole of Pharmacist in Reducing Healthcare CostsAnsar MushtaqBelum ada peringkat
- Annotated Bibliography For Obesity and SmokingDokumen5 halamanAnnotated Bibliography For Obesity and Smokingapi-240254375Belum ada peringkat
- Angelina Alphonce JohoDokumen80 halamanAngelina Alphonce JohoMerlina WijayawatiBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review On Hypertension in NigeriaDokumen5 halamanLiterature Review On Hypertension in Nigeriabsdavcvkg100% (1)
- Pa Issue Brief FinalDokumen21 halamanPa Issue Brief FinalAsja AvdićBelum ada peringkat
- 1064 4311 1 PBDokumen6 halaman1064 4311 1 PBFebri Nick Daniel SihombingBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension Protocol JeannineDokumen53 halamanHypertension Protocol JeannineAleile DRBelum ada peringkat
- Surviving Cancer, COVID-19, and Disease: The Repurposed Drug RevolutionDari EverandSurviving Cancer, COVID-19, and Disease: The Repurposed Drug RevolutionBelum ada peringkat
- A Descriptive Study of Adherence To Lifestyle Modification Factors Among Hypertensive PatientsDokumen23 halamanA Descriptive Study of Adherence To Lifestyle Modification Factors Among Hypertensive PatientsSt. KhodijahBelum ada peringkat
- Running Head: Improving Care For Patients With HypertensionDokumen6 halamanRunning Head: Improving Care For Patients With HypertensionCliff KaaraBelum ada peringkat
- Health Affairs September, 2001 - October, 2001 LENGTH: 3352 Words TITLE: Are The Benefits of Newer Drugs Worth Their Cost? Evidence From TheDokumen9 halamanHealth Affairs September, 2001 - October, 2001 LENGTH: 3352 Words TITLE: Are The Benefits of Newer Drugs Worth Their Cost? Evidence From Theapi-3711225Belum ada peringkat
- C04611526 PDFDokumen12 halamanC04611526 PDFPrifate BeheljambiBelum ada peringkat
- Medication Adherence and Blood Pressure Control Among Hypertensive Patients With Coexisting Long-Term Conditions in Primary Care SettingsDokumen10 halamanMedication Adherence and Blood Pressure Control Among Hypertensive Patients With Coexisting Long-Term Conditions in Primary Care SettingsmadhurocksktmBelum ada peringkat
- Anty - Hypertensive Need A Change RegimenDokumen4 halamanAnty - Hypertensive Need A Change RegimenSyifa MunawarahBelum ada peringkat
- Knowledge and Perceptions Related To Hypertension, Lifestyle Behavior Modifications and Challenges That Facing Hypertensive PatientsDokumen12 halamanKnowledge and Perceptions Related To Hypertension, Lifestyle Behavior Modifications and Challenges That Facing Hypertensive PatientsIOSRjournalBelum ada peringkat
- Annals of General PsychiatryDokumen9 halamanAnnals of General PsychiatryPutu Agus GrantikaBelum ada peringkat
- ManuscriptDokumen17 halamanManuscriptAnonymous y6NmP9NHkYBelum ada peringkat
- Coping Strategies and Blood Pressure Control Among Hypertensive Patients in A Nigerian Tertiary Health InstitutionDokumen6 halamanCoping Strategies and Blood Pressure Control Among Hypertensive Patients in A Nigerian Tertiary Health Institutioniqra uroojBelum ada peringkat
- Analytical Chemistry for Assessing Medication AdherenceDari EverandAnalytical Chemistry for Assessing Medication AdherenceBelum ada peringkat
- Asgedom2018 Article AntihypertensiveMedicationAdheDokumen8 halamanAsgedom2018 Article AntihypertensiveMedicationAdhehendriBelum ada peringkat
- TechnicalpaperDokumen10 halamanTechnicalpaperapi-280642857Belum ada peringkat
- Path Analysis On The Biopsychosocial Factors Associated With HypertensionDokumen11 halamanPath Analysis On The Biopsychosocial Factors Associated With HypertensionFitri RachmillahBelum ada peringkat
- Hypertension in The Asian Pacific Region The Problem and The SolutionDokumen14 halamanHypertension in The Asian Pacific Region The Problem and The SolutionJam Knows RightBelum ada peringkat
- Pfizer PBC BookletDokumen7 halamanPfizer PBC BookletDon HeymannBelum ada peringkat
- Precision Medicine Oncology: A PrimerDari EverandPrecision Medicine Oncology: A PrimerLorna Rodriguez-RodriguezBelum ada peringkat
- DPK Hypertension MMWR Vs 9-4-2012Dokumen7 halamanDPK Hypertension MMWR Vs 9-4-2012parkdhingraBelum ada peringkat
- 1161 Jphi QCRDDokumen6 halaman1161 Jphi QCRDamar prasadBelum ada peringkat
- Effect On Blood Pressure of A Continued Nursing Intervention Using Chronotherapeutics For Adult Chinese Hypertensive PatientsDokumen9 halamanEffect On Blood Pressure of A Continued Nursing Intervention Using Chronotherapeutics For Adult Chinese Hypertensive PatientsadeliadeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Risky Medicine: Our Quest to Cure Fear and UncertaintyDari EverandRisky Medicine: Our Quest to Cure Fear and UncertaintyPenilaian: 4 dari 5 bintang4/5 (2)
- Pharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacovigilance: Synergistic Tools to Better Investigate Drug SafetyDari EverandPharmacoepidemiology and Pharmacovigilance: Synergistic Tools to Better Investigate Drug SafetyPenilaian: 4.5 dari 5 bintang4.5/5 (3)
- Treating Opioid Use Disorder in General Medical SettingsDari EverandTreating Opioid Use Disorder in General Medical SettingsSarah E. WakemanBelum ada peringkat
- Souza Et Al., 2016Dokumen10 halamanSouza Et Al., 2016Ricardo Costa da SilvaBelum ada peringkat
- Journal Pone 0273439Dokumen23 halamanJournal Pone 0273439Jufri AkbarBelum ada peringkat
- High Blood Pressure and The Measures To Prevent Cardiovascular Disease of HypertensionDokumen4 halamanHigh Blood Pressure and The Measures To Prevent Cardiovascular Disease of HypertensionEto ShengeliaBelum ada peringkat
- Telemedicine and Asthma: An innovative approach to improve morbidity and mortality rates for active adults.: Effects of Telemedicine in Asthma care for remote and inner-city underserved populations.Dari EverandTelemedicine and Asthma: An innovative approach to improve morbidity and mortality rates for active adults.: Effects of Telemedicine in Asthma care for remote and inner-city underserved populations.Belum ada peringkat
- The Patient Priority: Solve Health Care's Value Crisis by Measuring and Delivering Outcomes That Matter to PatientsDari EverandThe Patient Priority: Solve Health Care's Value Crisis by Measuring and Delivering Outcomes That Matter to PatientsBelum ada peringkat
- Mediating Effect of Self-Ef Ficacy On The Relationship Between Medication Literacy and Medication Adherence Among Patients With HypertensionDokumen10 halamanMediating Effect of Self-Ef Ficacy On The Relationship Between Medication Literacy and Medication Adherence Among Patients With HypertensionNovri AndaBelum ada peringkat
- Effect of Evidence Based Lifestyle Guidelines On Self Efficacy of Patients With HypertensionDokumen20 halamanEffect of Evidence Based Lifestyle Guidelines On Self Efficacy of Patients With HypertensionMuhammad DeddyBelum ada peringkat
- Educational Intervention On Knowledge of Hypertension and Lifestyle/dietary Modification Among Hypertensive Patients Attending A Tertiary Health Facility in NigeriaDokumen11 halamanEducational Intervention On Knowledge of Hypertension and Lifestyle/dietary Modification Among Hypertensive Patients Attending A Tertiary Health Facility in NigeriaMediterr J Pharm Pharm SciBelum ada peringkat
- Research Paper HypertensionDokumen4 halamanResearch Paper Hypertensionfvf66j19100% (1)
- Chronic Health ConditionDokumen2 halamanChronic Health ConditionCeoDanielBelum ada peringkat
- HBM 3Dokumen10 halamanHBM 3renzelpacleb123Belum ada peringkat
- Finding the Path in Alzheimer’s Disease: Early Diagnosis to Ongoing Collaborative CareDari EverandFinding the Path in Alzheimer’s Disease: Early Diagnosis to Ongoing Collaborative CareBelum ada peringkat
- 1478 7547 3 2 PDFDokumen8 halaman1478 7547 3 2 PDFIzzaBelum ada peringkat
- Literature Review On Essential HypertensionDokumen5 halamanLiterature Review On Essential Hypertensionafdtrzkhw100% (1)
- Literature Review PolypharmacyDokumen12 halamanLiterature Review Polypharmacyea8p6td0100% (1)
- Drug-Related Problems in Hypertensive Patients With Multiple ComorbiditiesDokumen8 halamanDrug-Related Problems in Hypertensive Patients With Multiple ComorbiditiesHIDAYATBelum ada peringkat
- Cost-Effective Analysis of The Combination Therapies, Losartan + Hydrochlorothiazide and Bisoprolol + Hydrochlorothiazide For HypertensionDokumen1 halamanCost-Effective Analysis of The Combination Therapies, Losartan + Hydrochlorothiazide and Bisoprolol + Hydrochlorothiazide For Hypertensiontho2793Belum ada peringkat
- Dummy TablesDokumen2 halamanDummy Tablestho2793100% (1)
- Drug Incompatibilities and InteractionDokumen3 halamanDrug Incompatibilities and Interactiontho27930% (1)
- Curriculum VitaeDokumen4 halamanCurriculum Vitaetho2793Belum ada peringkat
- Update Stock PT KMD 14-6Dokumen46 halamanUpdate Stock PT KMD 14-6rio1995Belum ada peringkat
- Satera Gause Annotated BibDokumen3 halamanSatera Gause Annotated Bibapi-264107234Belum ada peringkat
- What Works in Therapy?Dokumen12 halamanWhat Works in Therapy?Ariel PollakBelum ada peringkat
- Academic Record Cgfns PDFDokumen2 halamanAcademic Record Cgfns PDFSdgfh Wanda100% (1)
- DVT And/or PE Treatment Dosage For Tinzaparin (Innohep®)Dokumen1 halamanDVT And/or PE Treatment Dosage For Tinzaparin (Innohep®)Kok Hui DiongBelum ada peringkat
- Capitol University Medical Center PoliciesDokumen5 halamanCapitol University Medical Center PoliciesCharles CagaananBelum ada peringkat
- Sustainable Medicine - Introduction: Whistle-Blowing On 21st-Century Medical PracticeDokumen4 halamanSustainable Medicine - Introduction: Whistle-Blowing On 21st-Century Medical PracticeChelsea Green PublishingBelum ada peringkat
- 24-Article Text-185-1-10-20220628Dokumen10 halaman24-Article Text-185-1-10-20220628REVA NINGTIA SARIBelum ada peringkat
- Cervical Cerclage: About The Cervix in PregnancyDokumen2 halamanCervical Cerclage: About The Cervix in Pregnancyamarendra Wardhana100% (1)
- Nursing InformaticsDokumen28 halamanNursing Informaticsd1choosenBelum ada peringkat
- 10 Penyakit Terbanyak Di Rawat Jalan Di Puskesmas Provinsi Dki Jakarta TW I Tahun 2019Dokumen9 halaman10 Penyakit Terbanyak Di Rawat Jalan Di Puskesmas Provinsi Dki Jakarta TW I Tahun 2019Klinik pratama Iqra' medical centreBelum ada peringkat
- The State of Mental Health in The Philippines PDFDokumen4 halamanThe State of Mental Health in The Philippines PDFKatrina Francesca SooBelum ada peringkat
- Art 1 - Frequency Evaluation of Different Extraction Protocols in Orthodotic Treatment During 35 YearsDokumen7 halamanArt 1 - Frequency Evaluation of Different Extraction Protocols in Orthodotic Treatment During 35 YearsAlejandro Aranzábal NavarreteBelum ada peringkat
- Davao Doctors College, Inc.: Gen. Malvar ST., Davao City College of Allied Health Sciences - Nursing ProgramDokumen20 halamanDavao Doctors College, Inc.: Gen. Malvar ST., Davao City College of Allied Health Sciences - Nursing ProgramPRECIOUS DIANNE BARDON-MEMPINBelum ada peringkat
- Laboratory Activity - HIS Lab - IDTOMISDokumen2 halamanLaboratory Activity - HIS Lab - IDTOMISFrance Cedrick RamosBelum ada peringkat
- Nurses in Implementation of National Rural Health Mission: Dr. Pratima Mittra Sr. Consultant, RCH - Ii / NRHM NihfwDokumen32 halamanNurses in Implementation of National Rural Health Mission: Dr. Pratima Mittra Sr. Consultant, RCH - Ii / NRHM NihfwPabhat KumarBelum ada peringkat
- Emergency Obstetric and Newborn CareDokumen4 halamanEmergency Obstetric and Newborn CaremnmrznBelum ada peringkat
- Health Center IPCR RN Ver 1.1 (With Program Management)Dokumen7 halamanHealth Center IPCR RN Ver 1.1 (With Program Management)RvBombeta50% (2)
- Factitious Disorder PaperDokumen9 halamanFactitious Disorder Paperapi-116302187100% (1)
- Mental Health BillDokumen5 halamanMental Health BillDave Jasm MatusalemBelum ada peringkat
- Assessment Report Cyproterone Acetate/ethinylestradiol (2 mg/0.035 MG) Containing Medicinal ProductsDokumen39 halamanAssessment Report Cyproterone Acetate/ethinylestradiol (2 mg/0.035 MG) Containing Medicinal ProductsFinna ChatrineBelum ada peringkat
- FDA AcetominofenDokumen2 halamanFDA AcetominofensindirdekBelum ada peringkat
- Scale Up and Postapproval Changes (Supac) Guidance For Industry: A Regulatory NoteDokumen9 halamanScale Up and Postapproval Changes (Supac) Guidance For Industry: A Regulatory NoteAKKAD PHARMABelum ada peringkat
- Scholarship ProgrammeDokumen3 halamanScholarship ProgrammeOmar HamidiBelum ada peringkat
- Template de Slide 4Dokumen15 halamanTemplate de Slide 4Caio ArmelleiBelum ada peringkat
- 2022 10 EMBASE JournalsDokumen520 halaman2022 10 EMBASE JournalsParul NandaBelum ada peringkat
- Case (Block A)Dokumen4 halamanCase (Block A)Angel EvangelistaBelum ada peringkat
- Cardiovascular Surgical InstrumentatorDokumen3 halamanCardiovascular Surgical Instrumentatorapi-626421480Belum ada peringkat
- RSRL-HSEMS-STW10-ECM - Employee Case ManagementDokumen8 halamanRSRL-HSEMS-STW10-ECM - Employee Case ManagementAnonymous FmXEu2cHxKBelum ada peringkat
- Document 12Dokumen1 halamanDocument 12selbal0% (1)